AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
AI Research Assist Your go-to AI-powered research assistant
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
Plan Writing & Consulting We create a business plan for you
Business Plan Review Get constructive feedback on your plan
Financial Forecasting We create financial projections for you
SBA Lending Assistance We help secure SBA loans for your business
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow

How to Write Competitive Analysis in a Business Plan (w/ Examples)

The Competitive Analysis Kit
- Vinay Kevadia
- January 9, 2024
- 14 Min Read

Every business wants to outperform its competitors, but do you know the right approach to gather information and analyze your competitors?
That’s where competitive analysis steps in. It’s the tool that helps you know your competition’s pricing strategies, strengths, product details, marketing strategies, target audience, and more.
If you want to know more about competitor analysis, this guide is all you need. It spills all the details on how to conduct and write a competitor analysis in a business plan, with examples.
Let’s get started and first understand the meaning of competitive analysis.
What is Competitive Analysis?
A competitive analysis involves collecting information about what other businesses in your industry are doing with their products, sales, and marketing.
Businesses use this data to find out what they are good at, where they can do better, and what opportunities they might have. It is like checking out the competition to see how and where you can improve.
This kind of analysis helps you get a clear picture of the market, allowing you to make smart decisions to make your business stand out and do well in the industry.
Competitive analysis is a section of utmost value for your business plan. The analysis in this section will form the basis upon which you will frame your marketing, sales, and product-related strategies. So make sure it’s thorough, insightful, and in line with your strategic objectives.
Let’s now understand how you can conduct a competitive analysis for your own business and leverage all its varied benefits.
How to Conduct a Competitive Analysis
Let’s break down the process of conducting a competitive analysis for your business plan in these easy-to-follow steps.
It will help you prepare a solid competitor analysis section in your business plan that actually highlights your strengths and opens room for better discussions (and funding).
Let’s begin.
1. Identify Your Direct and Indirect Competitors
First things first — identify all your business competitors and list them down. You can have a final, detailed list later, but right now an elementary list that mentions your primary competitors (the ones you know and are actively competing with) can suffice.
As you conduct more research, you can keep adding to it.
Explore your competitors using Google, social media platforms, or local markets. Then differentiate them into direct or indirect competitors.
Direct competitors
Businesses offering the same products or services, and targeting a similar target market are your direct competitors.
These competitors operate in the same industry and are often competing for the same market share.
Indirect competitors
On the other hand, indirect competitors are businesses that offer different products or services but cater to the same target customers as yours.
While they may not offer identical solutions, they compete for the same customer budget or attention. Indirect competitors can pose a threat by providing alternatives that customers might consider instead of your offerings.
2. Study the Overall Market
Now that you know your business competitors, deep dive into market research. Market research should involve a combination of both primary and secondary research methods.
Primary research
Primary research involves collecting market information directly from the source or subjects. Some examples of primary market research methods include:
- Purchasing competitors’ products or services
- Conducting interviews with their customers
- Administering online surveys to gather customer insights
Secondary research
Secondary research involves utilizing pre-existing gathered information from some relevant sources. Some of its examples include:
- Scrutinizing competitors’ websites
- Assessing the current economic landscape
- Referring to online market databases of the competitors.
Have a good understanding of the market at this point to write your market analysis section effectively.
3. Prepare a Competitive Framework
Now that you have a thorough understanding of your competitors’ market, it is time to create a competitive framework that enables comparison between two businesses.
Factors like market share, product offering, pricing, distribution channel, target markets, marketing strategies, and customer service offer essential metrics and information to chart your competitive framework .
These factors will form the basis of comparison for your competitive analysis. Depending on the type of your business, choose the factors that are relevant to you.
4. Take Note of Your Competitor’s Strategies
Now that you have an established framework, use that as a base to analyze your competitor’s strategies. Such analysis will help you understand what the customers like and dislike about your competitors.
Start by analyzing the marketing strategies, sales and marketing channels, promotional activities, and branding strategies of your competitors. Understand how they position themselves in the market and what USPs they emphasize.
Evaluate, analyze their pricing strategies and keep an eye on their distribution channel to understand your competitor’s business model in detail.
This information allows you to make informed decisions about your strategies, helping you identify opportunities for differentiation and improvement.
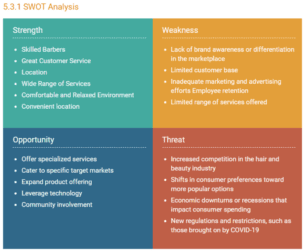
5. Perform a SWOT Analysis of Your Competitors
A SWOT analysis is a method of analyzing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of your business in the competitive marketplace.
While strengths and weaknesses focus on internal aspects of your company, opportunities and threats examine the external factors related to the industry and market.
It’s an important tool that will help determine the company’s competitive edge quite efficiently.
It includes the positive features of your internal business operations. For example, a strong brand, skilled workforce, innovative products/services, or a loyal customer base.
It includes all the hindrances of your internal business operations. For example, limited resources, outdated technology, weak brand recognition, or inefficient processes.
Opportunities
It outlines several opportunities that will come your way in the near or far future. Opportunities can arise as the industry or market trend changes or by leveraging the weaknesses of your competitors.
For example, details about emerging markets, technological advancements, changing consumer trends, profitable partnerships in the future, etc.
Threats define any external factor that poses a challenge or any risk for your business in this section. For example, intense competition, economic downturns, regulatory changes, or any advanced technology disruption.
This section will form the basis for your business strategies and product offerings. So make sure it’s detailed and offers the right representation of your business.
And that is all you need to create a comprehensive competitive analysis for your business plan.

Want to Perform Competitive Analysis for your Business?
Discover your competition’s secrets effortlessly with our user-friendly and Free Competitor Analysis Generator!
How to Write Competitive Analysis in a Business Plan
The section on competitor analysis is the most crucial part of your business plan. Making this section informative and engaging gets easier when you have all the essential data to form this section.
Now, let’s learn an effective way of writing your competitive analysis.
1. Determine who your readers are
Know your audience first, because that will change the whole context of your competitor analysis business plan.
The competitive analysis section will vary depending on the intended audience is the team or investors.
Consider the following things about your audience before you start writing this section:
Internal competitor plan (employees or partners)
Objective: The internal competitor plan is to provide your team with an understanding of the competitive landscape.
Focus: The focus should be on the comparison of the strengths and weaknesses of competitors to boost strategic discussions within your team.
Use: It is to leverage the above information to develop strategies that highlight your strengths and address your weaknesses.
Competitor plan for funding (bank or investors)
Objective: Here, the objective is to reassure the potential and viability of your business to investors or lenders.
Focus: This section should focus on awareness and deep understanding of the competitive landscape to persuade the readers about the future of your business.
Use: It is to showcase your market position and the opportunities that are on the way to your business.
This differentiation is solely to ensure that the competitive analysis serves its purpose effectively based on the specific needs and expectations of the respective audience.
2. Describe and Visualise Competitive Advantage
Remember how we determined our competitive advantage at the time of research. It is now time to present that advantage in your competitive analysis.
Highlight your edge over other market players in terms of innovation, product quality, features, pricing, or marketing strategy. Understanding your products’ competitive advantage will also help you write the products and services section effectively.
However, don’t limit the edge to your service and market segment. Highlight every area where you excel even if it is better customer service or enhanced brand reputation.
Now, you can explain your analysis through textual blocks. However, a more effective method would be using a positioning map or competitive matrix to offer a visual representation of your company’s competitive advantage.
3. Explain your strategies
Your competitor analysis section should not only highlight the opportunities or threats of your business. It should also mention the strategies you will implement to overcome those threats or capitalize on the opportunities.
Such strategies may include crafting top-notch quality for your products or services, exploring the unexplored market segment, or having creative marketing strategies.
Elaborate on these strategies later in their respective business plan sections.
4. Know the pricing strategy
To understand the pricing strategy of your competitors, there are various aspects you need to have information about. It involves knowing their pricing model, evaluating their price points, and considering the additional costs, if any.
One way to understand this in a better way is to compare features and value offered at different price points and identify the gaps in competitors’ offerings.
Once you know the pricing structure of your competitors, compare it with yours and get to know the competitive advantage of your business from a pricing point of view.
Let us now get a more practical insight by checking an example of competitive analysis.
Competitive Analysis Example in a Business Plan
Here’s a business plan example highlighting the barber shop’s competitive analysis.
1. List of competitors
Direct & indirect competitors.
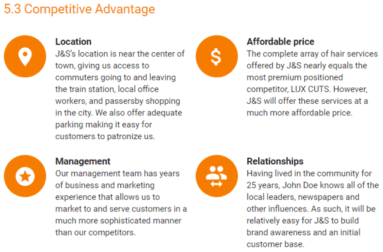
The following retailers are located within a 5-mile radius of J&S, thus providing either direct or indirect competition for customers:
Joe’s Beauty Salon
Joe’s Beauty Salon is the town’s most popular beauty salon and has been in business for 32 years. Joe’s offers a wide array of services that you would expect from a beauty salon.
Besides offering haircuts, Joe’s also offers nail services such as manicures and pedicures. In fact, over 60% of Joe’s revenue comes from services targeted at women outside of hair services. In addition, Joe’s does not offer its customers premium salon products.
For example, they only offer 2 types of regular hair gels and 4 types of shampoos. This puts Joe’s in direct competition with the local pharmacy and grocery stores that also carry these mainstream products. J&S, on the other hand, offers numerous options for exclusive products that are not yet available in West Palm Beach, Florida.
LUX CUTS has been in business for 5 years. LUX CUTS offers an extremely high-end hair service, with introductory prices of $120 per haircut.
However, LUX CUTS will primarily be targeting a different customer segment from J&S, focusing on households with an income in the top 10% of the city.
Furthermore, J&S offers many of the services and products that LUX CUTS offers, but at a fraction of the price, such as:
- Hairstyle suggestions & hair care consultation
- Hair extensions & coloring
- Premium hair products from industry leaders
Freddie’s Fast Hair Salon
Freddie’s Fast Hair Salon is located four stores down the road from J&S. Freddy’s has been in business for the past 3 years and enjoys great success, primarily due to its prime location.
Freddy’s business offers inexpensive haircuts and focuses on volume over quality. It also has a large customer base comprised of children between the ages of 5 to 13.
J&S has several advantages over Freddy’s Fast Hair Salon including:
- An entertainment-focused waiting room, with TVs and board games to make the wait for service more pleasurable. Especially great for parents who bring their children.
- A focus on service quality rather than speed alone to ensure repeat visits. J&S will spend on average 20 more minutes with its clients than Freddy’s.
While we expect that Freddy’s Fast Hair Salon will continue to thrive based on its location and customer relationships, we expect that more and more customers will frequent J&S based on the high-quality service it provides.
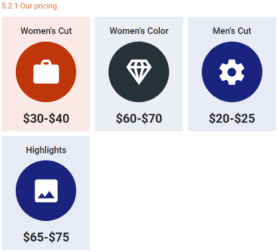
2. Competitive Pricing
John and Sons Barbing Salon will work towards ensuring that all our services are offered at highly competitive prices compared to what is obtainable in The United States of America.
We know the importance of gaining entrance into the market by lowering our pricing to attract all and sundry that is why we have consulted with experts and they have given us the best insights on how to do this and effectively gain more clients soon.
Our pricing system is going to be based on what is obtainable in the industry, we don’t intend to charge more (except for premium and customized services) and we don’t intend to charge less than our competitors are offering in West Palm Beach – Florida.
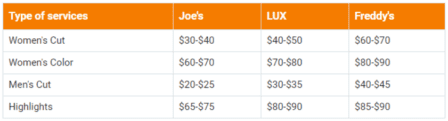
3. Our pricing
- Payment by cash
- Payment via Point of Sale (POS) Machine
- Payment via online bank transfer (online payment portal)
- Payment via Mobile money
- Check (only from loyal customers)
Given the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will help us achieve our payment plans without any itches.
4. Competitive advantage
5. SWOT analysis
Why is a Competitive Environment helpful?
Somewhere we all think, “What if we had no competition?” “What if we were the monopoly?” It would be great, right? Well, this is not the reality, and have to accept the competition sooner or later.
However, competition is healthy for businesses to thrive and survive, let’s see how:
1. Competition validates your idea
When people are developing similar products like you, it is a sign that you are on the right path. Having healthy competition proves that your idea is valid and there is a potential target market for your product and service offerings.
2. Innovation and Efficiency
Businesses competing with each other are motivated to innovate consistently, thereby, increasing their scope and market of product offerings. Moreover, when you are operating in a cutthroat environment, you simply cannot afford to be inefficient.
Be it in terms of costs, production, pricing, or marketing—you will ensure efficiency in all aspects to attract more business.
3. Market Responsiveness
Companies in a competitive environment tend to stay relevant and longer in business since they are adaptive to the changing environment. In the absence of competition, you would start getting redundant which will throw you out of the market, sooner or later.
4. Eases Consumer Education
Since your target market is already aware of the problem and existing market solutions, it would be much easier to introduce your business to them. Rather than focusing on educating, you would be more focused on branding and positioning your brand as an ideal customer solution.
Being the first one in the market is exciting. However, having healthy competition has these proven advantages which are hard to ignore.
A way forward
Whether you are starting a new business or have an already established unit, having a practical and realistic understanding of your competitive landscape is essential to developing efficient business strategies.
While getting to know your competition is essential, don’t get too hung up in the research. Research your competitors to improve your business plan and strategies, not to copy their ideas.
Create your unique strategies, offer the best possible services, and add value to your offerings—that will make you stand out.
While it’s a long, tough road, a comprehensive business plan can be your guide. Using modern business planning software is probably the easiest way to draft your plan.
Use Upmetrics. Simply enter your business details, answer the strategic questions, and see your business plan come together in front of your eyes.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is swot analysis a competitive analysis.
SWOT analysis is just a component of a competitive analysis and not the whole competitive analysis. It helps you identify the strengths and weaknesses of your business and determine the emerging opportunities and threats faced by the external environment.
Competitive analysis in reality is a broad spectrum topic wherein you identify your competitors, analyze them on different metrics, and identify your competitive advantage to form competitive business strategies.
What tools can i use for competitor analysis?
For a thorough competitor analysis, you will require a range of tools that can help in collecting, analyzing, and presenting data. While SEMrush, Google Alerts, Google Trends, and Ahrefs can help in collecting adequate competitor data, Business planning tools like Upmetrics can help in writing the competitors section of your business plan quite efficiently.
What are the 5 parts of a competitive analysis?
The main five components to keep in mind while having a competitor analysis are:
- Identifying the competitors
- Analyzing competitor’s strengths and weaknesses
- Assessing market share and trends
- Examining competitors’ strategies and market positioning
- Performing SWOT analysis
What is the difference between market analysis and competitive analysis?
Market analysis involves a comprehensive examination of the overall market dynamics, industry trends, and factors influencing a business’s operating environment.
On the other hand, competitive analysis narrows the focus to specific competitors within the market, delving into their strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more
Get started with Upmetrics Al
- 400+ sample business plans
- Al-powered financial planning
- Collaborative workspace
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning

- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
- project icon Project management
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- my-task icon Admin and security
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Project intake
- Resource planning
- Product launches
- View all use cases arrow-right icon

- Help Center
- Asana Academy
- Certifications
- Work management hub
- Customer stories
- Get support
- Developer support
- Customer Success
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Project planning |
- How to create a competitive analysis (w ...
How to create a competitive analysis (with examples)

Competitive analysis involves identifying your direct and indirect competitors using research to reveal their strengths and weaknesses in relation to your own. In this guide, we’ll outline how to do a competitive analysis and explain how you can use this marketing strategy to improve your business.
Whether you’re running a business or playing in a football game, understanding your competition is crucial for success. While you may not be scoring touchdowns in the office, your goal is to score business deals with clients or win customers with your products. The method of preparation for athletes and business owners is similar—once you understand your strengths and weaknesses versus your competitors’, you can level up.
What is a competitive analysis?
Competitive analysis involves identifying your direct and indirect competitors using research to reveal their strengths and weaknesses in relation to your own.
![business plan competitor analysis [inline illustration] What is a competitive analysis (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/c1a37dfd-53a8-44c4-b57b-10fc6a332ba1/inline-project-planning-competitive-analysis-example-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Direct competitors market the same product to the same audience as you, while indirect competitors market the same product to a different audience. After identifying your competitors, you can use the information you gather to see where you stand in the market landscape.
What to include in a competitive analysis
The purpose of this type of analysis is to get a competitive advantage in the market and improve your business strategy. Without a competitive analysis, it’s difficult to know what others are doing to win clients or customers in your target market. A competitive analysis report may include:
A description of your company’s target market
Details about your product or service versus the competitors’
Current and projected market share, sales, and revenues
Pricing comparison
Marketing and social media strategy analysis
Differences in customer ratings
You’ll compare each detail of your product or service versus the competition to assess strategy efficacy. By comparing success metrics across companies, you can make data-driven decisions.
How to do a competitive analysis
Follow these five steps to create your competitive analysis report and get a broad view of where you fit in the market. This process can help you analyze a handful of competitors at one time and better approach your target customers.
1. Create a competitor overview
In step one, select between five and 10 competitors to compare against your company. The competitors you choose should have similar product or service offerings and a similar business model to you. You should also choose a mix of both direct and indirect competitors so you can see how new markets might affect your company. Choosing both startup and seasoned competitors will further diversify your analysis.
Tip: To find competitors in your industry, use Google or Amazon to search for your product or service. The top results that emerge are likely your competitors. If you’re a startup or you serve a niche market, you may need to dive deeper into the rankings to find your direct competitors.
2. Conduct market research
Once you know the competitors you want to analyze, you’ll begin in-depth market research. This will be a mixture of primary and secondary research. Primary research comes directly from customers or the product itself, while secondary research is information that’s already compiled. Then, keep track of the data you collect in a user research template .
Primary market research may include:
Purchasing competitors’ products or services
Interviewing customers
Conducting online surveys of customers
Holding in-person focus groups
Secondary market research may include:
Examining competitors’ websites
Assessing the current economic situation
Identifying technological developments
Reading company records
Tip: Search engine analysis tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush can help you examine competitors’ websites and obtain crucial SEO information such as the keywords they’re targeting, the number of backlinks they have, and the overall health of their website.
3. Compare product features
The next step in your analysis involves a comparison of your product to your competitors’ products. This comparison should break down the products feature by feature. While every product has its own unique features, most products will likely include:
Service offered
Age of audience served
Number of features
Style and design
Ease of use
Type and number of warranties
Customer support offered
Product quality
Tip: If your features table gets too long, abbreviate this step by listing the features you believe are of most importance to your analysis. Important features may include cost, product benefits, and ease of use.
4. Compare product marketing
The next step in your analysis will look similar to the one before, except you’ll compare the marketing efforts of your competitors instead of the product features. Unlike the product features matrix you created, you’ll need to go deeper to unveil each company’s marketing plan .
Areas you’ll want to analyze include:
Social media
Website copy
Press releases
Product copy
As you analyze the above, ask questions to dig deeper into each company’s marketing strategies. The questions you should ask will vary by industry, but may include:
What story are they trying to tell?
What value do they bring to their customers?
What’s their company mission?
What’s their brand voice?
Tip: You can identify your competitors’ target demographic in this step by referencing their customer base, either from their website or from testimonials. This information can help you build customer personas. When you can picture who your competitor actively targets, you can better understand their marketing tactics.
5. Use a SWOT analysis
Competitive intelligence will make up a significant part of your competitor analysis framework, but once you’ve gathered your information, you can turn the focus back to your company. A SWOT analysis helps you identify your company’s strengths and weaknesses. It also helps turn weaknesses into opportunities and assess threats you face based on your competition.
During a SWOT analysis, ask yourself:
What do we do well?
What could we improve?
Are there market gaps in our services?
What new market trends are on the horizon?
Tip: Your research from the previous steps in the competitive analysis will help you answer these questions and fill in your SWOT analysis. You can visually present your findings in a SWOT matrix, which is a four-box chart divided by category.
6. Identify your place in the market landscape
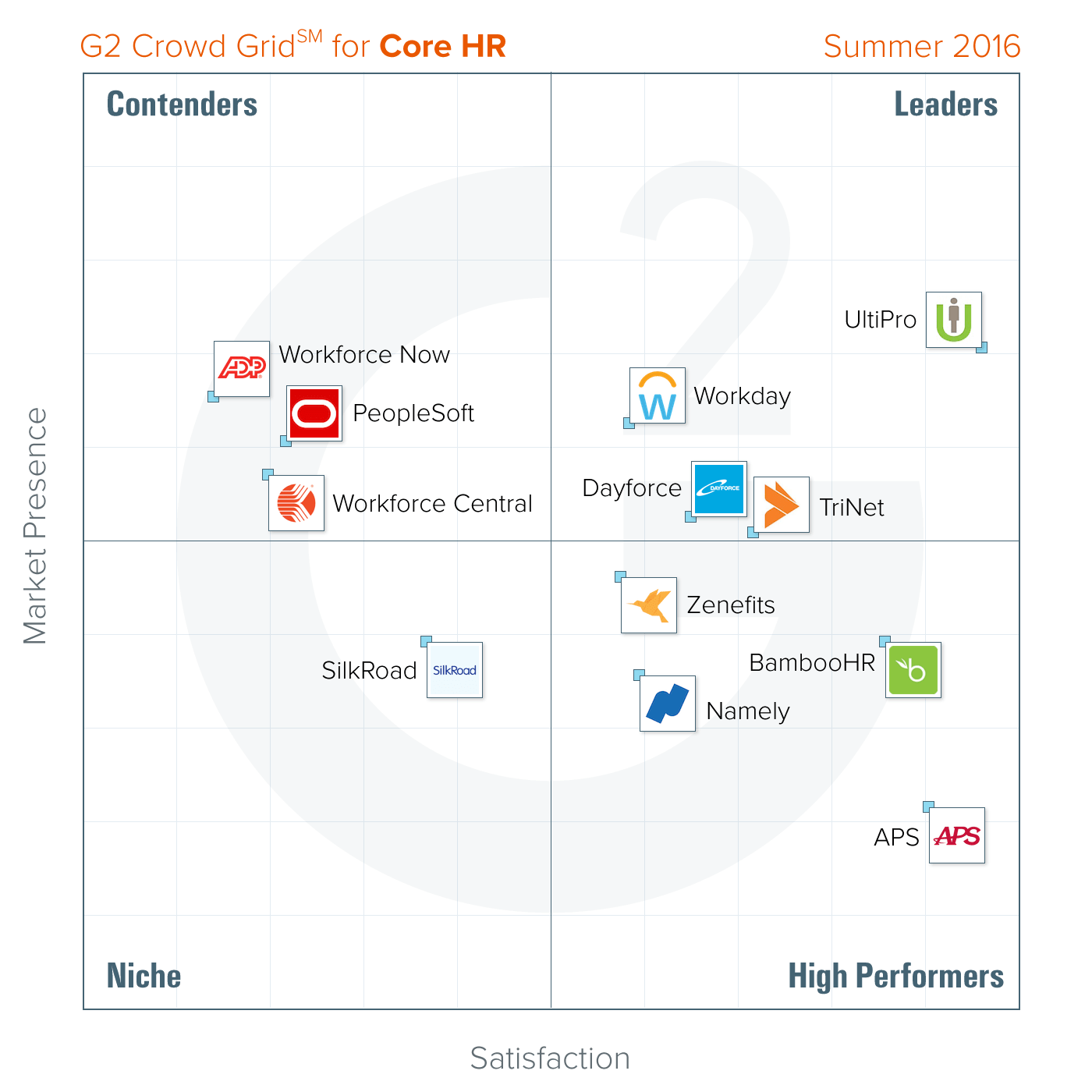
The last step in your competitive analysis is to understand where you stand in the market landscape. To do this, you’ll create a graph with an X and Y axis. The two axes should represent the most important factors for being competitive in your market.
For example, the X-axis may represent customer satisfaction, while the Y-axis may represent presence in the market. You’ll then plot each competitor on the graph according to their (x,y) coordinates. You’ll also plot your company on this chart, which will give you an idea of where you stand in relation to your competitors.
This graph is included for informational purposes and does not represent Asana’s market landscape or any specific industry’s market landscape.
![business plan competitor analysis [inline illustration] Identify your place in the market landscape (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/fb2a8437-bb5e-4f0c-b5d0-91d67116bebe/inline-project-planning-competitive-analysis-example-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Tip: In this example, you’ll see three companies that have a greater market presence and greater customer satisfaction than yours, while two companies have a similar market presence but higher customer satisfaction. This data should jumpstart the problem-solving process because you now know which competitors are the biggest threats and you can see where you fall short.
Competitive analysis example
Imagine you work at a marketing startup that provides SEO for dentists, which is a niche industry and only has a few competitors. You decide to conduct a market analysis for your business. To do so, you would:
Step 1: Use Google to compile a list of your competitors.
Steps 2, 3, and 4: Use your competitors’ websites, as well as SEO analysis tools like Ahrefs, to deep-dive into the service offerings and marketing strategies of each company.
Step 5: Focusing back on your own company, you conduct a SWOT analysis to assess your own strategic goals and get a visual of your strengths and weaknesses.
Step 6: Finally, you create a graph of the market landscape and conclude that there are two companies beating your company in customer satisfaction and market presence.
After compiling this information into a table like the one below, you consider a unique strategy. To beat out your competitors, you can use localization. Instead of marketing to dentists nationwide like your competitors are doing, you decide to focus your marketing strategy on one region, state, or city. Once you’ve become the known SEO company for dentists in that city, you’ll branch out.
![business plan competitor analysis [inline illustration] Competitive analysis framework (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/56c32354-f525-4610-9250-f878ea0b9f26/inline-project-planning-competitive-analysis-example-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
You won’t know what conclusions you can draw from your competitive analysis until you do the work and see the results. Whether you decide on a new pricing strategy, a way to level up your marketing, or a revamp of your product, understanding your competition can provide significant insight.
Drawbacks of competitive analysis
There are some drawbacks to competitive analysis you should consider before moving forward with your report. While these drawbacks are minor, understanding them can make you an even better manager or business owner.
Don’t forget to take action
You don’t just want to gather the information from your competitive analysis—you also want to take action on that information. The data itself will only show you where you fit into the market landscape. The key to competitive analysis is using it to problem solve and improve your company’s strategic plan .
Be wary of confirmation bias
Confirmation bias means interpreting information based on the beliefs you already hold. This is bad because it can cause you to hold on to false beliefs. To avoid bias, you should rely on all the data available to back up your decisions. In the example above, the business owner may believe they’re the best in the SEO dental market at social media. Because of this belief, when they do market research for social media, they may only collect enough information to confirm their own bias—even if their competitors are statistically better at social media. However, if they were to rely on all the data available, they could eliminate this bias.
Update your analysis regularly
A competitive analysis report represents a snapshot of the market landscape as it currently stands. This report can help you gain enough information to make changes to your company, but you shouldn’t refer to the document again unless you update the information regularly. Market trends are always changing, and although it’s tedious to update your report, doing so will ensure you get accurate insight into your competitors at all times.
Boost your marketing strategy with competitive analysis
Learning your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses will make you a better marketer. If you don’t know the competition you’re up against, you can’t beat them. Using competitive analysis can boost your marketing strategy and allow you to capture your target audience faster.
Competitive analysis must lead to action, which means following up on your findings with clear business goals and a strong business plan. Once you do your competitive analysis, you can use the templates below to put your plan into action.
Related resources

Stay on track with a project plan that actually works
What is project risk management? 6 steps to boost success
What is a product backlog? (And how to create one)
7 steps to crafting a winning event proposal (with template)
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing How to Create a Competitor Analysis Report (with Examples)
How to Create a Competitor Analysis Report (with Examples)
Written by: Midori Nediger Nov 09, 2023
Your business will always have competition.
And if you don’t know what that competition is up to, you could be missing out on huge opportunities.
That’s why a competitive analysis is so crucial to your success as a business. It gives you the tools to quickly adapt to any changes in the competitive landscape and potentially capitalize on industry trends that your competitors haven’t even noticed.
So let’s get some basics out of the way…
What is a competitive analysis report?
A competitive analysis report outlines the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors compared to those of your own business.
Typically, a competitive analysis report will contain:
- A description of your business’s target market
- Details about the features of your product compared to your competitors’ products
- A breakdown of current and projected market share, sales, and revenues
- Comparisons of pricing models
- An analysis of marketing strategy and social media strategy
- A description of customer ratings of the features of each competitor
Whether you’re a startup trying to break into the marketplace , a consultant trying to get results for your client, or an established company looking to cement your foothold against the competition, a well-researched competitive analysis gives you the tools you need to make strategic decisions.
Your competitive analysis should inform your marketing plan , your business plan , your consultant report and every part of your high-level business strategy.
But how do you actually create a competitive analysis report?
How to make competitor analysis report :
- Start with a competitor overview
- Conduct market research to uncover customer personas and industry trends
- Compare product features in a feature comparison matrix
- Summarize your strengths and weaknesses with a SWOT analysis
- Show where you fit in the competitive landscape
- Use a competitor analysis template for a professional look and feel
The level of detail you include in each section of your competitive analysis report will vary depending on the stage of your business growth and your goals. For example, a startup might create a report that focuses on market research, while an established business might dive into detail on an emerging competitor.
But let’s talk about the parts of a competitive analysis that every report should include.
1. Start with a competitor overview
A strong report shows exactly what a company must out-compete to be successful.
Meaning you must audit any product or service that currently solves the problem your business is trying to solve for customers and write a quick profile for each competitor.
Like the template below, each competitor profile might include:
- The company’s revenue and market share
- The company’s size and information about their management team
- A broad description of the company’s strengths and weaknesses
- An overview of how the company is perceived by customers

This overview will help your readers get a big-picture view of the market landscape.
2. Conduct market research to uncover customer personas and industry trends
You can’t create a competitive analysis report without doing extensive market research , which is all about gathering information to understand your customers, identify opportunities to grow, and recognize trends in the industry.
This research can help you put together the customer personas that will guide business and marketing decisions down the line, and allow you to plan for any shifts that might disrupt the marketplace.
You can conduct primary market research, with:
- Customer interviews
- Online surveys or questionnaires
- In-person focus groups
- Purchasing a competitor product to study packaging and delivery experience
Or secondary market research, by:
- Reading company records
- Examining the current economic conditions
- Researching relevant technological developments
When assembling your market research you may just want provide a high-level summary of the industry trends, like this competitor analysis example shows:
Or you may want to dive into detail on the demographics of a particular consumer segment, like this:
But if you’re a consultant or advisor struggling to get buy-in from skeptical stakeholders, the report below would be ideal. Covering everything from market forecasts to consumer profiles, it can help you get clients and decision-makers on board.
3. Compare product features in a feature comparison matrix
The feature comparison is arguably the most important part of the competitive analysis. Breaking down your product and your competitors’ products feature-by-feature will allow you to see what really sets everyone apart.
In addition to specific product features, here are some attributes that you might include in a feature comparison matrix:
- Product quality
- Number of features
- Ease of use
- Customer support
- Brand/style/image
The most common format for a features analysis is a simple matrix with you and your competitors along one side and all of the relevant features along the other. You can check off or rate how you perform in each area:
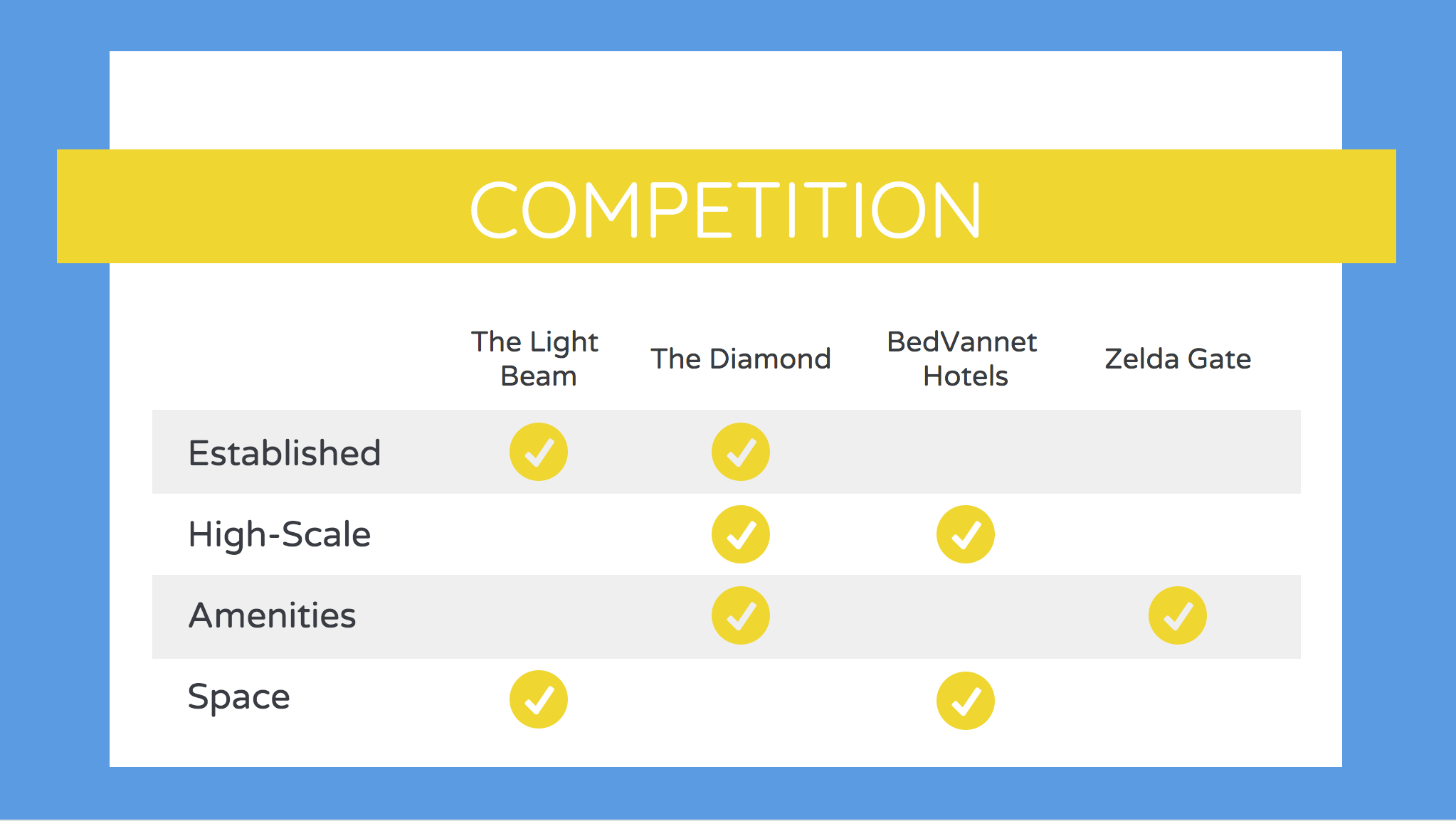
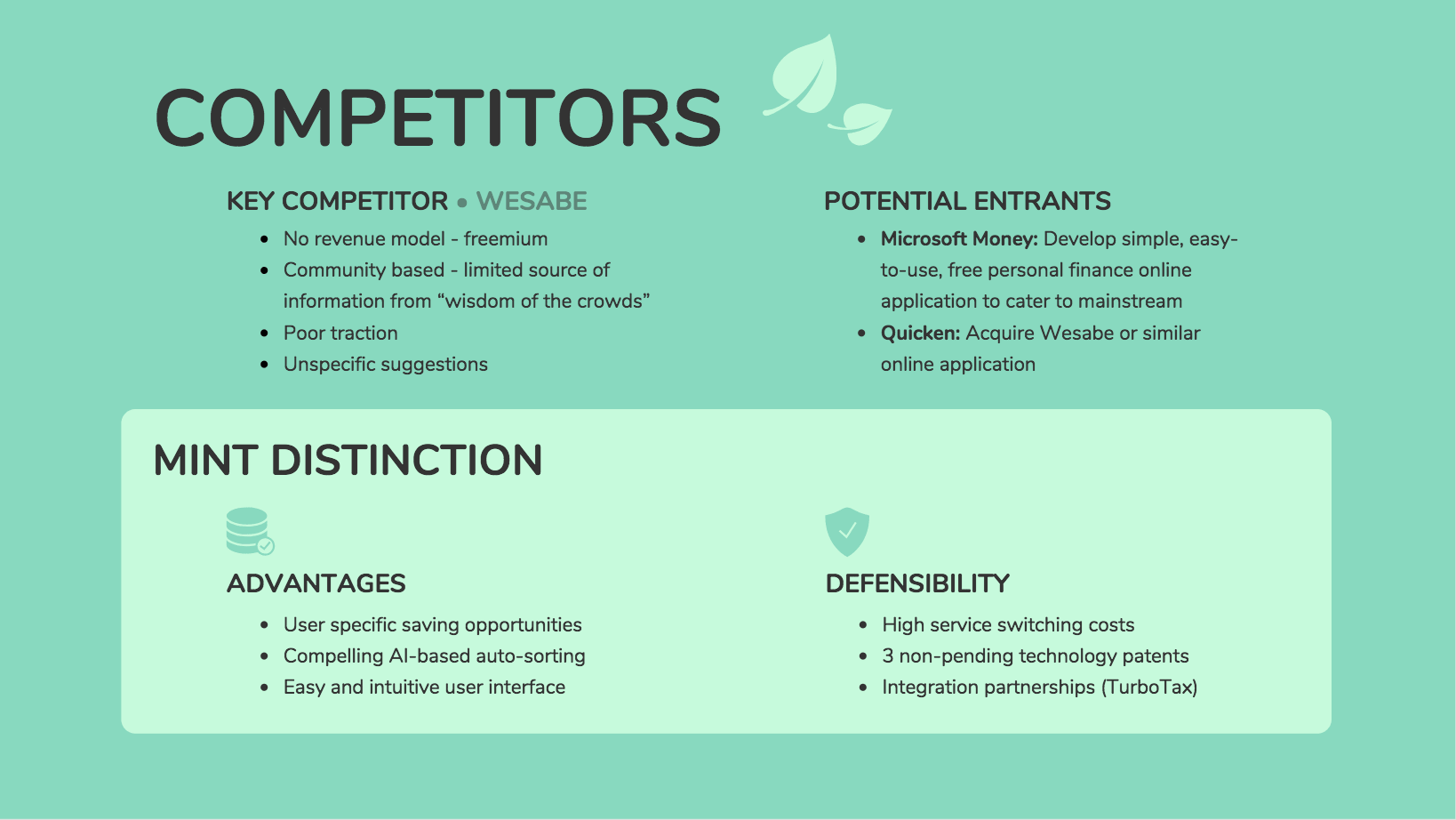
But these tables can get pretty long. Another approach is to focus on the things that provide the most value to the user, like in this competitor analysis example from Mint. It only includes ease of use, costs, and benefits:
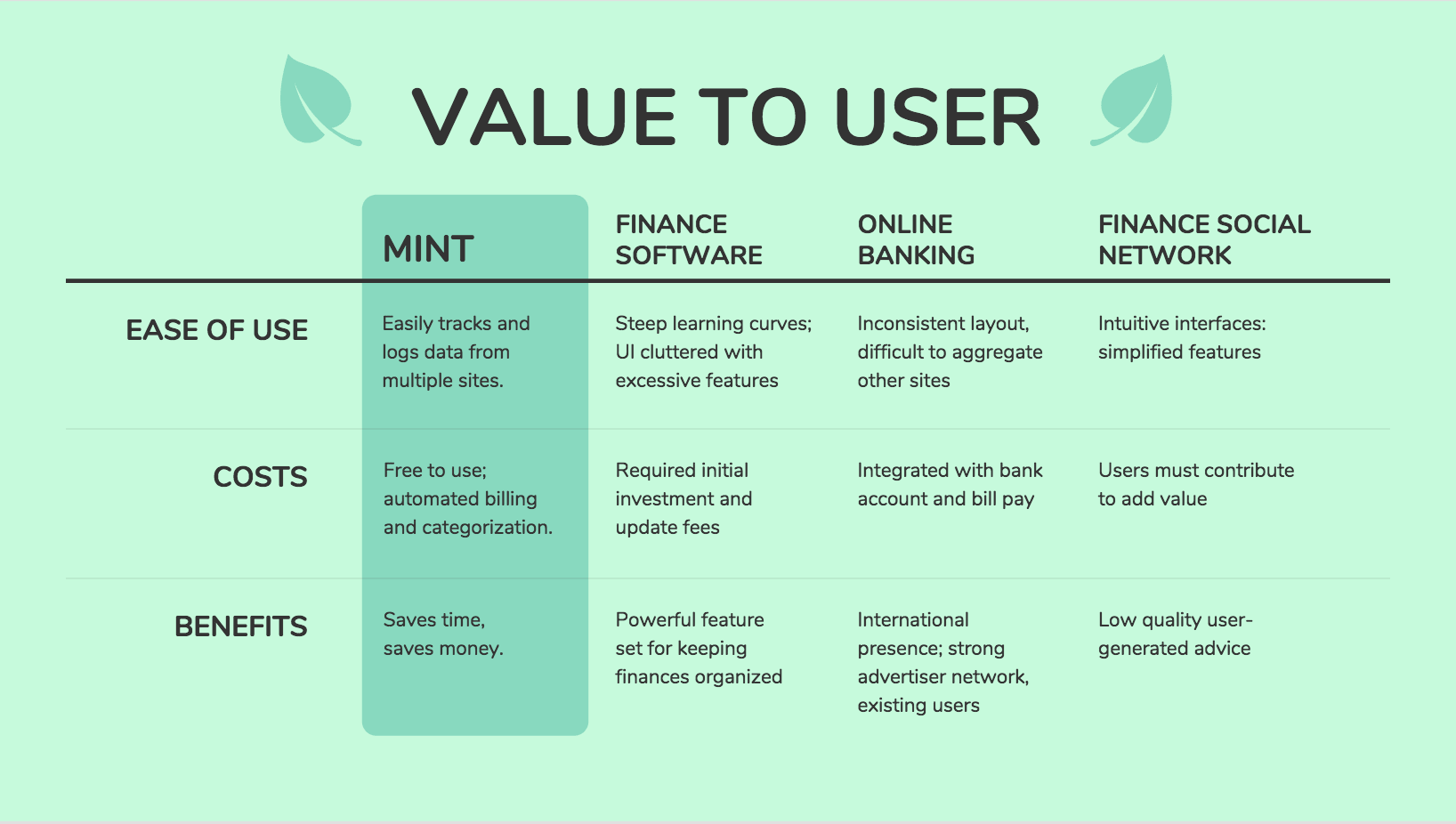
If you want to visualize your comparisons in an engaging way, you could use a comparison infographic .
Great resources for this section of your competitive analysis report are product rating sites like Capterra and G2Crowd . They’ll give you an unbiased view of your company and your competitors.
And as with any market research, it’s critical that you speak with real people who use your product and your competitors’ products. That’s the only way to get an accurate picture of how your target customers rate the competition .
4. Summarize your strengths and weaknesses in a SWOT analysis
When you’re conducting research for your competitive analysis, it’s going to be messy. You’ll have a lot of data and it’ll be hard for an outsider to understand.
That’s what makes the SWOT analysis so essential.
A SWOT analysis is a framework for evaluating your competitive position by listing your key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
It can act like a short summary of the rest of your competitive analysis report for anyone who doesn’t have time to dig into the details.
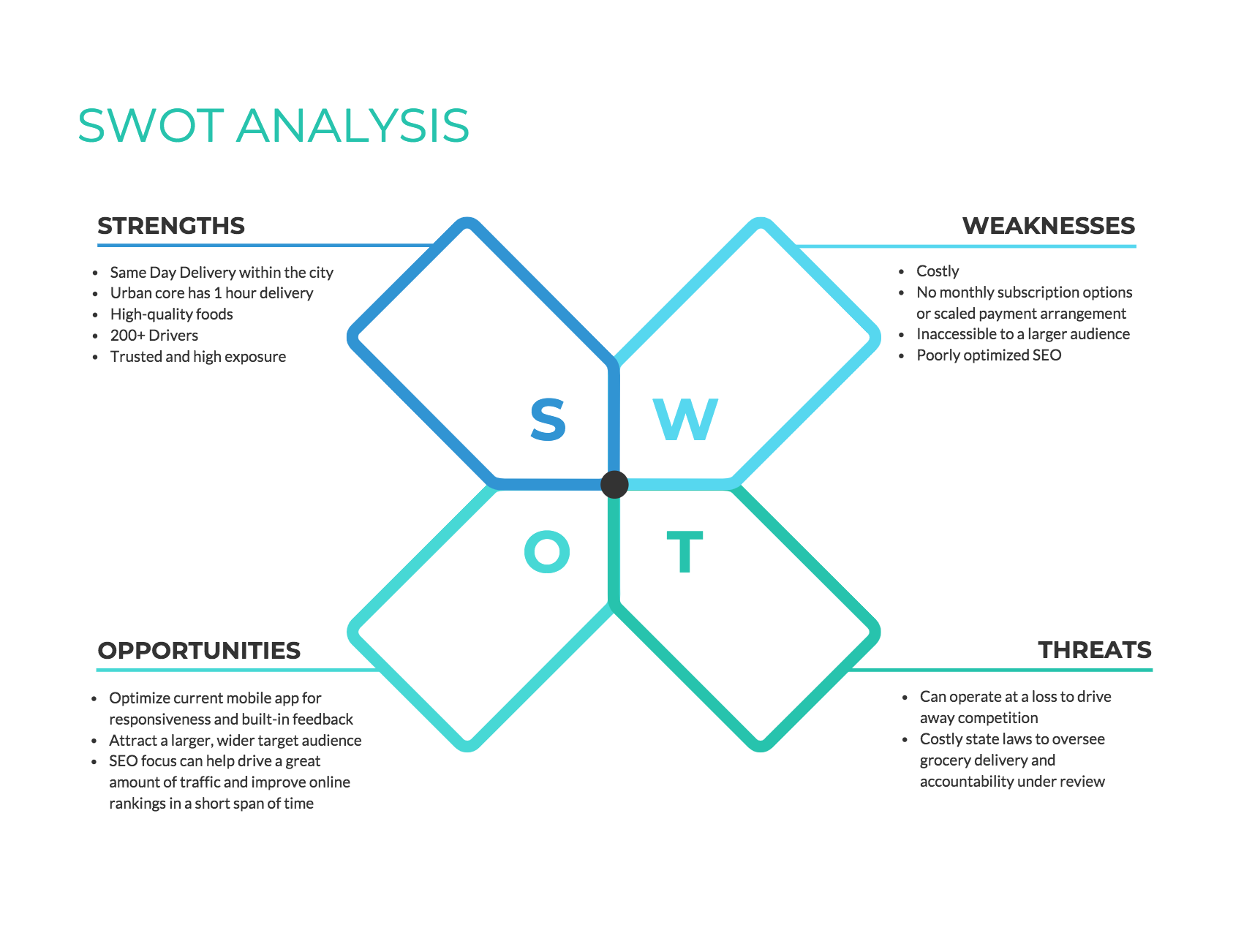
Click the template above to enter our online SWOT analysis maker tool. Customize the template to your liking–no design no-how required.
Here are some questions to kickstart your SWOT analysis:
- Strengths: What are we doing really well (in terms of marketing, products, sales, branding, technology, etc.)?
- Weaknesses: What are we struggling with? What’s holding us back?
- Opportunities: What’s the weakest area for our biggest competitor? Are there any gaps in the market that aren’t current being addressed? What has recently changed in our business or the market?
- Threats: What is our biggest competitor doing much better than us? What new products/features are they working on? What problems aren’t we currently addressing?
In your report, you could arrange your SWOT analysis in a simple list, but it can be helpful to use color-coded quadrants, like the competitor analysis example below. Note how each quadrant is paired with an icon:
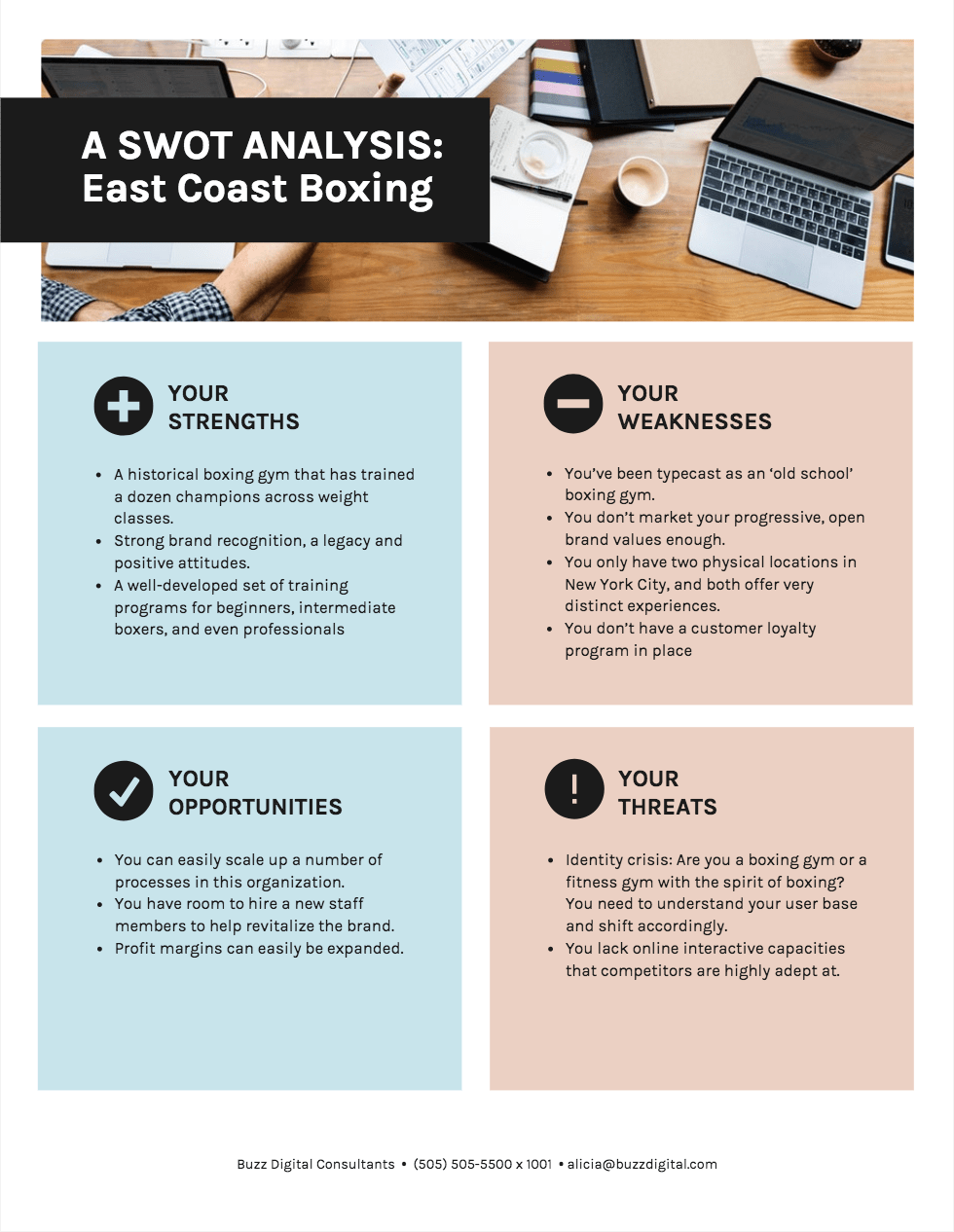
5. Show where you fit in the competitive landscape
After summarizing your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, it’s time to look at the bigger picture. It’s time to figure out where every major competitor currently fits into the competitive landscape.
The most popular way of doing this is to identify the two dimensions that are most important for being competitive in your industry and plot them on a matrix, like this one from the Boston Consulting Group:
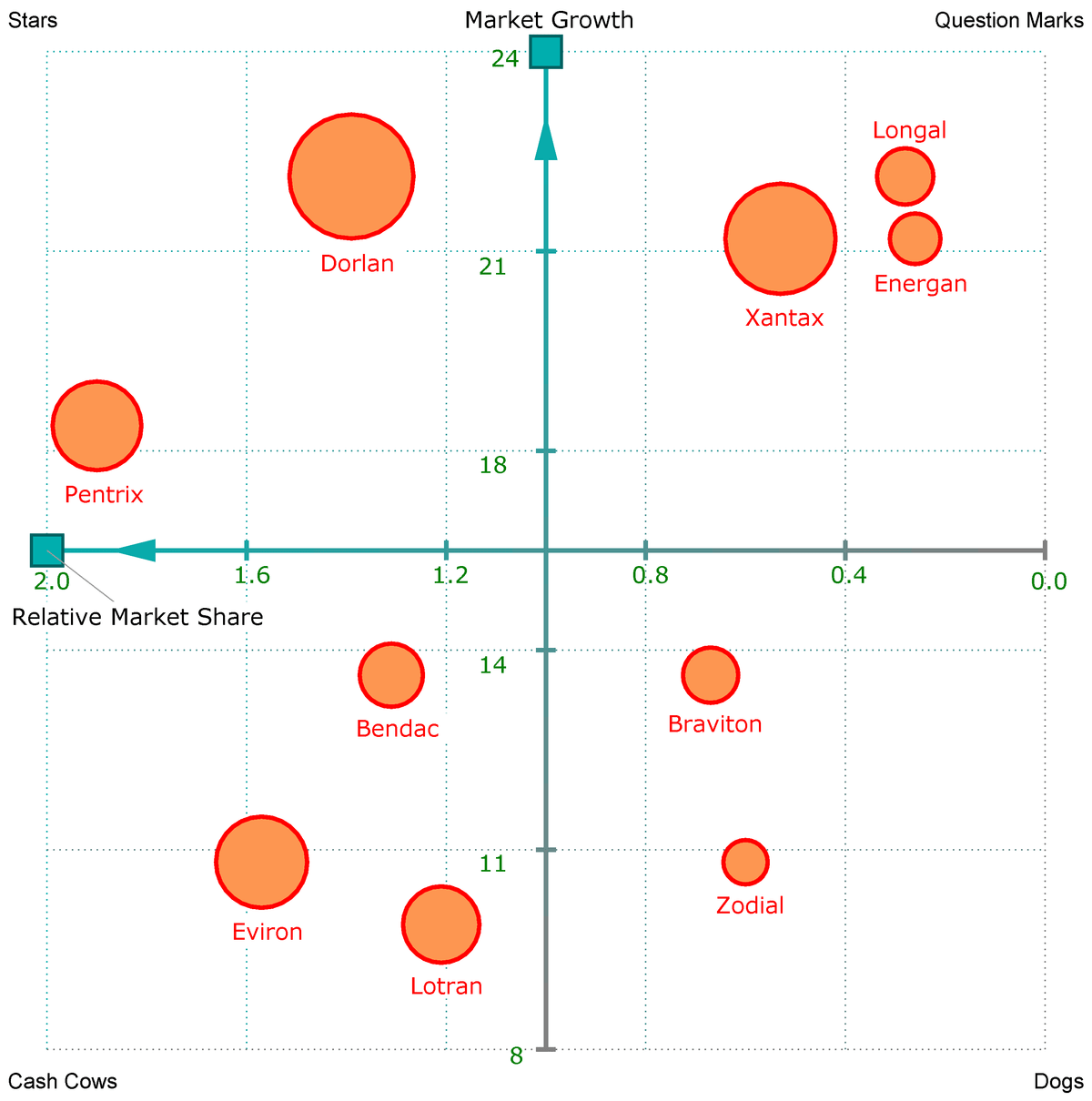
And this one from G2 Crowd (which looks at market presence and customer satisfaction ):
You may want to focus on where you fit in the market landscape based on your own biggest strengths and weaknesses, or the biggest threats and opportunities you identified in the SWOT analysis.
Or, it may be enough just to summarize in words the features and benefits that set your apart from your competitors (which is a great way to end your report on a high note).
Competitor analysis examples for strategic planning
Let’s delve into some competitor analysis examples that can empower your organization to navigate the market effectively.
1. Competitor analysis example for marketing specialists
Imagine this: You are a Marketing Specialist and your goal is to establish a strong online presence and attract a diverse user base. However, you face stiff competition from established players in the market. Here are some things you should look into when doing your competitor analysis:
Competitor analysis focus:
- SEO strategies: Analyze competitors’ websites to understand their SEO strategies. Identify high-ranking keywords , backlink strategies, and content optimization techniques . Alternatively, if you’re running a local business, you might want to analyze and scrape Google Maps listings to better assess how companies are optimizing Google My Business to generate leads.
- Social media engagement: Examine competitors’ social media presence. Evaluate the type of content that garners engagement, the frequency of posts, and audience interactions.
- Online advertising: Investigate competitors’ online advertising campaigns. Are they leveraging Google Ads, social media ads, or other platforms? Assess the messaging, visuals, and targeting criteria.
- Content marketing: Scrutinize competitors’ content marketing efforts. Identify the topics that resonate with their audience, the formats they use (blogs, videos, infographics), and the platforms they prioritize.
Here’s a SWOT analysis template to help you get started:
2. Competitor analysis example for SME business development managers
Imagine this: As the business development manager for a medium sized start up, you are tasked with expanding the client base. The market is crowded with similar service providers, and differentiation is key. When doing your competitor analysis report, look into:
- Client testimonials and case studies: Explore competitors’ websites for client testimonials and case studies. Identify success stories and areas where clients express satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
- Service offerings: Analyze the range of services offered by competitors. Identify gaps in their offerings or areas where you can provide additional value to clients.
- Pricing models: Investigate competitors’ pricing structures. Are they offering packages, subscription models, or customized solutions? Determine whether there’s room for a more competitive pricing strategy .
- Partnerships and collaborations: Explore potential partnerships or collaborations that competitors have formed. This can provide insights into untapped markets or innovative service delivery methods.
Here’s a competitor analysis comparison chart template that you could use:
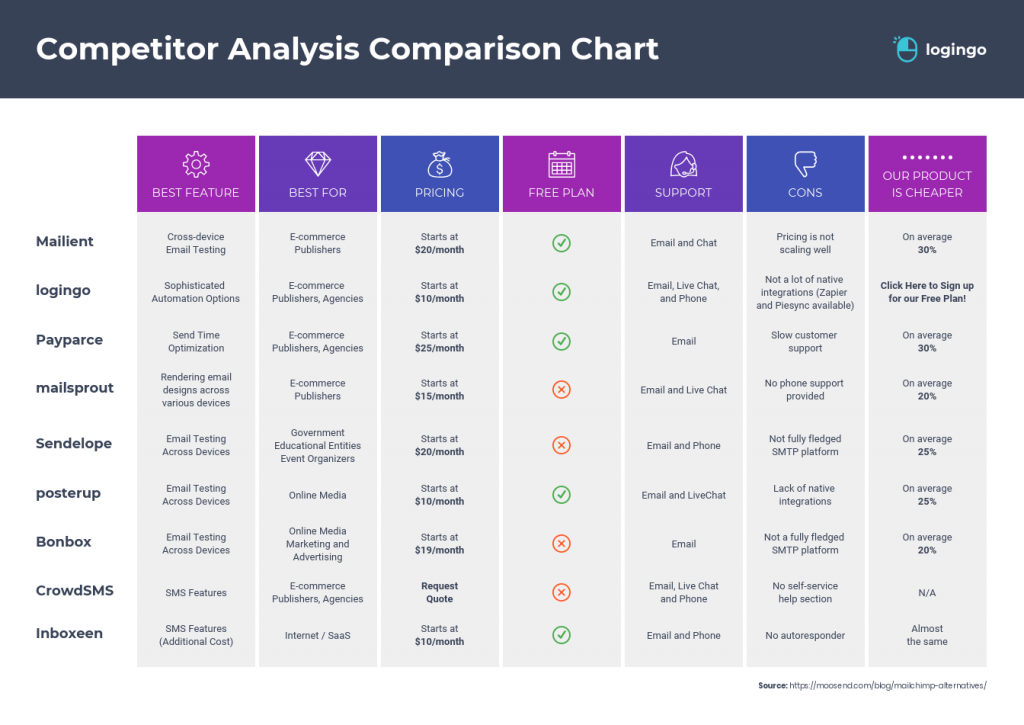
3. Competitor analysis example for product managers
Imagine this: You are a Product Manager for a consumer electronics company tasked with improving your company’s products and services. The market is buzzing with innovation, and staying ahead requires a deep understanding of competitor products.
- Feature comparison: Conduct a detailed feature-by-feature comparison of your product with competitors. Identify unique features that set your product apart and areas where you can enhance or differentiate.
- User experience (UX): Use a UX research tool to evaluate the user experience of competitors’ products. Analyze customer reviews, app ratings, and usability feedback to understand pain points and areas for improvement.
- Technological advancements: Investigate the technological capabilities of competitors. Are they integrating AI, IoT, or other cutting-edge technologies? Assess whether there are emerging technologies you can leverage.
- Product lifecycle management: Examine competitors’ product release cycles. Identify patterns in their product launches and assess whether there are opportunities for strategic timing or gap exploitation.
To help you get started, use this competitive analysis report template to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the product or service

How to present a competitor analysis
Presenting a competitor analysis effectively involves organizing and communicating information about your competitors in a clear and concise manner. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to present a competitor analysis:
- Introduction: Start with a brief introduction to set the stage. Outline the purpose of the competitor analysis and its significance in the current market context.
- Competitor identification: Clearly list and identify the main competitors. Include both direct and indirect competitors. Briefly describe each competitor’s core business and market presence.
- Key metrics and performance: Present key metrics and performance indicators for each competitor. This may include market share, revenue, growth rate, and any other relevant quantitative data.
- SWOT analysis: Conduct a concise SWOT analysis for each competitor. Summarize their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Use a simple visual representation if possible.
- Market positioning: Discuss how each competitor is positioned in the market. This could include their target audience, unique selling propositions, and any specific market niches they occupy. Also, focus on finding keywords , as your competitor’s targeted keywords are the main source of information on their online market performance.
- Strategic moves: Highlight recent strategic moves made by your competitors. This could include product launches, partnerships, mergers, acquisitions, or changes in pricing strategy. Discuss how these moves impact the competitive landscape.
- Recommendations and implications: Based on the analysis, provide recommendations and implications for your company. Identify opportunities to capitalize on competitors’ weaknesses and outline potential threats that need to be addressed. Discuss any adjustments to your own strategy that may be necessary in response to the competitive landscape.
3 tips to improve your competitive analysis report design
How you design your competitive analysis report can have a significant impact on your business success. The right report design can inspire stakeholders to take action based on your findings, while a mediocre design may reflect poorly on your hard work.
Here are a few report design best practices to keep in mind when designing your competitive analysis report:
- Start with a competitive analysis report template
- Keep core design elements like colors and fonts consistent
- Use visuals to summarize important information and keep your audience engaged

1. Start with a competitor analysis template
The quickest way to lose the confidence of your stakeholders is to present a messy, amateur report design. Besides distracting from the content of the report, it might even put your credibility at risk.
Starting with a pre-designed competitor analysis template, like the one below, takes almost all of the design work out of the mix so you can focus on the content (while still impressing your stakeholders).

And if you’re a consultant competing for a project, a pre-designed template may just give you the edge you need to land that client.
Click on any of our templates; you’ll enter our online drag and drop report maker tool. No design know-how required.
2. Keep core design elements like colors and fonts consistent
If you take a look at the competitor analysis template below, you might notice that the designer has switched up the layout from page to page, but many of the other design elements are kept consistent.
That consistency helps the report design feel cohesive while making it easier for readers to quickly skim for key pieces of information.
Here are a few quick guidelines for keeping important design elements consistent:
- Use the same color scheme throughout your report (with one highlight color to draw attention to key takeaways and important numbers)
- Use the same font styles for your headers, subheaders, and body text (with no more than 2-3 font styles per report)
- Use the same style of visuals throughout your report (like flat icons or illustrated icons… but not both)
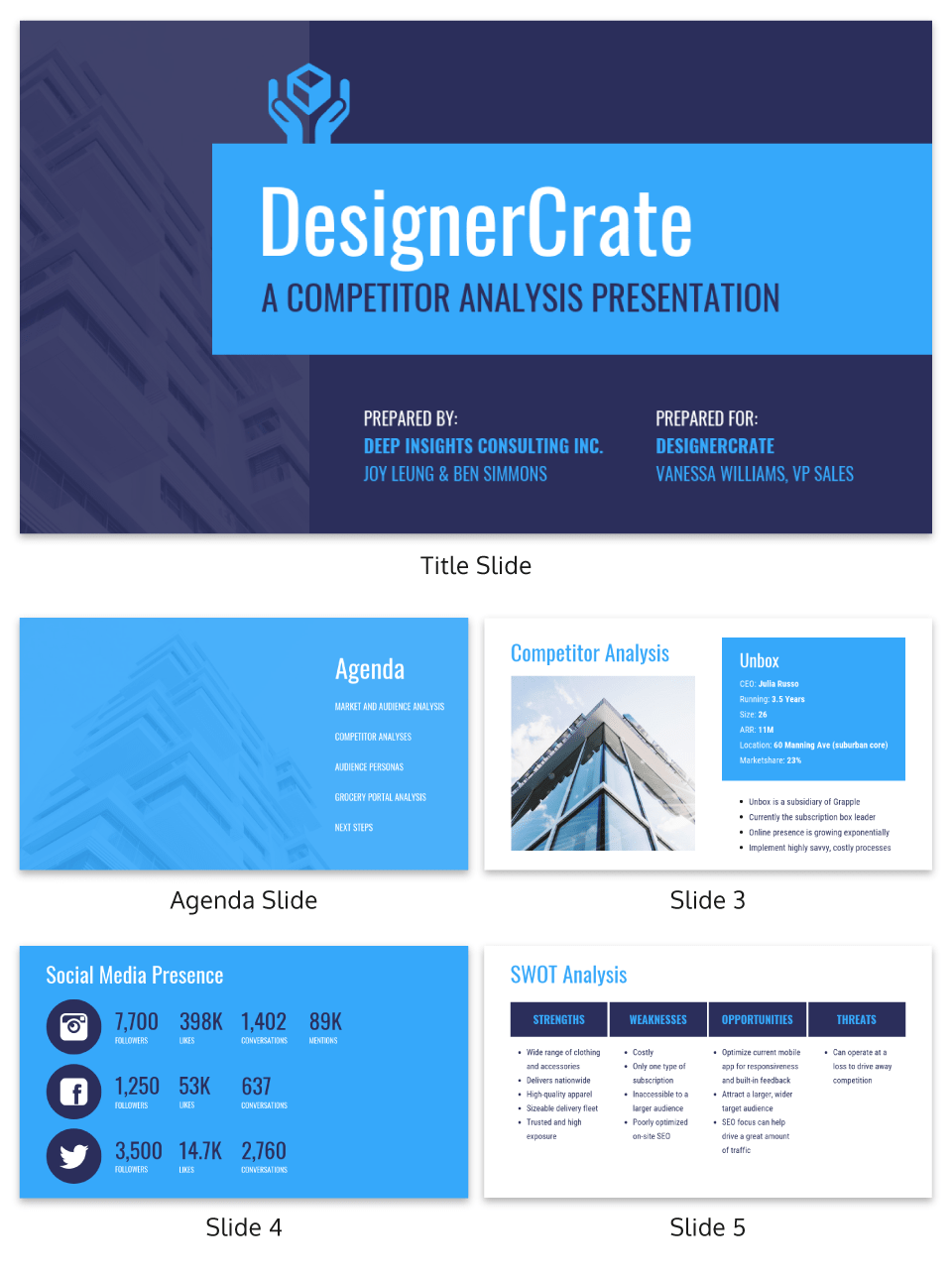
3. Use visuals to summarize important information and keep your audience engaged
The challenge with a competitive analysis report is that you collect heaps of background research, and you have to condense it into a brief report that your client will actually read.
And written summaries will only get you so far.
Visuals like charts and tables are a much better way to communicate a lot of research quickly and concisely, as seen in the market research summary below.
Even lists can be made more engaging and informative by spacing out list items and giving more emphasis to headers:
The more you can replace descriptive paragraphs and long lists with thoughtful visuals, the more your readers will thank you.
A competitive analysis will allow you to think up effective strategies to battle your competition and establish yourself in your target market.
And a report that communicates the findings of your competitive analysis will ensure stakeholders are on board and in the know.
Now that you know how to design a competitive analysis report, you’re ready to get started:
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast today!
How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan

11 min. read
Updated January 3, 2024

Do you know who your competitors are? If you do, have you taken the time to conduct a thorough competitor analysis?
Knowing your competitors, how they operate, and the necessary benchmarks you need to hit are crucial to positioning your business for success. Investors will also want to see an analysis of the competition in your business plan.
In this guide, we’ll explore the significance of competitive analysis and guide you through the essential steps to conduct and write your own.
You’ll learn how to identify and evaluate competitors to better understand the opportunities and threats to your business. And you’ll be given a four-step process to describe and visualize how your business fits within the competitive landscape.
- What is a competitive analysis?
A competitive analysis is the process of gathering information about your competitors and using it to identify their strengths and weaknesses. This information can then be used to develop strategies to improve your own business and gain a competitive advantage.
- How to conduct a competitive analysis
Before you start writing about the competition, you need to conduct your analysis. Here are the steps you need to take:
1. Identify your competitors
The first step in conducting a comprehensive competitive analysis is to identify your competitors.
Start by creating a list of both direct and indirect competitors within your industry or market segment. Direct competitors offer similar products or services, while indirect competitors solve the same problems your company does, but with different products or services.
Keep in mind that this list may change over time. It’s crucial to revisit it regularly to keep track of any new entrants or changes to your current competitors. For instance, a new competitor may enter the market, or an existing competitor may change their product offerings.
2. Analyze the market
Once you’ve identified your competitors, you need to study the overall market.
This includes the market size , growth rate, trends, and customer preferences. Be sure that you understand the key drivers of demand, demographic and psychographic profiles of your target audience , and any potential market gaps or opportunities.
Conducting a market analysis can require a significant amount of research and data collection. Luckily, if you’re writing a business plan you’ll follow this process to complete the market analysis section . So, doing this research has value for multiple parts of your plan.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
3. Create a competitive framework
You’ll need to establish criteria for comparing your business with competitors. You want the metrics and information you choose to provide answers to specific questions. (“Do we have the same customers?” “What features are offered?” “How many customers are being served?”)
Here are some common factors to consider including:
- Market share
- Product/service offerings or features
- Distribution channels
- Target markets
- Marketing strategies
- Customer service
4. Research your competitors
You can now begin gathering information about your competitors. Because you spent the time to explore the market and set up a comparison framework—your research will be far more focused and easier to complete.
There’s no perfect research process, so start by exploring sources such as competitor websites, social media, customer reviews, industry reports, press releases, and public financial statements. You may also want to conduct primary research by interviewing customers, suppliers, or industry experts.
You can check out our full guide on conducting market research for more specific steps.
5. Assess their strengths and weaknesses
Evaluate each competitor based on the criteria you’ve established in the competitive framework. Identify their key strengths (competitive advantages) and weaknesses (areas where they underperform).
6. Identify opportunities and threats
Based on the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, identify opportunities (areas where you can outperform them) and threats (areas where they may outperform you) for your business.
You can check out our full guide to conducting a SWOT analysis for more specific questions that you should ask as part of each step.
- How to write your competitive analysis
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to present your findings in your business plan. Here are the steps you need to take:
1. Determine who your audience is
Who you are writing a business plan for (investors, partners, employees, etc.) may require you to format your competitive analysis differently.
For an internal business plan you’ll use with your team, the competition section should help them better understand the competition. You and your team will use it to look at comparative strengths and weaknesses to help you develop strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
For fundraising, your plan will be shared with potential investors or as part of a bank loan. In this case, you’re describing the competition to reassure your target reader. You are showing awareness and a firm understanding of the competition, and are positioned to take advantage of opportunities while avoiding the pitfalls.
2. Describe your competitive position
You need to know how your business stacks up, based on the values it offers to your chosen target market. To run this comparison, you’ll be using the same criteria from the competitive framework you completed earlier. You need to identify your competitive advantages and weaknesses, and any areas where you can improve.
The goal is positioning (setting your business up against the background of other offerings), and making that position clear to the target market. Here are a few questions to ask yourself in order to define your competitive position:
- How are you going to take advantage of your distinctive differences, in your customers’ eyes?
- What are you doing better?
- How do you work toward strengths and away from weaknesses?
- What do you want the world to think and say about you and how you compare to others?
3. Visualize your competitive position
There are a few different ways to present your competitive framework in your business plan. The first is a “positioning map” and the second is a “competitive matrix”. Depending on your needs, you can use one or both of these to communicate the information that you gathered during your competitive analysis:
Positioning map
The positioning map plots two product or business benefits across a horizontal and vertical axis. The furthest points of each represent opposite extremes (Hot and cold for example) that intersect in the middle. With this simple chart, you can drop your own business and the competition into the zone that best represents the combination of both factors.
I often refer to marketing expert Philip Kohler’s simple strategic positioning map of breakfast, shown here. You can easily draw your own map with any two factors of competition to see how a market stacks up.

It’s quite common to see the price on one axis and some important qualitative factor on the other, with the assumption that there should be a rough relationship between price and quality.
Competitive matrix
It’s pretty common for most business plans to also include a competitive matrix. It shows how different competitors stack up according to the factors identified in your competitive framework.
How do you stack up against the others? Here’s what a typical competitive matrix looks like:

For the record, I’ve seen dozens of competitive matrices in plans and pitches. I’ve never seen a single one that didn’t show that this company does more of what the market wants than all others. So maybe that tells you something about credibility and how to increase it. Still, the ones I see are all in the context of seeking investment, so maybe that’s the nature of the game.
4. Explain your strategies for gaining a competitive edge
Your business plan should also explain the strategies your business will use to capitalize on the opportunities you’ve identified while mitigating any threats from competition. This may involve improving your product/service offerings, targeting underserved market segments, offering more attractive price points, focusing on better customer service, or developing innovative marketing strategies.
While you should cover these strategies in the competition section, this information should be expanded on further in other areas of your business plan.
For example, based on your competitive analysis you show that most competitors have the same feature set. As part of your strategy, you see a few obvious ways to better serve your target market with additional product features. This information should be referenced within your products and services section to back up your problem and solution statement.
- Why competition is a good thing
Business owners often wish that they had no competition. They think that with no competition, the entire market for their product or service will be theirs. That is simply not the case—especially for new startups that have truly innovative products and services. Here’s why:
Competition validates your idea
You know you have a good idea when other people are coming up with similar products or services. Competition validates the market and the fact that there are most likely customers for your new product. This also means that the costs of marketing and educating your market go down (see my next point).
Competition helps educate your target market
Being first-to-market can be a huge advantage. It also means that you will have to spend way more than the next player to educate customers about your new widget, your new solution to a problem, and your new approach to services.
This is especially true for businesses that are extremely innovative. These first-to-market businesses will be facing customers that didn’t know that there was a solution to their problem . These potential customers might not even know that they have a problem that can be solved in a better way.
If you’re a first-to-market company, you will have an uphill battle to educate consumers—an often expensive and time-consuming process. The 2nd-to-market will enjoy all the benefits of an educated marketplace without the large marketing expense.
Competition pushes you
Businesses that have little or no competition become stagnant. Customers have few alternatives to choose from, so there is no incentive to innovate. Constant competition ensures that your marketplace continues to evolve and that your product offering continues to evolve with it.
Competition forces focus & differentiation
Without competition, it’s easy to lose focus on your core business and your core customers and start expanding into areas that don’t serve your best customers. Competition forces you and your business to figure out how to be different than your competition while focusing on your customers. In the long term, competition will help you build a better business.
- What if there is no competition?
One mistake many new businesses make is thinking that just because nobody else is doing exactly what they’re doing, their business is a sure thing. If you’re struggling to find competitors, ask yourself these questions.
Is there a good reason why no one else is doing it?
The smart thing to do is ask yourself, “Why isn’t anyone else doing it?”
It’s possible that nobody’s selling cod-liver frozen yogurt in your area because there’s simply no market for it. Ask around, talk to people, and do your market research. If you determine that you’ve got customers out there, you’re in good shape.
But that still doesn’t mean there’s no competition.
How are customers getting their needs met?
There may not be another cod-liver frozen yogurt shop within 500 miles. But maybe an online distributor sells cod-liver oil to do-it-yourselfers who make their own fro-yo at home. Or maybe your potential customers are eating frozen salmon pops right now.
Are there any businesses that are indirect competitors?
Don’t think of competition as only other businesses that do exactly what you do. Think about what currently exists on the market that your product would displace.
It’s the difference between direct competition and indirect competition. When Henry Ford started successfully mass-producing automobiles in the U.S., he didn’t have other automakers to compete with. His competition was horse-and-buggy makers, bicycles, and railroads.
Do a competitive analysis, but don’t let it derail your planning
While it’s important that you know the competition, don’t get too caught up in the research.
If all you do is track your competition and do endless competitive analyses, you won’t be able to come up with original ideas. You will end up looking and acting just like your competition. Instead, make a habit of NOT visiting your competition’s website, NOT going into their store, and NOT calling their sales office.
Focus instead on how you can provide the best service possible and spend your time talking to your customers. Figure out how you can better serve the next person that walks in the door so that they become a lifetime customer, a reference, or a referral source.
If you focus too much on the competition, you will become a copycat. When that happens, it won’t matter to a customer if they walk into your store or the competition’s because you will both be the same.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Don't let competition derail planning
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

10 Min. Read
How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan

How to Set and Use Milestones in Your Business Plan
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

Our biggest savings of the year
Black Friday Save 60%
for life on the #1 rated business plan software
on the #1 rated business plan software
on the #1 Business Planning Software

How to Write a Competitive Analysis for a Business Plan + Example
Written by Dave Lavinsky

If you are writing a business plan , hopefully by this point you’ve conducted thorough market research to identify industry trends and the target audience for your business. Now it’s time to conduct a competitive analysis. This section is included in virtually every simple business plan template , and the information you include will depend on several factors such as how many competitors there are, what they offer, and how large they are in comparison to your company.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
What is a Competitive Analysis?
A competitive analysis is a type of market research that identifies your competitors, their strengths and weaknesses, the business strategies they are using to compete with you, and what makes your business unique. Before writing this section it’s important to have all the information you collected during your market research phase. This may include market data such as revenue figures, cost trends, and the size of the industry.
Why Do You Need a Competitive Analysis?
In this section of your business plan, you need to provide an overview of your business competitors.
This is important since readers want to know 1) you understand your competitive environment, and 2) have competitive advantages that will allow your own business to succeed.
If you are planning to raise capital, the investor will require a business plan that includes the competitive analysis section. When entrepreneurs tell investors they have no competition, it often raises a red flag. This is because if there’s no competition, it signals that a market does not exist. Sometimes competition is indirect. For instance, when washing machines were invented, while there were no direct competitors (other washing machine brands), there was indirect competition (consumers manually washing their clothing).
This section will also come in handy if your company is considering increasing prices or adding new products and services. You can use the information you find to determine how well-positioned your business is to perform in the competitive landscape.
How To Conduct a Thorough Competitive Analysis
A comprehensive competitive analysis involves the following three steps:
- Identify Your Competition
- Select the Appropriate Competitors to Analyze
- Determine Your Competitive Advantage
1. Identify Your Competition
To start, you must align your definition of competition with that of investors. Investors define competition as to any service or product that a customer can use to fulfill the same need(s) as the company fulfills. This includes companies that offer similar products, substitute products, and other customer options (such as performing the service or building the product themselves). Under this broad definition, any business plan that claims there are no competitors greatly undermines the credibility of the management team.
When identifying competitors, companies often find themselves in a difficult position. On one hand, you may want to show that the business is unique (even under the investors’ broad definition) and list few or no competitors. However, this has a negative connotation. If no or few companies are in a market space, it implies that there may not be a large enough base of potential customers to support the company’s products and/or services.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
2. select the appropriate competitors to analyze.
Once your competition has been identified, you want to consider selecting the most appropriate competitors to analyze. Investors will expect that not all competitors are “apples-to-apples” (i.e., they do not offer identical products or services) and therefore will understand if you choose only companies that are closest in nature. So, you must detail both direct and, when applicable, indirect competitors.
Direct Competitors
Direct competitors are companies that fill the same customer need you do with the same or a similar solution. They serve the same potential customers with similar products and services. For example, direct competitors of a pizza shop would be other local pizza shops.
If you sell your products or services online, your direct competitors would also include companies whose website ranks in the top 5 positions for the same target keyword on Google. For example, if you are a home-based candle-making company , you would consider direct competitors to be other candle makers that offer similar products at similar prices. Online competitors would also include companies who rank for the following keywords: “homemade candles”, “handmade candles”, or “custom candles.”
Detail your direct competitors. What products/services do they offer? At what price points?
Indirect Competitors
Indirect competitors are those that serve the same target market with different products and services or a different target market with similar products and services. They fill the same customer need you do with a different solution. For example, a supermarket that sells frozen pizzas would be an indirect competitor to a pizza shop.
In some cases, you can identify indirect competitors by looking at alternative channels of distribution. For example, a small business selling a product online may compete with a big-box retailer that sells similar products at a lower price.
Detail your indirect competitors. What products/services do they offer? At what price points? Use the same 9-point checklist mentioned above for direct competitors.
Analyze Competitors
After selecting the appropriate competitors, you must conduct primary and secondary research on them to learn more about how they are conducting their business and what drives customers to purchase from them. Here are some methods you can use to learn more about your competitors:
Primary Market Research Methods
- Customer Interviews: Directly ask customers about their preferences, needs, and perceptions of your competitors.
- Surveys: Gather quantitative data on customer satisfaction, brand awareness, and perceived value.
- Focus Groups: Facilitate discussions among a group of customers to gain insights into their decision-making processes.
- Mystery Shopping: Conduct undercover shopping experiences to assess competitor’s customer service, product quality, and pricing.
Secondary Market Research Methods
- Industry Reports: Analyze reports from market research firms to identify market trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Business Websites: Gather information on products, services, pricing, marketing strategies, and customer reviews.
- Social Media Monitoring: Track competitor’s social media activity to gauge brand perception and customer engagement.
- News Articles and Press Releases: Stay updated on competitor’s recent news, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships.
- Financial Reports: Analyze competitor’s financial performance to assess their strengths and weaknesses.
With these primary and secondary research methods, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your competitive landscape and develop effective strategies to differentiate your business.
For each of your primary competitors, perform a SWOT Analysis and create a competitive matrix to identify their strengths and weaknesses, market presence, compare product features, and more, and identify opportunities where your business can succeed.
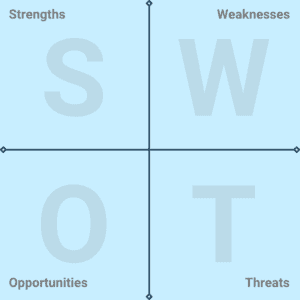
For each of your main competitors, you should research the following information:
- Competitor Name
- Competitor Overview (company history; how long have they been operating)
- Product and/or Service Offerings
- Pricing Strategy
- Revenue Streams
- Estimated Market Share
- Location(s)
- Target Customers (Service and Market Segment)
- Sales and Marketing Tactics
- Customer Reviews
By understanding what your competitors offer and how customers perceive them, you can determine your company’s competitive advantage against each competitor.
3. Determine Your Competitive Advantage
In this part of your competitive analysis, you need to detail the reasons your business is in a competitive position to outperform both direct and indirect competitors, and how the company’s business model creates barriers to entry. “Barriers to entry” are reasons why it would be difficult for new companies to enter into or compete in the same market.
For instance, you may have a patent that provides value to your customers and makes them less likely to switch suppliers, which protects your business from potential competitors. Or, you may have more resources than the competition and thus be able to provide superior customer service.
Below is a list of areas in which you might have competitive edge or advantage. Review each and expand upon the relevant ones:
- Size of the Company – Large companies have more resources and can usually offer lower prices than smaller businesses. This is a significant barrier to entry, as starting a small business and competing with a larger company may be difficult.
- Product or Service Differentiation – If your product or service is unique in some way, this will make it less likely that customers will switch to a competitor.
- Experience & Expertise – Experience and knowledge are valuable attributes that can help differentiate you from the competition.
- Location – If you are located in an area where there is high demand for your product or service, this can be a barrier to entry because competitors will not want to open new locations.
- Patents & Copyrights – Protecting intellectual property can prevent others from entering the same market and competing with your company.
- Brand Recognition – Customers are loyal to brands they have come to trust, which protects the company from new competitors.
- Customer Service – Providing excellent customer service can help you retain customers and prevent them from switching suppliers.
- Lowest Cost Offerings – If you can offer a lower price than your competitors, this makes it more difficult for them to compete with you.
- Technology – New technology that enables you to provide a better product or service than your competitors can be an advantage.
- Strategic Partnerships & Alliances – Collaborating with a company that your customers want to work with can help keep them from switching.
- Human Resources – If you have a highly skilled and talented workforce, it can be difficult for competitors to find and employ the same skills.
- Operational Systems – Strong operational systems that lead to greater efficiencies can protect your business from the competition.
- Marketing Strategy – Investing in strong marketing strategies can make your business difficult to compete with.
For instance, you could say that your [enter any of the bullets from above] is better than your competitors because [insert reason].
Competitive Analysis Example
The bend brew shop: competitive analysis.
The Bend Brew Shop is a new specialty coffee shop and brewery in Bend, Oregon. We offer a unique blend of high-quality coffee, craft beer, and a welcoming atmosphere. Our goal is to become a beloved local hangout, known for its exceptional beverages and friendly service.
Direct Competitors:
- Thump Coffee Roasters: A local roaster known for its dark roasts and strong coffee.
- Deschutes Brewery Public House: A popular brewery and restaurant offering a wide range of beers and food.
- Boneyard Beer Pub: A local brewery with a strong following, particularly among beer enthusiasts.
Indirect Competitors:
- Starbucks: A global coffee chain with multiple locations in Bend.
- McMenamins: A regional chain offering food, drinks, and lodging.
- Dutch Bros Coffee: A drive-thru coffee chain with a strong local presence.
SWOT Analysis
Competitive advantages.
- Unique Blend of Coffee and Beer: We offer a unique combination of high-quality coffee and craft beer, appealing to a wider range of customers.
- Community-Focused Atmosphere: We aim to create a welcoming and inclusive space for locals and visitors alike.
- High-Quality Ingredients and Expert Baristas: We source the finest beans and hops, and our staff is trained to create exceptional beverages.
- Strong Local Partnerships: We collaborate with local businesses to offer unique experiences and support the community.
By understanding our competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, we can position The Bend Brew Shop to capitalize on our unique selling points and build a loyal customer base.
The competitive landscape is one of the most important considerations in developing a business plan since it sets the stage by providing information on past and current competitors and their respective strengths and weaknesses. A strong understanding of the market landscape is needed before you can develop a business strategy for differentiating your company from the competition. Follow the above guidelines for conducting a thorough competitor analysis, and you will be well-prepared to create a winning competitive analysis section for your business plan.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies that have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how a Growthink business plan consultant can create your business plan for you.

A Guide to Competitive Analysis: It’s Not Just about Competitors
By Joe Weller | April 16, 2018 (updated October 25, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
If you were running a cross-country marathon, wouldn’t you want to know something of the terrain and expected weather conditions before you began? The same principle of preparation applies when starting and continuing a business. It’s not enough to focus on your own production and financial goals: You need to understand what’s happening around you, how others create goods or services, the economic forecast, changes in rules and regulations, and more. In other words, you need to conduct a competitive analysis. The thought of searching for and digesting the required information may seem overwhelming, but we make it easy.
In this article, we explain how to focus your analysis by first deciding what questions you want answered. Learn how to find current and potential competitors and how many of them you need to review. Then, we cover the specific aspects of your competitors that you need to consider as well as where to find more information about them. Marketing experts weigh in on how to maintain focus during analysis. We also offer free, downloadable competitive analysis templates to start you on your own information gathering and analysis.
What Is Competitor Analysis?
Competitor analysis (CA) is a process of identifying competitors and gauging their business and marketing strategies to understand both their strengths and weaknesses and those of your own business. Competitive analysis provides a higher-level perspective of the entire marketing landscape and competitive intelligence.

“Competitive analysis is the process of analyzing all collected information to derive some insight for reducing risk and making better decisions,” explains competitive intelligence expert and author Babette Bensoussan .
“It is about your broader competitive environment,” she says. “I always remind my clients that competitors make up only one element of a business’s competitive environment. Other elements include government, technology, buyers, and suppliers, to name a few that impact how well you can compete.”
What Is the Purpose of a Competitive Analysis?
Researching your competitive landscape is essential to business growth and survival, and helps you offer better products or services to customers. You should gain an understanding of how customers view your company, what you’re doing right, and what you’re doing wrong. Therefore, competitive analysis forms a crucial part of marketing plans to help you understand what differentiates your product or service. Particularly when applying for funding, competitive analysis provides valuable insight into business plans. However, competitive analysis offers much more:
- Branding possibilities
- Insight into how competitors design products and messages
- SEO possibilities
- CRO (conversion rate optimization)
- GTM strategies
- User experience (UX) advantages of your and others’ products and websites
- Gaps in the market
- New products and services to develop
- Market trends
According to a Conductor survey , 60 percent of marketers don’t feel proficient in competitive analysis. Many don’t practice it on a regular basis. Knowledge derived from these exercises is critical, and you need to assess competition regularly. Nevertheless, marketing departments often skip competitive analysis, which leaves them with a fragmentary understanding of the landscape and competitors. Being proactive can help you anticipate and prepare for competitor developments and provide you with the agility to take advantage of changes.
According to Bensoussan, “In today’s world of constant change and information overload (whether the information be real or fake), it is critical for any business person to understand the competitive landscape and the forces that impact the profitability and viability of a business.”
What Should Be Included in a Competitive Analysis?
In most cases, a competitive analysis contains a few basic sections, which may vary depending on the size and form of your company and the focus of your analysis:
- A list of your main competitors
- An overview or what you know about them
- Who their target customers are
- A list of their products or services
- What media they use to market their goods and services
- Their current and past marketing strategies
- Their value proposition and effectiveness
- An analysis of all of the strengths and weaknesses of your competition (and your own company)
- An overview of the strategies being used by the competition to achieve their objectives
- An overview of the market and projections for the future
How to Prepare for a Competitive Analysis
One of the crucial prerequisites for a successful competitive analysis is an open mind. Check your beliefs at the door — what you think about your company, your customers, or your competitors isn’t necessarily true. That can be a good thing.
In addition, it is vital to understand why you are conducting an analysis. What are your goals for the business? What are your goals for this analysis? “Always, always be very clear as to what the decision you will be making is all about,” advises Bensoussan. “If you are not clear about your decision, then you will never know if you have good competitive analysis or just some more information.”
She offers these two questions as examples of how different the impact of each answer can be: “Tell me who’s who in the [manufacturing] of zippers?” versus “Should I enter the zipper-manufacturing industry, and can I achieve a return on investment of, say, 15 percent in three years?”
“Which question would help you the most in delivering good quality CA? Which outcome do you think would provide the most value?” Bensoussan asks.
Companies often enlist the help of outside consulting firms dedicated to conducting competitive intelligence research. Guidance on competitive intelligence support, such as database information, software platforms for market program tracking, and more is available through the Society of Competitive Intelligence Professionals .
Competitor Analysis Frameworks
Over the decades, marketing gurus have developed or advocated several competitive analysis frameworks. Here are six well-known methods to consider.
- Porter’s Five Forces Model: First published in 1979 by Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter, the Five Forces model provides a view beyond competitors to factors in your industry landscape that may threaten or strengthen your position. The Five Forces include the following:
- Potential New Entrants: Consider how much money, time, and effort it would take for a company to displace you.
- Competitive Rivalry: Determine who your competitors are, who the closest competitors are, and their products, prices, and quality. Fewer rivals mean more opportunity for your unique qualities to shine; many rivals mean more competitors to steal your customers and potentially better deals to lead customers elsewhere.
- Suppliers: The more potential suppliers you have, the better for you. Consider how having fewer suppliers might impact your operation.
- Buyers: If you have many customers, you have the power. Otherwise, buyers can negotiate more advantageous deals elsewhere or find sources other than yours. Consider how you would treat that situation.
- Substitutes (or Complements): A competitor could create a product or model that replaces yours. On the other hand, a new product or service could also complement yours, which would create a symbiotic sales situation. Complements are sometimes considered the sixth force in the model.
Porter stressed the importance of not confusing these constants with temporary disruptions, such as technological innovations or government interventions in industry.
You can download the Five Forces model below to answer your own questions about an industry or business proposition.
Download Five Forces Model
Excel | PDF
Industry Life Cycle Overview: Both industries and individual products have life cycles, which reflect the state of sales, whether robust or diminishing. Understand which stage of the life cycle your industry, company, or product is in to help target your marketing efforts. Product life cycles contain such stages as these:
- Introduction: At the introductory stage, a new industry or product is not well known or proven. It is usually marketed to a few early adopters. Because resources focus on product development, testing, and refinement, few or no profits accrue. Marketing focuses on explaining the product, creating awareness around it, and establishing a niche.
- Growth: As awareness grows and the industry or product becomes established, profits may also grow. However, in the growth stage, rival products may also appear. Although improvements require funds, production efficiencies may also develop. Some products have only a short growth phase. For example, a particular fashion may last for only one season. Other products experience a long or extended growth phase, such as software products, which continue their usefulness through upgrades. During the growth stage, marketing centers on differentiating the product, so it stands out from competing products.
- Maturity: In the maturity stage of a product or industry, sales may expand, but at a less accelerated rate. Fewer competitors may dominate the market and may attempt to differentiate on quality or increase sales by touting low costs.
- Saturation: You reach the saturation stage when every customer who could buy the product already owns the product. A lack of innovation or competition from a superior product could result in saturation.
- Decline/Termination: Industries and products decline for several reasons. Innovations may overtake them and render them obsolete. Businesses and product lines may fail to upgrade and innovate. At the decline or termination stage, companies may fold, continue in a smaller market, or merge with larger, successful businesses.
Strategic Groups Analysis: You perform strategic groups analysis on companies within a business sector, such as automobiles, to see how they vie for their share of consumer expenditure. By dividing companies into strategic groups, you can understand how businesses of different sizes behave in the marketing landscape. Businesses within groups tend to be competitors, whereas businesses in other groups are related but not competitive. For example, running shoes and high-end women’s dress shoes are in different groups. Analyzing companies in this way can also reveal other significant information: direct competitors and their basis for competition; if and how a company can move to another group; and strategic problems and opportunities. Strategic groups are usually plotted on an x-y axis, where two highly relevant criteria form the axes. Here are some examples of criteria:
- Brand ownership
- Company size
- Capacity utilization
- Cost structure
- Geographical market segmentation
- Marketing activities
- Ownership structure
- Sales channels
- Product diversity
- Product quality
- R&D capability
- Vertical and horizontal integration
First, plot the companies where you think they belong on the graph. Now, with all companies plotted, create groupings. If you want, you can use larger or smaller circles to indicate market share. To gain greater insight, perform a Five Forces analysis on them, or consider the mobility barriers that prevent companies from shifting to other strategic groups.
SWOT: Perhaps one of the most commonly addressed marketing analyses is SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats). In essence, SWOT represents what competitors do and do not do well. As you look at SWOT for competitors, also consider it for your own products and services.
- Strengths: What do they do better than you? What are they known for? Is their pricing, inventory, convenience, and level of service better than yours?
- Weaknesses: How do they fall short of your company’s standards? Can you leverage their shortcomings to improve your standing with customers?
- Opportunities: What in your competitors’ landscape can you exploit to your advantage?
- Threats: What in your competitors’ landscape threatens their business position?
Note that strengths and weaknesses focus on internal characteristics, while opportunities and threats concern external forces. SWOT can be performed separately, but it may provide a useful frame for studying a business’ products and services, marketing, and sales.
Competitive Array: Competitive arrays, also known as competitive matrices , provide a way to quantify characteristics that may be unquantifiable. For example, if company A sells 500 widgets and company B sells 250, it’s clear which company sold more. But how do you quantify the attractiveness of online and print media or innovation? Creating the competitive array can be an individual or group exercise. To start, list your competitors across the top of your writing surface. In the left-most column, list important characteristics. Next, create a column for weighting the importance of each characteristic so that the sum of the characteristics totals one. The higher the weighting, the more important the characteristic (you may have a few characteristics with the same weight). Next, grade each competitor for each characteristic on a scale, such as from one to 10. Now, multiply the grade by the corresponding weight.
Competitive Value Proposition Analysis: The characteristics of a value proposition are exclusivity, clarity, and credibility. This method concerns how unique the product or service is, how clearly the product message is conveyed, and whether the message is credibly supported by evidence, such as testimonials, statistics, or test results. Because customers remember only a few key advantages of your product from your media promotion, the main value proposition must be correct and clear and mesh with your actual competitive advantage. To figure out how to differentiate your company, you must determine how competitors differentiate themselves from each other. POPs (points of parity), PODs (points of difference), and POIs (points of irrelevance) help you dissect value propositions.
- Points of Parity (POPs): These are elements of customer benefit that both you and your competitors offer.
- Points of Difference (PODs): These are features of customer benefit that you offer but competitors don’t. Keep in mind that not every point of difference is significant to consumers.
- Points of Irrelevance (POIs): These are characteristics that customers don’t care about.
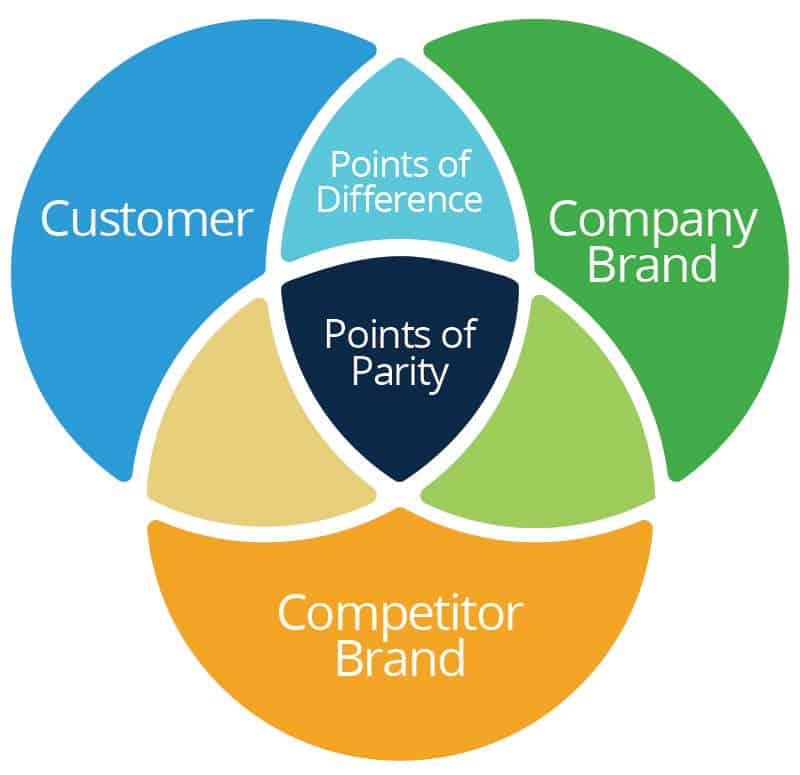
Your unique value proposition (differentiating characteristics) doesn’t need to appeal to every customer. Don’t make your value proposition too general. You can’t be all things to all customers, just as you can’t do what your competitors are doing.

Otherwise, there's no differentiation. You end up being like teenagers, everybody in the same jeans," says Sonia Schechter, Chief Marketing Officer of Marxent , a provider of virtual reality and augmented reality apps for furniture retailers. Therefore, target your message.
Discover your points of parity by using our POP template.
Download Points of Parity Template
Excel | Word | PDF
Who Are Your Competitors?
As a first step in competitive analysis, marketing guides typically suggest determining who your competitors are. Competitors can be divided into groups of direct competitors, indirect competitors, and future competitors.
- Direct Competitor: These are companies who sell a direct substitute for your product, operate in the same geographic area, and/or offer the same goods (such as groceries) to the same market. Ask who your customers would buy from if you weren’t in business.
- Indirect Competitor: These are companies in the same geographic area whose products occupy the same general, but not specific, category as your own (e.g., a general bakery versus a designer cake store). Indirect competition satisfies the customer’s need for a particular product or service, although that product or service may be different from yours. Similar products operating in different market segments do not represent direct competitors. For example, a high-end seafood restaurant doesn’t compete with a burger place.
- Future Competitor: Future competitors may currently be indirect competitors who change and expand solutions. In the bakery example, the general bakery could hire a high-end designer to compete with the specialty cake maker. Or, the designer cake store could branch out into breads and muffins.
It may be difficult at first to envision what types of organizations you need to analyze and whether you need to analyze all competitors.To identify competitors, ask yourself who your customers would buy from if your product did not exist. Perhaps even more important, consider who your customers think your competitors are. How many competitors you review depends: If only a few companies do what you do, analyze everyone. If you have many competitors, use Pareto analysis to focus on the critical 20 percent. Larger businesses may analyze the top 10, whereas a small business can focus on three. Disregard online competitors unless you plan to sell online.
Download Pareto Chart Template - Excel
How to Find Current Competitors
Some competitors may seem obvious, but sleuthing can reveal challengers you weren’t aware of.
- Google search for a product or service similar to yours. Consider the companies in paid ads and organic returns.
- Try SEMrush to check which domains are using which keywords.
- Ask your current customers who they would choose besides you.
- Check Alexa, Google Trends, or SimilarWeb for general estimates on the popularity of domain names and keywords.
- Review Dun & Bradstreet for new incorporations.
- Consult Derwent for new patent information.
- See who has booths at trade shows.
How to Find Potential Competitors
While you consider the current playing field, you must also keep your eye on what’s coming around the corner. These are the future new entrants in your niche. Consider who might start a business that would compete with yours. New competitors can be found in related markets, related technologies, or related products. Companies from other geographical areas with similar products may begin to sell in your area, and former employees or managers can start their own companies based on the themes of your business. In addition, consider the following conditions that may encourage competition:
- A company gains competitive advantage.
- Buyers are dissatisfied with suppliers.
- An unmet demand for goods exists.
- Few major barriers to entry exist.
- The industry offers high profit margins.
- The industry offers unrealized growth potential.
- Competitive rivalry is not intense.
It’s Not All about Competitors ( Competitive Doesn’t Always Mean Competitor )
Depending on what your product or service is and where it is in its life cycle, a competitor focus may not be optimal. For example, for emerging technologies, no true competitor may exist.
“Looking too closely at competition is a massive distraction,” Schechter notes. “If you’re selling a commodity or established product, such as a drugstore, which sells the same thing anywhere, you’d be looking at specific issues, like price, location, and assortment.”
Schecter says marketers themselves often don’t understand that what the competition is doing is not important: “Successful marketing is how you define yourself in the landscape. People don’t care about a feature-by-feature description, or even one feature. They buy the package. They like you. You’re different or you’re solving a particular problem. A new business must define and lay out the landscape for the customer.”
To succeed, understanding what customers want is key. “Marketers have nuanced detail, and customers don’t care about that detail,” Schechter continues. “But, you have to listen to their questions and engage in dialogue with them to gain real understanding,” she points out. She cites Apple’s promotion of the camera in the first iPhone as an example of marketers understanding what — out of thousands of potential functions — was important to consumers. “B2B marketing is the same. It’s about listening to customers, figuring out how they’re shopping, and trying to see through their eyes,” Schechter emphasizes.
“Obsessing over competition can get you off track. If you’re listening to customers, you’ll build the right product. But you don’t need to build your dreams on other people’s ideas,” she concludes.
Where to Find Information for a Competitive Analysis
Remember that every department of your business is a potential source for information, including the following areas:
- Sales: Questions for potential, current, and lost customers
- Research and Development: New patents
- Purchasing: Suppliers
- Marketing: Customers and other consumers
Once you’ve determined who your competitors are and what you want to learn about them and from them, you need to go information hunting:
- Visit offices or brick-and-mortar stores. What do they look like? Who’s there?
- Get financial and organizational information from public filings and from sources like Hoovers, Manta, and Dun & Bradstreet.
- Monitor PR Newswire for new developments and changes.
- Some marketing platforms may actually include information about your competitors.
Interviews and Research Surveys
Interviewing competitor customers and consumers who know little about your business is important to overcoming your preconceptions about the business landscape. You probably have specific questions in mind, but here are the basics:
- Why are you shopping for a solution?
- What were the main reasons you chose the company you did?
- Ranked from most important to least important, what are your five shopping criteria?
Media Scanning or Competitor Content Analysis
You can learn much about competitor products and messaging by scanning media. Media doesn’t just include online content (web pages, tweets, and Facebook posts) — it also includes such traditional marketing collateral as white papers, case studies, and data sheets. Moreover, consider reference materials, such as LexisNexis and Hoovers, and trade, business, or news publications for ads, news stories, and press releases. Media and content can reveal not only new products and new branding, but also new positioning and segmentation strategies, pricing, target markets, and promotion strategy.
What Information to Search for in Competitive Analysis
The approach to analysis depends on the questions requiring answers. To organize your analysis, divide it into three aspects: product or services, marketing, and sales. Each aspect contains its own questions and means of analysis.

Products and Services
Your understanding of products and services must be thorough. Investigate the complete product or service line. Try to understand who your competitors’ customers are and what they need. Look at their pricing strategy and see if it differs for online and brick-and-mortar stores. Also, consider how they differentiate from their competitors.
Tracking competitor sales processes can involve more legwork. For public companies, SEC filings provide some financial information about growth or contraction, but, for private companies, information is less readily available. Information about sales channels may be easy to find through a look in the phone book or online. You can also gather details about the sale process by asking current customers why they chose your product over others. You can also acquire valuable information by following up even after you lose a sale in order to understand the customer’s thinking. What do their partner resales programs look like? What are their revenues versus sales volume?
Marketing Efforts in Competitive Analysis
What does the competitor marketing plan entail? How do competitors invest marketing efforts? What can you do even better? A variety of approaches can help you define competitor marketing strategy.
When you identify marketing assets, take a reasonable sample of items — no need to review all of them. Just remember to keep samples consistent among competitors. Also, when reviewing items, consider the quality of the collateral. It should appear professional, with no typos, and in the formal, professional, idiomatic voice. In addition, a solid library of resources, such as consistent blog posts, whitepapers, case studies, videos, webinars, and podcasts may point you to themes and leads you should follow.
E-Marketing Strategy Competitive Analysis
Few businesses today can function without a web presence that helps generate traffic and inquiries or purchases. Some statistics say that prospective buyers visit a website as many as nine times before purchasing and, depending on the product, visit multiple sites before purchasing. Forrester research after 2010 suggests potential customers visit three sites on average before buying. The more sites visited, the more money the customer intends to spend.
Therefore, understanding how your site compares to your nearest competitors can be helpful. To drive eyes to websites, online purveyors use search engine optimization (SEO) to employ the keywords most likely to garner high search ratings in Google (and other search engines). Marketers frequently also use SEM (search engine marketing) to promote a business or product by increasing visits to a website through paid keywords. Look at how saturated their content is with keywords and where they use keywords, whether in H1 and H2 tags, page titles, content, or links. Also, look at the difficulty level of their keywords.
Consider the usability of the steps in the sales funnel as well as the navigation. What do the landing pages say? Also, look at backlinks (i.e., links from other pages to your competitor’s page) to your web page. See how many backlinks exist — and from which pages — to understand if this is something you can improve for your website.
Structure is important, but quality content also matters. Online marketing collateral appears as blogs, white papers, ebooks, case studies or user stories, videos, webinars, podcasts, and more. But words and pictures themselves are not valuable if they don’t offer any unique information or concise approaches to existing knowledge. Check whether content is shared and which topics attract attention, or, conversely, what that content and those topics are linked to. What do readers comment on, if they do comment? Who else is sharing what your competitors are publishing?
Social Media
Certain social media platforms appeal to some audiences more than others. The channels a company favors can reveal clues to the demographics of their target market. Make note of what social media buttons they include on pages and where on the page they include them.
Software Tools for Understanding Online Competitors

Besides monitoring content, you can monitor the mechanics of competitor websites to glean more data about how marketing strategy and product offerings are changing. Software helps to automate these investigations for you. Following are some of the many products available:
- BuiltWith : See what platform was used to build a page.
- Ghostery : Find trackers on a website.
- SEMrush : Discover company rankings, organic keywords, AdWords, and analyses of backlinks.
- Versionista : Track web page and website changes, SEO changes, and more.
- Visualping : Monitor webpage updates.
- SpyFu : Find competitor keywords and AdWords, including AdWord and keyword variations and history.
- iSpionage : Track PPC and other keywords in competitor campaigns.
- SimilarWeb : Compare competitor websites to your own.
- Heatmaps: Use large amounts of data to provide a visual representation of how users interact with a website. Heatmaps can indicate where users click and look and for how long. Levels of intensity of activity are usually displayed through colors.
- Session Recording Tools: Record user browsing sessions. Session recording tools can yield a wealth of rich data, but raise some privacy concerns.
- Tag Management Systems: Advanced e-marketing implementations use tags to aid analysis and reporting. Tags are snippets of code that are usually added to the <head> tags of a web page.
Web Page User Testing for UX in Competitive Analysis
It’s essential to understand how consumers approach your website, especially for web-based products and marketing. Allow customers to test your site, and even view it yourself from a customer’s perspective, to help eliminate unnecessary steps and streamline your sales funnel. Doing so can also help to illuminate the opportunities for upsells and cross-sells.
Limiting the analysis to two or three competitors offers a manageable amount of insight into usability, which helps you avoid reviewer overload and confusion. For impartial results, don’t reveal to test participants which website is yours.
Ask test participants to enter words in Google or list the words and phrases they would use to find a certain product or service. Not only does this yield potentially fruitful keywords, it also indicates whether your site appears in search returns.
To get a sense of each participant’s impression, have them look at each website for five seconds and answer the following questions:
- What three words would you use to describe the site?
- What is it about? What products or services are offered and for whom?
- How does this website make you feel?
To understand their process, give participants a task to perform on each website. Ask them to answer the following questions:
- What was the worst thing about your visit to this website?
- What aspects of the experience could be improved?
- What did you like about the website?
- What other comments do you have?
- Which website did you like best and why?
How Much Data Do You Need in a Competitive Analysis?
It may seem overwhelming to sit down and search out your competitors’ business situations. That’s why setting a clear intention before you begin an analysis is so important. In addition, Babette Bensoussan advises that you don’t need to analyze everything:
“Over the years, I have learned that once you have 70 percent of the information required for your chosen analytical technique, you can proceed to the analysis,” she explains. “You never really need all the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle to tell you what the picture is. This same philosophy applies to analysis. More information may not yield better insights nor improve predictive accuracy.”
How Do I Write a Competitor Analysis Report?
The format of your analysis depends on individual choice and the audience. You may also choose to use one kind of format while you work through the analysis, and another when you present findings.
Take a sheet of paper. In the left-most column, write the names of your closest competitors. Across the top of the page, list the main attributes of each product, such as target market, price, size, method of distribution, extent of customer service, prospective buyers, and so on. Then, make a check or a note for each attribute the competitor fulfils. An additional column can contain information about service or product availability, the website, a toll-free phone number, and other general information.
A competitor profile helps you make a detailed record about each competitor, and also allows you to capture snapshots of a business over time. Consider listing some of the following information:
- Location of offices and factories
- Key personalities, history, and trends
- Ownership, organizational structure, and corporate governance
- Number of employees and skill sets
- Management and management style
- Compensation, benefits, and retention rates
- Plant capacity, utilization rate, age of plant, capital investment
- Product mix per plant and shipping logistics
- Products and services
- Depth of product line
- New products developed and success rate
- Research and development details
- Brands and brand loyalty and awareness
- Patents and licenses
- Quality control conformance
- Cash flow and liquidity
- Profit growth profile
- Method of growth (organic or acquisitive)
- Objectives, mission statement, growth plans, acquisitions
- Marketing strategies
- Segments served, market shares, customer base, growth rate, and customer loyalty
- Promotional mix, promotional budgets, advertising themes, ad agency used, online promotional strategy
- Distribution channels (direct and indirect) and exclusivity agreements
Here is a step-by-step process for writing a competitor analysis report:
- Write down your competitors.
- Write what you know about them already.
- Discover who their target customers are.
- Discover their pricing methods.
- Investigate their marketing strategy.
- Figure out their competitive advantage.
Download our competitive analysis landscape template to get ideas for gathering information and reporting analysis results.

Download Competitive Analysis Landscape Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Competitive Analysis for Small Businesses
Small business can be competitive. Beyond meeting financial targets, you need to understand the competitive landscape (short of allowing it to distract you) and then target a niche market. Many of the same analyses that apply to large businesses also apply to small businesses. However, if this is your first business, or if you don’t have a marketing background, you may want to pay attention to a few aspects.
First, it is helpful to acknowledge how much or how little you know about your competitors by sketching a profile of your top two or three competitors. Next, try to learn all you can about your competition.
You can use the following template to perform a competitive analysis for your small business.
Download Small Business Competitive Analysis Template
Word | PDF
What Is a Competitive Analysis in a Business Plan?
Competitive analysis should play a key role in the preparation of a business plan. Particularly if you seek outside funding, your knowledge of the competitive landscape will show your understanding of your business and the market forces at play.
When starting a business, consider all the analysis questions described above, but pay particular attention to issues of growth and opportunity. Consider addressing the following circumstances:
- Whether current competitors target a specific niche or offer products to the mass market
- If, how, and why competitors are growing or reducing business
- How your company will be stronger than competitors and better able to exploit changes in the market landscape
- What you will offer customers that no one else does (your competitive advantage)
In the business plan, describe the competitive landscape as it relates to direct and indirect competitors and opportunities and risks, emphasizing your competitive advantage. This competitive analysis can form the basis for your first marketing plan.
Sharpen Your Competitive Analysis with Smartsheet for Marketing
The best marketing teams know the importance of effective campaign management, consistent creative operations, and powerful event logistics -- and Smartsheet helps you deliver on all three so you can be more effective and achieve more.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Improve your marketing efforts and deliver best-in-class campaigns.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write Competitive Analysis in a Business Plan. The section on competitor analysis is the most crucial part of your business plan. Making this section informative and engaging gets easier when you have all the essential data to form this section. Now, let's learn an effective way of writing your competitive analysis. 1.
Step 3: Perform a SWOT Analysis. A Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (SWOT) analysis helps you study what competitors are doing to win customers. You can also use it to identify gaps in your market.. For example, let's say a competitor's customer support team takes pretty long to get back to customers.
You decide to conduct a market analysis for your business. To do so, you would: Step 1: Use Google to compile a list of your competitors. ... which means following up on your findings with clear business goals and a strong business plan. Once you do your competitive analysis, you can use the templates below to put your plan into action.
Competitor analysis example for SME business development managers . Imagine this: As the business development manager for a medium sized start up, you are tasked with expanding the client base. The market is crowded with similar service providers, and differentiation is key. When doing your competitor analysis report, look into: Competitor ...
How to write your competitive analysis. Once you've done your research, it's time to present your findings in your business plan. Here are the steps you need to take: 1. Determine who your audience is. Who you are writing a business plan for (investors, partners, employees, etc.) may require you to format your competitive analysis differently.
A competitor analysis, also called competitive analysis and competition analysis, is the process of examining similar brands in your industry to gain insight into their offerings, branding, sales, and marketing approaches. Knowing your competitors in business analysis is important if you're a business owner, marketer, start-up founder, or ...
The Competitive Analysis section of your business plan is devoted to analyzing your competition--both your current competition and potential competitors who might enter your market.
1. Business & Company metrics 1.1. Company overview. Your analysis should start with digging up the basic info about your competitors: things like the company's founding year, the names of the CEO and other key people, locations of the company's offices, how many employees work there, etc.
A strong understanding of the market landscape is needed before you can develop a business strategy for differentiating your company from the competition. Follow the above guidelines for conducting a thorough competitor analysis, and you will be well-prepared to create a winning competitive analysis section for your business plan.
Competitor analysis (CA) is a process of identifying competitors and gauging their business and marketing strategies to understand both their strengths and weaknesses and those of your own business. Competitive analysis provides a higher-level perspective of the entire marketing landscape and competitive intelligence.