

How to Write an Effective Speech Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The Speaker Lab
- March 8, 2024
Table of Contents
Mastering the art of speaking starts with crafting a stellar speech outline. A well-structured outline not only clarifies your message but also keeps your audience locked in.
In this article, you’ll learn how to mold outlines for various speech types, weaving in research that resonates and transitions that keep listeners on track. We’ll also show you ways to spotlight crucial points and manage the clock so every second counts. When it’s time for final prep, we’ve got smart tips for fine-tuning your work before stepping into the spotlight.
Understanding the Structure of a Speech Outline
An effective speech outline is like a map for your journey as a speaker, guiding you from start to finish. Think of it as the blueprint that gives shape to your message and ensures you hit all the right notes along the way.
Tailoring Your Outline for Different Speech Types
Different speeches have different goals: some aim to persuade, others inform or celebrate. Each type demands its own structure in an outline. For instance, a persuasive speech might highlight compelling evidence while an informative one focuses on clear explanations. Crafting your outline with precision means adapting it to fit these distinct objectives.
Incorporating Research and Supporting Data
Your credibility hinges on solid research and data that back up your claims. When writing your outline, mark the places where you’ll incorporate certain pieces of research or data. Every stat you choose should serve a purpose in supporting your narrative arc. And remember to balance others’ research with your own unique insights. After all, you want your work to stand out, not sound like someone else’s.
The Role of Transitions in Speech Flow
Slick transitions are what turn choppy ideas into smooth storytelling—think about how bridges connect disparate land masses seamlessly. They’re not just filler; they carry listeners from one thought to another while maintaining momentum.
Incorporate transitions that feel natural yet keep people hooked. To keep things smooth, outline these transitions ahead of time so nothing feels left up to chance during delivery.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Outline
To make certain points pop off the page—and stage—you’ll need strategies beyond bolding text or speaking louder. Use repetition wisely or pause strategically after delivering something significant. Rather than go impromptu, plan out what points you want to emphasize before you hit the stage.
Timing Your Speech Through Your Outline
A watchful eye on timing ensures you don’t overstay—or undercut—your moment under the spotlight. The rhythm set by pacing can be pre-determined through practice runs timed against sections marked clearly in outlines. Practice will help ensure that your grand finale isn’t cut short by surprise.
Ready to Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig?
Download our free 26-page guide and get the 14 exact steps you can follow to book a paid speaking gig right now!
Depending on the type of speech you’re giving, your speech outline will vary. The key ingredients—introduction, body, and conclusion—are always there, but nuances like tone or message will change with each speaking occasion.
Persuasive Speeches: Convincing With Clarity
When outlining a persuasive speech, arrange your arguments from strong to strongest. The primacy effect works wonders here, so make sure to start off with a strong point. And just when they think they’ve heard it all, hit them with an emotional story that clinches the deal.
You might start by sharing startling statistics about plastic pollution before pivoting to how individuals can make a difference. Back this up with data on successful recycling programs which demonstrate tangible impact, a technique that turns facts into fuel for action.
Informative Speeches: Educating Without Overwhelming
An informative speech shouldn’t feel like drinking from a fire hose of facts and figures. Instead, lay out clear subtopics in your outline and tie them together with succinct explanations—not unlike stepping stones across a stream of knowledge.
If you’re talking about breakthroughs in renewable energy technology, use bullet points to highlight different innovations then expand upon their potential implications one at a time so the audience can follow along without getting lost in technical jargon or complexity.
Ceremonial Speeches: Creating Moments That Matter
In a ceremonial speech you want to capture emotion. Accordingly, your outline should feature personal anecdotes and quotes that resonate on an emotional level. However, make sure to maintain brevity because sometimes less really is more when celebrating milestones or honoring achievements.
Instead of just going through a hero’s whole life story, share the powerful tales of how they stepped up in tough times. This approach hits home for listeners, letting them feel the impact these heroes have had on their communities and sparking an emotional bond.
Incorporating Research in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting a speech, the backbone of your credibility lies in solid research and data. But remember, it’s not just about piling on the facts. It’s how you weave them into your narrative that makes listeners sit up and take notice.
Selecting Credible Sources
Finding trustworthy sources is like going on a treasure hunt where not all that glitters is gold. To strike real gold, aim for academic journals or publications known for their rigorous standards. Google Scholar or industry-specific databases are great places to start your search. Be picky. Your audience can tell when you’ve done your homework versus when you’ve settled for less-than-stellar intel.
You want to arm yourself with evidence so compelling that even skeptics start nodding along. A well-chosen statistic from a reputable study does more than decorate your point—it gives it an ironclad suit of armor.
Organizing Information Effectively
Your outline isn’t just a roadmap; think of it as scaffolding that holds up your argument piece by piece. Start strong with an eye-opening factoid to hook your audience right off the bat because first impressions matter—even in speeches.
To keep things digestible, group related ideas together under clear subheadings within your outline. Stick to presenting data that backs up each key idea without wandering down tangential paths. That way, everyone stays on track.
Making Data Relatable
Sure, numbers don’t lie but they can be hard to connect to. If you plan on using stats in your speech, make them meaningful by connecting them to relatable scenarios or outcomes people care about deeply. For instance, if you’re talking health statistics, relate them back to someone’s loved ones or local hospitals. By making the personal connection for your audience, you’ll get their attention.
The trick is using these nuggets strategically throughout your talk, not dumping them all at once but rather placing each one carefully where its impact will be greatest.
Imagine your speech as a road trip. Without smooth roads and clear signs, the journey gets bumpy, and passengers might miss the scenery along the way. That’s where transitions come in. They’re like your speech’s traffic signals guiding listeners from one point to another.
Crafting Seamless Bridges Between Ideas
Transitions are more than just linguistic filler. They’re strategic connectors that carry an audience smoothly through your narrative. Start by using phrases like “on top of this” or “let’s consider,” which help you pivot naturally between points without losing momentum.
To weave these seamlessly into your outline, map out each major turn beforehand to ensure no idea is left stranded on a tangent.
Making Use of Transitional Phrases Wisely
Be cautious: overusing transitional phrases can clutter up your speech faster than rush hour traffic. Striking a balance is key—think about how often you’d want to see signposts on a highway. Enough to keep you confident but not so many that it feels overwhelming.
Pick pivotal moments for transitions when shifting gears from one major topic to another or introducing contrasting information. A little direction at critical junctures keeps everyone onboard and attentive.
Leveraging Pauses as Transition Tools
Sometimes silence speaks louder than words, and pauses are powerful tools for transitioning thoughts. A well-timed pause lets ideas resonate and gives audiences time to digest complex information before moving forward again.
This approach also allows speakers some breathing room themselves—the chance to regroup mentally before diving into their next point with renewed vigor.
Connecting Emotional Threads Throughout Your Speech
Last but not least, don’t forget emotional continuity, that intangible thread pulling heartstrings from start-to-finish. Even if topics shift drastically, maintaining an underlying emotional connection ensures everything flows together cohesively within the larger tapestry of your message.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting your speech outline, shine a spotlight on what matters most so that your audience doesn’t miss your key points.
Bold and Italicize for Impact
You wouldn’t whisper your punchline in a crowded room. Similarly, why let your main ideas get lost in a sea of text? Use bold or italics to give those lines extra weight. This visual cue signals importance, so when you glance at your notes during delivery, you’ll know to emphasize those main ideas.
Analogies That Stick
A good analogy is like super glue—it makes anything stick. Weave them into your outline and watch as complex concepts become crystal clear. But remember: choose analogies that resonate with your target audience’s experiences or interests. The closer home it hits, the longer it lingers.
The Power of Repetition
If something’s important say it again. And maybe even once more after that—with flair. Repetition can feel redundant on paper, but audiences often need to hear critical messages several times before they take root.
Keep these strategies in mind when you’re ready to dive into your outline. You’ll transform those core ideas into memorable insights before you know it.
Picture this: you’re delivering a speech, and just as you’re about to reach the end, your time’s up. Ouch! Let’s make sure that never happens. Crafting an outline is not only about what to say but also how long to say it.
Finding Balance in Section Lengths
An outline isn’t just bullet points; it’s a roadmap for pacing. When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you’d like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part’s duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
The Magic of Mini Milestones
To stay on track, a savvy speaker will mark time stamps or “mini milestones” on their outline. These time stamps give the speaker an idea of where should be in their speech by the time, say, 15 minutes has passed. If by checkpoint three you should be 15 minutes deep and instead you’re hitting 20 minutes, it’s time to pick up the pace or trim some fat from earlier sections. This approach helps you stay on track without having to glance at the clock after every sentence.
Utilizing Visual Aids and Multimedia in Your Outline
Pictures speak louder than words, especially when you’re on stage. Think about it: How many times have you sat through a presentation that felt like an eternity of endless bullet points? Now imagine if instead, there was a vibrant image or a short video clip to break up the monotony—it’s game-changing. That’s why integrating visual aids and multimedia into your speech outline isn’t just smart. It’s crucial for keeping your audience locked in.
Choosing Effective Visuals
Selecting the right visuals is not about flooding your slides with random images but finding those that truly amplify your message. Say you’re talking about climate change. In this case, a graph showing rising global temperatures can hit hard and illustrate your chosen statistic clearly. Remember, simplicity reigns supreme; one powerful image will always trump a cluttered collage.
Multimedia Magic
Videos are another ace up your sleeve. They can deliver testimonials more powerfully than quotes or transport viewers to places mere descriptions cannot reach. But be warned—timing is everything. Keep clips short and sweet because no one came to watch a movie—they came to hear you . You might highlight innovations using short video snippets, ensuring these moments serve as compelling punctuations rather than pauses in your narrative.
The Power of Sound
We often forget audio when we think multimedia, yet sound can evoke emotions and set tones subtly yet effectively. Think striking chords for dramatic effect or nature sounds for storytelling depth during environmental talks.
Audiences crave experiences they’ll remember long after they leave their seats. With well-chosen visuals and gripping multimedia elements woven thoughtfully into every section of your speech outline, you’ll give them exactly that.
Rehearsing with Your Speech Outline
When you’re gearing up to take the stage, your speech outline is a great tool to practice with. With a little preparation, you’ll give a performance that feels both natural and engaging.
Familiarizing Yourself with Content
To start off strong, get cozy with your outline’s content. Read through your outline aloud multiple times until the flow of words feels smooth. This will help make sure that when showtime comes around, you can deliver those lines without tripping over tough transitions or complex concepts.
Beyond mere memorization, understanding the heart behind each point allows you to speak from a place of confidence. You know this stuff—you wrote it. Now let’s bring that knowledge front and center in an authentic way.
Mimicking Presentation Conditions
Rehearsing under conditions similar to those expected during the actual presentation pays off big time. Are you going to stand or roam about? Will there be a podium? Think about these details and simulate them during rehearsal because comfort breeds confidence—and we’re all about boosting confidence.
If technology plays its part in your talk, don’t leave them out of rehearsals either. The last thing anyone needs is tech trouble during their talk.
Perfecting Pace Through Practice
Pacing matters big time when speaking. Use timed rehearsals to nail down timing. Adjust speed as needed but remember: clarity trumps velocity every single time.
You want people hanging onto every word, which is hard to do if you’re talking so fast they can barely make out what you’re saying. During rehearsals, find balance between pacing and comprehension; they should go hand-in-hand.
Finalizing Your Speech Outline for Presentation
You’ve poured hours into crafting your speech, shaping each word and idea with precision. Now, it’s time to tighten the nuts and bolts. Finalizing your outline isn’t just about dotting the i’s and crossing the t’s. It’s about making sure your message sticks like a perfectly thrown dart.
Reviewing Your Content for Clarity
Your first task is to strip away any fluff that might cloud your core message. Read through every point in your outline with a critical eye. Think of yourself as an editor on a mission to cut out anything that doesn’t serve a purpose. Ask yourself if you can explain each concept clearly without needing extra words or complex jargon. If not, simplify.
Strengthening Your Argument
The meat of any good presentation lies in its argument, the why behind what you’re saying. Strengthen yours by ensuring every claim has iron-clad backing—a stat here, an expert quote there. Let this be more than just facts tossed at an audience; weave them into stories they’ll remember long after they leave their seats.
Crafting Memorable Takeaways
Audiences may forget details but never how you made them feel—or think. Embed memorable takeaways throughout your outline so when folks step out into fresh air post-talk, they carry bits of wisdom with them.
This could mean distilling complex ideas down to pithy phrases or ending sections with punchy lines that resonate. It’s these golden nuggets people will mine for later reflection.
FAQs on Speech Outlines
How do you write a speech outline.
To craft an outline, jot down your main ideas, arrange them logically, and add supporting points beneath each.
What are the 3 main parts of a speech outline?
An effective speech has three core parts: an engaging introduction, a content-rich body, and a memorable conclusion.
What are the three features of a good speech outline?
A strong outline is clear, concise, and structured in logical sequence to maximize impact on listeners.
What is a working outline for a speech?
A working outline serves as your blueprint while preparing. It’s detailed but flexible enough to adjust as needed.
Crafting a speech outline is like drawing your map before the journey. It starts with structure and flows into customization for different types of talks. Remember, research and evidence are your compass—they guide you to credibility. Transitions act as bridges, connecting one idea to another smoothly. Key points? They’re landmarks so make them shine.
When delivering your speech, keep an eye on the clock and pace yourself so that every word counts.
Multimedia turns a good talk into a great show. Rehearsing polishes that gem of a presentation until it sparkles.
Last up: fine-tuning your speech outline means you step out confident, ready to deliver something memorable because this isn’t just any roadmap—it’s yours.
- Last Updated: March 5, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter Eleven – Outlining the Speech
Why outline.
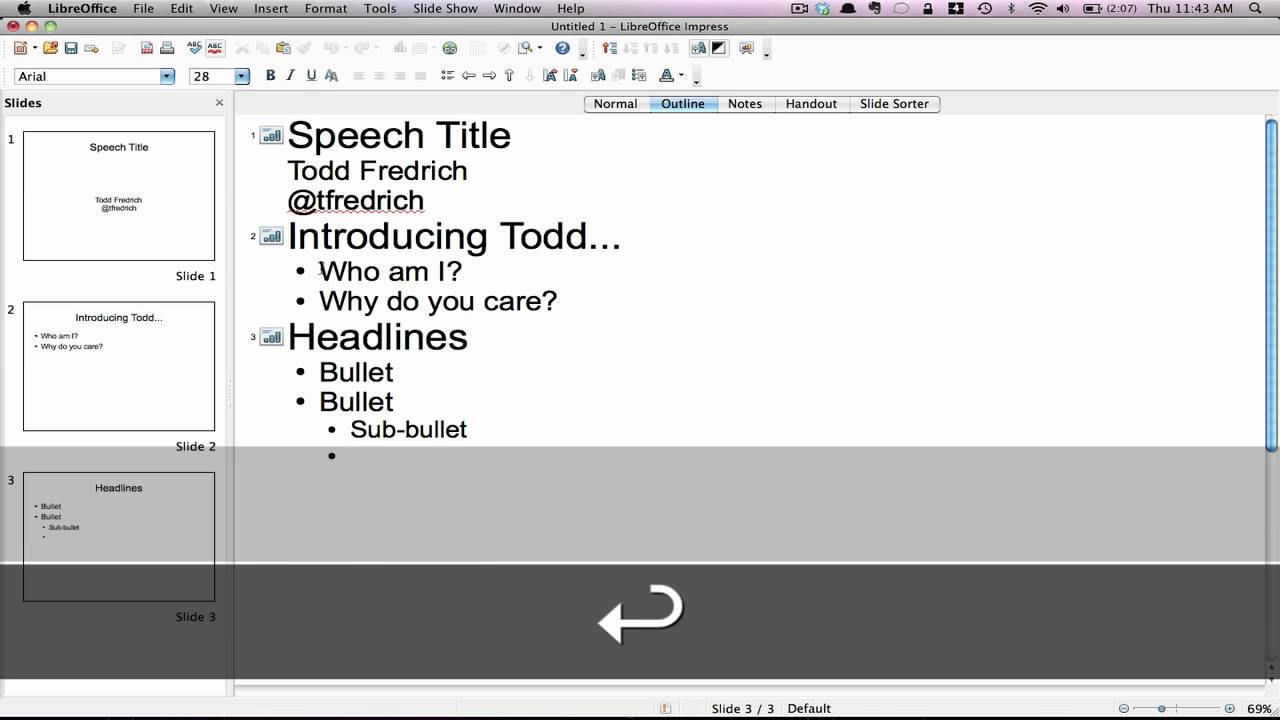
Screenshot from youtube video.
Most speakers and audience members would agree that an organized speech is both easier to present as well as more effective. Public speaking teachers especially believe in the power of organizing your speech, which is why they encourage (and often require) that you create an outline for your speech. Outlines , or textual arrangements of all the various elements of a speech, are a very common way of organizing a speech before it is delivered. Most extemporaneous speakers keep a brief outline with them during the speech as a way to ensure that they do not leave out any important elements and to keep them on track. Writing an outline is also important to the speechwriting process since doing so forces speakers to think about the main points and sub-points, the examples they wish to include, and the ways in which these elements correspond to one another. In short, the outline functions both as an organization tool and as a reference for delivering a speech.
A full-sentence outline lays a strong foundation for your message. It will call on you to have one clear and specific purpose for your message. As we have seen in other chapters of this book, writing your specific purpose in clear language serves you well:
It helps you frame a clear, concrete thesis statement. It helps you exclude irrelevant information. It helps you focus only on information that directly bears on your thesis. It reduces the amount of research you must do. It helps both you and your audience remember the central message of your speech. It suggests what kind of supporting evidence is needed, so less effort is expended in trying to figure out what to do next.
Finally, a solid full-sentence outline helps your audience understand your message because they will be able to follow your reasoning. Remember that live audiences for oral communications lack the ability to “rewind” your message to figure out what you said, so it is critically important to help the audience follow your reasoning as it reaches their ears.
Your authors have noted among their past and present students a reluctance to write full-sentence outlines. It’s a task too often perceived as busywork, unnecessary, time consuming, and restricted. On one hand, we understand that reluctance. But on the other hand, we find that students who carefully write a full-sentence outline show a stronger tendency to give powerful presentations of excellent messages.
Outlines Test the Scope of Content
When you begin with a clear, concrete thesis statement, it acts as kind of compass for your outline. Each of the main points should directly explicate. The test of the scope will be a comparison of each main point to the thesis statement. If you find a poor match, you will know you’ve wandered outside the scope of the thesis.
Let’s say the general purpose of your speech is to inform, and your broad topic area is wind-generated energy. Now you must narrow this to a specific purpose. You have many choices, but let’s say your specific purpose is to inform a group of property owners about the economics of wind farms where electrical energy is generated.
Your first main point could be that modern windmills require a very small land base, making the cost of real estate low. This is directly related to economics. All you need is information to support your claim that only a small land base is needed.
In your second main point, you might be tempted to claim that windmills don’t pollute in the ways other sources do. However, you will quickly note that this claim is unrelated to the thesis. You must resist the temptation to add it. Perhaps in another speech, your thesis will address environmental impact, but in this speech, you must stay within the economic scope. Perhaps you will say that once windmills are in place, they require virtually no maintenance. This claim is related to the thesis. Now all you need is supporting information to support this second claim.
Your third point, the point some audience members will want to hear, is the cost for generating electrical energy with windmills compared with other sources. This is clearly within the scope of energy economics. You should have no difficulty finding authoritative sources of information to support that claim.
When you write in outline form, it is much easier to test the scope of your content because you can visually locate specific information very easily and then check it against your thesis statement.
Outlines Test the Logical Relation of Parts
You have many choices for your topic, and therefore, there are many ways your content can be logically organized. In the example above, we simply listed three main points that were important economic considerations about wind farms. Often the main points of a speech can be arranged into a logical pattern; let’s review some of these patterns:
A chronological pattern arranges main ideas in the order events occur. In some instances, reverse order might make sense. For instance, if your topic is archaeology, you might use the reverse order, describing the newest artifacts first.
A cause-and-effect pattern calls on you to describe a specific situation and explain what the effect is. However, most effects have more than one cause. Even dental cavities have multiple causes: genetics, poor nutrition, teeth too tightly spaced, sugar, ineffective brushing, and so on. If you choose a cause-and-effect pattern, make sure you have enough reliable support to do the topic justice.
A biographical pattern is usually chronological. In describing the events of an individual’s life, you will want to choose the three most significant events. Otherwise, the speech will end up as a very lengthy and often pointless timeline or bullet point list. For example, Mark Twain had several clear phases in his life. They include his life as a Mississippi riverboat captain, his success as a world-renowned writer and speaker, and his family life. A simple timeline would present great difficulty in highlighting the relationships between important events. An outline, however, would help you emphasize the key events that contributed to Mark Twain’s extraordinary life.
Although a comparison-contrast pattern appears to dictate just two main points, McCroskey, Wrench, and Richmond explain how a comparison-and-contrast can be structured as a speech with three main points. They say that “you can easily create a third point by giving basic information about what is being compared and what is being contrasted. For example, if you are giving a speech about two different medications, you could start by discussing what the medications’ basic purposes are. Then you could talk about the similarities, and then the differences, between the two medications” [1] .
Whatever logical pattern you use, if you examine your thesis statement and then look at the three main points in your outline, you should easily be able to see the logical way in which they relate.
Outlines Test the Relevance of Supporting Ideas
When you create an outline, you can clearly see that you need supporting evidence for each of your main points. For instance, using the example above, your first main point claims that less land is needed for windmills than for other utilities. Your supporting evidence should be about the amount of acreage required for a windmill and the amount of acreage required for other energy generation sites, such as nuclear power plants or hydroelectric generators. Your sources should come from experts in economics, economic development, or engineering. The evidence might even be expert opinion but not the opinions of ordinary people. The expert opinion will provide stronger support for your point.
Similarly, your second point claims that once a wind turbine is in place, there is virtually no maintenance cost. Your supporting evidence should show how much annual maintenance for a windmill costs, and what the costs are for other energy plants. If you used a comparison with nuclear plants to support your first main point, you should do so again for the sake of consistency. It becomes very clear, then, that the third main point about the amount of electricity and its profitability needs authoritative references to compare it to the profit from energy generated at a nuclear power plant. In this third main point, you should make use of just a few well-selected statistics from authoritative sources to show the effectiveness of wind farms compared to the other energy sources you’ve cited.
Where do you find the kind of information you would need to support these main points? A reference librarian can quickly guide you to authoritative statistics and help you make use of them.
An important step you will notice is that the full-sentence outline includes its authoritative sources within the text. This is a major departure from the way you’ve learned to write a research paper. In a research paper, you can add that information to the end of a sentence, leaving the reader to turn to the last page for a fuller citation. In a speech, however, your listeners can’t do that. From the beginning of the supporting point, you need to fully cite your source so your audience can assess its importance.
Because this is such a profound change from the academic habits that you’re probably used to, you will have to make a concerted effort to overcome the habits of the past and provide the information your listeners need when they need it.
Outlines Test the Balance and Proportion of the Speech
Part of the value of writing a full-sentence outline is the visual space you use for each of your main points. Is each main point of approximately the same importance? Does each main point have the same number of supporting points? If you find that one of your main points has eight supporting points while the others only have three each, you have two choices: either choose the best three from the eight supporting points or strengthen the authoritative support for your other two main points.
Remember that you should use the best supporting evidence you can find even if it means investing more time in your search for knowledge.
As you write the preparation outline, you may find it necessary to rearrange your points or to add or subtract supporting material. You may also realize that some of your main points are sufficiently supported while others are lacking. The final draft of your preparation outline should include full sentences, making up a complete script of your entire speech. In most cases, however, the preparation outline is reserved for planning purposes only and is translated into a speaking outline before you deliver the speech.
Outlines Serve as Notes during the Speech
Although we recommend writing a full-sentence outline during the speech preparation phase, you should also create a shortened outline that you can use as notes, a speaking outline, which allows for strong delivery. If you were to use the full-sentence outline when delivering your speech, you would do a great deal of reading, which would limit your ability to give eye contact and use gestures, hurting your connection with your audience.
Although some cases call for reading a speech verbatim from the full-sentence outline (manuscript delivery), in most cases speakers will simply refer to their speaking outline for quick reminders and to ensure that they do not omit any important information. For this reason, we recommend writing a short phrase speaking outline on 5×7 notecards to use when you deliver your speech.
In the next section, we will explore more fully how to create preparation and speaking outlines.
Outline Structure
Because an outline is used to arrange all of the elements of your speech, it makes sense that the outline itself has an organizational hierarchy and a common format. Although there are a variety of outline styles, generally they follow the same pattern. Main ideas are preceded by Roman numerals (I, II, III, etc.). Sub-points are preceded by capital letters (A, B, C, etc.), then Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.), and finally lowercase letters (a, b, c, etc.). Each level of subordination is also differentiated from its predecessor by indenting a few spaces. Indenting makes it easy to find your main points, sub-points, and the supporting points and examples below them. Since there are three sections to your speech— introduction, body, and conclusion— your outline needs to include all of them. Each of these sections is titled and the main points start with Roman numeral I.
OUTLINE FORMATTING GUIDE
Title: Organizing Your Public Speech
Topic: Organizing public speeches
Specific Purpose Statement: To inform my audience about the various ways in which they can organize their public speeches.
Thesis Statement: A variety of organizational styles can used to organize public speeches.
Introduction Paragraph that gets the attention of the audience, establishes goodwill with the audience, states the purpose of the speech, and previews the speech and its structure.
(Transition)
I. Main point
A. Sub-point B. Sub-point C. Sub-point
1. Supporting point 2. Supporting point
Conclusion Paragraph that prepares the audience for the end of the speech, presents any final appeals, and summarizes and wraps up the speech.
Bibliography
In addition to these formatting suggestions, there are some additional elements that should be included at the beginning of your outline: the title, topic, specific purpose statement, and thesis statement. These elements are helpful to you, the speechwriter, since they remind you what, specifically, you are trying to accomplish in your speech. They are also helpful to anyone reading and assessing your outline since knowing what you want to accomplish will determine how they perceive the elements included in your outline. Additionally, you should write out the transitional statements that you will use to alert audiences that you are moving from one point to another. These are included in parentheses between main points. At the end of the outlines, you should include bibliographic information for any outside resources you mention during the speech. These should be cited using whatever citations style your professor requires. The textbox entitled “Outline Formatting Guide” above provides an example of the appropriate outline format.
Preparation Outline Examples
This book contains the preparation outline for an informative speech the author gave about making guacamole (see third section). In this example, the title, specific purpose, and thesis precedes the speech. Depending on your instructor’s requirements, you may need to include these details plus additional information (like visual aids). It is also a good idea to keep these details at the top of your document as you write the speech since they will help keep you on track to developing an organized speech that is in line with your specific purpose and helps prove your thesis. At the end of this text, in Part 3, you will find full-length examples of Preparation (Full Sentence) Outlines, written by students just like you!

Using the Speaking Outline

“TAG speaks of others first” by Texas Military Forces. CC-BY-ND .
A speaking outline is the outline you will prepare for use when delivering the speech. The speaking outline is much more succinct than the preparation outline and includes brief phrases or words that remind the speakers of the points they need to make, plus supporting material and signposts. [2] The words or phrases used on the speaking outline should briefly encapsulate all of the information needed to prompt the speaker to accurately deliver the speech. Although some cases call for reading a speech verbatim from the full-sentence outline, in most cases speakers will simply refer to their speaking outline for quick reminders and to ensure that they do not omit any important information. Because it uses just words or short phrases, and not full sentences, the speaking outline can easily be transferred to index cards that can be referenced during a speech.
Speaking instructors often have requirements for how you should format the speaking outline. When formatting your speaking outline, here are a few tips:
First, write large enough so that you do not have to bring the cards close to your eyes to read them. Second, make sure you have the cards in the correct order and bound together in some way so that they do not get out of order. Third, just in case your cards do get out of order (this happens too often!), be sure that you number each in the top right corner so you can quickly and easily get things organized. Fourth, try not to fiddle with the cards when you are speaking. It is best to lay them down if you have a podium or table in front of you. If not, practice reading from them in front of a mirror. You should be able to look down quickly, read the text, and then return to your gaze to the audience.
Any intelligent fool can make things bigger and more complex… It takes a touch of genius – and a lot of courage to move in the opposite direction. – Albert Einstein
- McCroskey, J. C., Wrench, J. S., & Richmond, V. P., (2003). Principles of public speaking . Indianapolis, IN: The College Network.
- Beebe, S. A. & Beebe, S. J. (2003). The public speaking handbook (5th edition). Boston: Pearson. ↵
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
Cc licensed content, shared previously.
- Stand up, Speak out by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Chapter 8 Outlining Your Speech. Authored by : Joshua Trey Barnett. Provided by : University of Indiana, Bloomington, IN. Located at : http://publicspeakingproject.org/psvirtualtext.html . Project : The Public Speaking Project. License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- TAG speaks of others first. Authored by : Texas Military Forces. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/texasmilitaryforces/5560449970/ . License : CC BY-ND: Attribution-NoDerivatives
Principles of Public Speaking Copyright © 2022 by Katie Gruber is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Learning Objectives
- Explain the principles of outlining.
- Create a formal outline.
- Explain the importance of writing for speaking.
- Create a speaking outline.
Think of your outline as a living document that grows and takes form throughout your speech-making process. When you first draft your general purpose, specific purpose, and thesis statement, you could create a new document on your computer and plug those in, essentially starting your outline. As you review your research and distill the information down into separate central ideas that support your specific purpose and thesis, type those statements into the document. Once you’ve chosen your organizational pattern and are ready to incorporate supporting material, you can quote and paraphrase your supporting material along with the bibliographic information needed for your verbal citations into the document. By this point, you have a good working outline, and you can easily cut and paste information to move it around and see how it fits into the main points, subpoints, and sub-subpoints. As your outline continues to take shape, you will want to follow established principles of outlining to ensure a quality speech.
The Formal Outline
The formal outline is a full-sentence outline that helps you prepare for your speech. It includes the introduction and conclusion, the main content of the body, key supporting materials, citation information written into the sentences in the outline, and a references page for your speech. The formal outline also includes a title, the general purpose, specific purpose, and thesis statement. It’s important to note that an outline is different from a script. While a script contains everything that will be said, an outline includes the main content. Therefore you shouldn’t include every word you’re going to say on your outline. This allows you more freedom as a speaker to adapt to your audience during your speech. Students sometimes complain about having to outline speeches or papers, but it is a skill that will help you in other contexts. Being able to break a topic down into logical divisions and then connect the information together will help ensure that you can prepare for complicated tasks or that you’re prepared for meetings or interviews. I use outlines regularly to help me organize my thoughts and prepare for upcoming projects.
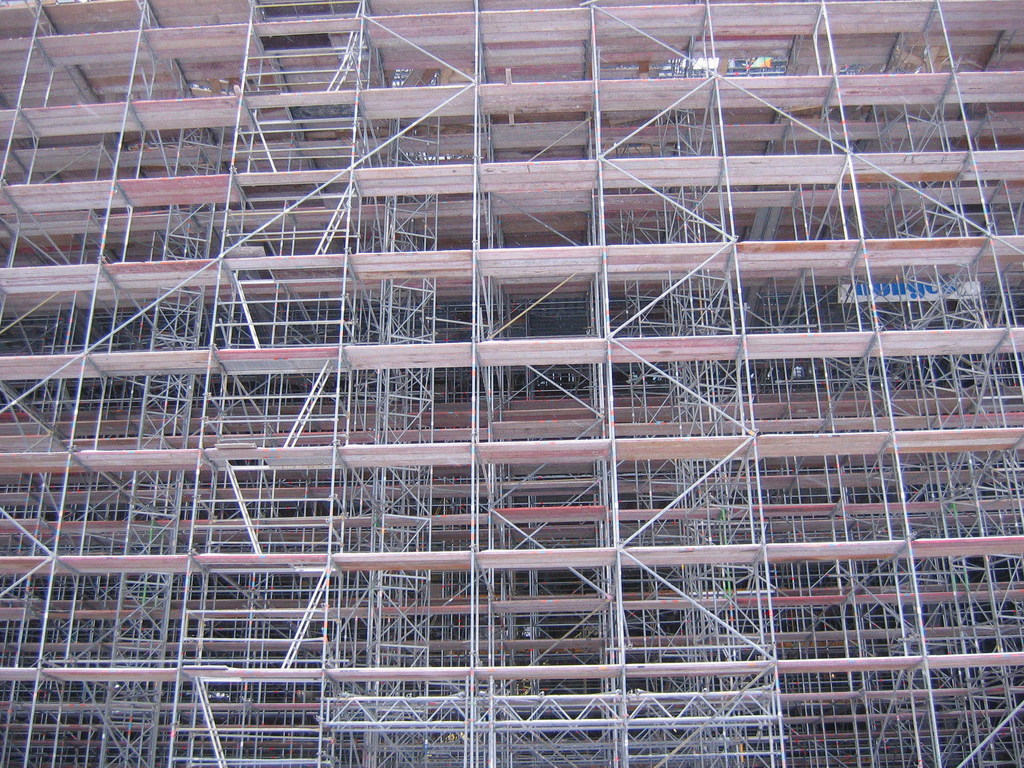
Outlining provides a scaffolding, or structure, that will help ensure your speech is logical, coherent, and organized.
Wikimedia Commons – CC BY 2.0.
Principles of Outlining
There are principles of outlining you can follow to make your outlining process more efficient and effective. Four principles of outlining are consistency, unity, coherence, and emphasis (DuBois, 1929). In terms of consistency, you should follow standard outlining format. In standard outlining format, main points are indicated by capital roman numerals, subpoints are indicated by capital letters, and sub-subpoints are indicated by Arabic numerals. Further divisions are indicated by either lowercase letters or lowercase roman numerals.
The principle of unity means that each letter or number represents one idea. One concrete way to help reduce the amount of ideas you include per item is to limit each letter or number to one complete sentence. If you find that one subpoint has more than one idea, you can divide it into two subpoints. Limiting each component of your outline to one idea makes it easier to then plug in supporting material and helps ensure that your speech is coherent. In the following example from a speech arguing that downloading music from peer-to-peer sites should be legal, two ideas are presented as part of a main point.
- Downloading music using peer-to-peer file-sharing programs helps market new music and doesn’t hurt record sales.
The main point could be broken up into two distinct ideas that can be more fully supported.
- Downloading music using peer-to-peer file-sharing programs helps market new music.
- Downloading music using peer-to-peer file-sharing programs doesn’t hurt record sales.
Following the principle of unity should help your outline adhere to the principle of coherence, which states that there should be a logical and natural flow of ideas, with main points, subpoints, and sub-subpoints connecting to each other (Winans, 1917). Shorter phrases and keywords can make up the speaking outline, but you should write complete sentences throughout your formal outline to ensure coherence. The principle of coherence can also be met by making sure that when dividing a main point or subpoint, you include at least two subdivisions. After all, it defies logic that you could divide anything into just one part. Therefore if you have an A , you must have a B , and if you have a 1 , you must have a 2 . If you can easily think of one subpoint but are having difficulty identifying another one, that subpoint may not be robust enough to stand on its own. Determining which ideas are coordinate with each other and which are subordinate to each other will help divide supporting information into the outline (Winans, 1917). Coordinate points are on the same level of importance in relation to the thesis of the speech or the central idea of a main point. In the following example, the two main points (I, II) are coordinate with each other. The two subpoints (A, B) are also coordinate with each other. Subordinate points provide evidence or support for a main idea or thesis. In the following example, subpoint A and subpoint B are subordinate to main point II. You can look for specific words to help you determine any errors in distinguishing coordinate and subordinate points. Your points/subpoints are likely coordinate when you would connect the two statements using any of the following: and , but , yet , or , or also . In the example, the word also appears in B, which connects it, as a coordinate point, to A. The points/subpoints are likely subordinate if you would connect them using the following: since , because , in order that , to explain , or to illustrate . In the example, 1 and 2 are subordinate to A because they support that sentence.
- They conclude that the rapid increase in music downloading over the past few years does not significantly contribute to declining record sales.
- Their research even suggests that the practice of downloading music may even have a “slight positive effect on the sales of the top albums.”
- A 2010 Government Accountability Office Report also states that sampling “pirated” goods could lead consumers to buy the “legitimate” goods.
The principle of emphasis states that the material included in your outline should be engaging and balanced. As you place supporting material into your outline, choose the information that will have the most impact on your audience. Choose information that is proxemic and relevant, meaning that it can be easily related to the audience’s lives because it matches their interests or ties into current events or the local area. Remember primacy and recency discussed earlier and place the most engaging information first or last in a main point depending on what kind of effect you want to have. Also make sure your information is balanced. The outline serves as a useful visual representation of the proportions of your speech. You can tell by the amount of space a main point, subpoint, or sub-subpoint takes up in relation to other points of the same level whether or not your speech is balanced. If one subpoint is a half a page, but a main point is only a quarter of a page, then you may want to consider making the subpoint a main point. Each part of your speech doesn’t have to be equal. The first or last point may be more substantial than a middle point if you are following primacy or recency, but overall the speech should be relatively balanced.
Sample Formal Outline
The following outline shows the standards for formatting and content and can serve as an example as you construct your own outline. Check with your instructor to see if he or she has specific requirements for speech outlines that may differ from what is shown here.
Title: The USA’s Neglected Sport: Soccer
General purpose: To persuade
Specific purpose: By the end of my speech, the audience will believe that soccer should be more popular in the United States.
Thesis statement: Soccer isn’t as popular in the United States as it is in the rest of the world because people do not know enough about the game; however, there are actions we can take to increase its popularity.
Introduction
Attention getter: GOOOOOOOOOOOOAL! GOAL! GOAL! GOOOOOOAL!
Introduction of topic: If you’ve ever heard this excited yell coming from your television, then you probably already know that my speech today is about soccer.
Credibility and relevance: Like many of you, I played soccer on and off as a kid, but I was never really exposed to the culture of the sport. It wasn’t until recently, when I started to watch some of the World Cup games with international students in my dorm, that I realized what I’d been missing out on. Soccer is the most popular sport in the world, but I bet that, like most US Americans, it only comes on your radar every few years during the World Cup or the Olympics. If, however, you lived anywhere else in the world, soccer (or football, as it is more often called) would likely be a much larger part of your life.
Preview: In order to persuade you that soccer should be more popular in the United States, I’ll explain why soccer isn’t as popular in the United States and describe some of the actions we should take to change our beliefs and attitudes about the game.
Transition: Let us begin with the problem of soccer’s unpopularity in America.
- The president of FIFA, which is the international governing body for soccer, was quoted in David Goldblatt’s 2008 book, The Ball is Round , as saying, “Football is as old as the world…People have always played some form of football, from its very basic form of kicking a ball around to the game it is today.”
- Basil Kane, author of the book Soccer for American Spectators , reiterates this fact when he states, “Nearly every society at one time or another claimed its own form of kicking game.”
- Our own “national sports” such as football, basketball, and baseball take up much of our time and attention, which may prevent people from engaging in an additional sport.
- Comparatively, 34 percent of those surveyed said that football was their favorite sport to watch.
- In fact, soccer just barely beat out ice skating, with 3 percent of the adults surveyed indicating that as their favorite sport to watch.
- According to the 2009 article from BleacherReport.com, “An American Tragedy: Two Reasons Why We Don’t Like Soccer,” the average length of a play in the NFL is six seconds, and there is a scoring chance in the NBA every twenty-four seconds.
- This stands in stark comparison to soccer matches, which are played in two forty-five-minute periods with only periodic breaks in play.
- The BleacherReport article also points out that unlike with football, basketball, and baseball—all sports in which the United States has most if not all the best teams in the world—we know that the best soccer teams in the world aren’t based in the United States.
- We also expect that sports will offer the same chances to compare player stats and obsess over data that we get from other sports, but as Chad Nielsen of ESPN.com states, “There is no quantitative method to compare players from different leagues and continents.”
- Last, as legendary sports writer Frank Deford wrote in a 2012 article on Sports Illustrated ’s website, Americans don’t like ties in sports, and 30 percent of all soccer games end tied, as a draw, deadlocked, or nil-nil.
Transition: Although soccer has many problems that it would need to overcome to be more popular in the United States, I think there are actions we can take now to change our beliefs and attitudes about soccer in order to give it a better chance.
- Fans argue every day, in bars and cafés from Baghdad to Bogotá, about statistics for goals and assists, but as Nielsen points out, with the game of soccer, such stats still fail to account for varieties of style and competition.
- So even though the statistics may be different, bonding over or arguing about a favorite team or player creates communities of fans that are just as involved and invested as even the most loyal team fans in the United States.
- The fact that soccer statistics aren’t poured over and used to make predictions makes the game more interesting.
- The fact that the segments of play in soccer are longer and the scoring lower allows for the game to have a longer arc, meaning that anticipation can build and that a game might be won or lost by only one goal after a long and even-matched game.
- There is most likely a minor or even a major league soccer stadium team within driving distance of where you live.
- You can also go to soccer games at your local high school, college, or university.
- We can also join the rest of the world in following some of the major soccer celebrities—David Beckham is just the tip of the iceberg.
- Soccer can easily be the most athletic sport available to Americans.
- In just one game, the popular soccer player Gennaro Gattuso was calculated to have run about 6.2 miles, says Carl Bialik, a numbers expert who writes for The Wall Street Journal .
- A press release on FIFA’s official website notes that one hour of soccer three times a week has been shown in research to provide significant physical benefits.
- If that’s not convincing enough, the website ScienceDaily.com reports that the Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports published a whole special issue titled Football for Health that contained fourteen articles supporting the health benefits of soccer.
- The nongovernmental organization Soccer for Peace seeks to use the worldwide popularity of soccer as a peacemaking strategy to bridge the divides of race, religion, and socioeconomic class.
- Over those ten years the organization has focused on using soccer to bring together people of different religious faiths, particularly people who are Jewish and Muslim.
- In 2012, three first-year college students, one Christian, one Jew, and one Muslim, dribbled soccer balls for 450 miles across the state of North Carolina to help raise money for Soccer for Peace.
- A press release on the World Association of Nongovernmental Organizations’s official website states that from the dusty refugee camps of Lebanon to the upscale new neighborhoods in Buenos Aires, “soccer turns heads, stops conversations, causes breath to catch, and stirs hearts like virtually no other activity.”
Transition to conclusion and summary of importance: In conclusion, soccer is a sport that has a long history, can help you get healthy, and can bring people together.
Review of main points: Now that you know some of the obstacles that prevent soccer from becoming more popular in the United States and several actions we can take to change our beliefs and attitudes about soccer, I hope you agree with me that it’s time for the United States to join the rest of the world in welcoming soccer into our society.
Closing statement: The article from BleacherReport.com that I cited earlier closes with the following words that I would like you to take as you leave here today: “We need to learn that just because there is no scoring chance that doesn’t mean it is boring. We need to see that soccer is not for a select few, but for all. We only need two feet and a ball. We need to stand up and appreciate the beautiful game.”
Araos, C. (2009, December 10). An American tragedy: Two reasons why we don’t like soccer. Bleacher Report: World Football . Retrieved from http://bleacherreport.com/articles/306338-an-american-tragedy-the-two-reasons-why-we-dont-like-soccer
Bialik, C. (2007, May 23). Tracking how far soccer players run. WSJ Blogs: The Numbers Guy . Retrieved from http://blogs.wsj.com/numbersguy/tracking-how-far-soccer-players-run-112
Deford, F. (2012, May 16). Americans don’t like ties in sports. SI.com : Viewpoint. Retrieved from http://sportsillustrated.cnn.com/2012/writers/frank_deford/05/16/Americans-do-not-like-ties/index.html
FIFA.com (2007, September 6). Study: Playing football provides health benefits for all. Retrieved from http://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/footballdevelopment/medical/news/newsid=589317/index.html
Goldblatt, D. (2008). The ball is round: A global history of soccer . New York, NY: Penguin.
Kane, B. (1970). Soccer for American spectators: A fundamental guide to modern soccer . South Brunswick, NJ: A. S. Barnes.
Nielsen, C. (2009, May 27). “What I do is play soccer.” ESPN . Retrieved from http://sports.espn.go.com/espn/news/story?id=4205057
Pew Research Center. (2006, June 14). Americans to rest of world: Soccer not really our thing. Pew Research Center . Retrieved from http://pewresearch.org/pubs/315/americans-to-rest-of-world-soccer-not-really-our-thing
ScienceDaily.com. (2010, April 7). Soccer improves health, fitness, and social abilities. ScienceDaily.com: Science news . Retrieved from http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/04/100406093524.htm
Selle, R. R. (n.d.). Soccer for peace. Wango.org: News . Retrieved from http://www.wango.org/news/news/psmp.htm
Soccer For Peace. (2012). Kicking across Carolina. SFP news . Retrieved from http://www.soccerforpeace.com/2012-10-03-17-18-08/sfp-news/44-kicking-across-carolina.html
Examples of APA Formatting for References
The citation style of the American Psychological Association (APA) is most often used in communication studies when formatting research papers and references. The following examples are formatted according to the sixth edition of the APA Style Manual. Links are included to the OWL Purdue website, which is one of the most credible online sources for APA format. Of course, to get the most accurate information, it is always best to consult the style manual directly, which can be found in your college or university’s library.
For more information on citing books in APA style on your references page, visit http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/08 .
Single Author
Two Authors
Warren, J. T., & Fassett, D. L. (2011). Communication: A critical/cultural introduction . Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Chapter from Edited Book
Mumby, D. K. (2011). Power and ethics. In G. Cheney, S. May, & D. Munshi (Eds.), The handbook of communication ethics (pp. 84–98). New York, NY: Routledge.
Periodicals
For more information on citing articles from periodicals in APA style on your references page, visit http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/07 .
Huang, L. (2011, August 1). The death of English (LOL). Newsweek, 152 (6), 8.
Kornblum, J. (2007, October 23). Privacy? That’s old-school: Internet generation views openness in a different way. USA Today , 1D–2D.
Journal Article
Bodie, G. D. (2012). A racing heart, rattling knees, and ruminative thoughts: Defining, explaining, and treating public speaking anxiety. Communication Education, 59 (1), 70–105.
Online Sources
For more information on citing articles from online sources in APA style on your references page, visit http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/10 .
Online Newspaper Article
Perman, C. (2011, September 8). Bad economy? A good time for a steamy affair. USA Today . Retrieved from http://www.usatoday.com/money/economy/story/2011-09-10/economy-affairs-divorce-marriage/50340948/1
Online News Website
Fraser, C. (2011, September 22). The women defying France’s full-face veil ban. BBC News . Retrieved from http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-15023308
Online Magazine
Cullen, L. T. (2007, April 26). Employee diversity training doesn’t work. Time . Retrieved from http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1615183,00.html
Government Document or Report Retrieved Online
Pew Research Center. (2010, November 18). The decline of marriage and rise of new families. Retrieved from http://pewsocialtrends.org/files/2010/11/pew-social-trends-2010-families.pdf
Kwintessential. (n.d.). Cross cultural business blunders. Retrieved from http://www.kwintessential.co.uk/cultural-services/articles/crosscultural-blunders.html
The Speaking Outline
The formal outline is a full-sentence outline that helps as you prepare for your speech, and the speaking outline is a keyword and phrase outline that helps you deliver your speech. While the formal outline is important to ensure that your content is coherent and your ideas are balanced and expressed clearly, the speaking outline helps you get that information out to the audience. Make sure you budget time in your speech preparation to work on the speaking outline. Skimping on the speaking outline will show in your delivery.

Using note cards for your speaking outline will help you be able to move around and gesture more freely than using full sheets of paper.
Justin See (coming back) – My Pile of Index Card – CC BY 2.0.
You may convert your formal outline into a speaking outline using a computer program. I often resave a file and then reformat the text so it’s more conducive to referencing while actually speaking to an audience. You may also choose, or be asked to, create a speaking outline on note cards. Note cards are a good option when you want to have more freedom to gesture or know you won’t have a lectern on which to place notes printed on full sheets of paper. In either case, this entails converting the full-sentence outline to a keyword or key-phrase outline. Speakers will need to find a balance between having too much or too little content on their speaking outlines. You want to have enough information to prevent fluency hiccups as you stop to mentally retrieve information, but you don’t want to have so much information that you read your speech, which lessens your eye contact and engagement with the audience. Budgeting sufficient time to work on your speaking outline will allow you to practice your speech with different amounts of notes to find what works best for you. Since the introduction and conclusion are so important, it may be useful to include notes to ensure that you remember to accomplish all the objectives of each.
Aside from including important content on your speaking outline, you may want to include speaking cues. Speaking cues are reminders designed to help your delivery. You may write “(PAUSE)” before and after your preview statement to help you remember that important nonverbal signpost. You might also write “(MAKE EYE CONTACT)” as a reminder not to read unnecessarily from your cards. Overall, my advice is to make your speaking outline work for you. It’s your last line of defense when you’re in front of an audience, so you want it to help you, not hurt you.
Writing for Speaking
As you compose your outlines, write in a way that is natural for you to speak but also appropriate for the expectations of the occasion. Since we naturally speak with contractions, write them into your formal and speaking outlines. You should begin to read your speech aloud as you are writing the formal outline. As you read each section aloud, take note of places where you had difficulty saying a word or phrase or had a fluency hiccup, then go back to those places and edit them to make them easier for you to say. This will make you more comfortable with the words in front of you while you are speaking, which will improve your verbal and nonverbal delivery.
Tips for Note Cards
- The 4 × 6 inch index cards provide more space and are easier to hold and move than 3.5 × 5 inch cards.
- Find a balance between having so much information on your cards that you are tempted to read from them and so little information that you have fluency hiccups and verbal fillers while trying to remember what to say.
- Use bullet points on the left-hand side rather than writing in paragraph form, so your eye can easily catch where you need to pick back up after you’ve made eye contact with the audience. Skipping a line between bullet points may also help.
- Include all parts of the introduction/conclusion and signposts for backup.
- Include key supporting material and wording for verbal citations.
- Only write on the front of your cards.
- Do not have a sentence that carries over from one card to the next (can lead to fluency hiccups).
- If you have difficult-to-read handwriting, you may type your speech and tape or glue it to your cards. Use a font that’s large enough for you to see and be neat with the glue or tape so your cards don’t get stuck together.
- Include cues that will help with your delivery. Highlight transitions, verbal citations, or other important information. Include reminders to pause, slow down, breathe, or make eye contact.
- Your cards should be an extension of your body, not something to play with. Don’t wiggle, wring, flip through, or slap your note cards.
Key Takeaways
- The formal outline is a full-sentence outline that helps you prepare for your speech and includes the introduction and conclusion, the main content of the body, citation information written into the sentences of the outline, and a references page.
- The principles of outlining include consistency, unity, coherence, and emphasis.
- Coordinate points in an outline are on the same level of importance in relation to the thesis of the speech or the central idea of a main point. Subordinate points provide evidence for a main idea or thesis.
- The speaking outline is a keyword and phrase outline that helps you deliver your speech and can include speaking cues like “pause,” “make eye contact,” and so on.
- Write your speech in a manner conducive to speaking. Use contractions, familiar words, and phrases that are easy for you to articulate. Reading your speech aloud as you write it can help you identify places that may need revision to help you more effectively deliver your speech.
- What are some practical uses for outlining outside of this class? Which of the principles of outlining do you think would be most important in the workplace and why?
- Identify which pieces of information you may use in your speech are coordinate with each other and subordinate.
- Read aloud what you’ve written of your speech and identify places that can be reworded to make it easier for you to deliver.
DuBois, W. C., Essentials of Public Speaking (New York: Prentice Hall, 1929), 104.
Winans, J. A., Public Speaking (New York: Century, 1917), 407.
Public Speaking Copyright © 2023 by University of Nebraska at Omaha is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

8.4 Outlining Your Speech

Most speakers and audience members would agree that an organized speech is both easier to present as well as easier for the audience to understand. Public speaking teachers especially believe in the power of organizing your speech, which is why they encourage (and often require) that you create an outline for your speech. Outlines, or textual arrangements of all the various elements of a speech, are a very common way of organizing a speech before it is delivered. Most extemporaneous speakers keep their outlines with them during the speech to ensure that they do not leave out any important elements and to keep them on track.
Writing an outline is also important to the speechwriting process, since doing so forces the speakers to think about the main ideas, known as main points, and subpoints, the examples they wish to include, and the ways in which these elements correspond to one another. In short, the outline functions both as an organization tool and as a reference for delivering a speech.
Outline Types
There are two types of outlines: the preparation outline and the speaking outline.
Preparation Outline
The first outline you will write is called the preparation outline . Also called a skeletal, working, practice, or rough outline, the preparation outline is used to work through the various components of your speech in an organized format. Stephen E. Lucas (2004) put it simply: “The preparation outline is just what its name implies—an outline that helps you prepare the speech.” When writing the preparation outline, you should focus on finalizing the specific purpose and thesis statement, logically ordering your main points, deciding where supporting material should be included, and refining the overall organizational pattern of your speech. As you write the preparation outline, you may find it necessary to rearrange your points or to add or subtract supporting material. You may also realize that some of your main points are sufficiently supported while others are lacking. The final draft of your preparation outline should include full sentences. In most cases, however, the preparation outline is reserved for planning purposes only and is translated into a speaking outline before you deliver the speech. Keep in mind though, even a full sentence outline is not an essay.
Speaking Outline
A speaking outline is the outline you will prepare for use when delivering the speech. The speaking outline is much more succinct than the preparation outline and includes brief phrases or words that remind the speakers of the points they need to make, plus supporting material and signposts (Beebe & Beebe, 2003). The words or phrases used on the speaking outline should briefly encapsulate all the information needed to prompt the speaker to accurately deliver the speech. Although some cases call for reading a speech verbatim from the full-sentence outline, in most cases speakers will simply refer to their speaking outline for quick reminders and to ensure that they do not omit any important information. Because it uses just words or short phrases, and not full sentences, the speaking outline can easily be transferred to index cards that can be referenced during a speech. However, check with your instructor regarding what you will be allowed to use for your speech.
Components of Outlines
The main components of the outlines are the main points, subordination and coordination, parallelism, division, and the connection of main points.
Main Points
Main points are the main ideas in the speech and support the thesis. In other words, the main points are what your audience should remember from your talk, and they are phrased as single, declarative sentences. These are never phrased as a question, nor can they be a quote or form of citation. Any supporting material you have will be put in your outline as a subpoint. Since this is a public speaking class, your instructor will decide how long your speeches will be, but in general, you can assume that no speech will be longer than 10 minutes in length. Given that alone, we can make one assumption. All speeches will fall between 2 to 5 main points based simply on length; however, 3 main points is the ideal for a speech of this length. If you are working on an outline and you have ten main points, something is wrong, and you need to revisit your ideas to see how you need to reorganize your points.
All main points are preceded by Roman numerals (I, II, III, etc.). Subpoints are preceded by capital letters (A, B, C, etc.), then Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.), lowercase letters (a, b, c, etc.). You can subordinate further than this. Speak with your instructor regarding his or her specific instructions. Each level of subordination is also differentiated from its predecessor by indenting a few spaces. Indenting makes it easy to find your main points, subpoints, and the supporting points and examples below them.
Let’s work on understanding how to take main points and break them into smaller ideas by subordinating them further and further as we go by using the following outline example:
Topic : Dogs
Specific Purpose : To inform my audience about characteristics of dogs
Thesis : There are many types of dogs that individuals can select from before deciding which would make the best family pet.
Preview : First, I will describe the characteristics of large breed dogs, and then I will discuss characteristics of small breed dogs.
Subordination and Coordination
You should have noticed that as ideas were broken down, or subordinated, there was a hierarchy to the order. To check your outline for coherence, think of the outline as a staircase. All of the points that are beneath and on a diagonal to the points above them are subordinate points. Using the above example, points A, B, and C dealt with characteristics of large breed dogs, and those points are all subordinate to main point I. Similarly, points 1 and 2 under point C both dealt with drool, so those are subordinate. This is the subordination of points. If we had discussed food under point C, you would know that something didn’t make sense. You will also see that there is coordination of points. As part of the hierarchy, coordination simply means that all of the numbers or letters should represent the same idea. In this example, A, B, and C were all characteristics, so those are all coordinated to each other. Had C been “German Shepherd,” then the outline would have been incorrect because that is a type of dog, not a characteristic.
Parallelism
Another important rule in outlining is known as parallelism . This means that when possible, you begin your sentences in a similar way, using a similar grammatical structure. For example, in the previous example on dogs, some of the sentences began “some large breed dogs.” This type of structure adds clarity to your speaking. Students often worry that parallelism will sound boring. It’s actually the opposite! It adds clarity. Remember that a speech is verbal and once the information is stated, it is gone. The key to creating a memorable speech is ensuring the audience can follow the speech and has something to remember at the end of the speech.
The principle of division is an important part of outlining. When you have a main point, you will be explaining it. You should have enough meaningful information that you can divide it into two subpoints A and B. If subpoint A has enough information that you can explain it, then it, too, should be able to be divided into two subpoints. So, division means this: If you have an A, then you need a B; if you have a 1, then you need a 2, and so on. What if you cannot divide the point? In a case like that you would simply incorporate the information in the point above.
Connecting Your Main Points
One way to connect points is to include transitional statements . Transitional statements are phrases or sentences that lead from one distinct-but-connected idea to another. They are used to alert the audience to the fact that you are getting ready to discuss something else. Transitions are the bridges that move the audience through the speech; it is important that the speech is organized and the audience is clear on what point or subpoint we are presenting. When moving from one point to another, your transition may just be a word or short phrase, known as a signpost. For instance, you might say “next,” “also,” or “moreover.” You can also enumerate your speech points and signal transitions by starting each point with “First,” “Second,” “Third,” et cetera. You might also incorporate non-verbal transitions, such as brief pauses or a movement across the stage. Pausing to look at your audience, stepping out from behind a podium, or even raising or lowering the rate of your voice can signal to audience members that you are transitioning.
Another way to incorporate transitions into your speech is by offering internal summaries and internal previews within your speech. Summaries provide a recap of what has already been said, making it more likely that audiences will remember the points that they hear again. For example, an internal summary may sound like this:
So far, we have seen that the pencil has a long and interesting history. We also looked at the many uses the pencil has that you may not have known about previously.
Like the name implies, internal previews lay out what will occur next in your speech. They are longer than transitional words or signposts .
Next, let us explore what types of pencils there are to pick from that will be best for your specific project.
Additionally, summaries can be combined with internal previews to alert audience members that the next point builds on those that they have already heard.
Now that I have told you about the history of the pencil, as well as its many uses, let’s look at what types of pencils you can pick from that might be best for your project.
It is important to understand that if you use an internal summary and internal preview between main points, you need to state a clear main point following the internal preview. Here’s an example integrating all the points on the pencil:
I. First, let me tell you about the history of the pencil.
So far we have seen that the pencil has a long and interesting history. Now, we can look at how the pencil can be used (internal summary, signpost, and internal preview).
II. The pencil has many different uses, ranging from writing to many types of drawing.
Now that I have told you about the history of the pencil, as well as its many uses, let’s look at what types of pencils you can pick from that might be best for your project (Signpost, internal summary, and preview).
III. There are over fifteen different types of pencils to choose from ranging in hardness and color.
In Conclusion
Had Meg, the student mentioned in the opening anecdote, taken some time to work through the organizational process, it is likely her speech would have gone much more smoothly when she finished her introduction. It is very common for beginning speakers to spend a great deal of their time preparing catchy introductions, fancy PowerPoint presentations, and nice conclusions, which are all very important. However, the body of any speech is where the speaker must make effective arguments, provide helpful information, entertain, and present all the important information in the speech, so it makes sense that speakers should devote a proportionate amount of time to these areas as well. By following this chapter, as well as studying the other chapters in this text, you should be prepared to craft interesting, compelling, and organized speeches.
used to work through the various components of your speech in an organized format
much more succinct than the preparation outline and includes brief phrases or words that remind the speakers of the points they need to make, plus supporting material and signposts
the main ideas in the speech
a hierarchy to the order of the points of a speech
all of the numbers or letters of points should represent the same idea
the repetition of grammatical structures that correspond in sound, meter, or meaning
if you have an A, then you need a B; if you have a 1, then you need a 2, and so on
phrases or sentences that lead from one distinct-but-connected idea to another
transition using just a word or short phrase
It’s About Them: Public Speaking in the 21st Century Copyright © 2022 by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 4: Organizing and Outlining
Outlining your speech.
Most speakers and audience members would agree that an organized speech is both easier to present as well as more persuasive. Public speaking teachers especially believe in the power of organizing your speech, which is why they encourage (and often require) that you create an outline for your speech. Outlines , or textual arrangements of all the various elements of a speech, are a very common way of organizing a speech before it is delivered. Most extemporaneous speakers keep their outlines with them during the speech as a way to ensure that they do not leave out any important elements and to keep them on track. Writing an outline is also important to the speechwriting process since doing so forces the speakers to think about the main points and sub-points, the examples they wish to include, and the ways in which these elements correspond to one another. In short, the outline functions both as an organization tool and as a reference for delivering a speech.
Outline Types

“Alpena Mayor Carol Shafto Speaks at 2011 Michigan Municipal League Convention” by Michigan Municipal League. CC-BY-ND .
There are two types of outlines. The first outline you will write is called the preparation outline . Also called a working, practice, or rough outline, the preparation outline is used to work through the various components of your speech in an inventive format. Stephen E. Lucas [1] put it simply: “The preparation outline is just what its name implies—an outline that helps you prepare the speech” (p. 248). When writing the preparation outline, you should focus on finalizing the purpose and thesis statements, logically ordering your main points, deciding where supporting material should be included, and refining the overall organizational pattern of your speech. As you write the preparation outline, you may find it necessary to rearrange your points or to add or subtract supporting material. You may also realize that some of your main points are sufficiently supported while others are lacking. The final draft of your preparation outline should include full sentences, making up a complete script of your entire speech. In most cases, however, the preparation outline is reserved for planning purposes only and is translated into a speaking outline before you deliver the speech.
A speaking outline is the outline you will prepare for use when delivering the speech. The speaking outline is much more succinct than the preparation outline and includes brief phrases or words that remind the speakers of the points they need to make, plus supporting material and signposts. [2] The words or phrases used on the speaking outline should briefly encapsulate all of the information needed to prompt the speaker to accurately deliver the speech. Although some cases call for reading a speech verbatim from the full-sentence outline, in most cases speakers will simply refer to their speaking outline for quick reminders and to ensure that they do not omit any important information. Because it uses just words or short phrases, and not full sentences, the speaking outline can easily be transferred to index cards that can be referenced during a speech.
Outline Structure
Because an outline is used to arrange all of the elements of your speech, it makes sense that the outline itself has an organizational hierarchy and a common format. Although there are a variety of outline styles, generally they follow the same pattern. Main ideas are preceded by Roman numerals (I, II, III, etc.). Sub-points are preceded by capital letters (A, B, C, etc.), then Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.), and finally lowercase letters (a, b, c, etc.). Each level of subordination is also differentiated from its predecessor by indenting a few spaces. Indenting makes it easy to find your main points, sub-points, and the supporting points and examples below them. Since there are three sections to your speech— introduction, body, and conclusion— your outline needs to include all of them. Each of these sections is titled and the main points start with Roman numeral I.
Outline Formatting Guide
Title: Organizing Your Public Speech
Topic: Organizing public speeches
Specific Purpose Statement: To inform listeners about the various ways in which they can organize their public speeches.
Thesis Statement: A variety of organizational styles can used to organize public speeches.
Introduction Paragraph that gets the attention of the audience, establishes goodwill with the audience, states the purpose of the speech, and previews the speech and its structure.
(Transition)
I. Main point
A. Sub-point B. Sub-point C. Sub-point
1. Supporting point 2. Supporting point
Conclusion Paragraph that prepares the audience for the end of the speech, presents any final appeals, and summarizes and wraps up the speech.
Bibliography
In addition to these formatting suggestions, there are some additional elements that should be included at the beginning of your outline: the title, topic, specific purpose statement, and thesis statement. These elements are helpful to you, the speechwriter, since they remind you what, specifically, you are trying to accomplish in your speech. They are also helpful to anyone reading and assessing your outline since knowing what you want to accomplish will determine how they perceive the elements included in your outline. Additionally, you should write out the transitional statements that you will use to alert audiences that you are moving from one point to another. These are included in parentheses between main points. At the end of the outlines, you should include bibliographic information for any outside resources you mention during the speech. These should be cited using whatever citations style your professor requires. The textbox entitled “Outline Formatting Guide” provides an example of the appropriate outline format.
If you do not change direction, you may end up where you are heading. – Lao Tzu
Preparation Outline
This chapter contains the preparation and speaking outlines for a short speech the author of this chapter gave about how small organizations can work on issues related to climate change (see appendices). In this example, the title, specific purpose, thesis, and list of visual aids precedes the speech. Depending on your instructor’s requirements, you may need to include these details plus additional information. It is also a good idea to keep these details at the top of your document as you write the speech since they will help keep you on track to developing an organized speech that is in line with your specific purpose and helps prove your thesis. At the end of the chapter, in Appendix A, you can find a full length example of a Preparation (Full Sentence) Outline.
Speaking Outline
In Appendix B, the Preparation Outline is condensed into just a few short key words or phrases that will remind speakers to include all of their main points and supporting information. The introduction and conclusion are not included since they will simply be inserted from the Preparation Outline. It is easy to forget your catchy attention-getter or final thoughts you have prepared for your audience, so it is best to include the full sentence versions even in your speaking outline.
Using the Speaking Outline

“TAG speaks of others first” by Texas Military Forces. CC-BY-ND .
Once you have prepared the outline and are almost ready to give your speech, you should decide how you want to format your outline for presentation. Many speakers like to carry a stack of papers with them when they speak, but others are more comfortable with a smaller stack of index cards with the outline copied onto them. Moreover, speaking instructors often have requirements for how you should format the speaking outline. Whether you decide to use index cards or the printed outline, here are a few tips. First, write large enough so that you do not have to bring the cards or pages close to your eyes to read them. Second, make sure you have the cards/pages in the correct order and bound together in some way so that they do not get out of order. Third, just in case the cards/pages do get out of order (this happens too often!), be sure that you number each in the top right corner so you can quickly and easily get things organized. Fourth, try not to fiddle with the cards/pages when you are speaking. It is best to lay them down if you have a podium or table in front of you. If not, practice reading from them in front of a mirror. You should be able to look down quickly, read the text, and then return to your gaze to the audience.
Any intelligent fool can make things bigger and more complex… It takes a touch of genius – and a lot of courage to move in the opposite direction. – Albert Einstein
- Lucas, Stephen E. (2004). The art of public speaking (8th edition). New York: McGraw-Hill. ↵
- Beebe, S. A. & Beebe, S. J. (2003). The public speaking handbook (5th edition). Boston: Pearson. ↵
- Chapter 8 Outlining Your Speech. Authored by : Joshua Trey Barnett. Provided by : University of Indiana, Bloomington, IN. Located at : http://publicspeakingproject.org/psvirtualtext.html . Project : The Public Speaking Project. License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Alpena Mayor Carol Shafto Speaks at 2011 Michigan Municipal League Convention. Authored by : Michigan Municipal League. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/aunJMR . License : CC BY-ND: Attribution-NoDerivatives
- TAG speaks of others first. Authored by : Texas Military Forces. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/texasmilitaryforces/5560449970/ . License : CC BY-ND: Attribution-NoDerivatives

Privacy Policy
- Personal Development
- Sales Training
- Business Training
- Time Management
- Leadership Training
- Book Writing
- Public Speaking
- Live Speaker Training With Brian
- See Brian Speak
- Coaching Programs
- Become a Coach
- Personal Success
- Sales Success
- Business Success
- Leadership Success
How To Write A Speech Outline
Do you have a speech coming up soon, but don’t know where to start when it comes to writing it?
Don’t worry.
The best way to start writing your speech is to first write an outline.
While to some, an outline may seem like an unnecessary extra step — after giving hundreds of speeches in my own career, I can assure you that first creating a speech outline is truly the best way to design a strong presentation that your audience will remember.
Should I Write A Speech Outline?
You might be wondering if you should really bother with a preparation outline. Is a speaking outline worth your time, or can you get through by just keeping your supporting points in mind?
Again, I highly recommend that all speakers create an outline as part of their speechwriting process. This step is an extremely important way to organize your main ideas and all the various elements of your speech in a way that will command your audience’s attention.
Good public speaking teachers will agree that an outline—even if it’s a rough outline—is the easiest way to propel you forward to a final draft of an organized speech that audience members will love.
Here are a few of the biggest benefits of creating an outline before diving straight into your speech.
Gain More Focus
By writing an outline, you’ll be able to center the focus of your speech where it belongs—on your thesis statement and main idea.
Remember, every illustration, example, or piece of information you share in your speech should be relevant to the key message you’re trying to deliver. And by creating an outline, you can ensure that everything relates back to your main point.
Keep Things Organized
Your speech should have an overall organizational pattern so that listeners will be able to follow your thoughts. You want your ideas to be laid out in a logical order that’s easy to track, and for all of the speech elements to correspond.
An outline serves as a structure or foundation for your speech, allowing you to see all of your main points laid out so you can easily rearrange them into an order that makes sense for easy listening.
Create Smoother Transitions
A speaking outline helps you create smoother transitions between the different parts of your speech.
When you know what’s happening before and after a certain section, it will be easy to accurately deliver transitional statements that make sense in context. Instead of seeming like several disjointed ideas, the parts of your speech will naturally flow into each other.
Save Yourself Time
An outline is an organization tool that will save you time and effort when you get ready to write the final draft of your speech. When you’re working off of an outline to write your draft, you can overcome “blank page syndrome.”
It will be much easier to finish the entire speech because the main points and sub-points are already clearly laid out for you.
Your only job is to finish filling everything in.
Preparing to Write A Speech Outline
Now that you know how helpful even the most basic of speech outlines can be in helping you write the best speech, here’s how to write the best outline for your next public speaking project.
How Long Should A Speech Outline Be?
The length of your speech outline will depend on the length of your speech. Are you giving a quick two-minute talk or a longer thirty-minute presentation? The length of your outline will reflect the length of your final speech.
Another factor that will determine the length of your outline is how much information you actually want to include in the outline. For some speakers, bullet points of your main points might be enough. In other cases, you may feel more comfortable with a full-sentence outline that offers a more comprehensive view of your speech topic.
The length of your outline will also depend on the type of outline you’re using at any given moment.
Types of Outlines
Did you know there are several outline types? Each type of outline is intended for a different stage of the speechwriting process. Here, we’re going to walk through:
- Working outlines
- Full-sentence outlines
- Speaking outlines
Working Outline
Think of your working outline as the bare bones of your speech—the scaffolding you’re using as you just start to build your presentation. To create a working outline, you will need:
- A speech topic
- An idea for the “hook” in your introduction
- A thesis statement
- 3-5 main points (each one should make a primary claim that you support with references)
- A conclusion
Each of your main points will also have sub-points, but we’ll get to those in a later step.
The benefit of a working outline is that it’s easy to move things around. If you think your main points don’t make sense in a certain order—or that one point needs to be scrapped entirely—it’s no problem to make the needed changes. You won’t be deleting any of your prior hard work because you haven’t really done any work yet.
Once you are confident in this “skeleton outline,” you can move on to the next, where you’ll start filling in more detailed information.
Full-sentence outline
As the name implies, your full-sentence outline contains full sentences. No bullet points or scribbled, “talk about x, y, z here.” Instead, research everything you want to include and write out the information in full sentences.
Why is this important? A full-sentence outline helps ensure that you are:
- Including all of the information your audience needs to know
- Organizing the material well
- Staying within any time constraints you’ve been given
Don’t skip this important step as you plan your speech.
Speaking outline
The final type of outline you’ll need is a speaking outline. When it comes to the level of detail, this outline is somewhere in between your working outline and a full-sentence outline.
You’ll include the main parts of your speech—the introduction, main points, and conclusion. But you’ll add a little extra detail about each one, too. This might be a quote that you don’t want to misremember or just a few words to jog your memory of an anecdote to share.
When you actually give your speech, this is the outline you will use. It might seem like it makes more sense to use your detailed full-sentence outline up on stage. However, if you use this outline, it’s all too easy to fall into the trap of reading your speech—which is not what you want to do. You’ll likely sound much more natural if you use your speaking outline.
How to Write A Speech Outline
We’ve covered the types of outlines you’ll work through as you write your speech. Now, let’s talk more about how you’ll come up with the information to add to each outline type.
Pick A Topic
Before you can begin writing an outline, you have to know what you’re going to be speaking about. In some situations, you may have a topic given to you—especially if you are in a public speaking class and must follow the instructor’s requirements. But in many cases, speakers must come up with their own topic for a speech.
Consider your audience and what kind of educational, humorous, or otherwise valuable information they need to hear. Your topic and message should of course be highly relevant to them. If you don’t know your audience well enough to choose a topic, that’s a problem.
Your audience is your first priority. If possible, however, it’s also helpful to choose a topic that appeals to you. What’s something you’re interested in and/or knowledgeable about?
It will be much easier to write a speech on a topic you care about rather than one you don’t. If you can come up with a speech topic that appeals to your audience and is interesting to you, that’s the sweet spot for writing and delivering an unforgettable speech.
Write A Thesis Statement
The next step is to ask yourself two important questions:
- What do you want your audience to take away from your speech?
- How will you communicate this main message?
The key message of your speech can also be called your “thesis statement.”
Essentially, this is your main point—the most important thing you hope to get across.
You’ll most likely actually say your thesis statement verbatim during your speech. It should come at the end of your introduction. Then, you’ll spend the rest of your talk expanding on this statement, sharing more information that will prove the statement is true.
Consider writing your thesis statement right now—before you begin researching or outlining your speech. If you can refer back to this statement as you get to work, it will be much easier to make sure all of the elements correspond with each other throughout your speech.
An example of a good thesis statement might read like this:
- Going for a run every day is good for your health.
- It’s important to start saving for retirement early.
- The COVID-19 pandemic had a negative impact on many small businesses.
The second part of this step is to know how you will communicate your main message . For example, if your key point is that running improves physical health, you might get this across by:
- Citing scientific studies that proved running is good for your health
- Sharing your personal experience of going for a run every day
Your goal is for all of your sub-points and supporting material to reflect and support your main point. At the end of the speech, your audience should be appropriately motivated, educated, or convinced that your thesis statement is true.
Once you have a topic for your presentation and a good thesis statement, you can move on to the bulk of the outline.
The first part of your speech is the introduction, which should include a strong “hook” to grab the attention of your audience. There are endless directions you can go to create this hook. Don’t be afraid to get creative! You might try:
- Telling a joke
- Sharing an anecdote
- Using a prop or visual aid
- Asking a question (rhetorical or otherwise)
These are just a few examples of hooks that can make your audience sit up and take notice.
The rest of your introduction shouldn’t be too long—as a general rule of thumb, you want your introduction to take up about 10% of your entire speech. But there are a few other things you need to say.
Briefly introduce yourself and who you are to communicate why the audience should trust you. Mention why you’re giving this speech.
Explain that you’re going to cover X main points—you can quickly list them—and include your thesis statement.
You could also mention how long your speech will be and say what your audience will take away from it (“At the end of our 15 minutes together today, you’ll understand how to write a resume”).
Then smoothly transition into the body of your speech.
Next, you’ll write the body of your speech. This is the bulk of your presentation. It will include your main points and their sub-points. Here’s how this should look:
Your subpoints might be anecdotes, visual aids, or studies. However you decide to support your main points, make them memorable and engaging. Nobody wants to sit and listen to you recite a dry list of facts.
Remember, the amount of detail you include right now will depend on which outline you’re on. Your first outline, or working outline, doesn’t have to include every last little detail. Your goal is to briefly encapsulate all of the most important elements in your speech.
But beyond that, you don’t need to write down every last detail or example right now. You don’t even have to write full sentences at this point. That will come in your second outline and other future drafts.
Your conclusion should concisely summarize the main points of your speech. You could do this by saying, “To recap as I finish up, today we learned…” and reiterate those primary points.
It’s also good to leave the audience with something to think about and/or discuss. Consider asking them a question that expands on your speech—something they can turn over in their minds the rest of the day.
Or share one final story or quote that will leave them with lasting inspiration. Bonus points if your conclusion circles back around to your introduction or hook.
In other cases, you may want to end with a call to action. Are you promoting something? Make sure your audience knows what it is, how it will benefit them, and where they can find it. Or, your CTA might be as simple as plugging your Twitter handle and asking listeners to follow you.
Finally, don’t forget to say thank you to your audience for taking the time to listen.
Additional Helpful Speechwriting Tips
Your speech outline is important, but it’s not the only thing that goes into preparing to give a presentation. Take a look at these additional tips I recommend to help your speech succeed.
Use Visual Aids
Visual aids are a good way to make sure your audience stays engaged—that they listen closely, and remember what you said. Visual aids serve as an attention-getter for people who may not be listening closely. These aids also ensure that your points are sufficiently supported.
You might choose to incorporate any of the following in your talk:
- A PowerPoint presentation
- A chart or graph
- A whiteboard or blackboard
- A flip chart
- A prop that you hold or interact with
Don’t overdo it. Remember, your speech is the main thing you’re presenting. Any visual aids are just that—aids. They’re a side dish, not the main entrée. Select one primary type of aid for your speech.
If you decide to include visual aids, use your speaking outline to make a note of which items you will incorporate where. You may want to place these items on your working outline. They should definitely be on your full-sentence outline.
Keep Your Audience Engaged
As you write and practice your speech, make sure you’re doing everything you can to keep your audience engaged the entire time. We’ve already talked about including stories and jokes, using visual aids, or asking questions to vary your talk and make it more interesting.
Your body language is another important component of audience engagement. Your posture should be straight yet relaxed, with shoulders back and feet shoulder-width apart. Keep your body open to the audience.
Make eye contact with different people in the audience. Incorporate hand gestures that emphasize certain points or draw attention to your visual aids.
Don’t be afraid to move around whatever space you have. Movement is especially helpful to indicate a clearer transition from one part of your speech to another. And smile! A simple smile goes a long way to help your audience relax.
Practice Your Speech
When you’re done with speechwriting, it’s time to get in front of the mirror and practice. Pay attention to your body language, gestures, and eye contact.
Practice working with any visual aids or props you will be using. It’s also helpful to make a plan B—for instance, what will you do if the projector isn’t working and you can’t use your slides?
Ask a friend or family member if you can rehearse your speech for them. When you’re through, ask them questions about which parts held their attention and which ones didn’t.
You should also use your speaking outline and whatever other notes you’ll be using in your speech itself. Get used to referring to this outline as you go. But remember, don’t read anything verbatim (except maybe a quote). Your speaking outline is simply a guide to remind you where you’re going.
Learn to Speak Like A Leader
There’s a lot of work that goes into writing a speech outline. That’s undeniable. But an outline is the best way to organize and plan your presentation. When your speech outline is ready, it will be a breeze to write and then present your actual speech.
If you’re looking for more help learning how to become a strong public speaker, I recommend my free 5 Minute Speech Formula . This will help you start writing your speech and turn any idea into a powerful message.
« Previous Post Productivity Tips – Be More Productive With Less Effort Next Post » How To Communicate Effectively In Any Situation
About Brian Tracy — Brian is recognized as the top sales training and personal success authority in the world today. He has authored more than 60 books and has produced more than 500 audio and video learning programs on sales, management, business success and personal development, including worldwide bestseller The Psychology of Achievement. Brian's goal is to help you achieve your personal and business goals faster and easier than you ever imagined. You can follow him on Twitter , Facebook , Pinterest , Linkedin and Youtube .
- Most Recent
- How to Write a Book: Proven Start-to-Finish Steps
- 117 Leadership Quotes for Inspiration
- 7 Tips for Writing Motivation: Stay Motivated When Writing a Book
- How to End a Speech: What You Need for a Bang
- Goal Setting for Success & Developing SMART Habits
- Free Webinar: How To Write a Book and Become a Published Author
- Free Video Series: 3-Part Sales Mastery Training Series
- Free Assessment: The Confidence Factor
- Free Assessment: Discovering Your Talents
Browse Categories
- Financial Success
Follow Brian & Join the Discussion
- Free Resources
- Best Sellers
- Knowledge Base
- Shipping & Returns
- Privacy Policy
- About Brian
- Brian Recommends
Your Privacy is Guaranteed. We will never give, lease or sell your personal information. Period!
© Copyright 2001-2024 Brian Tracy International. All Rights Reserved.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you'd like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part's duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
In short, the outline functions both as an organization tool and as a reference for delivering a speech. A full-sentence outline lays a strong foundation for your message. It will call on you to have one clear and specific purpose for your message. As we have seen in other chapters of this book, writing your specific purpose in clear language ...
The formal outline is a full-sentence outline that helps you prepare for your speech. It includes the introduction and conclusion, the main content of the body, key supporting materials, citation information written into the sentences in the outline, and a references page for your speech. The formal outline also includes a title, the general ...
An outline will show gaps in material or support. For example, you might notice you've got strong examples and testimony for your second main point, but that some research findings or statistics are still needed. Assessing your outline will enable you to double-check the flow or order of your speech. For instance, when you see your main ...
A preparation outline is a formal outline that follows a specific alphanumeric format and contains complete sentences. It is used to prepare for the speech. A speaking outline is informal, follows ...
Central Idea. Write your central idea at the top of your outline so you can refer to it frequently and verify that every component of your speech is directly tied to it. Labeled Sections. Label your introduction, main points, conclusions, transitions, and bibliography. Uniform Indentation. use uniform indentation to indicate main points, sub ...
8.4 Outlining Your Speech. Most speakers and audience members would agree that an organized speech is both easier to present as well as easier for the audience to understand. Public speaking teachers especially believe in the power of organizing your speech, which is why they encourage (and often require) that you create an outline for your ...
3. Speaking Outline A. The speaking outline is written after the preparation outline, and follows the same format. Speaking outlines are used for practicing your speech. B. Speaking outlines use key words, instead of full-sentences, they do not include citations (in-
A speaking outline is the outline you will prepare for use when delivering the speech. The speaking outline is much more succinct than the preparation outline and includes brief phrases or words that remind the speakers of the points they need to make, plus supporting material and signposts. [2] The words or phrases used on the speaking outline ...
preparation outline. Detailed outline a speaker builds when preparing a speech that includes the title, specific purpose, thesis statement, introduction, main points and subpoints, connectives, conclusion, and source citations of the speech. subpoint. Point in a speech that develops an aspect of a main point. sub-subpoint.
Speech Outline Definition. When trying to present information, whether to persuade or inform, creating an outline can assist in constructing and executing an effective speech. Through the use of ...
Because an outline is used to arrange all of the elements of your speech, it makes sense that the outline itself has an organizational hierarchy and a common format. Although there are a variety of outline styles, generally they follow the same pattern. Main ideas are preceded by Roman numerals (I, II, III, etc.).
This detailed map of a speech is. a preparation outline. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like True/False: The preparation outline should be in standard outline form., True/False: Write your preparation outline in phrases rather than complete sentences., True/False: It is unwise to ask a friend to listen to your ...
To create a working outline, you will need: A speech topic. An idea for the "hook" in your introduction. A thesis statement. 3-5 main points (each one should make a primary claim that you support with references) A conclusion. Each of your main points will also have sub-points, but we'll get to those in a later step.
Outlining PrinciplesOutlining is a systematic method of o. anizing your ideas. This organized approach ensures that your argument is clear and your information is in an appropriate pla. within the speech. There are three key tenets to outlining: subordination, coordi. ation, and division. Each of these three helps you create an organized ...
The preparation outline and the speaking outline are exactly the same. ... The outline is your script for the speech and should contain every word that you will share in the speech. False. Humor is an approved way to start a speech if it is appropriate to the topic and purpose of the speech.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like You should replace your presentation outline (a full- sentence outline) with a ______________ outline-an abbreviated outline (with only key words and phrases)- when you're getting ready to deliver your speech. a. formal b. preparation c. consolidated d. none of the above, A topical organizational pattern a. suggests a specaific ...
a) an effective method of managing speech anxiety that counteracts a performance orientation. The communication orientation is. b) spatially. When Sally provides a description of where the various buildings on campus are located to a new incoming student, Sally would best organize this information: b)
Q-Chat. Created by. bdscrogu. Created 6 months ago. The purpose of this quiz is to ensure you are grasping the concepts presented in the readings. In this case, you are checking your knowledge of Developing Topics for Your Speech (Chapter 4) and Organizing and Outline (Chapter 5).