
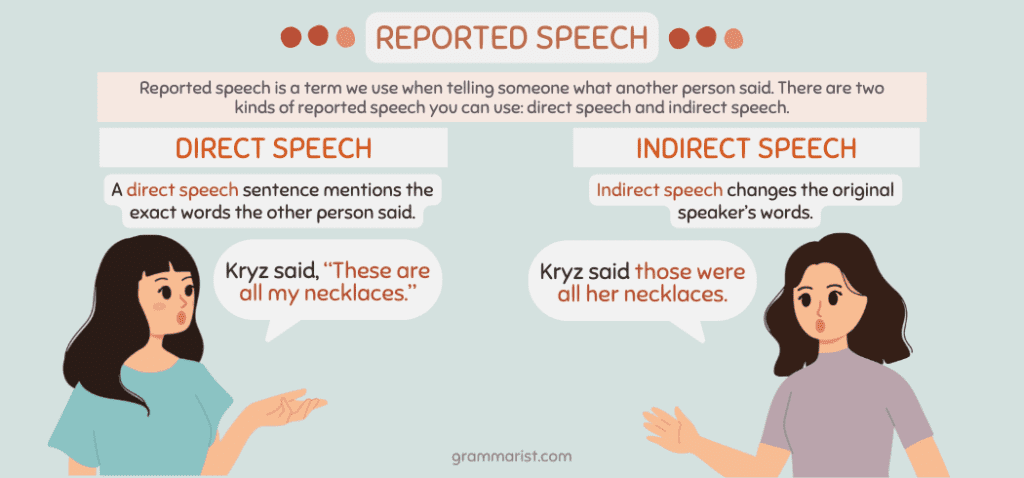
Reported speech - 1
Reported speech - 2
Reported speech - 3
Worksheets - handouts

Reported speech
Worksheets - pdf exercises.
- Reported statements - worksheet
- Worksheet - reported questions
- Reported yes/no questions
- Worksheet - reported speech
- Reported speech - exercises pdf
- Indirect speech - exercises
- Reported speech - exercises
- Mixed reported speech 1
- Mixed reported speech 2
- Reported speech 1
- Reported speech 2
- Reported speech 3
- Reported speech 4
- Reported speech 5
- Reported wh- questions
- Reported speech - worksheet
- Reported commands
- Reported questions
- Reported speech 1
- Reported speech 2
- Reported requests and orders
- Reported speech exercise
- Reported questions - worksheet
- Indirect speech - worksheet
- Worksheets pdf - print
- Grammar worksheets - handouts
Grammar - lessons
- Reported speech - grammar notes
- How to use reported speech - lesson
- Tense changes - grammar
Reported Speech Exercises
Perfect english grammar.

Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site:
( Click here to read the explanations about reported speech )
Reported Statements:
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Past Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Perfect Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Future Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Statement Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- 'Say' and 'Tell' (quite easy) (in PDF here)
Reported Questions:
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
Reported Orders and Requests:
- Reported Requests and Orders Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 1 (difficult) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 2 (difficult) (in PDF here)

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Direct and indirect speech exercises PDF
- English grammar PDF
- PDF worksheets
- Mixed PDF tests
- Present tenses
- Past tenses
- Future tenses
- Present perfect
- Past perfect
- Future perfect
- Irregular verbs
- Modal verbs
- If-conditional
- Passive voice
- Reported speech
- Time clauses
- Relative clauses
- Indirect questions
- Question tags
- Imperative sentence
- Gerund and infinitive
- Direct | indirect object
Direct and indirect speech
- Online exercises
- Grammar rules PDF
English grammar books PDF
PDF book 1: English grammar exercises PDF
PDF book 2: English grammar rules PDF
Direct and indirect speech exercises
Reported speech exercises PDF
- Learn how to change tenses, pronouns, expressions of time and place in the reported speech.
Reported questions + commands exercises PDF
- Practise the difference between the direct and indirect speech in questions, commands and requests.
Online exercises with answers:
Direct - indirect speech exercise 1 Rewrite sentences in the reported speech.
Direct - indirect speech exercise 2 Report a short dialogue in the reported speech.
Direct - indirect speech exercise 3 Find and correct mistakes in the reported speech.
Direct - indirect speech exercise 4 Choose correct answers in a multiple choice test.
Indirect - direct speech exercise 5 Rewrite sentences from the reported speech to direct speech.
Reported questions, commands and requests:
Reported questions exercise 6 Change the reported questions and orders into direct questions and orders.
Reported questions exercise 7 Change direct questions into reported questions.
Reported commands exercise 8 Make reported commands and requests.
Grammar rules PDF:
Reported speech rules PDF Changes of tenses, pronouns, time and place in reported statements, questions and commands.
English grammar PDF All PDF rules with examples on e-grammar.org.
Direct + indirect speech
See also: Reported questions + commands
The direct and indirect speech are used to say what other people said, thought or felt. "I like it," he said. - He said that he liked it. "Dan will come," she hoped. - She hoped Dan would come.
The reported (indirect) speech is typically introduced by verbs such as say, tell, admit, complain, explain, remind, reply, think, hope, offer, refuse etc. in the past tense. He said (that) he didn't want it. She explained that she had been at the seaside.
If these verbs are in the past tense, we change the following: a) verb tenses and verb forms b) pronouns c) the adverbs of time and place
A) Verb tenses
We change the tenses in the following way:
- Present - past "I never understand you," she told me. - She told me she never understood me. "We are doing exercises," he explained. - He explained that they were doing exercises.
- Present perfect - past perfect "I have broken the window," he admitted. - He admitted that he had broken the window. "I have been waiting since the morning," he complained. - He complained that he had been waiting since the morning.
- Past - past perfect "She went to Rome," I thought. - I thought that she had gone to Rome. "He was thinking of buying a new car," she said. - She said he had been thinking of buying a new car.
- Will - conditional Will changes into the conditional. I will come on Sunday," he reminded me. - He reminded me that he would come on Sunday.
As you can see, both the past tense and the present perfect change into the past perfect.
Notes 1. I shall, we shall usually become would . "I shall appreciate it," he said. - He said he would appreciate it. 2. I should, we should usually change into would . "We should be really glad," she told us. - She told us they would be really glad. 3. May becomes might . "I may write to him," she promised. - She promised that she might write to him.
The verb forms remain the same in the following cases:
- If we use the past perfect tense. Eva: "I had never seen him." - Eva claimed that she had never seen him.
- If the reporting verb is in the present tense. Bill: "I am enjoying my holiday." - Bill says he is enjoying his holiday. Sandy: "I will never go to work." - Sandy says she will never go to work.
- When we report something that is still true. Dan: "Asia is the largest continent." - Dan said Asia is the largest continent. Emma: "People in Africa are starving." - Emma said people in Africa are starving.
- When a sentence is made and reported at the same time and the fact is still true. Michael: "I am thirsty." - Michael said he is thirsty.
- With modal verbs would, might, could, should, ought to, used to. George: "I would try it." - George said he would try it. Mimi: "I might come." - Mimi said she might come. Steve: "I could fail." - Steve said he could fail. Linda: "He should/ought to stay in bed." - Linda said he should/ought to stay in bed. Mel: "I used to have a car." - Mel said he used to have a car.
- After wish, would rather, had better, it is time. Margo: "I wish they were in Greece." - Margo said she wished they were in Greece. Matt: "I would rather fly." - Matt said he would rather fly. Betty: "They had better go." - Betty said they had better go. Paul: "It is time I got up." - Paul said it was time he got up.
- In if-clauses. Martha: "If I tidied my room, my dad would be happy." - Martha said that if she tidied her room, her dad would be happy.
- In time clauses. Joe: "When I was staying in Madrid I met my best friend." - He said that when he was staying in Madrid he met his best friend.
- We do not change the past tense in spoken English if it is clear from the situation when the action happened. "She did it on Sunday," I said. - I said she did it on Sunday. We must change it, however, in the following sentence, otherwise it will not be clear whether we are talking about the present or past feelings. "I hated her," he said. - He said he had hated her.
- We do not usually change the modal verbs must and needn't . But must can become had to or would have to and needn't can become didn't have to or wouldn't have to if we want to express an obligation. Would/wouldn't have to are used to talk about future obligations. "I must wash up." - He said he must wash up/he had to wash up. "I needn't be at school today." - He said he needn't be/didn't have to be at school that day. "We must do it in June." - He said they would have to do it in June. If the modal verb must does not express obligation, we do not change it. "We must relax for a while." (suggestion) - He said they must relax for a while. "You must be tired after such a trip." (certainty) - He said we must be tired after such a trip.
B) Pronouns
We have to change the pronouns to keep the same meaning of a sentence. "We are the best students," he said. - He said they were the best students. "They called us," he said. - He said they had called them. "I like your jeans," she said. - She said she liked my jeans. "I can lend you my car," he said. - He said he could lend me his car.
Sometimes we have to use a noun instead of a pronoun, otherwise the new sentence is confusing. "He killed them," Kevin said. - Kevin said that the man had killed them. If we only make mechanical changes (Kevin said he had killed them) , the new sentence can have a different meaning - Kevin himself killed them.
This and these are usually substituted. "They will finish it this year," he said. - He said they would finish it that year. "I brought you this book," she said. - She said she had brought me the book. "We want these flowers," they said. - They said they wanted the flowers.
C) Time and place
Let's suppose that we talked to our friend Mary on Friday. And she said: "Greg came yesterday." It means that Greg came on Thursday. If we report Mary's sentence on Sunday, we have to do the following: Mary: "Greg came yesterday." - Mary said that Greg had come the day before. If we say: Mary said Greg had come yesterday , it is not correct, because it means that he came on Saturday.
The time expressions change as follows. now - then, today - that day, tomorrow - the next day/the following day, the day after tomorrow - in two days' time, yesterday - the day before, the day before yesterday - two days before, next week/month - the following week/month, last week/month - the previous week/month, a year ago - a year before/the previous year
Bill: "She will leave tomorrow." - Bill said she would leave the next day. Sam: "She arrived last week." - Sam said she had arrived the previous week. Julie: "He moved a year ago." - Julie said he had moved a year before.
Note If something is said and reported at the same time, the time expressions can remain the same. "I will go on holiday tomorrow," he told me today. - He told me today he would go on holiday tomorrow. "We painted the hall last weekend," she told me this week. - She told me this week they had painted the hall last weekend. On the other hand, if something is reported later, the time expressions are different in the indirect speech. Last week Jim said: "I'm playing next week." If we say his sentence a week later, we will say: Jim said he was playing this week.
Here usually becomes there . But sometimes we make different adjustments. At school: "I'll be here at 10 o'clock," he said. - He said he would be there at 10 o'clock. In Baker Street: "We'll meet here." - He said they would meet in Baker Street.
- All PDF exercises and grammar rules from this website.
Reported Speech Exercises (With Printable PDF)
| Candace Osmond
| Grammar , Quizzes
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
In English grammar, reported speech is used to tell someone what another person said. It takes another person’s words (direct speech) to create a report of what they said (indirect speech.) With the following direct and indirect speech exercises, it will be easier to understand how reported speech works.

Reported Speech Exercise #1
Complete the sentence in the reported speech.
Reported Speech Exercise #2
Fill in the gaps below with the correct pronouns required in reported speech. Ex. Mary said: “I love my new dress!” Sentence: Mary said ____ love ____ new dress. Answer: she, her
Reported Speech Exercise #3
Choose the correct reported speech phrase to fill in the sentences below.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
English Practice Downloadable PDF Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets
Grammar worksheets (b1).
This sections provides you with downloadable PDF worksheets and keys for grammar . Please choose from the grammar areas.
New Grammar Worksheets
- T056 - Past Tense Simple and Progressive
- PREP015 - Phrases with prepositions
- PREP014 - Prepositions
- PREP013 - Prepositions
- PREP012 - Prepositions AT, IN, ON
- T055 - Past Tense Simple and Progressive
- AD014 - Comparison of Adjectives
- WO003 - Word Order
- T054 - All Tenses
- T053 - All Tenses
- T052 - Past and Past Perfect Tense
- T051 - Tenses - Sentence Building
- AD013 - Adjective or Adverb
- GI014 - Gerund and Infinitive
- GI013 - Gerund and Infinitive
- GI012 - Gerund and Infinitive
- RS013 - Reported Speech
- RS012 - Reported Questions and Commands
- RS011 - Reported Speech
- RS010 - Reported Speech
- T050 - All Tenses
- T049 - A Cycling Holiday - Past Verb Forms
- T048 - Past Tense Simple and Progressive
- T047 - All Tenses
- PA016 - A Local Sports Centre - Passive Voice
- T046 - All Tenses
- PA015 - Verb Tenses - Active or Passive Voice
- T045 - Present Perfect Simple and Progressive
- T044 - Past Simple and Present Perfect (Simple and Progressive)
- QN002 - Ask for the underlined words
- T043 - Past Tense Simple and Progressive
- T042 - Present Tense Simple and Progressive
- PREP011 - AT, FOR, FROM, ON, TO
- T041 - Present Perfect Simple and Progressive
- T040 - Narrative Tenses : An Emergency Landing
- PREP010 - Prepositions: IN, AT, ON, BY, FOR
- T039 - Ways of Expressing Future Tense
- RS009 - Reported Commands
- RS008 - Reported Questions
- PREP009 - Prepositions : IN, AT, ON, BY, FOR
- QN001 - Ask for the underlined words
- T038 - Present Tense Simple and Progressive
- IF012 - IF Clauses - Type 3
- IF011 - IF Clauses - Type 2
- IF010 - IF Clauses - Type 1
- RC005 - Relative Clauses - Combine the TWO Sentences
- RC004 - Relative Pronouns
- T037 - Present Perfect Simple and Progressive
- MOD008 - Modal Verbs
- IF009 - IF-Clauses - All Types
- T036 - Past and Present Perfect Simple
- T035 - All Tenses
- T034 - All Tenses
- GI011 - Gerund and Infinitive
- PREP008 - Prepositions
- IF008 - IF-Clauses - Conditional 1
- Q004 - Quantifiers : LITTLE , A LITTLE , FEW , A FEW
- GI010 - Gerund and Infinitive
- RS007 - Reported Speech
- PA014 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- PA013 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- QT001 - Question Tags
- T033 - Irregular Verbs : Complete the table
- T032 - Irregular Verbs : Complete the table
- Q003 - SOME, ANY and compounds
- MOD007 - Modal Verbs
- T031 - Tenses - Sentence Building
- T030 - Tenses - Sentence Building
- PA012 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- PA011 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- T029 - All Tenses
- PREP007 - Prepositions
- PREP006 - Prepositions
- PA010 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- T028 - Past and Past Perfect Tense
- T027 - Past and Present Perfect Simple
- GI009 - Gerund and Infinitive
- T026 - Present Perfect Tense Simple and Progressive
- T025 - Present Perfect Tense Simple and Progressive
- T024 - Past Tense Simple and Progressive
- T023 - Past Tense Simple and Progressive
- T022 - Present Tense Simple and Progressive
- ART007 - Definite and Indefinite Articles
- T021 - Present Perfect Simple and Progressive
- PA009 - Active and Passive Voice
- T020 - All Tenses
- AD012 - TOO and ENOUGH
- Q002 - Quantifiers: EVERY, EACH , ONE , OTHER , OTHERS , ANOTHER
- GI008 - Gerund and Infinitive
- Q001 - SOME, ANY, EVERY , NO and compounds
- RC003 - Relative Clauses - Combine the TWO Sentences
- RS006 - Reported Speech
- PA008 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- PA007 - Passive Voice - Fill in the correct verb form
- T019 - Future Tenses
- MOD006 - Modal Verbs
- ART006 - Definite and Indefinite Articles
- ART005 - Definite and Indefinite Articles
- GI007 - Gerund and Infinitive
- PREP005 - Prepositions
- IF007 - Expressing a wish
- T018 - Past and Past Perfect Tense
- AD011 - Adjective or Adverb
- RS005 - Reported Speech
- WO002 - Word Order
- WO001 - Word Order
- MOD005 - Modal Verbs
- GI006 - Gerund and Infinitive
- ART004 - Definite Article THE
- PA006 - Passive Voice - Make sentences using the tenses in brackets
- PA005 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- PA004 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- PA003 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- AD010 - Adjective or Adverb
- RS004 - Reported Speech
- RS003 - Reported Speech
- RC002 - Relative Clauses - Combine the TWO Sentences
- PREP004 - Prepositions
- PREP003 - Prepositions
- RC001 - Relative Clauses
- MOD004 - Modal Verbs
- GI005 - Gerund and Infinitive
- IF006 - IF-Clauses - Missing Sentence Types
- IF005 - IF-Clauses - Missing Sentence Types
- GI004 - Gerund and Infinitive
- T017 - All Tenses
- T016 - Present Tense - Simple and Progressive
- PREP002 - Prepositions
- PREP001 - Prepositions
- T015 - All Tenses
- T014 - All Tenses
- T013 - All Tenses
- MOD003 - Modal Verbs
- T012 - Letter to Janet - Past and Present Perfect Tense
- PA002 - Passive Voice - Change from active to passive
- MOD002 - Modal Verbs : MUST, MUSTN'T and NEEDN'T
- AD009 - Adjective or Adverb
- PA001 - Passive Voice - Sentence Building
- T011 - All Tenses
- IF004 - IF-Clauses - All Types
- IF003 - IF-Clauses - All Types
- T010 - Tenses : Sentence Building
- AD008 - Adjective or Adverb
- ART003 - Definite and Indefinite Articles
- ART002 - Definite and Indefinite Articles
- ART001 - Definite and Indefinite Articles
- MOD001 - Modal Verbs : CAN, CAN'T, COULD, COULDN'T, MUST or MUSTN'T
- T009 - Past and Past Perfect Simple
- AD007 - Adjective and Adverb : Mixed Exercises
- T008 - Present Perfect Tense: Simple and Progressive
- GI003 - Gerund and Infinitive - Mixed Sentences
- GI002 - Gerund and Infinitive - Mixed Sentences
- T007 - All Tenses
- T006 - All Tenses
- T005 - All Tenses
- IF002 - IF-Clauses - All Types
- RS002 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises
- IF001 - IF-Clauses - All Types
- T004 - Present Tense - Simple and Continuous
- T003 - Present Tense - Simple and Continuous
- T002 - Present Tense - Simple and Continuous
- RS001 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises
- GI001 - Gerund and Infinitive - Mixed Sentences
- AD006 - Adjectives ending with -ED and -ING
- Adjective - Adverb
- Gerund and Infinitive
- Modal Verbs
- Reported Speech
- Passive Voice
- Definite and Indefinite Articles
- Quantifiers
- Relative Clauses
- Prepositions
- Questions and Negations
- Question Tags
- Language in Use
- Word Formation
- General Vocabulary
- Topical Vocabulary
- Key Word Transformation
News Articles
- Letters and Emails
- Blog Posts and Comments
- Connectives and Linking Phrases
- Phrasal Verbs
- Collocations and Phrases
Listening Comprehension
Privacy policy.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported speech 2. Reported requests and orders. Reported speech exercise. Reported questions - worksheet. Indirect speech - worksheet. Worksheets pdf - print. Grammar worksheets - handouts. Grammar - lessons. Reported speech - grammar notes.
RS008 - Reported Questions. RS007 - Reported Speech. RS006 - Reported Speech. RS005 - Reported Speech. RS004 - Reported Speech. RS003 - Reported Speech. RS002 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises. RS001 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises. Adjective and Adverbs - Downloadable PDF Worksheets for English Language Learners - Intermediate Level (B1)
A. Direct Speech cont. Position of Quoted Speech. Instructions. Examples. split by the subject and the verb. Begin with the first set of quotation marks. Capitalize the first letter of the sentence. At the end of the first part of the quote, place a comma and quotation marks. Insert the subject and reporting verb, and follow the verb with a comma.
Reported Speech. Greg: "I am cooking dinner Maya.". Maya: "Greg said he was cooking dinner.". So most often, the reported speech is going to be in the past tense, because the original statement, will now be in the past! *We will learn about reporting verbs in part 2 of this lesson, but for now we will just use said/told.
Reported Speech Exercises. Perfect English Grammar. Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site: (Click here to read the explanations about reported speech) Reported Statements: Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here) Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
Reported questions + commands exercises PDF. Practise the difference between the direct and indirect speech in questions, commands and requests. Online exercises with answers: Direct - indirect speech exercise 1 Rewrite sentences in the reported speech. Direct - indirect speech exercise 2 Report a short dialogue in the reported speech.
In English grammar, reported speech is used to tell someone what another person said. It takes another person's words (direct speech) to create a report of what they said (indirect speech.) With the following direct and indirect speech exercises, it will be easier to understand how reported speech works.
This sections provides you with downloadable PDF worksheets and keys for grammar . Please choose from the grammar areas. New Grammar Worksheets. T056 - Past Tense Simple and Progressive ... RS001 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises; GI001 - Gerund and Infinitive - Mixed Sentences; AD006 - Adjectives ending with -ED and -ING . B1 Grammar. Tenses ...
Take note: All of the above listed reporting verbs can also fit into structure 1: rep. verb (+that) + clause Billy denied (that) he had stolen the bag. She admitted (that) she had left the freezer door open. 4B. Reporting verbs followed by a gerund: rep. verb + preposition + verb+ing.
393 Reported speech English ESL worksheets pdf & doc. SORT BY. Most popular. TIME PERIOD. All-time. Zmarques. Reported Speech. It consists of seven. 104562 uses. Zmarques. Reported Speech. ... An exercise for prac. 8067 uses. estrelapolar. REPORTED SPEECH. A worksheet to pract. 6740 uses. anarti. REPORTED SPEECH. Here you have some p. 6477 uses.