

Module 1: Introduction: What is Research?

Learning Objectives
By the end of this module, you will be able to:
- Explain how the scientific method is used to develop new knowledge
- Describe why it is important to follow a research plan
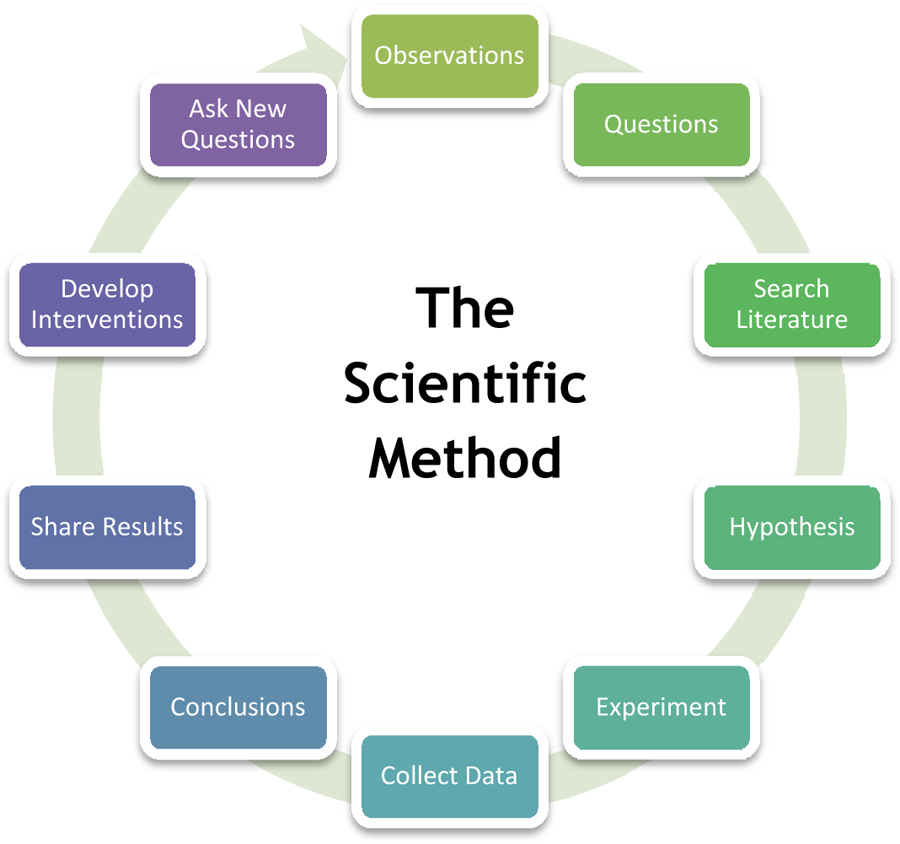
The Scientific Method consists of observing the world around you and creating a hypothesis about relationships in the world. A hypothesis is an informed and educated prediction or explanation about something. Part of the research process involves testing the hypothesis , and then examining the results of these tests as they relate to both the hypothesis and the world around you. When a researcher forms a hypothesis, this acts like a map through the research study. It tells the researcher which factors are important to study and how they might be related to each other or caused by a manipulation that the researcher introduces (e.g. a program, treatment or change in the environment). With this map, the researcher can interpret the information he/she collects and can make sound conclusions about the results.
Research can be done with human beings, animals, plants, other organisms and inorganic matter. When research is done with human beings and animals, it must follow specific rules about the treatment of humans and animals that have been created by the U.S. Federal Government. This ensures that humans and animals are treated with dignity and respect, and that the research causes minimal harm.
No matter what topic is being studied, the value of the research depends on how well it is designed and done. Therefore, one of the most important considerations in doing good research is to follow the design or plan that is developed by an experienced researcher who is called the Principal Investigator (PI). The PI is in charge of all aspects of the research and creates what is called a protocol (the research plan) that all people doing the research must follow. By doing so, the PI and the public can be sure that the results of the research are real and useful to other scientists.

Module 1: Discussion Questions
- How is a hypothesis like a road map?
- Who is ultimately responsible for the design and conduct of a research study?
- How does following the research protocol contribute to informing public health practices?
Email Updates
We use cookies on reading.ac.uk to improve your experience, monitor site performance and tailor content to you.
Read our cookie policy to find out how to manage your cookie settings.
This site may not work correctly on Internet Explorer. We recommend switching to a different browser for a better experience.
Research Services
Impact is the benefit that research has on the world outside of academia. Research and Enterprise provide context and support for impact at the pre-award phase, during the research and once impact has occurred.
These pages give information about the University’s internal committees and funding available for research.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research services are therefore specific to supporting research processes and tools, including the grid. They should include collaboration with experts and peers, encapsulation of complex procedures for non-experts (possibly using some form of workflow technology) to facilitate growth of interdisciplinary sciences and aids for results publication and proposal writing.
Conducting research involves a systematic and organized process that follows specific steps to ensure the collection of reliable and meaningful data. The research process typically consists of the following steps: Step 1. Identify the Research Topic. Choose a research topic that interests you and aligns with your expertise and resources.
research So, for QI/QA activities, always ask the same question - is it it a systematic investigation designed to contribut e to generalizable knowledge Calling something QI/QA or using words like "evaluation", etc., does not make a project NOT research. The terms are not mutually exclusive. QI/QA . Research . Research . 26
Research Program has the meaning set forth in Section 2.1. Research-based means a program or practice that has some research demonstrating effectiveness, but that does not yet meet the standard of evidence-based practices. Licensed Services means all functions performed by the Licensed System.
Describe why it is important to follow a research plan Research is a process to discover new knowledge. In the Code of Federal Regulations (45 CFR 46.102(d)) pertaining to the protection of human subjects research is defined as: "A systematic investigation (i.e., the gathering and analysis of information) designed to develop or contribute to ...
Research drives innovation by exploring new ideas, pushing boundaries, and challenging established norms. It leads to the developing of new technologies, products, and services that improve our quality of life. Research also fosters improvements in existing practices and processes by identifying inefficiencies, gaps, and areas for enhancement.
The definition of R&D just given is consistent with the definition of R&D used in the previous editions of the Frascati Manual and covers the same range of activities. 2.9 The term R&D covers three types of activity: basic research, applied research and experimental development. Basic research is experimental or theoretical work undertaken
Research Services (RES) are the principal source of support to academics and Schools to develop research and enterprise funding, supporting the development of research excellence and enterprise opportunities within the University. Preparing an application. We want your project to succeed. In this section, we offer advice on how to prepare a ...
Research is a systematic endeavor to acquire understanding, broaden knowledge, or find answers to unanswered questions. It is a methodical and structured undertaking to investigate the natural and ...
Research and development service providers are a form of external R & D, meaning they specialize in contracting with manufacturers and businesses to provide specialized research and development. This is in contrast to internal research and development which is performed in-house at a company laboratory or test facility.