Data presentation: A comprehensive guide
Learn how to create data presentation effectively and communicate your insights in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
Raja Bothra
Building presentations


Table of contents
Hey there, fellow data enthusiast!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on data presentation.
Whether you're an experienced presenter or just starting, this guide will help you present your data like a pro. We'll dive deep into what data presentation is, why it's crucial, and how to master it. So, let's embark on this data-driven journey together.
What is data presentation?
Data presentation is the art of transforming raw data into a visual format that's easy to understand and interpret. It's like turning numbers and statistics into a captivating story that your audience can quickly grasp. When done right, data presentation can be a game-changer, enabling you to convey complex information effectively.
Why are data presentations important?
Imagine drowning in a sea of numbers and figures. That's how your audience might feel without proper data presentation. Here's why it's essential:
- Clarity : Data presentations make complex information clear and concise.
- Engagement : Visuals, such as charts and graphs, grab your audience's attention.
- Comprehension : Visual data is easier to understand than long, numerical reports.
- Decision-making : Well-presented data aids informed decision-making.
- Impact : It leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Types of data presentation:
Now, let's delve into the diverse array of data presentation methods, each with its own unique strengths and applications. We have three primary types of data presentation, and within these categories, numerous specific visualization techniques can be employed to effectively convey your data.
1. Textual presentation
Textual presentation harnesses the power of words and sentences to elucidate and contextualize your data. This method is commonly used to provide a narrative framework for the data, offering explanations, insights, and the broader implications of your findings. It serves as a foundation for a deeper understanding of the data's significance.
2. Tabular presentation
Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points.
3. Graphical presentation
Graphical presentation harnesses the visual impact of charts and graphs to breathe life into your data. Charts and graphs are powerful tools for spotlighting trends, patterns, and relationships hidden within the data. Let's explore some common graphical presentation methods:
- Bar charts: They are ideal for comparing different categories of data. In this method, each category is represented by a distinct bar, and the height of the bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar charts provide a clear and intuitive way to discern differences between categories.
- Pie charts: It excel at illustrating the relative proportions of different data categories. Each category is depicted as a slice of the pie, with the size of each slice corresponding to the percentage of the total value it represents. Pie charts are particularly effective for showcasing the distribution of data.
- Line graphs: They are the go-to choice when showcasing how data evolves over time. Each point on the line represents a specific value at a particular time period. This method enables viewers to track trends and fluctuations effortlessly, making it perfect for visualizing data with temporal dimensions.
- Scatter plots: They are the tool of choice when exploring the relationship between two variables. In this method, each point on the plot represents a pair of values for the two variables in question. Scatter plots help identify correlations, outliers, and patterns within data pairs.
The selection of the most suitable data presentation method hinges on the specific dataset and the presentation's objectives. For instance, when comparing sales figures of different products, a bar chart shines in its simplicity and clarity. On the other hand, if your aim is to display how a product's sales have changed over time, a line graph provides the ideal visual narrative.
Additionally, it's crucial to factor in your audience's level of familiarity with data presentations. For a technical audience, more intricate visualization methods may be appropriate. However, when presenting to a general audience, opting for straightforward and easily understandable visuals is often the wisest choice.
In the world of data presentation, choosing the right method is akin to selecting the perfect brush for a masterpiece. Each tool has its place, and understanding when and how to use them is key to crafting compelling and insightful presentations. So, consider your data carefully, align your purpose, and paint a vivid picture that resonates with your audience.
What to include in data presentation?
When creating your data presentation, remember these key components:
- Data points : Clearly state the data points you're presenting.
- Comparison : Highlight comparisons and trends in your data.
- Graphical methods : Choose the right chart or graph for your data.
- Infographics : Use visuals like infographics to make information more digestible.
- Numerical values : Include numerical values to support your visuals.
- Qualitative information : Explain the significance of the data.
- Source citation : Always cite your data sources.
How to structure an effective data presentation?
Creating a well-structured data presentation is not just important; it's the backbone of a successful presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling and organized presentation that captivates your audience:
1. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is paramount. Consider their needs, interests, and existing knowledge about your topic. Tailor your presentation to their level of understanding, ensuring that it resonates with them on a personal level. Relevance is the key.
2. Have a clear message
Every effective data presentation should convey a clear and concise message. Determine what you want your audience to learn or take away from your presentation, and make sure your message is the guiding light throughout your presentation. Ensure that all your data points align with and support this central message.
3. Tell a compelling story
Human beings are naturally wired to remember stories. Incorporate storytelling techniques into your presentation to make your data more relatable and memorable. Your data can be the backbone of a captivating narrative, whether it's about a trend, a problem, or a solution. Take your audience on a journey through your data.
4. Leverage visuals
Visuals are a powerful tool in data presentation. They make complex information accessible and engaging. Utilize charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your points and enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Visuals should not just be an accessory; they should be an integral part of your storytelling.
5. Be clear and concise
Avoid jargon or technical language that your audience may not comprehend. Use plain language and explain your data points clearly. Remember, clarity is king. Each piece of information should be easy for your audience to digest.
6. Practice your delivery
Practice makes perfect. Rehearse your presentation multiple times before the actual delivery. This will help you deliver it smoothly and confidently, reducing the chances of stumbling over your words or losing track of your message.
A basic structure for an effective data presentation
Armed with a comprehensive comprehension of how to construct a compelling data presentation, you can now utilize this fundamental template for guidance:
In the introduction, initiate your presentation by introducing both yourself and the topic at hand. Clearly articulate your main message or the fundamental concept you intend to communicate.
Moving on to the body of your presentation, organize your data in a coherent and easily understandable sequence. Employ visuals generously to elucidate your points and weave a narrative that enhances the overall story. Ensure that the arrangement of your data aligns with and reinforces your central message.
As you approach the conclusion, succinctly recapitulate your key points and emphasize your core message once more. Conclude by leaving your audience with a distinct and memorable takeaway, ensuring that your presentation has a lasting impact.
Additional tips for enhancing your data presentation
To take your data presentation to the next level, consider these additional tips:
- Consistent design : Maintain a uniform design throughout your presentation. This not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in seamless comprehension.
- High-quality visuals : Ensure that your visuals are of high quality, easy to read, and directly relevant to your topic.
- Concise text : Avoid overwhelming your slides with excessive text. Focus on the most critical points, using visuals to support and elaborate.
- Anticipate questions : Think ahead about the questions your audience might pose. Be prepared with well-thought-out answers to foster productive discussions.
By following these guidelines, you can structure an effective data presentation that not only informs but also engages and inspires your audience. Remember, a well-structured presentation is the bridge that connects your data to your audience's understanding and appreciation.
Do’s and don'ts on a data presentation
- Use visuals : Incorporate charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Keep it simple : Avoid clutter and complexity.
- Highlight key points : Emphasize crucial data.
- Engage the audience : Encourage questions and discussions.
- Practice : Rehearse your presentation.
Don'ts:
- Overload with data : Less is often more; don't overwhelm your audience.
- Fit Unrelated data : Stay on topic; don't include irrelevant information.
- Neglect the audience : Ensure your presentation suits your audience's level of expertise.
- Read word-for-word : Avoid reading directly from slides.
- Lose focus : Stick to your presentation's purpose.
Summarizing key takeaways
- Definition : Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding.
- Importance : Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact.
- Types : Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
- Choosing methods : Select the right method based on data, audience, and purpose.
- Components : Include data points, comparisons, visuals, infographics, numerical values, and source citations.
- Structure : Know your audience, have a clear message, tell a compelling story, use visuals, be concise, and practice.
- Do's and don'ts : Do use visuals, keep it simple, highlight key points, engage the audience, and practice. Don't overload with data, include unrelated information, neglect the audience's expertise, read word-for-word, or lose focus.
FAQ's on a data presentation
1. what is data presentation, and why is it important in 2024.
Data presentation is the process of visually representing data sets to convey information effectively to an audience. In an era where the amount of data generated is vast, visually presenting data using methods such as diagrams, graphs, and charts has become crucial. By simplifying complex data sets, presentation of the data may helps your audience quickly grasp much information without drowning in a sea of chart's, analytics, facts and figures.
2. What are some common methods of data presentation?
There are various methods of data presentation, including graphs and charts, histograms, and cumulative frequency polygons. Each method has its strengths and is often used depending on the type of data you're using and the message you want to convey. For instance, if you want to show data over time, try using a line graph. If you're presenting geographical data, consider to use a heat map.
3. How can I ensure that my data presentation is clear and readable?
To ensure that your data presentation is clear and readable, pay attention to the design and labeling of your charts. Don't forget to label the axes appropriately, as they are critical for understanding the values they represent. Don't fit all the information in one slide or in a single paragraph. Presentation software like Prezent and PowerPoint can help you simplify your vertical axis, charts and tables, making them much easier to understand.
4. What are some common mistakes presenters make when presenting data?
One common mistake is trying to fit too much data into a single chart, which can distort the information and confuse the audience. Another mistake is not considering the needs of the audience. Remember that your audience won't have the same level of familiarity with the data as you do, so it's essential to present the data effectively and respond to questions during a Q&A session.
5. How can I use data visualization to present important data effectively on platforms like LinkedIn?
When presenting data on platforms like LinkedIn, consider using eye-catching visuals like bar graphs or charts. Use concise captions and e.g., examples to highlight the single most important information in your data report. Visuals, such as graphs and tables, can help you stand out in the sea of textual content, making your data presentation more engaging and shareable among your LinkedIn connections.
Create your data presentation with prezent
Prezent can be a valuable tool for creating data presentations. Here's how Prezent can help you in this regard:
- Time savings : Prezent saves up to 70% of presentation creation time, allowing you to focus on data analysis and insights.
- On-brand consistency : Ensure 100% brand alignment with Prezent's brand-approved designs for professional-looking data presentations.
- Effortless collaboration : Real-time sharing and collaboration features make it easy for teams to work together on data presentations.
- Data storytelling : Choose from 50+ storylines to effectively communicate data insights and engage your audience.
- Personalization : Create tailored data presentations that resonate with your audience's preferences, enhancing the impact of your data.
In summary, Prezent streamlines the process of creating data presentations by offering time-saving features, ensuring brand consistency, promoting collaboration, and providing tools for effective data storytelling. Whether you need to present data to clients, stakeholders, or within your organization, Prezent can significantly enhance your presentation-making process.
So, go ahead, present your data with confidence, and watch your audience be wowed by your expertise.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven journey. Stay tuned for more insights, and remember, data presentation is your ticket to making numbers come alive! Sign up for our free trial or book a demo !
More zenpedia articles
.webp)
14 Best AI tools for business to boost productivity

Best blue color palettes for presentations: Make your next project stunning

Mastering virtual communication: Tips to enhance virtual team communication
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)
Call Us Today! +91 99907 48956 | [email protected]
Data presentation - types & its importance, what is data presentation.
Data Analysis and Data Presentation have a practical implementation in every possible field. It can range from academic studies, commercial, industrial and marketing activities to professional practices.
In its raw form, data can be extremely complicated to decipher and in order to extract meaningful insights from the data, data analysis is an important step towards breaking down data into understandable charts or graphs.
Data analysis tools used for analyzing the raw data which must be processed further to support N number of applications.
Therefore, the processes or analyzing data usually helps in the interpretation of raw data and extract the useful content out of it. The transformed raw data assists in obtaining useful information.
Once the required information is obtained from the data, the next step would be to present the data in a graphical presentation.
The presentation is the key to success. Once the information is obtained the user transforms the data into a pictorial Presentation so as to be able to acquire a better response and outcome.
Methods of Data Presentation in Statistics
1. pictorial presentation.
It is the simplest form of data Presentation often used in schools or universities to provide a clearer picture to students, who are better able to capture the concepts effectively through a pictorial Presentation of simple data.
2. Column chart
It is a simplified version of the pictorial Presentation which involves the management of a larger amount of data being shared during the presentations and providing suitable clarity to the insights of the data.
3. Pie Charts
Pie charts provide a very descriptive & a 2D depiction of the data pertaining to comparisons or resemblance of data in two separate fields.

4. Bar charts
A bar chart that shows the accumulation of data with cuboid bars with different dimensions & lengths which are directly proportionate to the values they represent. The bars can be placed either vertically or horizontally depending on the data being represented.
5. Histograms
It is a perfect Presentation of the spread of numerical data. The main differentiation that separates data graphs and histograms are the gaps in the data graphs.
6. Box plots
Box plot or Box-plot is a way of representing groups of numerical data through quartiles. Data Presentation is easier with this style of graph dealing with the extraction of data to the minutes of difference.
Map Data graphs help you with data Presentation over an area to display the areas of concern. Map graphs are useful to make an exact depiction of data over a vast case scenario.
All these visual presentations share a common goal of creating meaningful insights and a platform to understand and manage the data in relation to the growth and expansion of one’s in-depth understanding of data & details to plan or execute future decisions or actions.
Importance of Data Presentation
Data Presentation could be both can be a deal maker or deal breaker based on the delivery of the content in the context of visual depiction.
Data Presentation tools are powerful communication tools that can simplify the data by making it easily understandable & readable at the same time while attracting & keeping the interest of its readers and effectively showcase large amounts of complex data in a simplified manner.
If the user can create an insightful presentation of the data in hand with the same sets of facts and figures, then the results promise to be impressive.
There have been situations where the user has had a great amount of data and vision for expansion but the presentation drowned his/her vision.
To impress the higher management and top brass of a firm, effective presentation of data is needed.
Data Presentation helps the clients or the audience to not spend time grasping the concept and the future alternatives of the business and to convince them to invest in the company & turn it profitable both for the investors & the company.
Although data presentation has a lot to offer, the following are some of the major reason behind the essence of an effective presentation:-
- Many consumers or higher authorities are interested in the interpretation of data, not the raw data itself. Therefore, after the analysis of the data, users should represent the data with a visual aspect for better understanding and knowledge.
- The user should not overwhelm the audience with a number of slides of the presentation and inject an ample amount of texts as pictures that will speak for themselves.
- Data presentation often happens in a nutshell with each department showcasing their achievements towards company growth through a graph or a histogram.
- Providing a brief description would help the user to attain attention in a small amount of time while informing the audience about the context of the presentation
- The inclusion of pictures, charts, graphs and tables in the presentation help for better understanding the potential outcomes.
- An effective presentation would allow the organization to determine the difference with the fellow organization and acknowledge its flaws. Comparison of data would assist them in decision making.
Recommended Courses
Data Visualization
Using powerbi &tableau, tableau for data analysis, mysql certification program, the powerbi masterclass, need help call our support team 7:00 am to 10:00 pm (ist) at (+91 999-074-8956 | 9650-308-956), keep in touch, email: [email protected].
WhatsApp us
- Interactive Presentation
10 Methods of Data Presentation That Really Work in 2024
Leah Nguyen • 20 August, 2024 • 13 min read
Have you ever presented a data report to your boss/coworkers/teachers thinking it was super dope like you’re some cyber hacker living in the Matrix, but all they saw was a pile of static numbers that seemed pointless and didn't make sense to them?
Understanding digits is rigid . Making people from non-analytical backgrounds understand those digits is even more challenging.
How can you clear up those confusing numbers and make your presentation as clear as the day? Let's check out these best ways to present data. 💎
More Tips with AhaSlides
- Marketing Presentation
- Survey Result Presentation
- Types of Presentation

Start in seconds.
Get any of the above examples as templates. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Data Presentation - What Is It?
The term ’data presentation’ relates to the way you present data in a way that makes even the most clueless person in the room understand.
Some say it’s witchcraft (you’re manipulating the numbers in some ways), but we’ll just say it’s the power of turning dry, hard numbers or digits into a visual showcase that is easy for people to digest.
Presenting data correctly can help your audience understand complicated processes, identify trends, and instantly pinpoint whatever is going on without exhausting their brains.
Good data presentation helps…
- Make informed decisions and arrive at positive outcomes . If you see the sales of your product steadily increase throughout the years, it’s best to keep milking it or start turning it into a bunch of spin-offs (shoutout to Star Wars👀).
- Reduce the time spent processing data . Humans can digest information graphically 60,000 times faster than in the form of text. Grant them the power of skimming through a decade of data in minutes with some extra spicy graphs and charts.
- Communicate the results clearly . Data does not lie. They’re based on factual evidence and therefore if anyone keeps whining that you might be wrong, slap them with some hard data to keep their mouths shut.
- Add to or expand the current research . You can see what areas need improvement, as well as what details often go unnoticed while surfing through those little lines, dots or icons that appear on the data board.
Methods of Data Presentation and Examples
Imagine you have a delicious pepperoni, extra-cheese pizza. You can decide to cut it into the classic 8 triangle slices, the party style 12 square slices, or get creative and abstract on those slices.
There are various ways to cut a pizza and you get the same variety with how you present your data. In this section, we will bring you the 10 ways to slice a pizza - we mean to present your data - that will make your company’s most important asset as clear as day. Let's dive into 10 ways to present data efficiently.
#1 - Tabular
Among various types of data presentation, tabular is the most fundamental method, with data presented in rows and columns. Excel or Google Sheets would qualify for the job. Nothing fancy.
This is an example of a tabular presentation of data on Google Sheets. Each row and column has an attribute (year, region, revenue, etc.), and you can do a custom format to see the change in revenue throughout the year.
When presenting data as text, all you do is write your findings down in paragraphs and bullet points, and that’s it. A piece of cake to you, a tough nut to crack for whoever has to go through all of the reading to get to the point.
- 65% of email users worldwide access their email via a mobile device.
- Emails that are optimised for mobile generate 15% higher click-through rates.
- 56% of brands using emojis in their email subject lines had a higher open rate.
(Source: CustomerThermometer )
All the above quotes present statistical information in textual form. Since not many people like going through a wall of texts, you’ll have to figure out another route when deciding to use this method, such as breaking the data down into short, clear statements, or even as catchy puns if you’ve got the time to think of them.
#3 - Pie chart
A pie chart (or a ‘donut chart’ if you stick a hole in the middle of it) is a circle divided into slices that show the relative sizes of data within a whole. If you’re using it to show percentages, make sure all the slices add up to 100%.
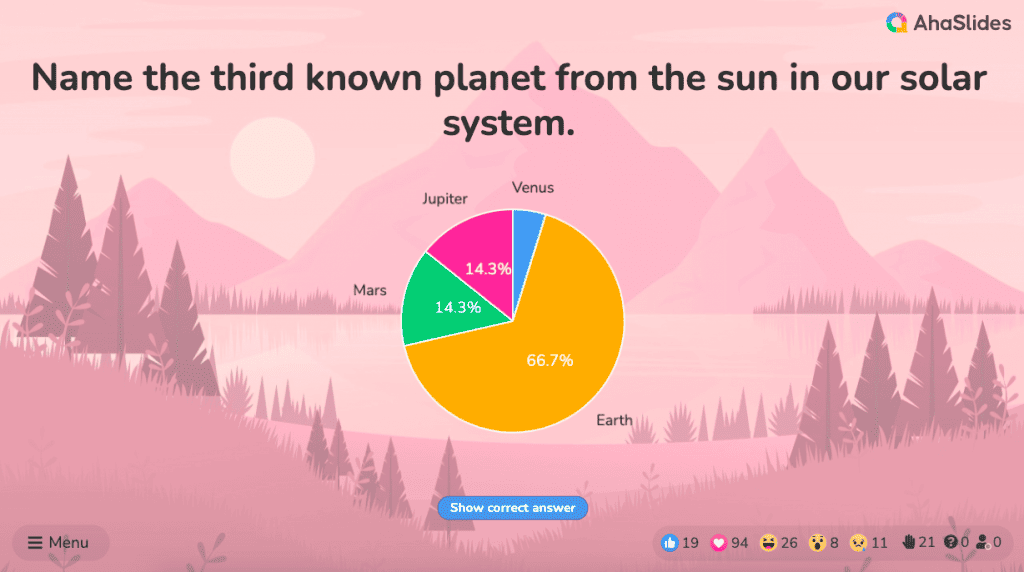
The pie chart is a familiar face at every party and is usually recognised by most people. However, one setback of using this method is our eyes sometimes can’t identify the differences in slices of a circle, and it’s nearly impossible to compare similar slices from two different pie charts, making them the villains in the eyes of data analysts.
#4 - Bar chart
The bar chart is a chart that presents a bunch of items from the same category, usually in the form of rectangular bars that are placed at an equal distance from each other. Their heights or lengths depict the values they represent.
They can be as simple as this:
Or more complex and detailed like this example of data presentation. Contributing to an effective statistic presentation, this one is a grouped bar chart that not only allows you to compare categories but also the groups within them as well.
#5 - Histogram
Similar in appearance to the bar chart but the rectangular bars in histograms don’t often have the gap like their counterparts.
Instead of measuring categories like weather preferences or favourite films as a bar chart does, a histogram only measures things that can be put into numbers.
Teachers can use presentation graphs like a histogram to see which score group most of the students fall into, like in this example above.
#6 - Line graph
Recordings to ways of displaying data, we shouldn't overlook the effectiveness of line graphs. Line graphs are represented by a group of data points joined together by a straight line. There can be one or more lines to compare how several related things change over time.
On a line chart’s horizontal axis, you usually have text labels, dates or years, while the vertical axis usually represents the quantity (e.g.: budget, temperature or percentage).
#7 - Pictogram graph
A pictogram graph uses pictures or icons relating to the main topic to visualise a small dataset. The fun combination of colours and illustrations makes it a frequent use at schools.
Pictograms are a breath of fresh air if you want to stay away from the monotonous line chart or bar chart for a while. However, they can present a very limited amount of data and sometimes they are only there for displays and do not represent real statistics.
#8 - Radar chart
If presenting five or more variables in the form of a bar chart is too stuffy then you should try using a radar chart, which is one of the most creative ways to present data.
Radar charts show data in terms of how they compare to each other starting from the same point. Some also call them ‘spider charts’ because each aspect combined looks like a spider web.
Radar charts can be a great use for parents who’d like to compare their child’s grades with their peers to lower their self-esteem. You can see that each angular represents a subject with a score value ranging from 0 to 100. Each student’s score across 5 subjects is highlighted in a different colour.
If you think that this method of data presentation somehow feels familiar, then you’ve probably encountered one while playing Pokémon .
#9 - Heat map
A heat map represents data density in colours. The bigger the number, the more colour intensity that data will be represented.
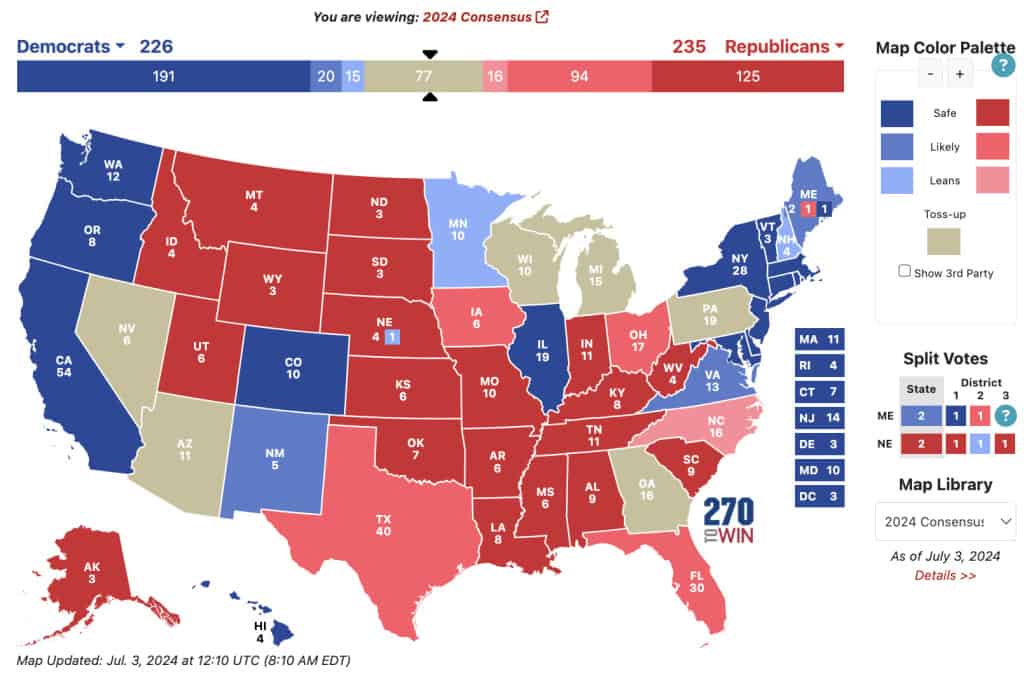
Most US citizens would be familiar with this data presentation method in geography. For elections, many news outlets assign a specific colour code to a state, with blue representing one candidate and red representing the other. The shade of either blue or red in each state shows the strength of the overall vote in that state.
Another great thing you can use a heat map for is to map what visitors to your site click on. The more a particular section is clicked the ‘hotter’ the colour will turn, from blue to bright yellow to red.
#10 - Scatter plot
If you present your data in dots instead of chunky bars, you’ll have a scatter plot.
A scatter plot is a grid with several inputs showing the relationship between two variables. It’s good at collecting seemingly random data and revealing some telling trends.
For example, in this graph, each dot shows the average daily temperature versus the number of beach visitors across several days. You can see that the dots get higher as the temperature increases, so it’s likely that hotter weather leads to more visitors.
5 Data Presentation Mistakes to Avoid
#1 - assume your audience understands what the numbers represent.
You may know all the behind-the-scenes of your data since you’ve worked with them for weeks, but your audience doesn’t.
Showing without telling only invites more and more questions from your audience, as they have to constantly make sense of your data, wasting the time of both sides as a result.
While showing your data presentations, you should tell them what the data are about before hitting them with waves of numbers first. You can use interactive activities such as polls , word clouds , online quizzes and Q&A sections , combined with icebreaker games , to assess their understanding of the data and address any confusion beforehand.
#2 - Use the wrong type of chart
Charts such as pie charts must have a total of 100% so if your numbers accumulate to 193% like this example below, you’re definitely doing it wrong.
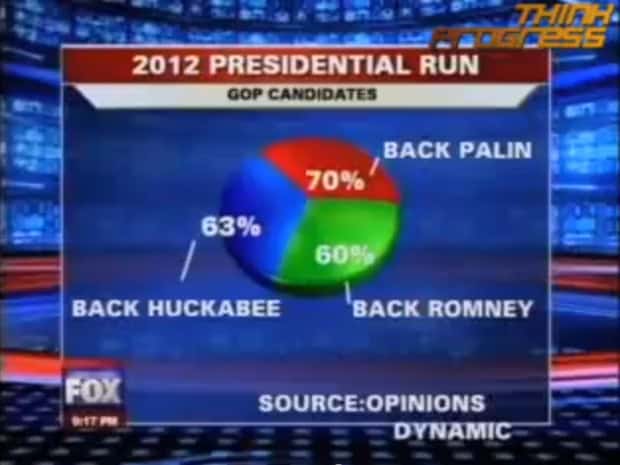
Before making a chart, ask yourself: what do I want to accomplish with my data? Do you want to see the relationship between the data sets, show the up and down trends of your data, or see how segments of one thing make up a whole?
Remember, clarity always comes first. Some data visualisations may look cool, but if they don’t fit your data, steer clear of them.
#3 - Make it 3D
3D is a fascinating graphical presentation example. The third dimension is cool, but full of risks.
Can you see what’s behind those red bars? Because we can’t either. You may think that 3D charts add more depth to the design, but they can create false perceptions as our eyes see 3D objects closer and bigger than they appear, not to mention they cannot be seen from multiple angles.
#4 - Use different types of charts to compare contents in the same category
This is like comparing a fish to a monkey. Your audience won’t be able to identify the differences and make an appropriate correlation between the two data sets.
Next time, stick to one type of data presentation only. Avoid the temptation of trying various data visualisation methods in one go and make your data as accessible as possible.
#5 - Bombard the audience with too much information
The goal of data presentation is to make complex topics much easier to understand, and if you’re bringing too much information to the table, you’re missing the point.
The more information you give, the more time it will take for your audience to process it all. If you want to make your data understandable and give your audience a chance to remember it, keep the information within it to an absolute minimum. You should end your session with open-ended questions to see what your participants really think.
What are the Best Methods of Data Presentation?
Finally, which is the best way to present data?
The answer is…
There is none! Each type of presentation has its own strengths and weaknesses and the one you choose greatly depends on what you’re trying to do.
For example:
- Go for a scatter plot if you’re exploring the relationship between different data values, like seeing whether the sales of ice cream go up because of the temperature or because people are just getting more hungry and greedy each day?
- Go for a line graph if you want to mark a trend over time.
- Go for a heat map if you like some fancy visualisation of the changes in a geographical location, or to see your visitors' behaviour on your website.
- Go for a pie chart (especially in 3D) if you want to be shunned by others because it was never a good idea👇
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a chart presentation.
A chart presentation is a way of presenting data or information using visual aids such as charts, graphs, and diagrams. The purpose of a chart presentation is to make complex information more accessible and understandable for the audience.
When can I use charts for the presentation?
Charts can be used to compare data, show trends over time, highlight patterns, and simplify complex information.
Why should you use charts for presentation?
You should use charts to ensure your contents and visuals look clean, as they are the visual representative, provide clarity, simplicity, comparison, contrast and super time-saving!
What are the 4 graphical methods of presenting data?
Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
Leah Nguyen
Words that convert, stories that stick. I turn complex ideas into engaging narratives - helping audiences learn, remember, and take action.
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides


IMAGES
VIDEO