- Open access
- Published: 25 November 2022

A study on occupational health and safety
- Lídia Maria Costa Araújo Magalhães 1 ,
- Ketyllem Tayanne da Silva Costa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0304-2639 2 ,
- Gustavo Nepomuceno Capistrano 2 ,
- Maryanna Damasceno Leal 3 &
- Fábia Barbosa de Andrade 4
BMC Public Health volume 22 , Article number: 2186 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
11k Accesses
3 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
This study aimed to evaluate and describe the indicators of occupational health, with a focus on the medical expertise and periodic medical examination.
This is exploratory-descriptive, cross-sectional, documentary, quantitative, and retrospective research, in the historical series: 2011 to 2015.
The number of lost days of work per worker and the frequency of licenses increased despite the decrease in the Absenteeism Duration Index and stabilization of the Frequency of Medical Workers. As for the adhesion of the workers to the Periodic Medical Examinations, it was decreasing, with a higher percentage in the year 2012 (35.3%). During the analyzed period, 5,186 workers performed the Periodic Medical Examination, and the majority (60.6%) presented non-ideal weight, 41.1% were sedentary, 33.2% had dyslipidemia, 29.0% were alcoholic, 3.2% were smokers, 5.9% had diabetics, and 16.4% reported high noise in the workplace, 27.8% inadequate lighting and 35.9% inadequate work furniture.
Conclusions
The results highlight the need to maintain and strengthen the Worker Health and Safety Policy with emphasis on surveillance, aiming at the promotion and protection of the health of the workers, based on the elaboration of the epidemiological profile of health and, consequently, the implementation of positive impact strategies.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Historically, in Brazil, Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) is strongly associated with the political-social and economic evolution of the country and is presented as the achievement of rights resulting from claims and struggles of the workers. Work is one of the determinants that most impact man’s conditions, quality of life, and health.
Working is essential for human beings since it is the way in which respect, integration, sociability, recognition, and bonds of friendship are obtained. On the other hand, the living conditions of Brazilian workers are aggravated by the alternation of stages of growth and accelerated industrialization with moments of recession, resulting in the government’s adoption of adjustment measures and financial cuts in social policies, such as education, health, safety, transportation, housing, and work, among others [ 1 , 2 ].
Nowadays, the epidemiological profile of workers' morbidity and mortality in Brazil is characterized by the coexistence of diseases that have an intrinsic relationship with working conditions: diseases related to work and typical work accidents, which have their frequency, appearance, and severity modified by the activity. Added to this reality are diseases common to the population as a whole, which have no etiological relationship with work [ 3 ].
Health Promotion and Surveillance refer to the pillar of the Occupational Safety and Health Care Policy (PASS, in Portuguese) that encompasses quality of life and vigilance actions in the environmental and work processes. Standing out among these are the institution of guidelines and programs in the area of mental health and occupational diseases of higher prevalence; the mandatory provision of Periodic Medical Examinations (PME) for all employees; the training in health and safety at work; the creation of an Internal Committee on Health and Safety at Work and a survey of environmental risks, with a stimulus to the active participation of employees in processes involving their health [ 4 , 5 ].
The PME aims, mainly, the prevention, enabling the health surveillance of the employees of a certain company or institution, contributing to the early identification of diseases related or not to work. It is carried out by an occupational doctor and employers must provide examinations for employees at specific times such as dismissal, admission, leaves of absence or change of function, in addition to periodic examinations, which will vary in frequency according to the workers' age (every two years for those between 18 and 45 years old and annually for those outside this age group) [ 6 ].
The PME is performed through clinical examinations, anamnesis, general and specific laboratory tests, according to the function developed by each worker. In addition, the occupational physician must adapt the exams to the particularities of each case, for example, people with disabilities or people who work with noise and may experience deafness caused by this fact. The result of the PME is not given by score or a question of approve or disapprove workers, it is related to the early diagnosis of health problems [ 6 ].
It is noteworthy that the information generated during the expertise act are important indicators of worker's health, privileged instruments for the construction of the morbidity and mortality profile of public servants, which will help to conduct the development of health promotion actions, since the expert databases issue a variety of data on the most prevalent diseases and the professionals who get sick [ 7 ].
It is of great importance to deepen the study in relation to the health of the federal public servant, considering the need to research, know and analyze the determining and conditioning factors of health problems related to processes and work environments. In this way, it is important to analyze workers' health indicators, which are reflections of the real health conditions of the server, with the objective of guiding managers in the planning and control of activities, in addition to allowing deductions regarding the effects of decisions and their results.
From this perspective, this study aimed to evaluate and describe occupational health indicators focusing on the Official Health Expertise and PME of federal public servants, including professors from the institution and administrative technicians from the education sector of the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte.
Materials and methods
This is a cross-sectional, retrospective study with a quantitative approach, where secondary data were obtained regarding PME and official health expertise, specifically the SIAPE HEALTH module of federal public servants of a public institution of higher education in Brazil.
The information contained in this system is federal level and is entered by the experts who perform the exams, uploading them directly into the system, enabling access to the information by users. For the study, secondary and aggregated data from the SIAPE SAÚDE system database were evaluated, as well as management reports made available by the SIASS Unit (Subsistema Integrado de Atenção à Saúde do Servidor) from UFRN, responsible for storing such data.
The study was carried out at the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte, Central Campus, especially at the Directorate of Attention to Servant Health (DAS), where the SIASS Unit is located, the latter being responsible for coordinating actions in attention to the health of the institution's servants, specifically, the performance of the Periodic Medical Examination and the Official Health Survey, objects of this study.
The period chosen for the study was from 2011 to 2015. The preference for this time interval was justified by the fact that the year 2011 marks the beginning of the PME through the computerized system SIAPE HEALTH, and the end of the study period in 2015 characterizes five complete years and the historical nature of epidemiological studies.
The population chosen for the study can be divided into levels of education, the teachers, technical-administrative in education, higher level positions are level E, while the technical-administrative in education, middle and basic level positions are levels C and D.
The official health expertise and the PME were used as a dependent variable. For each indicator, independent variables were selected: a) Official Health Expertise: gender, age, position, number of active statutory employees away, number of days of leave and number of days away; and b) PME: Gender, age, position, ethnicity, smoking, physical activity, BMI, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, spinal pain, inadequate furniture, inadequate lighting, likes what you do, good relationship with the boss, good relationship with colleagues and fast pace. In addition, the following indicators were observed: Absence Severity Index (IGA), Medical Frequency Leave (FML), Frequency of Workers on Sick Leave (FWML) and Absenteeism Duration Index (IDA), as recommended by the Permanent Commission and International Association on Occupational Health [ 8 ] and the authors Hensing et al. [ 9 ].
The information was obtained from Microsoft Excel spreadsheets, being possible to organize and sort the variables into categories. Then, the data were exported and analyzed in the software Statistical Package for the Social Science (SPSS). Relative and absolute frequency distribution was used for categorical variables, as well as measures of central tendency (average), measures of dispersion (standard deviation), and student's t-test for quantitative variables.
For data analysis, the chi-square test and the calculation of the odds ratio were used for correlation of the indicators, adopting a confidence interval of 95% and a significance level of 5% ( p < 0.05) for all tests.
Concerning the ethical aspects, the project was submitted to the Research Ethics Committee of Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte where it was appraised and subsequently approved under opinion no. 1.707.691, from the principles of ethical and legal aspects that govern scientific research on human beings, as recommended by Resolution no. 466/12 [ 10 ], and the principles expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki.
The results showed that there were 4,293 (35%) departures from administrative records and 7,946 (65%) absences from work granted by expert examination.
This expert examination is a procedure carried out by a medical expert, whose function is to identify if there is the presence of an illness or to identify if there has been an accident that has made you totally or partially, temporarily, or permanently unable to perform your professional activities [ 11 ]. The magnitude of these absences can be portrayed when we calculate the sum of lost work time over the five years, which generated 179,916 days of absenteeism due to illness.
Data regarding the sociodemographic characteristics of the studied population revealed that 67.9% (8,312) of the departures occurred in female workers and, for males, 32.1% (3,927). Regarding the age group, 34.6% (4,234) of the licenses were approved for workers between 51 and 60 years old, 24.0% (2,934) from 41 to 50 years, 19.2% (2,355) from 31 to 40 years, 11.8% (1,449) from 18 to 30 years, and 10.4% (1,267) over 60 years.
In relation to the post variable, the number of workers occupying the position of administrative technician in education levels C and D predominated, with a prevalence of 62.2% (4,941), while 23.8% (1,889) workers were in higher-level positions.
Figure 1 shows the absence of workers at work due to health care in the period from 2011 to 2015. It is noteworthy that there is an increase between 2011 and 2013, when there is a peak of 7.1 days not worked. The following years show an oscillation, but with a tendency for growth.
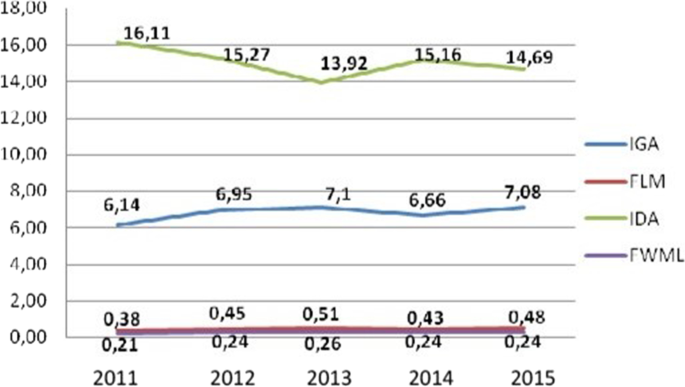
Source: Elaborated by the Authors
Indicators of absenteeism, 2011–2015. Natal/RN, Brazel, 2017. Legend IGA = Absenteeism Severity Index; FLM = Frequency of Medical Licence; IDA = Absenteeism Duration Index; FTLM = Frequency of Workers on Medical Licence.
In this sense, it is also relevant to present the individual absence duration, according to the cause of illness, in order to facilitate the adoption of specific measures focused on the pathologies with the greatest impact on lost days of work. Figure 2 shows the IDA according to each International Classification of Diseases (ICD), 10 chapter, and the highest indexes refer to neoplasms (45.64), mental disorders (32.40), congenital malformations (27.00), and diseases of the circulatory system (23.96), respectively. These findings reveal that absences of longer duration were caused by pathologies of a chronic non-transmissible nature, except for causes of absences in chapter XVII of ICD-10.
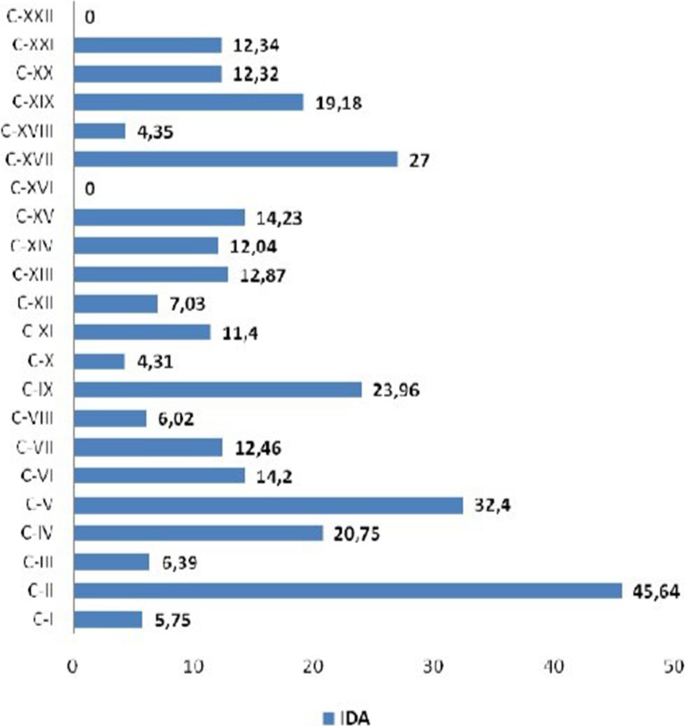
Source: Elaborated by the author
Distribution of IDA, 2011–2015. Natal/RN, Brazil, 2017. Legend: C = ICD.10 chapter.
Figure 3 presents the results of this study regarding the adherence of the workers to the Periodic Medical Exam (PME), considering the historical series from 2011 to 2015, when an average of 4,362 workers were called.

Source: Elaborated by the authors
Distribution of call, adhesion, non-adhesion, and coverage ratio to PME, 2011–2015. Natal/RN, Brazil, 2017.
The Periodic Medical Exam consists of the periodic clinical and laboratorial evaluation of the worker, due to the existing risks in the work environment and occupational or professional diseases. The PME foresees the adoption of prevention, tracking, and early diagnosis measures for work-related diseases, besides those more prevalent in the general population, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, neoplasms, dyslipidemias, and ophthalmologic diseases. Also, the PME will be carried out during working hours, without any burden or need for compensating schedules on the part of the employees. It is important to point out that absenteeism is taken into consideration only due to the worker's personal illness, and this diagnosis cannot be related to someone in the employee's care.
Regarding the operationalization for the PME, it is important to mention that at the moment the server is called for the evaluation of occupational health, through personal e-mail, he/she must fill out the consent form as a way to prove the agreement to participate in periodic medical examinations. Thus, going from the situation "INVITED" to "CONFIRMED". It is worth pointing out the importance and potential of the PME, once it allows the early identification of risk factors for getting sick, as well as the construction of collective diagnoses in the Worker's Health area, which makes this action a health management instrument, for monitoring the health situation and work conditions, and the subsidies for interventions to improve the quality of life of the workers.
It can be observed that the call-up ratio increased by 42.0% from 2011 (0.49) to 2012 (0.91). From the year 2013 (0.84), there were oscillations characterized by drop and growth in the calls.
As for non-adherence, in 2012, there was a decrease, and in 2013 (0.78), 2014 (0.8), and 2015 (0.86), there was an increase in the results, characterizing a relevant increase of 15. 0% between the years of 2011 (0.71) and 2015 (0.86).
About PME membership, it is clear that growth occurred only in 2012 (0.35). Then, the index decreased throughout the series, namely: 2013 (0.22), 2014 (0.2) and 2015 (0.14), which explains the non-adherence data, that comprehends the number of called servers that didn't do the PME in the analyzed year, having as reference the total number of UFRN's servers summoned in the evaluated year as being an unfavorable reality in relation to the PME recommendation. This may be related to factors such as excessive work activities of workers, periodic examinations performed through private health insurance, and to the lack of recognition of the importance of PME by workers.
The coverage ratio of the PME represents the servers that have concluded the PME and those that have an updated Occupational Health Certificate in the analyzed year, with the total number of servers at UFRN in the analyzed period as a reference. This coverage ratio increased significantly in the year 2012 (0.4), showing a growth of 26.0% in relation to 2011. Thereafter, the ratio decreased, with an average of 0.26 between the years of 2013 (0.33), 2014 (0.26) and 2015 (0.2), as shown in Fig. 3 .
In the list of risk factors, health indicators of different epidemiological natures were analyzed. Among them, those related to cardiovascular diseases and occupational risk factors, such as the existence of inadequate work furniture and accelerated work rhythm, are presented in Tables 1 and 2 .
In the list of chronic pathologies covering categories II and III of the Schilling classification, the most common causes of morbidity among workers are: Systemic Arterial Hypertension (SAH), chronic respiratory diseases, diseases of the locomotor system and mental disorders. These are pathologies of multiple etiology in which work is considered a risk factor associated with the increased probability of occurrence of these diseases [ 12 ]. Thus, the present study highlights cardiovascular diseases, especially SAH.
Table 1 shows the distribution of the aforementioned risk factors associated with SAH. It is pointed out that 60.6% (3,143) of the workers that performed the EMP presented non-ideal weight; 58.7% (3,044) practiced some type of physical activity; 70.8% (3,670) denied alcohol use; 96.5% (5.005) did not smoke; 93.9% (4,870) did not have diabetes mellitus (DM); and 66.6% (3,453) did not have dyslipidemia. The association between hypertension and all correlated variables was significant at p < 0.001. As for the Odds Ratio calculation, we considered the hypertension disease in relation to the following variables: BMI, sedentary lifestyle, alcoholism, smoking, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. The OR calculation does not imply a cause-and-effect relationship, it only suggests that there is an association.
In Table 2 , it is possible to observe that 35.9% of the interviewed workers are not adequate for their activities. In addition, 16.4% report loud noise in the workplace and 27.8% do not have adequate lighting. Social factors were also obtained, noting that 3.7% of the workers surveyed say they do not have a good relationship with their co-workers, while 4.4% do not have a good relationship with their boss and 2.5% show dissatisfaction with what they are doing.
It should be noted that absenteeism is a term used to denote the employee's absence from work [ 13 ]. The International Organization of Work (OIT) defines it as the period of absence of work that is accepted as attributable to an incapacity of the individual, except for that derived from normal pregnancy or prison [ 14 ].
According to the report of the National Audit Office [ 15 ], in the city of Guernsey, United Kingdom, approximately 3.8% of working time was lost due to illness, and civil workers became sick for an average of 8.7 days in 2005. In Chile, health workers belong to the category that has the highest rates of disability due to illness, with 14.3 days of absence per worker per year; unlike the university workers, who present 6 days of work lost per year, similar to the results of this research [ 16 ]. These findings highlight the data shown in Fig. 1 .
Studies found an average of 7.5 lost days of work per year per worker in the nursing area of a university hospital in Brazil [ 17 ]. Santos and Mattos [ 18 ] observed 9.3 days of absenteeism due to disease for each municipal worker of the city of Porto Alegre in 2005. The studies reported 9.1 and 10.3 days of absence due to illness for each public worker of the municipalities of Goiânia and São Paulo, respectively [ 19 , 20 ].
The worker and financial conditions can cause work accidents and environmental conditions, increase work capacity and the market, which may exclude work and consumption capacity. The employee is also hit with productivity, lack of manpower, loss of manpower and/or equipment damage [ 21 ].
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates about 36 million annual deaths from Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs), composed mainly of circulatory diseases, neoplasms, chronic respiratory diseases and Diabetes Mellitus (DM), which have risk factors.—smoking, alcohol, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet and obesity—modifiable in common [ 22 , 23 ].
An important characteristic of epidemiological patterns in Brazil concerns the changes in the composition of morbidity and mortality by groups of causes. Thus, the high prevalence of deaths from infectious and parasitic diseases, present at the beginning of the twentieth century, gave way to NCDs and injuries related to accidents and violence [ 24 ].
In Brazil, according to the Ministry of Health [ 23 ], NCDs are among the main causes of hospital admissions, and the financial cost to the Unified Health System (SUS) represents a growing impact. Estimates for Brazil suggest that the loss of productivity at work and the decrease in family income resulting from chronic pathologies such as diabetes, heart disease and stroke involved spending of US$ 4.18 billion between 2006 and 2015 [ 25 ].
The researchers Moura, Carvalho and Silva (2007) [ 26 ] carried out a study on the repercussion of CNCDs in the granting of social security benefits by the National Institute of Social Security (INSS) and identified musculoskeletal and circulatory system diseases as the main causes for granting sick pay.
This reality is also revealed among public servants in several studies that present the main groups of causes of sick leave for this category of workers, with high rates of absenteeism due to diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue, mental and behavioral disorders, chronic respiratory diseases and circulatory system diseases [ 7 , 19 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ].
The implementation of strategies to reduce absenteeism is a great challenge for employers, and it is necessary to analyze the events in the workplace to delineate situational diagnoses and guarantee actions to promote worker health. For the authors, the change in the epidemiological profile of illness and the increase in the prevalence of chronic diseases, as shown in Fig. 2 , reveal concern for the global scenario regarding the impact of these diseases on workers' health, due to the growth in the number of lost workdays [ 21 ].
The epidemiological profile of morbidity and mortality in Brazilian workers is characterized by the coexistence of diseases that have an intrinsic relation with working conditions, and in addition, diseases common to the population are observed, which are not etiologically related to the work [ 3 ]. In this reality, it is important to emphasize the importance of the employees performing the Periodic Medical Examination (PME), for the prevention and/or possible early detection of the pathologies that generate the greatest impact on the lost days of work, highlighting the neoplasms [ 22 ].
The importance of performing the PME in the screening of risk factors for chronic non-communicable diseases, such as dyslipidemia, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, and smoking is highlighted. In addition, through the PME, the workers will be guided and sent to participate in the various health promotion programs offered by the institution. Through these strategies, it is possible to reduce the prevalence of diseases of the circulatory system, another important cause of absenteeism, as shown in Fig. 2 .
As for Fig. 3 , which shows data on the PME, despite weaknesses, it is evident that the most satisfactory results of PME adherence occurred in the year 2012, a time when workers composed the Integrated Subsystem Unit (SIASS in Portuguese), as well as the constant discussion in forums, national meetings, and events related to the PASS, in a context of articulation in defense of the strengthening of the actions of attention to workers' health, which may have contributed to the results [ 23 , 24 , 25 ].
On the other hand, the situational diagnosis of low PME adherence throughout the historical series was possibly influenced by the recent history of PASS construction and the negative impact of the lack of structuring, planning, and evaluation of the actions. Plus, the largest investments and training, by the Ministry of Planning of Brazil, were related to the expert area which reflects as the main activity of the PASS [ 4 ].
The implementation of actions of health surveillance and promotion are major challenges for the consolidation of SIASS, since it is still a recent practice to promote health in public sector workplaces. It is necessary to elaborate indicators to support the actions and allow the evaluation of the results, considering that the information generated through indicators consolidates the control and planning of the organizational processes, as well as supports the decision making [ 25 , 26 ].
This is a prevention tool that has been implemented in Brazil with workers from federal agencies to identify risk factors associated with future illnesses. This approach in the federal public service has had an impact on the quality of preventive health, avoiding the removal of workers from their workplace for a cause classified as a possible prevention of this disease. Another aspect is the increasing number of absences that have been occurring in recent years, that is, the numbers of absenteeism due to physical and mental illnesses, a fact that occurs at increasingly younger workers' ages, which reveals the need for special attention and protector follow-up in their quality of life.
The results presented in this study deserve attention and can contribute to discussions between the professionals of the technical team and managers of the SIASS Unit and PROGESP/UFRN, as it is believed that the production of knowledge about the subject under study can provide the University with instruments, as well as other institutions at the federal public service level, through the PME as an indicator for planning and evaluating Occupational Health actions.
Thus, continuous investments in health policies aimed at public servants are suggested, which contributes to the reduction of illness and early retirement, resulting from disability. In this sense, investment in research that allows a better understanding of the relationship between health and work in the public service is also recommended.
It should be noted that this study had some limitations, as the use of self-reported data by employees who completed the PME may underestimate or overestimate the results presented.
In order to meet the proposed objective, there was the occurrence of neoplasms, mental disorders, and diseases of the circulatory system in terms of duration of absenteeism (IDA), which were the causes of the absences with a longer duration, which ratifies the epidemiological importance and the impact of non-communicable chronic diseases on workers' health. The gravity index of absenteeism revealed that the number of lost days of work per year per worker increased over the historical series, as well as the frequency of absences.
With regard to the epidemiological profile of the employees who underwent the PME throughout the historical series, it was possible to identify a significant prevalence of overweight in the population. The working conditions were considered satisfactory in the perception of the workers. It should be noted that this study presented some limitations, since the use of self-reported data by the workers may underestimate or overestimate the presented results.
Also observed through this study is the need to maintain and strengthen the PASS with emphasis on surveillance, aiming at the promotion and protection of the health of the workers, based on the elaboration of the epidemiological health profile and, consequently, the implementation of strategies of positive impact for OHS.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
International Classification of Diseases
Diabetes mellitus
Frequency of Medical Licence
Frequency of Workers on Medical Licence
Occupational Health and Safety
Absenteeism Duration Index
Absence Severity Index
International Organization of Work
Occupational Safety and Health Care Policy
Periodic Medical Examinations
Systemic Arterial Hypertension
Integrated Subsystem Unit
Statistical Package for Social Science
Medeiros Júnior A. Representação social sobre o acidente de trabalho na área da saúde. 172f. Tese (Doutorado em Ciências da Saúde) - Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Ciências da Saúde, Natal, 2005. Available from: https://repositorio.ufrn.br/handle/123456789/13370 . Accessed 10 Oct 2016.
Costa D, et al. Saúde do Trabalhador no SUS: desafios para uma política pública. Revista Brasileira de Saúde Ocupacional. 2013;38(127):11–21. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0303-76572013000100003 (Accessed 10 Oct 2016).
Article Google Scholar
Dias EC, Ribeiro EEN (Cord.). Construindo ações de Saúde do Trabalhador no âmbito das superintendências e gerências regionais de saúde. Belo Horizonte: Secretaria do Estado da Saúde de Minas Gerais, 2011. Available from: https://www.nescon.medicina.ufmg.br/biblioteca/imagem/2839.pdf . Accessed 10 Oct 2016.
Bizarria FPA, et al. Ações públicas voltadas para a promoção da saúde do trabalhador: Análise da política destinada à saúde do servidor público federal. Revista Eletrônica Gestão e Saúde. 2014;5(3):2019–30. Available from: https://periodicos.unb.br/index.php/rgs/article/view/669/565 Accessed 10 Oct 2016.
Google Scholar
Carneiro SAM. Saúde do trabalhador público: questão para a gestão de pessoas – a experiência na Prefeitura de São Paulo. Revista do Serviço Público. 2006;57(1):23–49. https://doi.org/10.21874/rsp.v57i1.188 (Accessed 10 Oct 2016).
Rebello CHB, Sortica MA. Exame Médico Periódico de Saúde [TCC on the Internet]. Santa Catarina: Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina; 2000. Exame Médico Periódico de Saúde; [cited 2022 Jun 10]; Available from: https://repositorio.ufsc.br/bitstream/handle/123456789/104977/Exame%20medico%20periodico%20de%20saude.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Gasparini SM, Barreto SM, Assunção AA. O professor, as condições de trabalho e os efeitos sobre sua saúde. Educ Pesqui. 2005;31(2):189–99.
Permanent Commission and International Association on Occupational Health. Subcommittee on absenteeism: draft recommendations. Br J Ind Med. 1973;30(4):402–3. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.30.4.402 (Accessed 10 Oct 2016).
Hensing G, et al. How to measure sickness absence? Literature review and suggestion of five basic measures. Scand J Soc Med. 1998;26(2):133–44. https://doi.org/10.1177/14034948980260020201 (Accessed 10 Oct 2016).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ministério da Saúde (BR). Conselho Nacional de Saúde. Resolução nº 466, de 12 de dezembro de 2012. Aprova diretrizes e normas regulamentadoras de pesquisas envolvendo seres humanos. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde, 2012. Available from: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/cns/2013/res0466_12_12_2012.html . Accessed 10 Oct 2016.
Perícia médica do INSS: veja 10 principais dúvidas e respostas [Internet]. [place unknown]; 2021 Oct 06. Perícia médica do INSS: veja 10 principais dúvidas e respostas; [cited 2022 Jun 14]; Available from: https://motaadvocacia.com/10-perguntas-e-respostas-sobre-pericia-medica/ .
Mendes R. O impacto dos efeitos da ocupação sobre a saúde de trabalhadores: I. morbidade. Rev Saude Publica. 1988;22(4):311–26. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89101988000400007 Accessed 10 Oct 2016.
Oenning NSX, Carvalho FM, Lima VMC. Indicadores de absenteísmo e diagnósticos associados às licenças médicas de trabalhadores da área de serviços de uma indústria de petróleo. Revista Brasileira de Saúde Ocupacional. 2012;37(125):150–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0303-76572012000100018 ( Accessed 10 Oct 2016 ).
Organización Internacional del Trabajo (OIT). Absentismo: causa y control. In: Enciclopedia de salud y seguridad en el trabajo. Madrid: OIT, 1989, 1:5-12. Accessed 10 Oct 2016
National Audite Office. Managing Sickness Absencein the States of Guernsey. Report by the national audit office for the public accounts committee, 2006. Available from: https://gov.gg/CHttpHandler.ashx?id=5139&p=0 . Accessed 10 Oct 2016.
Mesa MFR, Kaempffer RAM. 30 años de estudio sobre ausentismo laboral en Chile: una perspectiva por tipos de empresas. Rev Med Chil. 2004;132(9):1100–8. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0034-98872004000900012 (Accessed 10 Oct 2016).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Silva DMPP, Marziale MHP. Absenteísmo de trabalhadores de enfermagem em um hospital universitário. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2000;8(5):44–51. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-11692000000500007 (Accessed 10 Oct 2016).
Santos JP, Mattos AP. Absentismo-doença na prefeitura municipal de Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul. Brasil Revista Brasileira de Saúde Ocupacional. 2010;35(121):148–56. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0303-76572010000100016 (Accessed 10 Oct 2016).
Leão ALM. et al. Absenteísmo-doença no serviço público municipal de Goiânia. Revista Brasileira de Epidemiologia, 2015, 18(1): 262–77. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5497201500010020 . Accessed 10 Oct 2016.
Sala A, et al. Licenças médicas entre trabalhadores da Secretaria de Estado da Saúde de São Paulo no ano de 2004. Cad Saude Publica. 2009;25(10):2168–78. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-311X2009001000008 (Accessed 10 Oct 2016).
Bedin B. Prevenção de acidentes sob a ótica de incentivos econômicos. 123f. Dissertação (mestrado) Universidade de Caxias do Sul, 2009.
World Health Organization. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2010. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
Ministério da Saúde (BR). Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Departamento de Análise de Situação de Saúde. Plano de Ações Estratégicas para o Enfrentamento das Doenças Crônicas Não Transmissíveis (DCNT) no Brasil 2011–2022. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde, 2011a. 160 p. Available from: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/plano_acoes_enfrent_dcnt_2011.pdf . Accessed 27 Jun 2022
Carmo EH, Barreto ML, Jarbas BSJ. Mudanças nos padrões de morbimortalidade da população brasileira: os desafios para um novo século. Epidemiol. Serv. Saúde [Internet]. 2003 Jun [citado 2022 Jun 27] ; 12( 2 ): 63–75. Available from: http://scielo.iec.gov.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1679-49742003000200002&lng=pt . Accessed 27 Jun 2022.
Abegunde DO, Mathers CD, Adam T, Ortegon M, Strong K. The burden and costs of chronic diseases in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2007;370(9603):1929–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61696-1 (Accessed 27 Jun 2022).
Moura AAG, Carvalho EF, Silva NJC. Impacts of non-transmissible chronic diseases on social security benefits. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva. 2007; 12(6) Available from: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=63013517027 . Accessed 27 Jun 2022
Silva DO. Fatores associados à ocorrência e a duração dos afastamentos para tratamento da saúde em trabalhadores de uma Instituição Federal de Ensino Superior na Bahia [Dissertação]. Bahia: Universidade Federal da Bahia; 2010. Available from: https://repositorio.ufba.br/bitstream/ri/10324/1/77777777777777.pdf . Acessed 27 Jun 2022.
Sala A, Carro ARL, Correa AN, Seixas PHDA. Licenças médicas entre trabalhadores da Secretaria de Estado da Saúde de São Paulo no ano de 2004. Cad Saúde Pública. 2009;25(10):2168–78. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-311X2009001000008 (Acessed 27 Jun 2022).
do Vale SF, Maciel RH, do Nascimento APT, Vasconcelos JWO, Pimentel FHP. Análise de diagnósticos associados às licenças médicas de servidores públicos do Ceará. revpsico, 2015;6(1):68–1. Available from: http://www.periodicos.ufc.br/psicologiaufc/article/view/1694 . Acessed 27 Jun 2022.
Cunha JB, Blank VLG, Boing AF. Tendência temporal de afastamento do trabalho em servidores públicos (1995–2005). Rev. bras. epidemiol., 2009; 12(2):226–236. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-790X2009000200012 . Acessed 27 Jun 2022.
Marangoni VSL, Neves ALM, Filho ZAS, Martins GC. Afastamento laboral por transtornos mentais entre os servidores da prefeitura municipal de Manaus: uma análise preliminar. Semina: Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde, 2016;37(2):13–24. doi: https://doi.org/10.5433/1679-0367.2016v37n2p13 . Acessed 27 Jun 2022.
Andrade TB, et al. Prevalência de absenteísmo entre trabalhadores do serviço público. Scientia Medica. 2008;18(4):166–71. Available from https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/lil-503535 Accessed 10 Oct 2016.
Pawlina MMC, Campos AF de, Ribeiro LS. Características de absenteísmo entre trabalhadores da saúde: nível central da Secretaria de Estado de Saúde/MT de 2005 a 2006. PPP, 2022;(33). Disponível em: // www.ipea.gov.br/ppp/index.php/PPP/article/view/158 . Acessed 27 Jun 2022.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This study was partially funded by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel—Brazil (CAPES)—Financial Code 001. Funders have no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, publication decision or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nurse. Master in Public Health, Federal University of Rio Grande Do Norte, Natal, Brazil
Lídia Maria Costa Araújo Magalhães
Nursing Student. Federal University of Rio Grande Do Norte, National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), Natal, Brazil
Ketyllem Tayanne da Silva Costa & Gustavo Nepomuceno Capistrano
Nursing Student, Federal University of Rio Grande Do Norte, Natal, Brazil
Maryanna Damasceno Leal
Nurse. Doctor in Health Sciences. Post Graduate Program. Federal University of Rio Grande Do Norte, Natal, Brazil
Fábia Barbosa de Andrade
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
L.M.C.A.M. was the principal investigator of the project and responsible for administration, coordination, and funding acquisition. L.M.C.A.M. and F.B.A. were involved in conceptualization and in the study design. L.M.C.A.M. carried out the investigation. L.M.C.A.M., K.T.S.C., G.N.C. and M.D.L. were involved in formal analysis and data curation and wrote the main manuscript text. F.B.A. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ketyllem Tayanne da Silva Costa .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This project was submitted to the Research Ethics Committee of Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte where it was appraised and subsequently approved under opinion no. 1.707.691, from the principles of ethical and legal aspects that govern scientific research on human beings, as recommended by Resolution no. 466/12 [ 8 ], and the principles expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Magalhães, L.M.C.A., Silva Costa, K.T., Capistrano, G.N. et al. A study on occupational health and safety. BMC Public Health 22 , 2186 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14584-w
Download citation
Received : 05 April 2022
Accepted : 09 November 2022
Published : 25 November 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14584-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Occupational health
- Occupational health services
- Surveillance
- Workers health
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Occupational health and safety

Related Papers
kenneth mivule
Basic of risk management in malaysia
BERNARD NKEMBOH
Due to inadequacy in industries in Cameroon, approximately 12 fatalities and hundreds of workers become permanently disabled in occupational accidents. Occupational accidents cause serious financial loss for both the company and the country economies. This study is conducted to analyze causes and results of occupational accidents and illnesses in a process industry with case study, LA PASTA S.A coupled with the aim to promote safety in industries. Research data consists of the occupational accidents and illnesses statistics of 2014 – 2015 (January to June) time period in LA PASTA S.A Douala – Cameroon, which is obtained using ‘Pareto Chart and Retrospective Cohort’ method. In this study, causes and results of occupational accidents and illnesses, which occurred in LA PASTA, are investigated. The main reasons for accidents occurrence are the being stung by something, cuts, caught between objects, slipping, stumbling and falling from heights and from the same level. As a result of occupational accidents, injuries occurred in the form of incision, exposure to flour particles/ metal burns, contusion, transient loss of vision, amputations, trauma, and fracture. Back, arm, foot, leg, hand, finger and shoulder injuries are the most common accidents. The most important occupational illnesses/ diseases is low back pain and back pain due to the fact that most workers do overexertion manually. The most important reason of occupational accidents is ‘unsafe behaviors’ with a rate of 51% which is defined as not to obey the rules although the necessary occupational safety measures are provided. According to our research, about 1400 industrial accidents occur each year in Cameroon since 2010, this figure has not been review due to the fact that occupational accidents and illnesses statistics are not kept enough in Cameroon also, industries do not declare these accidents promptly.
omniScriptum GmbH & Co.KG, BahnhofstraBe 28,66111 Saarbrucken, Deutshland/Germany,[email protected],
Madhav Prasad Koirala
Construction is a dominant part of any country’s infrastructure and industrial development. Construction industries are being associated with it direct and indirect linkages with various other industries like cement, steel bricks etc. generate employment in the country. Construction industry contributed economic activity next to agriculture. But there is a darker side to this explosive growth. For all the big money involved, the sector has barely regarded for the safety of those who work in its lowest rungs. In Nepal, Construction safety in the industry still suffers from ignorance and lack of supervision and accident rate on construction projects is very high. It need to identify the awareness lunched in the construction industries that relate to safety, problems related ergonomic health and safety, and the status of safety engineering management as perceived by construction and consultancies to help reduction of accidents.
Nicholas Petrovski
Occupational safety and health management is being increasingly practiced on a global scale. Therefore, it is important for professionals working in this field to be well informed about existing international programs, organizations, practices, and issues. This handbook is a starting point for someone interested in learning more about global health and safety topics. Occupational health and safety professionals with responsibilities for worker health and safety policy, planning, and operations internationally should be well versed in many of the subjects discussed in this handbook. Ready access to relevant guidelines and information on specific topics makes this handbook a valuable tool for the health and safety practitioner traveling abroad to work, or managing those that do. The aim of the handbook is to provide a reference and guide to those who, within organizations or governments, may hold key responsibilities for occupational safety and health of workers in foreign countries. Thus, its underlying purpose is to assist occupational hygienists and managers in attaining standards of professionalism that will enable them to deal with day-today health and safety management across international borders and in an expansive range of cultural, political, and regulatory situations.
Mazurah Mohamad Ikhwan
Green Productivity (GP) is the concept applicable to whole humane activities. By GP promotion and implementation, quality, environment and productivity improvement could be realized. (Win-Win Approach) Occupational environmental health and safety (OEHS) is the most important targeted area of GP application. Especially, small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs), which generally have difficulty in tackling OEHS problem systematically (Knowledge, experience, human resources and fund), are recommended to apply and implement GP efficiently and effectively, leading to excellent OEHS company. Governmental and other institutional supports such as appropriate law/regulation enforcement, presentation of guideline and monitoring are important. However the most important thing to make comfortable working place is the collaboration among owners, management and employers in the organization. The integration of occupational health and safety, environment and quality have been studied recently; 1) Guideline for Occupational Safety and Health Management System (OHMS) by International Labor Organization (ILO), 2) Integration of ISO 9000 (Quality) and ISO14000 (Environment). The integration of OEHS, frequently discussed as above, is difficult to be realized because of wide range of themes contained. However OEHS themes could be classified into common and individual natures. GP is the most effective measures to provide effective answer to solve common problem. To promote and implement OEHS in organization efficiently basic information is required. This manual provides basic information of OEHS and GP based on the information and data of seminars and workshops hosted by APO. Also in this manual, experimental integration of GP and OEHS themes are studied and contained. Based on this information, the maximum application of GP in the area of occupational environmental health and safety will create comfortable, safe and healthy working places.
ARID ZONE JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING, TECHNOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT
Lekha Laxman
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Leonell Cantos
American Journal of Industrial Medicine
ilise feitshans
Castro Gyamfi
Shams Ullah
Technological University (Myitkyina)
Hkyeng Seng Naw Awng
Lynda Diane Mull
Immortal Blackheart
WORKPLACE HAZARD AMONG AUTOMECHANICS
Williams Mathias
N. Petersson , Kaj Elgstrand , Thomas Patrick Dwyer Dwyer , Gunnar Broms , Bahira Lotfy , Martha Blomqvist , Kerstin Ahlberg , João de Souza
9.Uluslararası İş sağlığı ve güvenliği kongresi
AHMET FATIH KOCAER
Phineas Haluse
GETAHUN ABEYE
Rendiconti Del Circolo Matematico Di Palermo
Book Abstracts - Integration of safety in management tasks in onshore transport SME´s
Marco Antonio Pereira Querol
Marius Dumitrascu
Shuvo Hassan
mesut kandemir
sinisa stojakovic
Royston Tang
SHATRUGHNA QEHS
Chhabi Ranabhat
Shivnarayan Singh
Summaries chapters 1 to 8 Occupational Health and Safety
Juliana Escovar
Dr. Shamsul Bahri Mohd Tamrin
Yoseph Zelalem
Bello RS, PhD
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- DOI: 10.26686/nzjhsp.v1i2.9550
- Corpus ID: 271832472
What’s missing in the New Zealand workplace health and safety system?
- Christopher Peace
- Published in New Zealand Journal of Health… 8 August 2024
- Law, Environmental Science
- New Zealand Journal of Health and Safety Practice
44 References
A new conceptual framework to improve the application of occupational health and safety management systems, due diligence: a panacea for health and safety risk governance, compliance: regulation and environment, work fatalities, bereaved families and the enforcement of ohs legislation, the court of appeal, employer's liability at common law, proceeds of crime act, why do key decision-makers fail to foresee extreme 'black swan' events a case study of the pike river mine disaster, new zealand, in search of excellence : lessons from america's best-run companies, a fine is a more effective financial deterrent when framed retributively and extracted publicly, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Occup Environ Med
- v.26(2); Apr-Jun 2022
A Study of the Effectiveness of Workplace Health and Safety Programmes in a University Setting in Canada
Zakia hoque.
Division of Community Health and Humanities, Faculty of Medicine, Memorial University, St John's, NL, A1B 3V6, Canada
Veeresh Gadag
Atanu sarkar, introduction:.
Nearly a quarter-million people work in universities in Canada, making it one of the fastest-growing sectors. Although each university provides occupational health and safety services and training programmes to their employees, there have been no studies conducted on the impact of such programmes on employees’ knowledge, attitude and behaviour. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of dissemination of information of workplace health and safety programmes to workers at a Canadian university.
The study compared two cross-sectional online surveys of employees of a Canadian university regarding workplace health and safety with a previously conducted cross-sectional study and thematic analysis of key informant interviews to address the issues raised in the surveys.
Participation in health and safety presentations could enhance understanding and practices of safety. Age, employment status and duration of employment were associated with the levels of knowledge, attitudes and behaviour of employees and graduate students. The key informant interviews highlighted some new initiatives such as the establishment of workplace health and safety committees in all university buildings; the development of a safety app and health and safety management system; routine annual inspections of all university building offices and laboratories; new orientation for undergraduate students where general safety rules are described.

Discussion:
University should have regular presentations on the available health and safety programmes and should increase the number of safety training programmes and keep track of the employees that have not received any training, particularly for those working in hazardous environments.
I NTRODUCTION
The labour force in the university sector in Canada is large and has considerable occupational diversity. According to Statistics Canada, out of 17 million-member workforce, 1.3 million (8%) are in educational services, and almost 20% of these individuals (~250,000) work in various universities.[ 1 ] The 2016 census shows that educational services in Canada had the fourth-highest rate of growth and more than half of this increase was in universities.[ 2 ] The working environment in universities is highly diverse, as there are a wide range of disciplines involving teaching, research, administration and maintenance. Due to this multifaceted working environment in the universities, employees encounter various types of occupational health risks. Despite the complexity of occupational risks, little has been written about occupational health and safety programmes of the university employment sector.[ 3 ]
In Canada, workers are covered by provincial or federal labour codes, depending on the sectors in which they work. While workers in mining, transportation, and the federal government are covered by the Canada Labor Codes, other workers such as employees of universities are covered by provincial health and safety legislation.[ 4 ]
Venables and Allender (2007) described the occupational health services in 93 universities in the UK by drawing on data from surveys carried out in 2002, 2003 and 2004. Most survey responses were received from universities and in-house services. The surveys requested self-completed information on occupational health services from each university. The results indicated that 50% of the universities had an in-house health service, 32% relied on a contractor, 9% used the campus student health service, and a further 9% had an ad hoc arrangement or no arrangement. On average, the service was poor, as usually only one half-day doctor with one full-time nurse and a part-time clerk were available to provide service. The wide variation among universities in staffing levels suggested that some universities might have less-adequate services than others.[ 3 ] A study examining the safety concerns of faculty members of a university campus in USA (Alabama) showed that women faculty members took more personal safety precautions than men and felt more strongly about the need for the improvement of safety features on campus. A 160-item questionnaire was distributed to the faculty members asking about socio-demographic information, daily campus activities, personal safety protection taken while on campus, awareness and attitudes about safety on campus, and reported cases of victimization on campus. A few months later, the authors examined the safety awareness of male and female staff members in the same university using the same questionnaire. The results indicated that although female staff members reported more regarding acts of violence against them than male staff members, there was not much difference in their attitudes towards improving safety features on campus. Faculty and staff members identified that they like to use avoidance strategies such as walking with a friend or using objects as a weapon rather than contacting campus security.[ 5 ]
All Canadian universities have Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) or similar departments through which Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) services are provided. All the universities follow a similar practice such as a) having health and safety committees on the campus, b) promoting health and safety and providing risk management services, c) conducting regular workplace inspections and reviewing incident investigative reports, e) creating annual reports about incidents, lessons learned, and providing recommendations to senior administrators, and e) organizing health and safety information session for the employees. The EHS unit mainly offers training on fire safety, first aid, laboratory safety, biosafety, X-ray safety, radiation and laser safety, WHMIS (Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System), contractor safety, respiratory protection, ergonomics, hazardous waste management and disposal and also provides health and safety committee representative training.[ 6 ]
Despite the existence of occupational health and safety programmes in various Canadian universities, recorded evaluation of such programmes is sparse. Considering the large workforces in universities and their unabated positive growth, it is crucial to evaluate the existing occupational health and safety programmes in Canadian university settings. The aims of this study were: a) to evaluate the effectiveness of health and safety programmes through well-designed surveys of faculty members, staff and graduate students of a Canadian university (Memorial University of Newfoundland or MUN); and b) to conduct a key informant interview of the officials of MUN responsible for the operation of the health and safety unit to address the issues raised in the surveys.
In 2013, MUN contracted a third-party consultant to conduct an impartial assessment of the safety culture at the university. The consulting group was asked to do a complete assessment of the current state of health and safety programmes offered by MUN through the Office of the Chief Risk Officer and to identify gaps in the programme. The consulting group surveyed about 10% of the permanent employees of MUN in 2013 and produced a report in 2014. The Office of the Chief Risk Officer called the report a ‘Gap Analysis (GA) survey’. In 2015, to address the identified gaps and to increase awareness about the health and safety programmes, the Office of the Chief Risk Officer organized several health and safety presentations for MUN employees. We sought to examine if these presentations had any effect on the knowledge, attitudes and behaviour of the employees and graduate students at MUN and if their level of knowledge, attitudes and behaviour are sustainable over time. As a result, in consultation with the EHS Unit in 2016, we administered two identical online surveys to employees and graduate students at MUN. The purpose of the first survey was to answer the following research questions:
- Has there been any significant improvement in the perception of the workplace health and safety of MUN employees since 2013 when the survey on gap analysis in safety culture was conducted?
- Do knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding the health and safety of MUN employees differ with respect to demographic variables?
- Is there any significant difference in the perception of safety practices between those who attended the health and safety presentations and those who did not attend these presentations?
The purpose of the second survey (using the same questionnaires of the first survey) was to assess the retention of health and safety knowledge over the period of 6 months. The intent of conducting the surveys was to gain insight into important factors that could make MUN's health and safety programmes more effective. The study also intended to explore the responses of the officials to the issues raised in the surveys.
We used a mixed-methods approach by collecting, analysing and integrating quantitative (surveys) and qualitative (interviews) data to gain in-depth understanding and corroboration while offsetting the weaknesses inherent in using each approach by itself.[ 7 , 8 , 9 ] Approval from the ethics committee was obtained. The date of the approval 23rd August 2016.
Survey participants
The survey participants in the two surveys that we conducted, included graduate students/researchers, faculty members and staff, as they work for the MUN as employees. As the surveys were anonymous, the second survey was sent to the same entire population and not to only the respondents of the first survey. This allowed us to compare the results with those of the independent surveys to determine if there are any changes in the knowledge level of the employees on health and safety-related information.
Survey design
Two identical online surveys of MUN employees were conducted between 1) October 19, 2016 and November 30, 2016, and 2) April 10, 2017 and June 10, 2017. The purpose of the first survey was to gauge the level of uptake of the information on health and safety, disseminated by the EHS Unit to the MUN Community through their safety workshops in 2015–2016 as well as through their broader reach-out mechanisms. Further, we wanted to study the effect of the knowledge about health and safety on the attitudes and behaviour of the employees and graduate students at MUN. The second survey was conducted six months after the first survey. It targeted the same population and followed the same methodology as the first survey and aimed to understand the retention of knowledge over time and whether the knowledge, attitudes and behaviour of the employees changed over time.
Our survey was developed based on input from the EHS unit. Some questions were based on questions from the GA survey with the intent of comparing the results. We also adopted some questions from the survey questionnaire of the study ‘Montana Tech Campus Safety, Security and Safety Awareness Survey’ conducted by Kristine Witt in 2011 at Montana Tech University, USA.[ 10 ] We conducted a pilot survey of some faculty members, staff and graduate students to ensure the readability, clarity, and organization of the survey questionnaire. We sent e-mails to all faculty and departments of MUN's main campus in St. John's and affiliated Grenfell campus in Corner Brooke, detailing the nature of the survey and provided a web-link (Survey Monkey ® ) to access the survey. The questionnaire with the references is presented in a supplementary file (S1) . At the beginning of the survey, online consent was obtained. The survey instrument was prepared to capture the awareness, attitudes and behaviour of employees and graduate students toward health and safety programmes offered by MUN. The questions were divided into three groups: 1. Knowledge (refers to the awareness and perception of the participants related to health and safety); 2. Attitudes (collects information on the viewpoints and beliefs of the participants about occupational health and safety); and 3. Behaviour (collects information on participants’ day-to-day safety practices/protocols at the workplace).[ 11 ] Questions 7-18, 21, 22, 25, 29, 31 and 40 were designed to test the knowledge of the participants regarding occupational health and safety; questions 19–20, 26–27 were combined to assess their attitudes; and questions 28, 30, 32, 34, 36 and 41 were grouped under behavioural questions (please refer to the questionnaire in supplementary file S1 ). The last few questions were on the perceptions of the participants about safety in specific areas on the campuses.
In the knowledge group, there are 18 questions. For each question, we assigned a score of 1 for the answer “No” and a score of 2 for the answer “Yes”. We added the scores of these 18 questions, which ranged from 18 to 36. We divided this range of responses into halves, 18–27 representing lower score and 28–36 representing higher score, following the procedure described in.[ 12 , 13 ] we used a similar procedure with four questions representing attitudes and six questions representing behaviour groups. The purpose of creating these categories was to test for the association between the levels of the knowledge, attitude, and behaviour of the participants among themselves and with the demographic variables, using frequency analysis technique.
In order to compare with the GA survey, we selected only the Yes/No-type questions (similar to the GA survey) and divided them into three broad themes: i) Environmental Health and Safety Office-related questions, ii) Faculty/Building-related questions, and iii) Department/Division-related questions.
Key informant interviews (KII)
After completing the cross-sectional surveys, we conducted KII with eight officials who have been responsible for the development and implementation of health and safety programmes at MUN. Among them, five officials were from the Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) unit, two officials were from the Workplace Health and Safety Committee (WHSC) and one official was from Facilities Management (FM). The interviews were recorded in writing. A thematic content analysis approach was used for data analysis. Each transcript was reviewed and coded to identify key emerging themes. We then compared the coding of the transcripts. The first question of the interview is about the initiatives taken by the EHS unit to raise awareness about health and safety among MUN employees after 2013. For further analysis, we divided the rest of the questions into three groups. The first group is about knowledge and awareness of safety policies. Questions 2–6, 12 are included in this group. Questions 7–10 are in the group on laboratory safety and workplace hazards. Questions 11, and 13–15 are in the group of MUN facilities and services (please refer to the questionnaire in supplementary file S2 ). The primary motivation of the KII was to collect further information related to the survey questionnaire and to find answers to some of the comments made by the participants in the surveys. Therefore, some questions asked in the KII were based on the outcomes of the survey results.
Data analysis
Apart from descriptive statistics, Chi-square tests were conducted for correlation and P - value less than 0.05 was considered significant. For data analysis, SPSS (version 24) was used. For a detailed statistical analysis, please refer to the supplementary file (S3) .
In the first and second surveys, 148 and 103 valid independent respondents were identified, respectively. Table 1 shows demographic information of survey 1 and survey 2 participants. There was an increase in the level of the participants’ knowledge/awareness about MUN's health and safety policies, when compared to GA survey (please see detailed findings in Supplementary file (S4) ). There was an increase in the level of awareness among the employees about the presence of the EHS unit at MUN and improved communication with the Health and Safety Committee compared to GA results. On the other hand, there were lower levels of knowledge about MUN's working alone procedures, and about AED (automated external defibrillator) locations. In all three surveys, the participants demonstrated little familiarity with the OHS Act.
Demographic characteristics of the university worker participants
| Demographic information | Survey 1 =148 | Survey 2 =103 |
|---|---|---|
| Employment status | ||
| Faculty | 19 | 24 |
| Staff/administrator | 48 | 35 |
| Graduate student/researcher | 33 | 41 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 51 | 52 |
| Female | 49 | 48 |
| Department? | ||
| Medicine | 21 | 22 |
| Pharmacy | 1 | 2 |
| Nursing | 1 | 1 |
| Science | 8 | 8 |
| Engineering | 38 | 42 |
| Business | 5 | 7 |
| Education | 1 | 1 |
| Arts | 2 | 2 |
| Administrative and other offices | 23 | 15 |
| Years of Age | ||
| Less than 30 | 22 | 20 |
| 30-39 | 26 | 29 |
| 40-49 | 23 | 31 |
| 50-59 | 20 | 12 |
| 60 or more | 9 | 8 |
| Duration of employment | ||
| Less than 4 years | 43 | 53 |
| 4-9 years | 24 | 19 |
| 10-14 years | 9 | 13 |
| 15-19 years | 11 | 5 |
| 20-24 years | 5 | 2 |
| 25 years or more | 8 | 8 |
| Attended the safety presentation at MUN | ||
| No | 42 | 44 |
| Yes | 47 | 41 |
| I don’t remember | 11 | 15 |
We have observed some association between demographic variables and knowledge, attitudes and behaviour (safety practices) of employees regarding health and safety programmes. Table 2 presents the association between the knowledge level score and demographics of the employees. In the first survey, there are associations between ‘the level of health and safety knowledge of the participants’ and their (a) ‘attendance at the safety presentations’ ( P < 0.05), b) ‘employment status’ i.e., faculty/staff/graduate student ( P < 0.05) and c) ‘age’ ( P < 0.05). For a detailed statistical analysis, please refer to supplementary file (S3) [Tables # S3.3.1 , S3.3.2 , S3.3.3 ]. In the second survey, there are associations between: ‘the level of health and safety knowledge’ and (a) ‘employment status’ ( P < 0.05), b) ‘age’ ( P < 0.05), and c) ‘duration of employment’ ( P < 0.05). For a detailed statistical analysis, please refer to supplementary file (S3) [Tables # S3.3.4 , S3.3.5 , S3.3.6 ].
Cross-tabulation between demographics and Knowledge level score
| Whether attended the safety presentation at MUN | Survey 1 | Survey 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low score | High score | Low score | High score | |
| No | 23 | 23 | 15 | 20 |
| Yes | 9 | 50 | 8 | 28 |
| Employment status | ||||
| Faculty | 6 | 16 | 6 | 15 |
| Staff/administrator | 6 | 52 | 4 | 26 |
| Researcher/graduate student | 24 | 13 | 17 | 17 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 20 | 35 | 14 | 32 |
| Female | 17 | 44 | 13 | 26 |
| Age | ||||
| Below 40 years | 24 | 30 | 18 | 22 |
| 40 years or more | 13 | 50 | 8 | 35 |
| Duration of employment | ||||
| Less than 4 years | 5 | 13 | 7 | 11 |
| 4 years or more | 8 | 53 | 3 | 28 |
* Low score: 18-27; High score: 28-36; α significant for survey 1, β significant for survey 2
Table 3 presents the attitude level score and demographics of the participants. In the first survey, there are associations between ‘the level of attitude towards safety’ and: a) ‘employment status’ a) ( P < 0.05), and b) ‘age’ ( P < 0.05). In the second survey, no association was found between any of the demographic information and attitude towards safety. Please refer to Supplementary file S3 for a detailed statistical analysis [Tables # S3.4.1 , S3.4.2 ].
Cross-tabulation between demographics and attitude level and behaviour level scores
| Survey 1 | Survey 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attitude level score | ||||
| Whether attended the safety presentation at MUN | Low | High | Low | High |
| No | 35 | 42 | 30 | 13 |
| Yes | 23 | 19 | 24 | 14 |
| Employment status | ||||
| Faculty | 16 | 9 | 14 | 10 |
| Staff/administrator | 49 | 16 | 26 | 9 |
| Researcher/graduate student | 22 | 21 | 24 | 13 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 44 | 20 | 32 | 19 |
| Female | 42 | 27 | 32 | 13 |
| Age | ||||
| Below 40 years | 35 | 28 | 32 | 13 |
| 40 years or more | 52 | 18 | 31 | 18 |
| Duration of employment | ||||
| Less than 4 years | 15 | 4 | 13 | 8 |
| 4 years or more | 49 | 21 | 26 | 10 |
| Behaviour level score | ||||
| Whether attended the safety presentation at MUN | ||||
| No | 44 | 9 | 32 | 3 |
| Yes | 39 | 23 | 21 | 15 |
| Employment status | ||||
| Faculty | 19 | 5 | 17 | 4 |
| Staff/administrator | 38 | 27 | 22 | 9 |
| Researcher/graduate student | 36 | 5 | 26 | 7 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 47 | 14 | 33 | 14 |
| Female | 47 | 22 | 32 | 6 |
| Age | ||||
| Below 40 years | 46 | 14 | 30 | 9 |
α significant for survey 1, β significant for survey 2
Table 4 also presents the association between ‘the behaviour (safety practice) level score’ and ‘demographic variables’ of the participants. In the first survey, there are associations between ‘behaviour level score’ and: a) ‘attendance at the safety presentation’ ( P < 0.05), and b) ‘employment status’ ( P < 0.05). In the second survey, there is an association between ‘attendance of the safety presentation’ and ‘behaviour level score’ related to health and safety ( P < 0.05). Please refer to Supplementary file S3 for a detailed statistical analysis [Tables # S3.5.1 , S3.5.2 , S3.5.3 ].
Laboratory safety related responses from different groups (in percentage)
| Faculty/staff/administrator | Survey 1 | Survey 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agree | Neutral | Disagree | Agree | Neutral | Disagree | |
| I feel safe in campus labs | 70 | 28 | 2 | 82 | 18 | 0 |
| PPE is available in the labs | 62 | 33 | 5 | 78 | 21 | 1 |
| Lab safety is properly explained | 66 | 26 | 8 | 65 | 35 | 0 |
| I received training on appropriate use of eyewash station | 57 | 27 | 16 | 63 | 29 | 8 |
| I know the location of the nearest safety shower | 63 | 24 | 13 | 76 | 16 | 8 |
| Overall the lab is safe | 59 | 37 | 4 | 63 | 37 | 0 |
| Graduate student/researcher | ||||||
| I feel safe in campus labs | 51 | 43 | 6 | 37 | 53 | 10 |
| PPE is available in the labs | 63 | 34 | 3 | 46 | 47 | 7 |
| Lab safety is properly explained | 58 | 34 | 8 | 38 | 52 | 10 |
| I received training on appropriate use of eyewash station | 53 | 30 | 17 | 45 | 39 | 16 |
| I know the location of the nearest safety shower | 58 | 31 | 11 | 50 | 38 | 12 |
| Overall the lab is safe | 50 | 40 | 10 | 44 | 39 | 17 |
In our two surveys, we observed that those who attended safety presentations had a better level of safety practices than those who did not attend the safety presentations. Overall, there is no significant difference in the knowledge, attitudes, and behaviour of the employees and graduate students between the two surveys. In Tables Tables2 2 and and3, 3 , the Chi square test results indicate that the levels of knowledge, attitudes and behaviour of the employees and graduate students have not changed much over the period of six months.
The only change we observed is a decrease in the knowledge of graduate students and researchers regarding laboratory safety in the second survey [ Table 4 ]. In both surveys, the participants reported that some places on the campus are safe [ Table 4 ]. In the first survey, 70% of the faculty/staff reported that they felt safe in the campus labs, and 51% of graduate students/researchers reported that they felt safe in the campus labs. Compared to the first survey, the difference in knowledge regarding lab safety between faculty/staff/administrators and graduate students/researchers decreased in the second survey (Please refer to Table 5 for the results). It can, therefore, be stated that the graduate students/researchers need more awareness sessions and training on laboratory safety.
Group wise health and safety ratings of different on-campus areas (except laboratories) (in percentage)
| Faculty/staff/administrator | Survey 1 | Survey 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Safe | Neutral | Unsafe | Safe | Neutral | Unsafe | |
| Parking Lots | 55 | 32 | 13 | 62 | 33 | 5 |
| Elevators | 63 | 31 | 6 | 60 | 34 | 6 |
| Library | 78 | 16 | 6 | 89 | 11 | 0 |
| Classrooms | 77 | 20 | 3 | 85 | 13 | 2 |
| Restrooms | 69 | 23 | 7 | 68 | 30 | 2 |
| Gym | 78 | 22 | 0 | 86 | 14 | 0 |
| Student Union Building | 75 | 22 | 3 | 85 | 15 | 0 |
| Dormitories | 64 | 30 | 6 | 73 | 27 | 0 |
| Graduate student/researcher | ||||||
| Parking Lots | 52 | 42 | 6 | 55 | 40 | 5 |
| Elevators | 56 | 25 | 19 | 40 | 43 | 17 |
| Library | 87 | 7 | 6 | 81 | 19 | 0 |
| Classrooms | 85 | 15 | 0 | 69 | 26 | 5 |
| Restrooms | 63 | 37 | 0 | 49 | 43 | 8 |
| Gym | 82 | 18 | 0 | 64 | 33 | 3 |
| Student Union Building | 79 | 21 | 0 | 60 | 39 | 1 |
| Dormitories | 55 | 42 | 3 | 50 | 39 | 11 |
For KII, five officials from the Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) unit of MUN, two officials were from the Workplace Health and Safety Committee (WHSC) and one official was from Facilities Management (FM). During the interviews, the participants from the EHS unit highlighted several initiatives undertaken by their unit since the release of 2013 Gap Analysis (GA) results. Some important recent initiatives undertaken by EHS were: (a) Five to seven safety campus-wide presentations were organized, some of which were geared towards senior management and WHSC members; (b) MUN restructured 27 WHSCs on its campuses to provide adequate safety services and to meet the legislated requirements of CCOHS and the University OHS Act and Regulations. Each of the 27 WHSCs covered few buildings on campus; (c) In 2014, MUN implemented electronic safety reporting system (e-alert) (d) MUN Safe App was introduced in 2016; (e) Inspections of all university building offices and 350 laboratories are being conducted annually; (f) Orientation sessions for new undergraduate students each year are being organized, where general safety rules are described; (g) Established a chemical management system for labs; and (h) Created annual water sampling procedure for drinking water safety. The participants from WHSCs also mentioned some initiatives undertaken by the EHS unit such as (a) an increase in the participation of representatives from the EHS Unit to sit on the WHSC meetings and (b) more frequent laboratory inspections. The participant from FM mentioned some initiatives such as maintaining a good database to track the expiry date of the employee training; and more engagement in the weekly Toolbox Talks to discuss potential hazard assessment.
Most of the KII participants mentioned that the graduate students’ supervisors are responsible for providing information to the students on laboratory safety rules and whom to call first in the event of an incident/accident. They placed the responsibility for providing laboratory safety equipment on the Department Heads. The participants emphasized budget and manpower as the main bottlenecks for addressing workplace hazards in a timely manner. There were some suggestions from the KII participants to improve health and safety at MUN such as (i) making attendance of safety presentations mandatory and included as part of the new employee and student orientation packages, (ii) demonstrating the AED in every building, (iii) encouraging all university members to install the MUN Safe App on their phones, and (iv) constantly improving app on a regular basis.
D ISCUSSION
The survey results indicate that there are significant associations between: a) ‘attendance at the safety presentation’ and ‘participant's health and safety knowledge’, b) ‘level of attitude’ and ‘behaviour levels’, c) ‘employment status’ and ‘participant's knowledge level on health and safety’, d) ‘participant's age’ and 'safety knowledge level’, and e) ‘length of service’ and ‘participants’ level of knowledge on health and safety. In our two surveys, we observed that those who attended safety presentations had much better understanding and practices of health and safety than those who did not attend. It is clear from the results that there should be more emphasis on dissemination of the activities of the EHS unit to a larger number of MUN employees and students on a regular basis. The results of the cross-sectional surveys (our two surveys and the GA survey) show consistency in the three survey results. As presented in Table 2 , the respondents increased their awareness about the presence of the EHS unit at MUN and improved their (respondents) communication with the Health and Safety Committee over time. On the other hand, we identified some issues that need to be addressed such as less familiarity with MUN's working alone procedures, AED locations, and OHS Act. The dissemination of information on the OHS Act needs improvement, as this is the basis of all health and safety-related regulations, responsibilities, and rights.
Health and safety programmes should be evaluated periodically to ensure that best practices are being followed on a regular basis. Programme Evaluation always helps the institute to update guidelines as necessary, and to address areas of need or concern in the institute. In some of the previous studies, periodical evaluations were conducted to investigate any change or improvement in population health. Two cross-sectional surveys were conducted in1990 and in 1998 in Copenhagen, Denmark to investigate whether the prevalence of skin-prick-test (SPT)-positive allergic rhinitis had increased in an adult general population in Copenhagen, Denmark. A screening questionnaire on respiratory symptoms was distributed in random samples of 15–41-year-old people in 1990 and in 1998. Among the responders, random samples were invited to a health examination including SPT.[ 14 ] Two International Studies on Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) - questionnaires based surveys were carried out in 1994 and in 2001 among school children in Singapore to evaluate the hypothesis that the prevalence of asthma would further increase and approach to western figures over time.[ 15 ] A questionnaire-based survey was conducted in 1973 among 12 years old children in South Wales, Britain. In 1988, the survey was repeated in the same area among 12 years old children to again to observe whether the prevalence of asthma had increased.[ 16 ] Frequency of prescribed drugs use was assessed by a sample of elderly people 65 years and over in Nottingham in 1985 and 1989. The aim was to observe the change in numbers in the use of prescribed drugs.[ 17 ] Though in our study, we do not observe any significant difference overall in the knowledge, attitude, and behaviour of the employees between the two surveys, we observe a significant decrease in the knowledge regarding laboratory safety in the second survey. Our study is therefore, successful to investigate the change in perceptions of the employees regarding workplace health and safety over time.
This study used a mixed-methods approach as such a method allows for a more robust analysis.[ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ] We conducted online surveys as online survey can easily obtain large sample, it can control answer order, it required completion of answers, and online survey can ensure that respondents answer only the questions that pertain specifically to them.[ 18 ] Through the quantitative online survey analysis of MUN employees and graduate students, we learned of their perceptions regarding MUN's workplace health and safety programmes. These perceptions are a one-sided view of the survey participants, and quantitative survey analysis does not provide a detailed explanation of several issues. Through the KIIs, we collected further information related to health and safety programmes at MUN and clarified some of the issues raised by the participants in the surveys. Such as, the KII participants clarified that the graduate students’ supervisors are responsible for providing information to the students on laboratory safety rules and whom to call first in the event of an incident/accident; the Department Heads are responsibility for providing laboratory safety equipment; and budget and manpower are the two main bottlenecks for addressing workplace hazards in a timely manner. The KII participants also mentioned some recent beneficial initiatives such as, the arrangement of five to seven safety presentations campus-wide, restructuring of the WHS and EHS committees, the implementation of an electronic safety reporting system and the MUN Safe App, new orientation for undergraduate students where general safety rules are described, and development of the Health and Safety Management System. There had been a gap in understanding about health and safety matters between the employees and MUN health and safety officials. The qualitative analysis of the KII has filled this gap.
Our study is the first of this kind in the context of Health and Safety Program evaluation in Canadian university. Our study focused on the level of uptake of the information on health and safety disseminated by the university EHS unit through their safety presentations and workshops. We have also studied the effect of employee's and graduate student's knowledge about health and safety programmes at MUN on levels of their attitudes and behaviours. In addition, we have conducted KII interviews of the officials who are engaged in developing workplace health and safety programmes at MUN. As a result, improvements in the health and safety programmes have been planned by university officials. This is the practical implication of this study as the KII participants suggested some future procedures to improve health and safety at MUN such as making attending safety presentations mandatory for all employees and students; demonstrating the AED in every building; and encouraging all university residents to install the MUN Safe App on their phones.
There were some limitations of our study. The sample sizes of the surveys were small as participation was voluntary, and there was no incentive for participating in the surveys. The survey participants were not equally distributed across the disciplines, as the numbers of respondents from some faculties were much higher (Engineering faculty) than the number of respondents from other faculties (Arts and Education faculties). The survey data were anonymous, so our assertion on sustenance of the perceptions of the health and safety of respondents over the six-month period of time is not stronger.
In future surveys, undergraduate students should be included, as they are also exposed to similar risks as graduate students, and they outnumber graduate students. There is a sizable workforce involved in post-secondary university institutions in Canada, and this sector is growing. Varying ranges of working environments in the universities expose employees to multiple occupational risks. Safety training in a university is often not mandatory, and the survey analysis clearly indicates that there is need to increase the level of uptake on the information on health and safety programmes of university by employees and graduate students. Therefore, the universities should increase the number of safety training programmes and keep track of the employees that have not received training, particularly for those working in hazardous environments. Assured provision of financial resources is the key to maintaining a safe work environment and practices.
Key Messages
Universities should make safety training mandatory for all employees and graduate students. Therefore, there is a need to increase the number of training sessions to accommodate all eligible persons. Also, the universities should keep track of the employees and students that have not received training, particularly for those working in hazardous working conditions. The universities have to set aside financial resources for such regular trainings.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Associate Director of the EHS Unit of the Office of the Chief Risk Officer, Memorial University, Ms. Barbara Battcock, for her valuable suggestions throughout the survey. We would also like to thank all the anonymous participants who volunteered for the surveys and for the key informant interviews.
Supplementary File S1
Memorial University-Workplace Health and Safety Survey .
1. Did you attend the Safety-Presentation provided by Environmental Health and Safety Unit at Memorial University?
[ ] I don’t remember.
2. Employment Status
[ ]Faculty.
[ ]Researcher/Graduate student.
[ ]Administrator.
4. Which faculty/office do you belong to?
[ ] Medicine
[ ]Pharmacy
[ ]Engineering
[ ]Business
[ ]Education
[ ]Administrative office
[ ]Other (Please specify)
5. In which age group do you fall?
[ ] Less than 30
[ ] 60 or more
6. How long have you been on the Campus as an employee?
[ ] less than 5 years
[ ] 5-9 years.
[ ] 10 -14 years
[ ] 15-19 years
[ ] 20-24 years
[ ] 25 years or more
7. Are you aware of the presence of the Environmental Health and Safety Unit at Memorial University? (GA Survey, 2013)
8. Are you aware of Workplace Health and Safety Committees (WHSC- formerly known as Occupational Health and Safety Committees) of the building you work in? (GA Survey, 2013)
9. Does the WHSC in your building communicate with you? (GA Survey, 2013)
10. Do you read newsletters, brochures, bulletins, etc., relating to health and safety e-mailed by Environmental Health and Safety Unit? (GA Survey, 2013)
[ ] I don’t receive any of them.
11. Were you informed about the Occupational Health and Safety Act? (GA Survey, 2013)
12 Do you know where to report a safety concern, a safety hazard or accident? (GA Survey, 2013)
13 Do you know your role in the event of an emergency? (GA Survey, 2013)
14) Do you know the campus emergency telephone number? (GA Survey, 2013)
15. Do you know the shortest exit route from your work area (s)? (GA Survey, 2013)
16. Do you know whom you call first if you get injured at work? (GA Survey, 2013)
17. Are you aware that there are Automated External Defibrillators (AED) available in campus buildings? (GA Survey, 2013)
18. Do you know where the AEDs are located in the buildings you work? (GA Survey, 2013)
19. If AED training is made available through MUN, would you be interested in participating in the training? (GA Survey, 2013)
[ ] I am already trained in using AED.
20. In your experience, do you think that safety is a priority within your department/division/faculty/office? (GA Survey, 2013)
21. Do you understand your responsibilities for your and your colleagues’ health and safety? (GA Survey, 2013)
22. Are you familiar with MUN's health and safety policies? (GA Survey, 2013)
23. Please rate how safe you feel in the following areas on campus. (Montana Tech Safety Awareness Survey, 2011).
| Safe | Neutral | Unsafe | N/A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parking Lots | ||||
| Elevators | ||||
| Gym | ||||
| Library | ||||
| Student Union Building | ||||
| Classrooms | ||||
| Laboratories | ||||
| Restrooms | ||||
| Dormitories |
Please elaborate on any other particular areas you feel unsafe.
24. What precautions do you think you should take to increase your safety on campus? (Check all that apply). (Montana Tech Safety Awareness Survey, 2011).
- i) Carry a cellular phone.
- ii) Let others know where I will be.
- iii Take safety- training classes.
- iv Other, please specify.
25. Are you aware of Memorial's online reporting system for the health and safety issues/concerns? (GA Survey, 2013)
26. Do you report unsafe acts/conditions if you see them? (GA Survey, 2013)
’Toolbox Talks’ is the name of a meeting, which gives opportunity to Memorial University workers, supervisors and Department Heads a means of communicating health, safety and environmental initiatives as well as accident/incident ‘Lessons learned’ and expressing concerns, obtaining information, and resolving issues related to safety in the workplace.
27. Are toolbox talks/safety meetings relevant to your task? (GA Survey, 2013)
[ ] I do not know.
28. Have you participated in a toolbox talk/safety meeting? (GA Survey, 2013)
29. Are you aware of MUN's working alone procedures? (GA Survey, 2013)
30. Do you work after hours at least some times? (GA Survey, 2013)
31. Are you aware of MUN's safety escort service? (GA Survey, 2013)
32. Do you work at a lab or visit one frequently?
33. Please rate the following regarding laboratories on campus.
| Agree | Neutral | Disagree | N/A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I feel safe in campus labs (Montana Tech Safety Awareness Survey, 2011) | ||||
| PPE is available in the labs. (Montana Tech Safety Awareness Survey, 2011) | ||||
| Lab safety is properly explained. (Montana Tech Safety Awareness Survey, 2011) | ||||
| I received training on appropriate use of eye wash station | ||||
| I Know the location of nearest safety shower |
34. Is safety discussed in your workplace? (GA Survey, 2013)
35. Were you provided information/training on the safe use and maintenance of tools and equipment necessary for your job? (GA Survey, 2013)
36. Have you requested specific safety training appropriate to your position? (GA Survey, 2013)
37. Were you informed about the hazardous materials that are present in your workplace? (GA Survey, 2013)
For the purpose of this survey a hazard is defined as: ‘Any source of potential damage, harm or adverse health effects on something or someone under certain conditions at work’.
38. How many hazards have you identified in your work place in the last one year.
0 1 2 3 4 or more.
In the above question if your answer is 1 or more than 1 go to question 34 or else go to question 35.
39. How many of them have been corrected in a timely manner?
40. Are Employees given feedback on accidents that occur in your workplace? (GA Survey, 2013)
41. Do you have any concerns regarding your safety and/or security in your faculty or department?
If you answered yes please specify.
42. Which of the following do you think MUN should provide to help increase the safety of the campus community? (Check all that apply). (Montana Tech Safety Awareness Survey, 2011)
- Improve safety escort service.
- More emergency call boxes.
- Additional lighting.
- More security guards.
- More safety presentations.
- Self-defence classes.
- Other, please specify
Supplementary File S2
Key Informant Interview Questions
Q1. After the 2013 Gap Analysis survey on safety culture, can you recall any additional initiatives that EHS Unit has initiated to create awareness on health and safety among MUN employees?
Q2. In the surveys less than 50% respondents (first survey 46.6%, second survey 40.8%) notified that they had participated in the safety presentation/workshop in 2015. Is this level of participation satisfactory? If not what additional steps can be taken to reach out to more people at MUN?
Q3. The survey results indicate that, the graduate students and researchers have low level of knowledge/awareness on occupational health and safety programmes compared to the faculty and staff. Knowing that the graduate students and researchers are more exposed group to different safety critical scenarios,
- i Does this appear as a concern?
- ii How do you think the safety awareness of graduate students and researchers can be improved?
Q4. In the surveys less than 65% of the participants know whom to call first if they get injured at work. Is this level of awareness acceptable? What are the current mechanisms to educate researchers/employees about this information? How do you think this information can be disseminated more effectively?
Q5. The respondents have suggested to improve communication and implementation of the policies and to provide more auditing of safety policies by EHS department to ensure compliance, do you have a similar observation? Is there any continuing effort to improve this concern?
Q6. The surveys indicate that, among the people who said Tool Box Talk is relevant to them, the level of participation in toolbox talk decreased over time. Does your observation support this finding? If so, what can be done to increase the participation?
Q7. The survey analysis indicates that, the graduate students and researchers need more training on eyewash station and safety shower, can you explain the current mechanisms for training graduate students on these basic safety practices? Do you see any way to improve the provision of training and increase the level of participation?
Q8. The respondents suggested to install more flammable gas detectors and improve the splash proof safety goggles. In your opinion are the units/labs equipped with adequate gas detectors and splash proof safety goggles?
Q9. The respondents commented on shortage of lab space and shortage of PPE (Personal Protective Equipment).
- i) Is there any continuing effort to create more lab space?
- ii) Who is normally responsible to provide the PPE to the researchers/graduate students? How can one address the shortage of PPE in labs at MUN?
Q10. In the surveys over 50% of the respondents mentioned that, none of the hazards at their workplaces had been addressed in a timely manner.
- (i) What are the current practices for reporting, follow-up and correction of hazards?
- (ii) Do you see any bottleneck in the addressing the hazards in a timely fashion?
Q11. The survey results show that over 70% of the respondents want to participate in AED training. Is there any continuing effort to provide AED training to the employees and students at MUN?
Q12. The surveys indicate that a significant portion of the employees is not aware of MUN's working alone procedure though most of the employees are working after hours at the office. Is this a concern? If so what can be done to increase awareness on working alone procedure among the employees?
Q13. The participants have suggested repair of walkways and parking lots and removal of thick layer of ice from the parking lots to prevent slips and falls. Does this come under the purview of EHS Unit? If yes how can one address this issue?
Q14. Many respondents showed their concern about the design and usage of MUN Safe App. Is there a continuing effort to improve the App and make it user friendly?
Q15. In the surveys many of the participants have suggested the improvement of the on-campus safety escort service. How is the current safety escort service implemented and what additional steps can be taken to improve it?
Supplementary File S3
Table s3.3.1.
Chi-Square Tests for table 3
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | Exact Sig. (2-sided) | Exact Sig. (1-sided) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 14.728 | 1 | 0.000 | ||
| Continuity Correction | 13.133 | 1 | 0.000 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio | 14.951 | 1 | 0.000 | ||
| Fisher’s Exact Test | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 14.587 | 1 | 0.000 | ||
| No. of Valid Cases | 105 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 14.02, * p-value < 0.05 considered significant
Table S3.3.2
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 30.585 | 2 | 0.000 |
| Likelihood Ratio | 31.058 | 2 | 0.000 |
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 14.304 | 1 | 0.000 |
| N of Valid Cases | 115 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 6.89
Table S3.3.3
Chi-Square Tests for Table 3
| Value | Df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | Exact Sig. (2-sided) | Exact Sig. (1-sided) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 7.623 | 1 | 0.006 | ||
| Continuity Correction | 6.562 | 1 | 0.010 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio | 7.681 | 1 | 0.006 | ||
| Fisher’s Exact Test | 0.009 | 0.005 | |||
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 7.558 | 1 | 0.006 | ||
| N of Valid Cases | 117 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 17.08
Table S3.3.4
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 10.017 | 2 | 0.007 |
| Likelihood Ratio | 10.442 | 2 | 0.005 |
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 4.060 | 1 | 0.044 |
| N of Valid Cases | 85 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 6.67
Table S3.3.5
Chi Square Tests for Table 3
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | Exact Sig. (2-sided) | Exact Sig. (1-sided) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 6.711 | 1 | 0.010 | ||
| Continuity Correction | 5.541 | 1 | 0.019 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio | 6.830 | 1 | 0.009 | ||
| Fisher’s Exact Test | 0.017 | 0.009 | |||
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 6.631 | 1 | 0.010 | ||
| N of Valid Cases | 83 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 12.53
Table S3.3.6
| Value | Df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided) | Exact Sig. (2-sided)* | Exact Sig. (1-sided) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 5.982 | 1 | 0.014 | ||
| Continuity Correction | 4.319 | 1 | 0.038 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio | 5.820 | 1 | 0.016 | ||
| Fisher’s Exact Test | 0.025 | 0.020 | |||
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 5.860 | 1 | 0.015 | ||
| N of Valid Cases | 49 |
a. 1cells (25.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 3.67
Table S3.4.1
Chi-Square Tests for table 4
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 6.455 | 2 | 0.040 |
| Likelihood Ratio | 6.440 | 2 | 0.040 |
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 2.187 | 1 | 0.139 |
| N of Valid Cases | 132 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 8.71
Table S3.4.2
Chi-Square Tests for Table 4
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | Exact Sig. (2-sided) | Exact Sig. (1-sided) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 5.142 | 1 | 0.023 | ||
| Continuity Correction | 4.347 | 1 | 0.037 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio | 5.166 | 1 | 0.023 | ||
| Fisher’s Exact Test | 0.029 | 0.018 | |||
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 5.103 | 1 | 0.024 | ||
| N of Valid Cases | 133 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 21.79
Table S3.5.1
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | Exact Sig. (2-sided) | Exact Sig. (1-sided) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 5.757 | 1 | 0.016 | ||
| Continuity Correction | 4.799 | 1 | 0.028 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio | 5.933 | 1 | 0.015 | ||
| Fisher’s Exact Test | 0.022 | 0.013 | |||
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 5.707 | 1 | 0.017 | ||
| N of Valid Cases | 115 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 14.75
Table S3.5.2
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 12.299 | 2 | 0.002 |
| Likelihood Ratio | 12.920 | 2 | 0.002 |
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 1.858 | 1 | 0.173 |
| N of Valid Cases | 128 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 6.94
Table S3.5.3
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-sided)* | Exact Sig. (2-sided) | Exact Sig. (1-sided) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 10.271 | 1 | 0.001 | ||
| Continuity Correction | 8.597 | 1 | 0.003 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio | 11.019 | 1 | 0.001 | ||
| Fisher’s Exact Test | 0.002 | 0.001 | |||
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 10.126 | 1 | 0.001 | ||
| N of Valid Cases | 71 |
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 8.87
Supplementary File S4
Comparison of surveys
| GA Survey, 2013, =293 | Survey 1, 2016, =148 | Survey 2, 2017, =103 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| EHS Office related questions | ||||||
| Are you aware of the presence of the EHS Unit at MUN ? | 62 | 38 | 90 | 10 | 91 | 9 |
| Do you read newsletters, brochures, bulletins e-mailed by EHS Unit? | 52 | 48 | 78 | 22 | 68 | 32 |
| Were you informed about the Occupational Health and Safety Act? | 69 | 31 | 68 | 32 | 68 | 32 |
| Do you know where to report a safety concern, a safety hazard or accident? | 84 | 16 | 85 | 15 | 86 | 14 |
| Do you know the campus emergency telephone number? | N/A | N/A | 73 | 27 | 73 | 27 |
| Are you familiar with MUN’s Health and Safety Policies? | 41 | 59 | 66 | 34 | 76 | 24 |
| Are you aware of Memorial’s online reporting system for health and safety concerns? | 66 | 34 | 61 | 39 | 75 | 25 |
| Are you aware of MUN’s Safety Escort Service? | N/A | N/A | 49 | 51 | 68 | 32 |
| Faculty/Building related questions | ||||||
| Are you aware of Workplace Health and Safety Committee of the building you work in? | 38 | 62 | 92 | 9 | 90 | 10 |
| Does the WHSC in your building communicate with you? | 37 | 63 | 75 | 25 | 73 | 27 |
| Do you know your role in the event of an emergency? | 54 | 46 | 72 | 28 | 89 | 11 |
| Do you know the shortest exit rout from your work area (s)? | N/A | N/A | 95 | 5 | 95 | 5 |
| Do you know whom you call first if you get injured at work? | 76 | 24 | 64 | 36 | 61 | 39 |
| Are you aware of Automated External Defibrillator available in campus buildings? | N/A | N/A | 87 | 13 | 81 | 19 |
| Do you know where the AEDs are located in the buildings you work? | N/A | N/A | 73 | 27 | 66 | 34 |
| If AED training is made available through MUN, would you be interested in participating the training? | N/A | N/A | 76 | 24 | 74 | 26 |
| In your experience, do you think safety is a priority within your department/faculty/office? | 72 | 28 | 81 | 19 | 86 | 14 |
| Do you report unsafe acts/conditions if you see them? | 94 | 6 | 86 | 14 | 90 | 10 |
| Department/Division related questions | ||||||
| Do you understand your responsibilities for your and your colleagues’ health and safety? | 63 | 37 | 85 | 15 | 88 | 12 |
| Are toolbox talk/safety meeting relevant to your task? | 24 | 76 | 59 | 41 | 47 | 53 |
| Have you participated in a toolbox talk/safety meeting? | 29 | 71 | 38 | 62 | 25 | 75 |
| Is safety discussed in your workplace? | 74 | 26 | 82 | 18 | 84 | 16 |
| Were you provided information/training on the safe use of tools necessary for your job? | 43 | 67 | 81 | 19 | 76 | 24 |
| Have you requested specific safety training that is appropriate to your position? | 23 | 77 | 53 | 47 | 45 | 55 |
| Were you informed about the hazardous materials that are present in your workplace? | 55 | 45 | 71 | 29 | 67 | 33 |
| Are employees given feedback on accidents that occur in your workplace? | 73 | 27 | 59 | 41 | 68 | 32 |
| Do you work after hours at least sometimes? | 75 | 25 | 85 | 15 | 81 | 19 |
| Are you aware of MUN’s working alone procedures? | 81 | 19 | 45 | 55 | 54 | 46 |
R EFERENCES

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This paper is among the first systematic literature reviews to analyze how safety management practices have been associated with occupational health and safety performance and provide potential ...
Occupational h ealth is defined as the highest degree o f physical, men tal, and s ocial well-. being of workers in all occupations. It is the branch of health care which deals with all. aspects ...
Background This study aimed to evaluate and describe the indicators of occupational health, with a focus on the medical expertise and periodic medical examination. Methods This is exploratory-descriptive, cross-sectional, documentary, quantitative, and retrospective research, in the historical series: 2011 to 2015. Results The number of lost days of work per worker and the frequency of ...
Occupational health and safety is a key element in achieving sustained decent working conditions and strong preventive safety cultures (Timpe, 1993). Close to 80 per cent of all ILO standards and instruments are either wholly or partly concerned with issues related to occupational safety and health (Yates, 1992).
Abstract and Figures. This literature review focuses on researches undertaken since 1980s onwards. The purpose of the study is to identify existing gaps on workplace safety and health management ...
evidence linking both long and, to a lesser extent, short work weeks to negative health and safety outcomes. Section 3 focuses on working time arrangements (work schedules) and occupational health and safety. Part one examines the impact of the various features or parameters involved in defining work schedules. A critical issue in this regard ...
In addition to relying on the knowledge foundation and research methods of public health and more specifically, traditional occupational safety and health, it will be necessary to bridge disciplinary boundaries across the fields of economics, sociology, psychology, organizational management, social work, public policy, industrial relations, law ...
Occupational health and safety (OHS) is a multidisciplinary activity that aims to identify, evaluate, and control hazards arising in or from the workplace that may impair the health and well-being of workers. Assessing the risk of occupational hazards is one of pivotal steps to handle an OHS risk analysis problem.
Official peer-reviewed journal of Occupational Safety and Health Research Institute, Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency. Safety and Health at Work (SH@W) is an international, peer-reviewed, interdisciplinary journal published quarterly in English beginning in 2010. The journal is aimed at providing grounds for the exchange of ideas and data developed through research experience in the ...
trends, we identify key conclusions and opportunities for future research. Keywords: safety, history, review, occupational health The focus on occupational safety over the last 100 years has contributed significantly to saving thousands of lives. In the early 1900s, workplace deaths and injuries were quite common. For
ILO Global strategy on occupational safety and health, adopted in 2003, provides a framework for these activities. Crucially, the global burden of occupational accidents, work-related diseases and deaths, is a signi!cant contributor to the growing global issue of non-communicable and chronic diseases. When we look to the future of safety and health
ISSN 2222-1735 (Paper) ISSN 2222-288X (Online) Vol.7, No.29, 2016 ... To accomplish this, there are provisions for safety and health standards, research, information, and education and training in occupational safety and health (De Reamer, 1980). OSHA is comprehensive, covering such things as record keeping, inspection, compliance, and ...
Introduction. Healthcare workers constituting 12% of the working population worldwide operate in an environment that is considered to be one of the most hazardous occupational settings.[1,2,3] In addition to the usual workplace related exposures, healthcare workers encounter diverse hazards because of their work-related activities.[4,5]Occupational health and safety is a discipline with a ...
The global spread of COVID-19 pandemic has created many unprecedented issues concerning the protection of safety and health of workers. Although the biological hazard has been one of the main targets of prevention in certain workplaces such as medical and nursing facilities, we are realizing that the novel virus pandemic can pose far more complicated and extensive challenges to the total area ...
1. Toward an effective occupational heal th and safety culture: A multiple. stakeholder perspective. Abstract. This paper uses an extensive review of the sa fety culture literature to identify ...
OSHA's history is an intimate part of a long struggle over the rights of working people to a safe and healthy workplace. In the early decades, strikes over working conditions multiplied. The New Deal profoundly increased the role of the federal government in the field of occupational safety and health. In the 1960s, unions helped mobilize ...
Historically, in Brazil, Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) is strongly associated with the political-social and economic evolution of the country and is presented as the achievement of rights resulting from claims and struggles of the workers. Work is one of the determinants that most impact man's conditions, quality of life, and health.
2.2 Occupational Health and Safety Under occupational safety legislation no.1 of 1970 Article 2, occupational safety protection covers all aspects of hazardous work of any workplace, whether on land, in the soil, on the surface of water, in water or in the air within the jurisdiction of the Republic of Indonesia. By this regulation, then every
Description from website: The twentieth century witnessed remarkable reductions in the number and rate of occupational fatalities and injuries. However, many preventable injuries and deaths still occur. Barriers to progress in occupational injury prevention are discussed, along with strategies for overcoming them.
Occupational health and safety important: Work plays a central role in people's lives, since most workers spend at least eight hours a day in the workplace, whether it is on a plantation, in an office, factory, etc. Therefore, work environments should be safe and healthy. Yet this is not the case for many workers.
Abstract: Occupational safety and health is an to caring the safety, health and wellbeing of people occupied. in work. The aim of the study is to study the occupational health an d safety of the ...
This article was initially planned to mark the 50th anniversary of the UK Health and Safety at Work etc Act which came into force on 31 July 2024. It was expanded to help respond to consultation by the New Zealand Government on experience with the New Zealand Act of the same name. I briefly review aspects of system thinking and then report on the origins of the New Zealand Health and Safety at ...
Venables and Allender (2007) described the occupational health services in 93 universities in the UK by drawing on data from surveys carried out in 2002, 2003 and 2004. Most survey responses were received from universities and in-house services. The surveys requested self-completed information on occupational health services from each university.
Health and Safety of Employees in Organizations. Dr. Radhika Kapur. Abstract. The main objective of this research paper is to acquire an understanding of health and. safety of employees in ...
Chiropractic is the largest complementary integrative health profession in the United States 6 and focuses on the diagnosis and management neuromusculoskeletal conditions. 7,8 Given the standardization and value of integrated health care, it is essential for all health care professionals to be competent and able to collaborate as part of an interdisciplinary team, working together for the ...
Objective: This study investigates occupational safety in a construction materials development laboratory at a public university, identifying risks and irregularities.