
The Will to Teach

Critical Thinking in the Classroom: A Guide for Teachers
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, teaching students the skill of critical thinking has become a priority. This powerful tool empowers students to evaluate information, make reasoned judgments, and approach problems from a fresh perspective. In this article, we’ll explore the significance of critical thinking and provide effective strategies to nurture this skill in your students.
Why is Fostering Critical Thinking Important?
Strategies to cultivate critical thinking, real-world example, concluding thoughts.
Critical thinking is a key skill that goes far beyond the four walls of a classroom. It equips students to better understand and interact with the world around them. Here are some reasons why fostering critical thinking is important:
- Making Informed Decisions: Critical thinking enables students to evaluate the pros and cons of a situation, helping them make informed and rational decisions.
- Developing Analytical Skills: Critical thinking involves analyzing information from different angles, which enhances analytical skills.
- Promoting Independence: Critical thinking fosters independence by encouraging students to form their own opinions based on their analysis, rather than relying on others.

Creating an environment that encourages critical thinking can be accomplished in various ways. Here are some effective strategies:
- Socratic Questioning: This method involves asking thought-provoking questions that encourage students to think deeply about a topic. For example, instead of asking, “What is the capital of France?” you might ask, “Why do you think Paris became the capital of France?”
- Debates and Discussions: Debates and open-ended discussions allow students to explore different viewpoints and challenge their own beliefs. For example, a debate on a current event can engage students in critical analysis of the situation.
- Teaching Metacognition: Teaching students to think about their own thinking can enhance their critical thinking skills. This can be achieved through activities such as reflective writing or journaling.
- Problem-Solving Activities: As with developing problem-solving skills , activities that require students to find solutions to complex problems can also foster critical thinking.
As a school leader, I’ve seen the transformative power of critical thinking. During a school competition, I observed a team of students tasked with proposing a solution to reduce our school’s environmental impact. Instead of jumping to obvious solutions, they critically evaluated multiple options, considering the feasibility, cost, and potential impact of each. They ultimately proposed a comprehensive plan that involved water conservation, waste reduction, and energy efficiency measures. This demonstrated their ability to critically analyze a problem and develop an effective solution.
Critical thinking is an essential skill for students in the 21st century. It equips them to understand and navigate the world in a thoughtful and informed manner. As a teacher, incorporating strategies to foster critical thinking in your classroom can make a lasting impact on your students’ educational journey and life beyond school.
1. What is critical thinking? Critical thinking is the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment.
2. Why is critical thinking important for students? Critical thinking helps students make informed decisions, develop analytical skills, and promotes independence.
3. What are some strategies to cultivate critical thinking in students? Strategies can include Socratic questioning, debates and discussions, teaching metacognition, and problem-solving activities.
4. How can I assess my students’ critical thinking skills? You can assess critical thinking skills through essays, presentations, discussions, and problem-solving tasks that require thoughtful analysis.
5. Can critical thinking be taught? Yes, critical thinking can be taught and nurtured through specific teaching strategies and a supportive learning environment.
Related Posts
7 simple strategies for strong student-teacher relationships.
Getting to know your students on a personal level is the first step towards building strong relationships. Show genuine interest in their lives outside the classroom.

Connecting Learning to Real-World Contexts: Strategies for Teachers
When students see the relevance of their classroom lessons to their everyday lives, they are more likely to be motivated, engaged, and retain information.

Encouraging Active Involvement in Learning: Strategies for Teachers
Active learning benefits students by improving retention of information, enhancing critical thinking skills, and encouraging a deeper understanding of the subject matter.

Collaborative and Cooperative Learning: A Guide for Teachers
These methods encourage students to work together, share ideas, and actively participate in their education.

Experiential Teaching: Role-Play and Simulations in Teaching
These interactive techniques allow students to immerse themselves in practical, real-world scenarios, thereby deepening their understanding and retention of key concepts.

Project-Based Learning Activities: A Guide for Teachers
Project-Based Learning is a student-centered pedagogy that involves a dynamic approach to teaching, where students explore real-world problems or challenges.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Eight Instructional Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking

- Share article
(This is the first post in a three-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom?
This three-part series will explore what critical thinking is, if it can be specifically taught and, if so, how can teachers do so in their classrooms.
Today’s guests are Dara Laws Savage, Patrick Brown, Meg Riordan, Ph.D., and Dr. PJ Caposey. Dara, Patrick, and Meg were also guests on my 10-minute BAM! Radio Show . You can also find a list of, and links to, previous shows here.
You might also be interested in The Best Resources On Teaching & Learning Critical Thinking In The Classroom .
Current Events
Dara Laws Savage is an English teacher at the Early College High School at Delaware State University, where she serves as a teacher and instructional coach and lead mentor. Dara has been teaching for 25 years (career preparation, English, photography, yearbook, newspaper, and graphic design) and has presented nationally on project-based learning and technology integration:
There is so much going on right now and there is an overload of information for us to process. Did you ever stop to think how our students are processing current events? They see news feeds, hear news reports, and scan photos and posts, but are they truly thinking about what they are hearing and seeing?
I tell my students that my job is not to give them answers but to teach them how to think about what they read and hear. So what is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom? There are just as many definitions of critical thinking as there are people trying to define it. However, the Critical Think Consortium focuses on the tools to create a thinking-based classroom rather than a definition: “Shape the climate to support thinking, create opportunities for thinking, build capacity to think, provide guidance to inform thinking.” Using these four criteria and pairing them with current events, teachers easily create learning spaces that thrive on thinking and keep students engaged.
One successful technique I use is the FIRE Write. Students are given a quote, a paragraph, an excerpt, or a photo from the headlines. Students are asked to F ocus and respond to the selection for three minutes. Next, students are asked to I dentify a phrase or section of the photo and write for two minutes. Third, students are asked to R eframe their response around a specific word, phrase, or section within their previous selection. Finally, students E xchange their thoughts with a classmate. Within the exchange, students also talk about how the selection connects to what we are covering in class.
There was a controversial Pepsi ad in 2017 involving Kylie Jenner and a protest with a police presence. The imagery in the photo was strikingly similar to a photo that went viral with a young lady standing opposite a police line. Using that image from a current event engaged my students and gave them the opportunity to critically think about events of the time.
Here are the two photos and a student response:
F - Focus on both photos and respond for three minutes
In the first picture, you see a strong and courageous black female, bravely standing in front of two officers in protest. She is risking her life to do so. Iesha Evans is simply proving to the world she does NOT mean less because she is black … and yet officers are there to stop her. She did not step down. In the picture below, you see Kendall Jenner handing a police officer a Pepsi. Maybe this wouldn’t be a big deal, except this was Pepsi’s weak, pathetic, and outrageous excuse of a commercial that belittles the whole movement of people fighting for their lives.
I - Identify a word or phrase, underline it, then write about it for two minutes
A white, privileged female in place of a fighting black woman was asking for trouble. A struggle we are continuously fighting every day, and they make a mockery of it. “I know what will work! Here Mr. Police Officer! Drink some Pepsi!” As if. Pepsi made a fool of themselves, and now their already dwindling fan base continues to ever shrink smaller.
R - Reframe your thoughts by choosing a different word, then write about that for one minute
You don’t know privilege until it’s gone. You don’t know privilege while it’s there—but you can and will be made accountable and aware. Don’t use it for evil. You are not stupid. Use it to do something. Kendall could’ve NOT done the commercial. Kendall could’ve released another commercial standing behind a black woman. Anything!
Exchange - Remember to discuss how this connects to our school song project and our previous discussions?
This connects two ways - 1) We want to convey a strong message. Be powerful. Show who we are. And Pepsi definitely tried. … Which leads to the second connection. 2) Not mess up and offend anyone, as had the one alma mater had been linked to black minstrels. We want to be amazing, but we have to be smart and careful and make sure we include everyone who goes to our school and everyone who may go to our school.
As a final step, students read and annotate the full article and compare it to their initial response.
Using current events and critical-thinking strategies like FIRE writing helps create a learning space where thinking is the goal rather than a score on a multiple-choice assessment. Critical-thinking skills can cross over to any of students’ other courses and into life outside the classroom. After all, we as teachers want to help the whole student be successful, and critical thinking is an important part of navigating life after they leave our classrooms.

‘Before-Explore-Explain’
Patrick Brown is the executive director of STEM and CTE for the Fort Zumwalt school district in Missouri and an experienced educator and author :
Planning for critical thinking focuses on teaching the most crucial science concepts, practices, and logical-thinking skills as well as the best use of instructional time. One way to ensure that lessons maintain a focus on critical thinking is to focus on the instructional sequence used to teach.
Explore-before-explain teaching is all about promoting critical thinking for learners to better prepare students for the reality of their world. What having an explore-before-explain mindset means is that in our planning, we prioritize giving students firsthand experiences with data, allow students to construct evidence-based claims that focus on conceptual understanding, and challenge students to discuss and think about the why behind phenomena.
Just think of the critical thinking that has to occur for students to construct a scientific claim. 1) They need the opportunity to collect data, analyze it, and determine how to make sense of what the data may mean. 2) With data in hand, students can begin thinking about the validity and reliability of their experience and information collected. 3) They can consider what differences, if any, they might have if they completed the investigation again. 4) They can scrutinize outlying data points for they may be an artifact of a true difference that merits further exploration of a misstep in the procedure, measuring device, or measurement. All of these intellectual activities help them form more robust understanding and are evidence of their critical thinking.
In explore-before-explain teaching, all of these hard critical-thinking tasks come before teacher explanations of content. Whether we use discovery experiences, problem-based learning, and or inquiry-based activities, strategies that are geared toward helping students construct understanding promote critical thinking because students learn content by doing the practices valued in the field to generate knowledge.

An Issue of Equity
Meg Riordan, Ph.D., is the chief learning officer at The Possible Project, an out-of-school program that collaborates with youth to build entrepreneurial skills and mindsets and provides pathways to careers and long-term economic prosperity. She has been in the field of education for over 25 years as a middle and high school teacher, school coach, college professor, regional director of N.Y.C. Outward Bound Schools, and director of external research with EL Education:
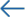
Although critical thinking often defies straightforward definition, most in the education field agree it consists of several components: reasoning, problem-solving, and decisionmaking, plus analysis and evaluation of information, such that multiple sides of an issue can be explored. It also includes dispositions and “the willingness to apply critical-thinking principles, rather than fall back on existing unexamined beliefs, or simply believe what you’re told by authority figures.”
Despite variation in definitions, critical thinking is nonetheless promoted as an essential outcome of students’ learning—we want to see students and adults demonstrate it across all fields, professions, and in their personal lives. Yet there is simultaneously a rationing of opportunities in schools for students of color, students from under-resourced communities, and other historically marginalized groups to deeply learn and practice critical thinking.
For example, many of our most underserved students often spend class time filling out worksheets, promoting high compliance but low engagement, inquiry, critical thinking, or creation of new ideas. At a time in our world when college and careers are critical for participation in society and the global, knowledge-based economy, far too many students struggle within classrooms and schools that reinforce low-expectations and inequity.
If educators aim to prepare all students for an ever-evolving marketplace and develop skills that will be valued no matter what tomorrow’s jobs are, then we must move critical thinking to the forefront of classroom experiences. And educators must design learning to cultivate it.
So, what does that really look like?
Unpack and define critical thinking
To understand critical thinking, educators need to first unpack and define its components. What exactly are we looking for when we speak about reasoning or exploring multiple perspectives on an issue? How does problem-solving show up in English, math, science, art, or other disciplines—and how is it assessed? At Two Rivers, an EL Education school, the faculty identified five constructs of critical thinking, defined each, and created rubrics to generate a shared picture of quality for teachers and students. The rubrics were then adapted across grade levels to indicate students’ learning progressions.
At Avenues World School, critical thinking is one of the Avenues World Elements and is an enduring outcome embedded in students’ early experiences through 12th grade. For instance, a kindergarten student may be expected to “identify cause and effect in familiar contexts,” while an 8th grader should demonstrate the ability to “seek out sufficient evidence before accepting a claim as true,” “identify bias in claims and evidence,” and “reconsider strongly held points of view in light of new evidence.”
When faculty and students embrace a common vision of what critical thinking looks and sounds like and how it is assessed, educators can then explicitly design learning experiences that call for students to employ critical-thinking skills. This kind of work must occur across all schools and programs, especially those serving large numbers of students of color. As Linda Darling-Hammond asserts , “Schools that serve large numbers of students of color are least likely to offer the kind of curriculum needed to ... help students attain the [critical-thinking] skills needed in a knowledge work economy. ”
So, what can it look like to create those kinds of learning experiences?
Designing experiences for critical thinking
After defining a shared understanding of “what” critical thinking is and “how” it shows up across multiple disciplines and grade levels, it is essential to create learning experiences that impel students to cultivate, practice, and apply these skills. There are several levers that offer pathways for teachers to promote critical thinking in lessons:
1.Choose Compelling Topics: Keep it relevant
A key Common Core State Standard asks for students to “write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.” That might not sound exciting or culturally relevant. But a learning experience designed for a 12th grade humanities class engaged learners in a compelling topic— policing in America —to analyze and evaluate multiple texts (including primary sources) and share the reasoning for their perspectives through discussion and writing. Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care about and connect with can ignite powerful learning experiences.
2. Make Local Connections: Keep it real
At The Possible Project , an out-of-school-time program designed to promote entrepreneurial skills and mindsets, students in a recent summer online program (modified from in-person due to COVID-19) explored the impact of COVID-19 on their communities and local BIPOC-owned businesses. They learned interviewing skills through a partnership with Everyday Boston , conducted virtual interviews with entrepreneurs, evaluated information from their interviews and local data, and examined their previously held beliefs. They created blog posts and videos to reflect on their learning and consider how their mindsets had changed as a result of the experience. In this way, we can design powerful community-based learning and invite students into productive struggle with multiple perspectives.
3. Create Authentic Projects: Keep it rigorous
At Big Picture Learning schools, students engage in internship-based learning experiences as a central part of their schooling. Their school-based adviser and internship-based mentor support them in developing real-world projects that promote deeper learning and critical-thinking skills. Such authentic experiences teach “young people to be thinkers, to be curious, to get from curiosity to creation … and it helps students design a learning experience that answers their questions, [providing an] opportunity to communicate it to a larger audience—a major indicator of postsecondary success.” Even in a remote environment, we can design projects that ask more of students than rote memorization and that spark critical thinking.
Our call to action is this: As educators, we need to make opportunities for critical thinking available not only to the affluent or those fortunate enough to be placed in advanced courses. The tools are available, let’s use them. Let’s interrogate our current curriculum and design learning experiences that engage all students in real, relevant, and rigorous experiences that require critical thinking and prepare them for promising postsecondary pathways.

Critical Thinking & Student Engagement
Dr. PJ Caposey is an award-winning educator, keynote speaker, consultant, and author of seven books who currently serves as the superintendent of schools for the award-winning Meridian CUSD 223 in northwest Illinois. You can find PJ on most social-media platforms as MCUSDSupe:
When I start my keynote on student engagement, I invite two people up on stage and give them each five paper balls to shoot at a garbage can also conveniently placed on stage. Contestant One shoots their shot, and the audience gives approval. Four out of 5 is a heckuva score. Then just before Contestant Two shoots, I blindfold them and start moving the garbage can back and forth. I usually try to ensure that they can at least make one of their shots. Nobody is successful in this unfair environment.
I thank them and send them back to their seats and then explain that this little activity was akin to student engagement. While we all know we want student engagement, we are shooting at different targets. More importantly, for teachers, it is near impossible for them to hit a target that is moving and that they cannot see.
Within the world of education and particularly as educational leaders, we have failed to simplify what student engagement looks like, and it is impossible to define or articulate what student engagement looks like if we cannot clearly articulate what critical thinking is and looks like in a classroom. Because, simply, without critical thought, there is no engagement.
The good news here is that critical thought has been defined and placed into taxonomies for decades already. This is not something new and not something that needs to be redefined. I am a Bloom’s person, but there is nothing wrong with DOK or some of the other taxonomies, either. To be precise, I am a huge fan of Daggett’s Rigor and Relevance Framework. I have used that as a core element of my practice for years, and it has shaped who I am as an instructional leader.
So, in order to explain critical thought, a teacher or a leader must familiarize themselves with these tried and true taxonomies. Easy, right? Yes, sort of. The issue is not understanding what critical thought is; it is the ability to integrate it into the classrooms. In order to do so, there are a four key steps every educator must take.
- Integrating critical thought/rigor into a lesson does not happen by chance, it happens by design. Planning for critical thought and engagement is much different from planning for a traditional lesson. In order to plan for kids to think critically, you have to provide a base of knowledge and excellent prompts to allow them to explore their own thinking in order to analyze, evaluate, or synthesize information.
- SIDE NOTE – Bloom’s verbs are a great way to start when writing objectives, but true planning will take you deeper than this.
QUESTIONING
- If the questions and prompts given in a classroom have correct answers or if the teacher ends up answering their own questions, the lesson will lack critical thought and rigor.
- Script five questions forcing higher-order thought prior to every lesson. Experienced teachers may not feel they need this, but it helps to create an effective habit.
- If lessons are rigorous and assessments are not, students will do well on their assessments, and that may not be an accurate representation of the knowledge and skills they have mastered. If lessons are easy and assessments are rigorous, the exact opposite will happen. When deciding to increase critical thought, it must happen in all three phases of the game: planning, instruction, and assessment.
TALK TIME / CONTROL
- To increase rigor, the teacher must DO LESS. This feels counterintuitive but is accurate. Rigorous lessons involving tons of critical thought must allow for students to work on their own, collaborate with peers, and connect their ideas. This cannot happen in a silent room except for the teacher talking. In order to increase rigor, decrease talk time and become comfortable with less control. Asking questions and giving prompts that lead to no true correct answer also means less control. This is a tough ask for some teachers. Explained differently, if you assign one assignment and get 30 very similar products, you have most likely assigned a low-rigor recipe. If you assign one assignment and get multiple varied products, then the students have had a chance to think deeply, and you have successfully integrated critical thought into your classroom.

Thanks to Dara, Patrick, Meg, and PJ for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones won’t be available until February). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- Order Tracking
- Create an Account

200+ Award-Winning Educational Textbooks, Activity Books, & Printable eBooks!
- Compare Products
Reading, Writing, Math, Science, Social Studies
- Search by Book Series
- Algebra I & II Gr. 7-12+
- Algebra Magic Tricks Gr. 2-12+
- Algebra Word Problems Gr. 7-12+
- Balance Benders Gr. 2-12+
- Balance Math & More! Gr. 2-12+
- Basics of Critical Thinking Gr. 4-7
- Brain Stretchers Gr. 5-12+
- Building Thinking Skills Gr. Toddler-12+
- Building Writing Skills Gr. 3-7
- Bundles - Critical Thinking Gr. PreK-9
- Bundles - Language Arts Gr. K-8
- Bundles - Mathematics Gr. PreK-9
- Bundles - Multi-Subject Curriculum Gr. PreK-12+
- Bundles - Test Prep Gr. Toddler-12+
- Can You Find Me? Gr. PreK-1
- Complete the Picture Math Gr. 1-3
- Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Gr. 5-12+
- Cranium Crackers Gr. 3-12+
- Creative Problem Solving Gr. PreK-2
- Critical Thinking Activities to Improve Writing Gr. 4-12+
- Critical Thinking Coloring Gr. PreK-2
- Critical Thinking Detective Gr. 3-12+
- Critical Thinking Tests Gr. PreK-6
- Critical Thinking for Reading Comprehension Gr. 1-5
- Critical Thinking in United States History Gr. 6-12+
- CrossNumber Math Puzzles Gr. 4-10
- Crypt-O-Words Gr. 2-7
- Crypto Mind Benders Gr. 3-12+
- Daily Mind Builders Gr. 5-12+
- Dare to Compare Math Gr. 2-7
- Developing Critical Thinking through Science Gr. 1-8
- Dr. DooRiddles Gr. PreK-12+
- Dr. Funster's Gr. 2-12+
- Editor in Chief Gr. 2-12+
- Fun-Time Phonics! Gr. PreK-2
- Half 'n Half Animals Gr. K-4
- Hands-On Thinking Skills Gr. K-1
- Inference Jones Gr. 1-6
- James Madison Gr. 10-12+
- Jumbles Gr. 3-5
- Language Mechanic Gr. 4-7
- Language Smarts Gr. 1-4
- Mastering Logic & Math Problem Solving Gr. 6-9
- Math Analogies Gr. K-9
- Math Detective Gr. 3-8
- Math Games Gr. 3-8
- Math Mind Benders Gr. 5-12+
- Math Ties Gr. 4-8
- Math Word Problems Gr. 4-10
- Mathematical Reasoning Gr. Toddler-11
- Middle School Science Gr. 6-8
- Mind Benders Gr. PreK-12+
- Mind Building Math Gr. K-1
- Mind Building Reading Gr. K-1
- Novel Thinking Gr. 3-6
- OLSAT® Test Prep Gr. PreK-K
- Organizing Thinking Gr. 2-8
- Pattern Explorer Gr. 3-9
- Practical Critical Thinking Gr. 8-12+
- Punctuation Puzzler Gr. 3-8
- Reading Detective Gr. 3-12+
- Red Herring Mysteries Gr. 4-12+
- Red Herrings Science Mysteries Gr. 4-9
- Science Detective Gr. 3-6
- Science Mind Benders Gr. PreK-3
- Science Vocabulary Crossword Puzzles Gr. 4-6
- Sciencewise Gr. 4-12+
- Scratch Your Brain Gr. 2-12+
- Sentence Diagramming Gr. 3-12+
- Smarty Pants Puzzles Gr. 3-12+
- Snailopolis Gr. K-4
- Something's Fishy at Lake Iwannafisha Gr. 5-9
- Teaching Technology Gr. 3-12+
- Tell Me a Story Gr. PreK-1
- Think Analogies Gr. 3-12+
- Think and Write Gr. 3-8
- Think-A-Grams Gr. 4-12+
- Thinking About Time Gr. 3-6
- Thinking Connections Gr. 4-12+
- Thinking Directionally Gr. 2-6
- Thinking Skills & Key Concepts Gr. PreK-2
- Thinking Skills for Tests Gr. PreK-5
- U.S. History Detective Gr. 8-12+
- Understanding Fractions Gr. 2-6
- Visual Perceptual Skill Building Gr. PreK-3
- Vocabulary Riddles Gr. 4-8
- Vocabulary Smarts Gr. 2-5
- Vocabulary Virtuoso Gr. 2-12+
- What Would You Do? Gr. 2-12+
- Who Is This Kid? Colleges Want to Know! Gr. 9-12+
- Word Explorer Gr. 4-8
- Word Roots Gr. 3-12+
- World History Detective Gr. 6-12+
- Writing Detective Gr. 3-6
- You Decide! Gr. 6-12+
- Special of the Month
- Sign Up for our Best Offers
- Bundles = Greatest Savings!
- Sign Up for Free Puzzles
- Sign Up for Free Activities
- Toddler (Ages 0-3)
- PreK (Ages 3-5)
- Kindergarten (Ages 5-6)
- 1st Grade (Ages 6-7)
- 2nd Grade (Ages 7-8)
- 3rd Grade (Ages 8-9)
- 4th Grade (Ages 9-10)
- 5th Grade (Ages 10-11)
- 6th Grade (Ages 11-12)
- 7th Grade (Ages 12-13)
- 8th Grade (Ages 13-14)
- 9th Grade (Ages 14-15)
- 10th Grade (Ages 15-16)
- 11th Grade (Ages 16-17)
- 12th Grade (Ages 17-18)
- 12th+ Grade (Ages 18+)
- Test Prep Directory
- Test Prep Bundles
- Test Prep Guides
- Preschool Academics
- Store Locator
- Submit Feedback/Request
- Sales Alerts Sign-Up
- Technical Support
- Mission & History
- Articles & Advice
- Testimonials
- Our Guarantee
- New Products
- Free Activities
- Libros en Español
How To Promote Critical Thinking In Your Classroom
Promoting Thinking
November 25, 2006, by The Critical Thinking Co. Staff
Modeling of critical thinking skills by instructors is crucial for teaching critical thinking successfully. By making your own thought processes explicit in class - explaining your reasoning, evaluating evidence for a claim, probing the credibility of a source, or even describing what has puzzled or confused you - you provide a powerful example to students, particularly if you invite them to join in; e.g., "Can you see where we're headed with this?" "I can't think of other explanations; can you?" "This idea/principle struck me as difficult or confusing at first, but here's how I figured it out." You can encourage students to emulate this by using them in demonstrations, asking them to "think out loud" in order for classmates to observe how they reason through a problem.
Develop the habit of asking questions that require students to think critically, and tell students that you really expect them to give answers! In particular, Socratic questioning encourages students to develop and clarify their thinking: e.g., "Would your answer hold in all cases?" "How would you respond to a counter-example or counter-argument?" "Explain how you arrived at that answer?"
This is another skill that students can learn from your example, and can use in working with each other. Providing regular opportunities for pair or small group discussions after major points or demonstrations during lectures is also important: this allows students to process the new material, connect it to previously learned topics, and practice asking questions that promote further critical thinking. Obviously, conveying genuine respect for student input is essential. Communicating the message that you value and support student contributions and efforts to think critically increases confidence, and motivates students to continue building their thinking skills. An essential component of this process is the creation of a climate where students feel comfortable with exploring the process of reasoning through a problem without being "punished" for getting the wrong answer.
Researchers have found consistently that interaction among students, in the form of well-structured group discussions plays a central role in stimulating critical thinking. Discussing course material and its applications allows students to formulate and test hypotheses, practice asking thought-provoking questions, hear other perspectives, analyze claims, evaluate evidence, and explain and justify their reasoning. As they become more sophisticated and fluent in thinking critically, students can observe and critique each others' reasoning skills.

50 Super-Fun Critical Thinking Strategies to Use in Your Classroom
by AuthorAmy
Teaching students to be critical thinkers is perhaps the most important goal in education. All teachers, regardless of subject area, contribute to the process of teaching students to think for themselves. However, it’s not always an easy skill to teach. Students need guidance and practice with critical thinking strategies at every level.
One problem with teaching critical thinking is that many different definitions of this skill exist. The Foundation for Critical Thinking offers four different definitions of the concept. Essentially, critical thinking is the ability to evaluate information and decide what we think about that information, a cumulative portfolio of skills our students need to be successful problem solvers in an ever-changing world.
Here is a list of 50 classroom strategies for teachers to use to foster critical thinking among students of all ages.
1. Don’t give them the answers
Learning is supposed to be hard, and while it may be tempting to jump in and direct students to the right answer, it’s better to let them work through a problem on their own. A good teacher is a guide, not an answer key. The goal is to help students work at their “challenge” level, as opposed to their “frustration” level.
2. Controversial issue barometer
In this activity, a line is drawn down the center of the classroom. The middle represents the neutral ground, and the ends of the line represent extremes of an issue. The teacher selects an issue and students space themselves along the line according to their opinions. Being able to articulate opinions and participate in civil discourse are important aspects of critical thinking.
3. Play devil’s advocate
During a robust classroom discussion, an effective teacher challenges students by acting as devil’s advocate, no matter their personal opinion. “I don’t care WHAT you think, I just care THAT you think” is my classroom mantra. Critical thinking strategies that ask students to analyze both sides of an issue help create understanding and empathy.
4. Gallery walk
In a gallery walk, the teacher hangs images around the classroom related to the unit at hand (photographs, political cartoons, paintings). Students peruse the artwork much like they are in a museum, writing down their thoughts about each piece.
5. Review something
A movie, TV show , a book, a restaurant, a pep assembly, today’s lesson – anything can be reviewed. Writing a review involves the complex skill of summary without spoilers and asks students to share their opinion and back it up with evidence.
6. Draw analogies
Pick two unrelated things and ask students how those things are alike (for example, how is a museum like a snowstorm). The goal here is to encourage creativity and look for similarities.
7. Think of 25 uses for an everyday thing
Pick an everyday object (I use my camera tripod) and set a timer for five minutes. Challenge students to come up with 25 things they can use the object for within that time frame. The obvious answers will be exhausted quickly, so ridiculous answers such as “coatrack” and “stool” are encouraged.
8. Incorporate riddles
Students love riddles. You could pose a question at the beginning of the week and allow students to ask questions about it all week.
9. Crosswords and sudoku puzzles
The games section of the newspaper provides great brainteasers for students who finish their work early and need some extra brain stimulation.
10. Fine tune questioning techniques
A vibrant classroom discussion is made even better by a teacher who asks excellent, provocative questions. Questions should move beyond those with concrete answers to a place where students must examine why they think the way they do.
11. Socratic seminar
The Socratic seminar is perhaps the ultimate critical thinking activity. Students are given a universal question, such as “Do you believe it is acceptable to break the law if you believe the law is wrong?” They are given time to prepare and answer, and then, seated in a circle, students are directed to discuss the topic. Whereas the goal of a debate is to win, the goal of a Socratic discussion is for the group to reach greater understanding.
12. Inquiry based learning
In inquiry-based learning, students develop questions they want answers to, which drives the curriculum toward issues they care about. An engaged learner is an essential step in critical thinking.
13. Problem-based learning
In problem-based learning, students are given a problem and asked to develop research-based solutions. The problem can be a school problem (the lunchroom is overcrowded) or a global problem (sea levels are rising).
14. Challenge all assumptions
The teacher must model this before students learn to apply this skill on their own. In this strategy, a teacher helps a student understand where his or her ingrained beliefs come from. Perhaps a student tells you they believe that stereotypes exist because they are true. An effective teacher can ask “Why do you think that?” and keep exploring the issue as students delve into the root of their beliefs. Question everything.
15. Emphasize data over beliefs
Data does not always support our beliefs, so our first priority must be to seek out data before drawing conclusions.
16. Teach confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is the human tendency to seek out information that confirms what we already believe, rather than letting the data inform our conclusions. Understanding that this phenomenon exists can help students avoid it.
17. Visualization
Help students make a plan before tackling a task.
18. Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual way to organize information. Students start with a central concept and create a web with subtopics that radiate outward.
19. Develop empathy
Empathy is often cited as an aspect of critical thinking. To do so, encourage students to think from a different point of view. They might write a “con” essay when they believe the “pro,” or write a letter from someone else’s perspective.
20. Summarization
Summarizing means taking all the information given and presenting it in a shortened fashion.
21. Encapsulation
Encapsulation is a skill different from summarization. To encapsulate a topic, students must learn about it and then distill it down to its most relevant points, which means students are forming judgements about what is most and least important.
22. Weigh cause and effect
The process of examining cause and effect helps students develop critical thinking skills by thinking through the natural consequences of a given choice.
23. Problems in a jar
Perfect for a bell-ringer, a teacher can stuff a mason jar with dilemmas that their students might face, such as, “Your best friend is refusing to talk to you today. What do you do?” Then, discuss possible answers. This works well for ethical dilemmas, too.
24. Transform one thing into another
Give students an object, like a pencil or a mug. Define its everyday use (to write or to drink from). Then, tell the students to transform the object into something with an entirely separate use. Now what is it used for?
25. Which one doesn’t belong?
Group items together and ask students to find the one that doesn’t belong. In first grade, this might be a grouping of vowels and a consonant; in high school, it might be heavy metals and a noble gas.
26. Compare/contrast
Compare and contrast are important critical thinking strategies. Students can create a Venn diagram to show similarities or differences, or they could write a good old-fashioned compare/contrast essay about the characters of Romeo and Juliet .
27. Pick a word, find a related word
This is another fun bell-ringer activity. The teacher starts with any word, and students go around the room and say another word related to that one. The obvious words go quickly, meaning the longer the game goes on, the more out-of-the-box the thinking gets.
28. Ranking of sources
Give students a research topic and tell them to find three sources (books, YouTube videos, websites). Then ask them, what resource is best – and why.
29. Hypothesize
The very act of hypothesizing is critical thinking in action. Students are using what they know to find an answer to something they don’t know.
30. Guess what will happen next
This works for scientific reactions, novels, current events, and more. Simply spell out what we know so far and ask students “and then what?”
31. Practice inference
Inference is the art of making an educated guess based on evidence presented and is an important component of critical thinking.
32. Connect text to self
Ask students to draw connections between what they are reading about to something happening in their world. For example, if their class is studying global warming, researching how global warming might impact their hometown will help make their studies relevant.
33. Levels of questioning
There are several levels of questions (as few as three and as many as six, depending on who you ask). These include factual questions, which have a right or wrong answer (most math problems are factual questions). There are also inferential questions, which ask students to make inferences based on both opinion and textual evidence. Additionally, there are universal questions, which are “big picture” questions where there are no right or wrong answers.
Students should practice answering all levels of questions and writing their own questions, too.
34. Demand precise language
An expansive vocabulary allows a student to express themselves more exactly, and precision is a major tool in the critical thinking toolkit.
35. Identify bias and hidden agendas
Helping students to critically examine biases in sources will help them evaluate the trustworthiness of their sources.
36. Identify unanswered questions
After a unit of study is conducted, lead students through a discussion of what questions remain unanswered. In this way, students can work to develop a lifelong learner mentality.
37. Relate a topic in one subject area to other disciplines
Have students take something they are studying in your class and relate it to other disciplines. For example, if you are studying the Civil War in social studies, perhaps they could look up historical fiction novels set during the Civil War era or research medical advancements from the time period for science.
38. Have a question conversation
Start with a general question and students must answer your question with a question of their own. Keep the conversation going.
39. Display a picture for 30 seconds, then take it down
Have students list everything they can remember. This helps students train their memories and increases their ability to notice details.
40. Brainstorm, free-write
Brainstorming and freewriting are critical thinking strategies to get ideas on paper. In brainstorming, anything goes, no matter how off-the-wall. These are great tools to get ideas flowing that can then be used to inform research.
41. Step outside your comfort zone
Direct students to learn about a topic they have no interest in or find particularly challenging. In this case, their perseverance is being developed as they do something that is difficult for them.
42. The answer is, the question might be
This is another bell-ringer game that’s great for engaging those brains. You give students the answer and they come up with what the question might be.
43. Cooperative learning
Group work is a critical thinking staple because it teaches students that there is no one right way to approach a problem and that other opinions are equally valid.
44. What? So what? Now what?
After concluding a unit of study, these three question frames can be used to help students contextualize their learning.
45. Reflection
Ask students to reflect on their work – specifically, how they can improve moving forward.
46. Classify and categorize
These are higher level Bloom’s tasks for a reason. Categorizing requires students to think about like traits and rank them in order of importance.
47. Role play
Roleplay allows students to practice creative thinking strategies. Here, students assume a role and act accordingly.
48. Set goals
Have students set concrete, measurable goals in your class so they understand why what they do matters.
No matter your subject area, encourage students to read voraciously. Through reading they will be exposed to new ideas, new perspectives, and their worlds will grow.
50. Cultivate curiosity
A curious mind is an engaged mind. Students should be encouraged to perform inquiry simply for the sake that it is a joy to learn about something we care about.

TREAT YO' INBOX!
All the trending teacher stories, resources, videos, memes, podcasts, deals, and the laughter you need in your life!
- Our Mission
A Critical Thinking Framework for Elementary Students
Guiding young students to engage in critical thinking fosters their ability to create and engage with knowledge.

Critical thinking is using analysis and evaluation to make a judgment. Analysis, evaluation, and judgment are not discrete skills; rather, they emerge from the accumulation of knowledge. The accumulation of knowledge does not mean students sit at desks mindlessly reciting memorized information, like in 19th century grammar schools. Our goal is not for learners to regurgitate facts by rote without demonstrating their understanding of the connections, structures, and deeper ideas embedded in the content they are learning. To foster critical thinking in school, especially for our youngest learners, we need a pedagogy that centers knowledge and also honors the ability of children to engage with knowledge.
This chapter outlines the Critical Thinking Framework: five instructional approaches educators can incorporate into their instruction to nurture deeper thinking. These approaches can also guide intellectual preparation protocols and unit unpackings to prepare rigorous, engaging instruction for elementary students. Some of these approaches, such as reason with evidence, will seem similar to other “contentless” programs professing to teach critical thinking skills. But others, such as say it in your own words or look for structure, are targeted at ensuring learners soundly understand content so that they can engage in complex thinking. You will likely notice that every single one of these approaches requires students to talk—to themselves, to a partner, or to the whole class. Dialogue, specifically in the context of teacher-led discussions, is essential for students to analyze, evaluate, and judge (i.e., do critical thinking ).
The Critical Thinking Framework

Say it in your own words : Students articulate ideas in their own words. They use unique phrasing and do not parrot the explanations of others. When learning new material, students who pause to explain concepts in their own words (to themselves or others) demonstrate an overall better understanding than students who do not (Nokes-Malach et al., 2013). However, it’s not enough for us to pause frequently and ask students to explain, especially if they are only being asked to repeat procedures. Explanations should be effortful and require students to make connections to prior knowledge and concepts as well as to revise misconceptions (Richey & Nokes-Malach, 2015).
Break it down : Students break down the components, steps, or smaller ideas within a bigger idea or procedure. In addition to expressing concepts in their own words, students should look at new concepts in terms of parts and wholes. For instance, when learning a new type of problem or task, students can explain the steps another student took to arrive at their answer, which promotes an understanding that transfers to other tasks with a similar underlying structure. Asking students to explain the components and rationale behind procedural steps can also lead to more flexible problem solving overall (Rittle-Johnson, 2006). By breaking down ideas into component parts, students are also better equipped to monitor the soundness of their own understanding as well as to see similar patterns (i.e., regularity) among differing tasks. For example, in writing, lessons can help students see how varying subordinating conjunction phrases at the start of sentences can support the flow and readability of a paragraph. In math, a solution can be broken down into smaller steps.
Look for structure : Students look beyond shallow surface characteristics to see deep structures and underlying principles. Learners struggle to see regularity in similar problems that have small differences (Reed et al., 1985). Even when students are taught how to complete one kind of task, they struggle to transfer their understanding to a new task where some of the superficial characteristics have been changed. This is because students, especially students who are novices in a domain, tend to emphasize the surface structure of a task rather than deep structure (Chi & Van Lehn, 2012).
By prompting students to notice deep structures—such as the characteristics of a genre or the needs of animals—rather than surface structures, teachers foster the development of comprehensive schemata in students’ long-term memories, which they are more likely to then apply to novel situations. Teachers should monitor for student understanding of deep structures across several tasks and examples.
Notice gaps or inconsistencies in ideas : Students ask questions about gaps and inconsistencies in material, arguments, and their own thinking . When students engage in explanations of material, they are more likely to notice when they misunderstand material or to detect a conflict with their prior knowledge (Richey & Nokes-Malach, 2015). In a classroom, analyzing conflicting ideas and interpretations allows students to revise misconceptions and refine mental models. Noticing gaps and inconsistencies in information also helps students to evaluate the persuasiveness of arguments and to ask relevant questions.
Reason with evidence : Students construct arguments with evidence and evaluate the evidence in others’ reasoning. Reasoning with evidence matters in every subject, but what counts for evidence in a mathematical proof differs from what is required in an English essay. Students should learn the rules and conventions for evidence across a wide range of disciplines in school. The habits of looking for and weighing evidence also intersect with some of the other critical thinking approaches discussed above. Noticing regularity in reasoning and structure helps learners find evidence efficiently, while attending to gaps and inconsistencies in information encourages caution before reaching hasty conclusions.
Countering Two Critiques
Some readers may be wondering how the Critical Thinking Framework differs from other general skills curricula. The framework differs in that it demands application in the context of students’ content knowledge, rather than in isolation. It is a pedagogical tool to help students make sense of the content they are learning. Students should never sit through a lesson where they are told to “say things in their own words” when there is nothing to say anything about. While a contentless lesson could help on the margins, it will not be as relevant or transferable. Specific content matters. A checklist of “critical thinking skills” cannot replace deep subject knowledge. The framework should not be blindly applied to all subjects without context because results will look quite different in an ELA or science class.
Other readers may be thinking about high-stakes tests: how does the Critical Thinking Framework fit in with an overwhelming emphasis on assessments aligned to national or state standards? This is a valid concern and an important point to address. For teachers, schools, and districts locked into an accountability system that values performance on state tests but does not communicate content expectations beyond general standards, the arguments I make may seem beside the point. Sure, knowledge matters, but the curriculum demands that students know how to quickly identify the main idea of a paragraph, even if they don’t have any background knowledge about the topic of the paragraph.
It is crucial that elementary practitioners be connected to both evolving research on learning and the limiting realities we teach within. Unfortunately, I can provide no easy answers beyond saying that teaching is a balancing act. The tension, while real and relevant to teachers’ daily lives, should not cloud our vision for what children need from their school experiences.
I also argue it is easier to incorporate the demands of our current standardized testing environment into a curriculum rich with history, science, art, geography, languages, and novels than the reverse. The Critical Thinking Framework presents ways to approach all kinds of knowledge in a way that presses students toward deeper processing of the content they are learning. If we can raise the bar for student work and thinking in our classrooms, the question of how students perform on standardized tests will become secondary to helping them achieve much loftier and important goals. The choice of whether to emphasize excellent curriculum or high-stakes tests, insofar as it is a choice at all, should never be existential or a zero-sum game.
From Critical Thinking in the Elementary Classroom: Engaging Young Minds with Meaningful Content (pp. 25–29) by Erin Shadowens, Arlington, VA: ASCD. Copyright © 2023 by ASCD. All rights reserved.

- All Articles
- Education Technology
- Industry News
- Op-Ed Submission Guidelines
- Write For Us

How to Promote Critical Thinking in the Classroom
By elearning inside, february 05, 2024.
Promoting critical thinking is an essential goal in education, equipping students with problem-solving skills that extend beyond the classroom. In this article, we’ll explore practical strategies for teachers and schools to foster critical thinking among students.
Fostering a Growth Mindset
Encouraging a growth mindset is fundamental to promoting critical thinking. Teachers can cultivate this mindset by praising effort rather than innate abilities.
When students understand that their abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work, they are more likely to embrace challenges and think critically to overcome obstacles.
Questioning Techniques
One of the most effective ways to promote critical thinking is through questioning. Teachers can employ various questioning techniques to stimulate thought, such as Socratic questioning.
By asking open-ended questions that require students to think deeply, analyze, and evaluate, teachers can guide students to explore complex issues and construct well-reasoned responses.
Real-World Problem Solving
Incorporating real-world problem-solving scenarios into the curriculum can provide students with practical opportunities to apply critical thinking. These problems can range from scientific experiments to ethical dilemmas, encouraging students to assess situations, weigh evidence, and make informed decisions.
Encouraging group collaboration on these tasks can further enhance critical thinking by promoting different perspectives and solutions.
Creating a Physical Environment that Supports Critical Thinking
Classroom design and furniture also play a role in promoting critical thinking. A flexible classroom setup allows for collaborative learning and group discussions, encouraging students to engage in critical dialogue.
By providing comfortable seating options and ensuring that the classroom layout is adaptable, teachers can foster a more dynamic learning environment conducive to critical thinking.
Encouraging Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking is a vital component of critical thinking, as it involves generating multiple solutions to a problem. Teachers can encourage this by using brainstorming techniques, mind maps, or role-playing exercises.
By allowing students to explore various angles and creative solutions, educators nurture their capacity for innovative problem-solving.
Analyzing Multiple Perspectives
Critical thinking is not limited to one perspective; it involves considering multiple viewpoints. Teachers can introduce debates, case studies, or simulations where students must analyze and argue from different angles.
Encouraging students to appreciate different viewpoints and make informed judgments fosters a more well-rounded and critical thinker.
Scaffolding Critical Thinking
To ensure that students of all ages can develop critical thinking skills, educators can scaffold the learning process. This involves providing support and gradually increasing the complexity of tasks.
For instance, younger students may begin by identifying problems, while older students progress to proposing solutions and evaluating their effectiveness.
Metacognition and Self-Reflection
Metacognition is the practice of thinking about thinking. It encourages students to assess their thought processes and strategies. Teachers can promote metacognition by encouraging students to self-reflect on their learning experiences.
When students consider how they approach problems and what strategies work best for them, they can refine their critical thinking skills.
Interdisciplinary Learning
Breaking down the barriers between subjects can also promote critical thinking. Interdisciplinary learning allows students to make connections between different fields of knowledge, encouraging them to draw on a wider range of information and skills to address problems.
Teachers can collaborate to create lesson plans that bridge the gaps between subjects, promoting a more holistic approach to critical thinking.
Feedback and Assessment
Effective feedback and assessment play a significant role in promoting critical thinking. Constructive feedback helps students understand where they can improve and refine their thinking.
Moreover, formative assessment strategies can help educators gauge students’ critical thinking abilities and adjust their teaching accordingly.
In summary, cultivating critical thinking within educational settings is a complex task that necessitates fostering a growth mentality, utilizing efficient questioning methods, advocating for real-life problem resolution, and supporting diverse thought processes.
Moreover, it entails emphasizing metacognition, appreciating numerous viewpoints, integrating interdisciplinary education, and offering evaluation and feedback. By adopting these pragmatic strategies, teachers can enable students to develop critical thinking skills, equipping them to face future obstacles effectively.
If you liked this article, check out Higher Education: Using AI to Meet Student Needs .

Five Trends to Watch During the 2018-2019 School Year

Pearson Will Open Four New Connections Academy Virtual Charter Schools for the 2019 Fall Semester

Why EdTech Companies Need Superintendents: Interview With the CEO of the Institute For Education Innovation, Doug Roberts

How Online Education Can Help Students Weather the Hurricane Season

Will EdTech Weather the Post-Coronavirus Recession?

Careers: 5 Essential Salary Questions
No comments, leave a reply, most popular post.

© 2023 eLearningInside.com All Rights Reserved.
Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom: Strategies and Activities
ritical thinking is a valuable skill that empowers students to analyze information, think deeply, and make reasoned judgments. By promoting critical thinking in the classroom, educators can foster intellectual curiosity, enhance problem-solving abilities, and prepare students for success in an ever-evolving world. This article explores effective strategies and engaging activities to promote critical thinking among students.
1. Ask Thought-Provoking Questions
Encourage critical thinking by asking open-ended and thought-provoking questions that stimulate students' analytical thinking. For example, in a history class, instead of asking "When did World War II start?" you could ask "What were the underlying causes of World War II and how did they contribute to its outbreak?" This prompts students to go beyond simple factual recall and encourages them to analyze historical events, evaluate multiple factors, and develop a deeper understanding of the topic. Instead of seeking one correct answer, focus on guiding students to explore different perspectives, evaluate evidence, and justify their reasoning. Engage students in discussions that require them to analyze, compare, and synthesize information.
2. Provide Real-World Examples
Connect classroom learning to real-world applications by providing relevant examples and case studies. By presenting authentic scenarios, students can apply critical thinking skills to analyze and solve complex problems. Encourage students to think critically about the implications of their decisions and consider the broader impact of their choices.
3. Foster Collaboration and Debate
Promote collaborative learning environments where students can engage in respectful debates and discussions. Encourage students to express diverse opinions, support their arguments with evidence, and listen actively to others' viewpoints. Through collaborative activities, students can learn to evaluate different perspectives, challenge assumptions, and develop their critical thinking skills.
4. Encourage Reflection and Metacognition
Provide opportunities for students to reflect on their thinking processes and metacognition. Ask students to evaluate their own problem-solving strategies, analyze their decision-making processes, and assess the effectiveness of their critical thinking skills. By promoting self-awareness and reflection, students can enhance their critical thinking abilities and become more independent learners.
5. Incorporate Problem-Based Learning
Integrate problem-based learning activities that require students to apply critical thinking skills to solve complex problems. For example, in a science class, present a real-world scenario where students need to design an experiment to test the effectiveness of different fertilizers on plant growth. This activity prompts students to analyze information about fertilizers, evaluate different options, and develop a well-reasoned experimental design. By engaging in hands-on problem-solving experiences like this, students can develop their critical thinking abilities while also building their content knowledge.
Promoting critical thinking in the classroom is essential for developing students' analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, and intellectual curiosity. By incorporating strategies such as asking thought-provoking questions, providing real-world examples, fostering collaboration and debate, encouraging reflection and metacognition, and incorporating problem-based learning, educators can create an environment that nurtures critical thinking skills. By equipping students with this valuable skill set, we empower them to navigate complex challenges and become lifelong learners.
Top 10 Educational Apps for Interactive Learning in the Classroom
10 ways to foster creativity in the classroom, top 10 educational podcasts for teachers on the go, best platforms to create a classroom blog: a comprehensive overview, join our newsletter and get the latest posts to your inbox, 10 reasons why you should teach abroad: expanding horizons and making a difference, teacher burnout: recognizing and preventing exhaustion, stay in touch.

There is More Posts
The adventure begins: exploring exotic teaching destinations around the globe, unconventional teaching jobs abroad: thinking outside the classroom for exciting opportunities, teaching abroad with a teaching fellowship: gaining professional development and global experience.

Award-Winning!

Thinking Classrooms: How To Promote Critical Thinking In Class
The Thinking Classroom is an approach to teaching that prioritizes the development of students’ critical thinking skills. In this type of classroom, the teacher acts as a facilitator rather than a traditional lecturer. Students are encouraged to actively engage with the material and collaborate with their peers.
The key to a Thinking Classroom is to focus on the process of learning rather than simply the acquisition of knowledge. This means that teachers must create opportunities for students to think critically, solve problems, and reflect on their learning.
We’ve rounded up the 14 practices of a Thinking Classroom below.

What are the 14 Practices of a Thinking Classroom?
The fourteen principles of a Thinking Classroom are designed to promote a classroom environment that encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration.
Here’s a summary of each principle to help teachers create an engaging and effective learning environment:
1. Classroom Culture of Thinking
Create a classroom culture that values thinking, learning, and intellectual development. Start with thinking tasks that are separate from your curriculum. This eases the transition to everyday thinking classroom activities. It’s hard for students to think deeper and for longer periods, so this transition should be gradual. You can start with non-curricular tasks as an ice breaker at the beginning of the school year.
2. Opportunities to Think in Groups
Provide opportunities for students to think and engage in meaningful group learning experiences. The Thinking Classroom practices emphasize “visibly random groups” that change frequently. This reduces social anxiety in the group and decreases communication barriers.
3. Vertical and Non-permanant Workspaces
You may have noticed that the traditional method of having students sit at their desks and take notes is only sometimes the best way to promote active thinking in your classroom. Recent research has shown that students are more engaged and productive when standing and working on vertical non-permanent surfaces (VNPSs) like whiteboards, blackboards, or windows. The fact that the surface is non-permanent encourages risk-taking and experimentation, while the vertical orientation prevents students from disengaging.
4. Room Layout
Research has shown that traditional, front-facing classrooms promote passive learning. At the same time, a more flexible, de-fronted setup—where students are free to face any direction—can be much more effective in promoting active thinking and engagement. So when designing your classroom layout, it’s essential to consider how the physical space can support the learning you want to see.
5. Answer Questions that Promote Thinking
You answer hundreds of questions each day in class. But not all of the questions encourage your students to keep thinking. Here are the common types:
- Proximity questions: Questions students ask because you’re close by and convenient.
- Stop-thinking questions: Questions students ask so they can mark a task complete. (i.e., Is this right?)
- Keep-thinking questions: Questions that help them along, so they can continue working through a task.
Answer only questions that keep students thinking.
6. Give Tasks in the Right Manner
Give tasks early in class while students are standing around a teacher. Give verbal tasks, and avoid visual cues that promote passive learning. This differs from the traditional manner of giving examples from the textbook or a worksheet.
7. Homework
Stop giving homework and instead give students opportunities to check their understanding. Make it optional so students can freely engage with authentic practice.
8. Promote Student Autonomy
As step 5 outlines, don’t solve problems for students. Let them struggle so they build confidence in their independence. This may mean asking a peer for help or looking around the room for a hint. When students are on their own, they take ownership of their learning.
9. Give Support So Students Can Learn at Their Own Pace
Encourage students to learn at their own pace by creating hints, extensions, and practice that meets them where they are in their learning. This is different from the typical guided practice that occurs in most classrooms.
10. Consolidate Lessons
Consolidation is crucial to help students combine different parts of a task or activity and ultimately form a more comprehensive understanding of the concept taught. Traditionally, teachers have relied on methods like showing, telling, or explaining to help students achieve their learning objectives.
In a thinking classroom, consolidation takes a different approach. Instead of relying on teacher-led instruction, consolidation works upward from the basic foundation of a concept. By drawing on the student work produced during their thinking on a common set of tasks, teachers can help students develop a deeper understanding of the concept.
To facilitate this process, teachers should provide open-ended questions, encourage peer-to-peer discussions, or engage in activities that allow students to explore and experiment with the concept taught.
11. Give Students Autonomy Over Notes
Only one in five students review their notes again after taking them in class. Give students the option of choosing which notes to take while learning. They are more likely to refer back to notes later.
12. Evaluate Values That Matter Most
If you want your students to participate, take risks, and persevere in the classroom, you should incorporate these values into evaluations. Assessment should go beyond curriculum knowledge.
13. Bring Students into Formative Assessment
Your students need to understand where they are and where they need to be with their learning. This means that they need to be a partner in formative assessment . Like students taking the lead over homework, they need to take the lead on owning their success in formative assessment.
14. Assessment Needs to Connect to an Outcome
Use assessments that measure and value thinking and understanding, not just rote memorization. This may look like standards-based grading. Students need to understand what they know and don’t know after they complete an assessment.
By implementing these principles, teachers can create a dynamic and engaging classroom that promotes deep learning and helps students develop the critical thinking and problem-solving skills they need to succeed in school and beyond.
TeacherMade helps teachers infuse technology into their Thinking Classrooms.
TeacherMade does more than convert PDFs into online activities. Teachers use TeacherMade to promote critical thinking skills. You can incorporate the Thinking Classroom practices with TeacherMade:
- Every TeacherMade assignment is a non-permanent surface. Students can complete assignments again and again until they have reached mastery.
- Create a culture of practice rather than homework and worksheets. With TeacherMade, you can choose to grade or not grade assignments. Students can complete practice as many times as they need.
- TeacherMade supports asynchronous learning so that students can learn at their own pace.
- Students are more involved with formative assessment when they receive instant feedback via auto-grading.
- You can leave feedback, hints, and notes so that students fully understand their assessment results.

TeacherMade transforms teaching materials into interactive digital lessons and saves teachers time with instant autograding. Our platform integrates seamlessly with major systems for personalized student engagement.

© 2024 All Rights Reserved.
- Research Article
Critical Thinking Skills in the Classroom and Beyond
Teaching Strategies
Becoming a critical thinker isn’t an unreachable goal. As Arthur Aufderheide, the Mummy Doctor, once said, “All knowledge is connected to all other knowledge. The fun is in making the connections.”
What does that have to do with critical thinking? Everything! Critical thinking is taking our natural curiosity and making meaningful connections. We solve problems daily, and critical thinking plays an essential role in the process. Observing, analyzing, and maybe even failing as we process solutions to life’s everyday puzzles is necessary. Critical thinking isn’t about acting on your beliefs. It extends to reasoning, communication, reflection, and action.
With roots dating back to the mid-late 20th century , the term "critical thinking" has evolved through the years. It takes discipline to critically think because it requires questioning, open-mindedness, and problem-solving skills . Developing critical thinking skills in students is vital to success in all content areas and extracurricular activities.
What does critical thinking look like in the classroom?
Critical thinking in the classroom looks like examining and brainstorming. It’s a fearlessness to analyze, test, and even reject ideas. It’s metacognition , which is simply thinking about thinking. Critical thinking happens when teachers ask thought-provoking questions and resist the urge to generate ideas for students.
What can teachers do to foster critical thinking?
- Ask questions without one specific answer to find.
- Allow students to explain their thinking with pictures, numbers, or words.
- Support the productive struggle .
- Brainstorm as a whole class so that students hear the thoughts of others.
- Compare and contrast! Get students to recognize and understand different sides to one issue.
- Make connections to prior knowledge.
- Encourage students to dig deeper by considering and analyzing alternatives to their first reactions and answers.
- Have students explain why they chose to do tasks in certain ways.
- Share helpful processes to try when things seem tricky. Invite students to give their tips.
- Provide opportunities for students to gather and evaluate information .
- Don’t stop when an assignment is over. Take valuable time for reflection.
Critical thinking beyond the classroom
Critical thinking is one skill that transfers from the classroom to the real world. It’s also necessary for success in academic and professional careers . Every single one of us has to ask purposeful questions and communicate our thoughts effectively. Critical thinking is more than that! It improves decision-making and objective reasoning. It allows us to move beyond emotional reactions to analysis, conclusions, and positive and negative consequences. True critical thinking also involves reflection to see the cause and effect of our decisions.
Critical thinking is one skill that transfers from the classroom to the real world.
Helping your students develop critical thinking skills benefits the whole child. A lot is going on in their worlds. Understanding how to think through decisions is a crucial skill. Set your students up for success with plenty of opportunities for critical thinking in your classroom!
ExploreLearning delivers critical thinking opportunities in math and science that are serious fun! Take a closer look!
Incite curiosity and invite interactions in STEM for students 3-12.
Help students 3-5 build deep conceptual fractions understanding.
Give students 2-5 the foundation they need to succeed at math.
Prepare K-2 students for success in STEM with Science4Us.
You might also like these stories...
Sign up to get the latest updates from ExploreLearning via occasional email.
Critical Thinking: Facilitating and Assessing the 21st Century Skills in Education
So many times we hear our students say, “Why am I learning this?”

I believe that Critical Thinking is the spark that begins the process of authentic learning. Before going further, we must first develop an idea of what learning is… and what learning is not. So many times we hear our students say, “Why am I learning this?” The reason they ask is because they have not really experienced the full spectrum of learning, and because of this are actually not learning to a full rewarding extent! We might say they are being exposed to surface learning and not authentic (real) learning. The act of authentic learning is actually an exciting and engaging concept. It allows students to see real meaning and begin to construct their own knowledge. Critical Thinking is core to learning. It is rewarding, engaging, and life long. Without critical thinking students are left to a universe of concepts and memorization. Yes… over twelve years of mediocrity! When educators employ critical thinking in their classrooms, a whole new world of understanding is opened up. What are some reasons to facilitate critical thinking with our students? Let me begin:
Ten Reasons For Student Critical Thinking in the classroom
- Allows for necessary inquiry that makes learning exciting
- Provides a method to go beyond memorization to promote understanding.
- Allows students to visualize thoughts, concepts, theories, models & possibilities.
- Promotes curriculum standards, trans-disciplinary ideas & real world connections.
- Encourages a classroom culture of collaboration that promotes deeper thinking.
- Builds skills of problem solving, making implications, & determining consequences.
- Facilitates goal setting, promotion of process, and perseverance to achieve.
- Teaches self reflection and critique, and the ability to listen to others’ thoughts.
- Encourages point of view while developing persuasive skills.
- Guides interpretation while developing a skill to infer and draw conclusions.
I am excited by the spark that critical thinking ignites to support real and authentic learning in the classroom. I often wonder how much time students spend in the process of critical thinking in the classroom. I ask you to reflect on your typical school day. Are your students spending time in area of surface learning , or are they plunging into the engaging culture of deeper (real) learning? At the same time … how are you assessing your students? So many times as educators, we are bound by the standards, and we forget the importance of promoting that critical thinking process that makes our standards come alive with understanding. A culture of critical thinking is not automatic, though with intentional planning it can become a reality. Like the other 21st century skills, it must be built and continuously facilitated. Let’s take a look at how, we as educators, can do this.
Ten Ways to Facilitate Student Critical Thinking in the Classroom and School
- Design Critical Thinking Activities. (This might include mind mapping, making thinking visible, Socratic discussions, meta-cognitive mind stretches, Build an inquiry wall with students and talk about the process of thinking”
- Provide time for students to collaborate. (Collaboration can be the button that starts critical thinking. It provides group thinking that builds on the standards. Have students work together while solving multi-step and higher order thinking problems. Sometimes this might mean slow down to increase the learning.)
- Provide students with a Critical Thinking rubric. (Have them look at the rubric before a critical thinking activity, and once again when they are finished)
- Make assessment of Critical Thinking an ongoing effort. (While the teacher can assess, have students assess themselves. Self assessment can be powerful)
- Concentrate on specific indicators in a rubric. (There are various indicators such as; provides inquiry, answers questions, builds an argument etc. Concentrate on just one indicator while doing a lesson. There can even be an exit ticket reflection)
- Integrate the idea of Critical Thinking in any lesson. ( Do not teach this skill in isolation. How does is work with a lesson, stem activity, project built, etc. What does Critical Thinking look like in the online or blended environment? Think of online discussions.)
- Post a Critical Thinking Poster in the room. (This poster could be a copy of a rubric or even a list of “I Can Statements”. Point it out before a critical thinking activity.
- Make Critical Thinking part of your formative and summative assessment. (Move around the room, talk to groups and students, stop the whole group to make adjustments.)
- Point out Critical Thinking found in the content standards. (Be aware that content standards often have words like; infer, debate, conclude, solve, prioritize, compare and contrast, hypothesize, and research. Critical Thinking has always been part of the standards. Show your students Bloom’s Taxonomy and post in the room. Where are they in their learning?
- Plan for a school wide emphasis. (A culture that builds Critical Thinking is usually bigger then one classroom. Develop school-wide vocabulary, posters, and initiatives.)
I keep talking about the idea of surface learning and deeper learning. This can best be seen in Bloom’s Taxonomy. Often we start with Remembering. This might be essential in providing students the map to the further areas of Bloom’s. Of course, we then find the idea of Understanding. This is where I believe critical thinking begins. Sometimes we need to critically think in order to understand. In fact, you might be this doing right now. I believe that too much time might be spent in Remembering, which is why students get a false idea of what learning really is. As we look at the rest of Bloom’s ( Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create) we can see the deeper learning take place. and even steps toward the transfer and internalization of the learning. Some educators even tip Bloom’s upside down, stating that the Creating at the top will build an understanding. This must be done with careful facilitation and intentional scaffold to make sure there is some surface learning. After-all, Critical Thinking will need this to build on.
I have been mentioning rubrics and assessment tools through out this post. To me, these are essential in building that culture of critical thinking in the classroom. I want to provide you with some great resources that will give your some powerful tools to assess the skill of Critical Thinking. Keep in mind that students can also self assess and journal using prompts from a Critical Thinking Rubric.
Seven Resources to Help with Assessment and Facilitation of Critical Thinking
- Habits of Mind – I think this is an awesome place to help teachers facilitate and assess critical thinking and more. Check out the free resources page which even has some wonderful posters. One of my favorites is the rubrics found on this research page . Decide on spending some time because there are a lot of great resources.
- PBLWorks – The number one place for PBL in the world is at PBLWorks. You may know it as the BUCK Institute or BIE. I am fortunate to be part of their National Faculty which is probably why I rank it as number one. I encourage you to visit their site for everything PBL. This link brings you to the resource area where you will discover some amazing rubrics to facilitate Critical Thinking. You will find rubrics for grade bands K-2, 3-5, and 6-12. This really is a great place to start. You will need to sign up to be a member of PBLWorks. This is a wonderful idea, after-all it is free!
- Microsoft Innovative Learning – This website contains some powerful rubrics for assessing the 21st Century skills. The link will bring you to a PDF file with Critical Thinking rubrics you can use tomorrow for any grade level. Check out this two page document defining the 4 C’s and a movie giving you even more of an explanation.
- New Tech School – This amazing PBL group of schools provide some wonderful Learning Rubrics in their free area. Here you will find an interesting collection of rubrics that assesses student learning in multiple areas. These are sure to get you off and started.
- Foundation for Critical Thinking – Check out this amazing page to help give you descriptors.
- Project Zero – While it is not necessarily assessment based, you will find some powerful routines for making thinking visible . As you conduct these types of activities you will find yourself doing some wonderful formative assessment of critical thinking.
- Education Week – Take a look at this resource that provides some great reasoning and some interesting links that provide a glimpse of critical thinking in the classroom.
Critical Thinking “I Can Statements”
As you can see, I believe that Critical Thinking is key to PBL, STEM, and Deeper Learning. It improves Communication and Collaboration, while promoting Creativity. I believe every student should have these following “I Can Statements” as part of their learning experience. Feel free to copy and use in your classroom. Perhaps this is a great starting place as you promote collaborative and powerful learning culture!
- I can not only answer questions, but can also think of new questions to ask
- I can take time to see what I am thinking to promote even better understanding
- I can attempt to see other peoples’ thinking while explaining my own
- I can look at a problem and determine needed steps to find a solution
- I can use proper collaboration skills to work with others productively to build solutions
- I can set a goal, design a plan, and persevere to accomplish the goal.
- I can map out strategies and processes that shows the action involved in a task.
- I can define and show my understanding of a concept, model, theory, or process.
- I can take time to reflect and productively critique my work and the work of others
- I can understand, observe, draw inferences, hypothesize and see implications.
cross-posted at 21centuryedtech.wordpress.com
Michael Gorman oversees one-to-one laptop programs and digital professional development for Southwest Allen County Schools near Fort Wayne, Indiana. He is a consultant for Discovery Education, ISTE, My Big Campus, and November Learning and is on the National Faculty for The Buck Institute for Education. His awards include district Teacher of the Year, Indiana STEM Educator of the Year and Microsoft’s 365 Global Education Hero. Read more at 21centuryedtech.wordpress.com .
Tech & Learning Newsletter
Tools and ideas to transform education. Sign up below.
PRODUCT SPOTLIGHT: LocknCharge FUYL Smart Locker System Simplifies Device Management for Schools
Colleges Are Using AI To Predict Student Success. These Predictions Are Often Wrong
How Implementing Coding, STEM, and Robotics Early Can Benefit Students
Most Popular
- 2 Colleges Are Using AI To Predict Student Success. These Predictions Are Often Wrong
- 3 How Implementing Coding, STEM, and Robotics Early Can Benefit Students
- 4 A New Book Argues Grades Are Failing Students. Here’s Why
- 5 Facing History and Ourselves: How to Use It to Teach
BLOG | PODCAST NETWORK | ADMIN. MASTERMIND | SWAG & MERCH | ONLINE TRAINING

- Meet the Team
- Join the Team
- Our Philosophy
- Teach Better Mindset
- Custom Professional Development
- Livestream Shows & Videos
- Administrator Mastermind
- Academy Online Courses
- EDUcreator Club+
- Podcast Network
- Speakers Network
- Free Downloads
- Ambassador Program
- Free Facebook Group
- Professional Development
- Request Training
- Speakers Network Home
- Keynote Speakers
Strategies to Increase Critical Thinking Skills in students
Teach Better Team October 2, 2019 Blog , Engage Better , Lesson Plan Better , Personalize Student Learning Better

In This Post:
- The importance of helping students increase critical thinking skills.
- Ways to promote the essential skills needed to analyze and evaluate.
- Strategies to incorporate critical thinking into your instruction.
We ask our teachers to be “future-ready” or say that we are teaching “for jobs that don’t exist yet.” These are powerful statements. At the same time, they give teachers the impression that we have to drastically change what we are doing .
So how do we plan education for an unknown job market or unknown needs?
My answer: We can’t predict the jobs, but whatever they are, students will need to think critically to do them. So, our job is to teach our students HOW to think, not WHAT to think.
Helping Students Become Critical Thinkers
My answer is rooted in the call to empower our students to be critical thinkers. I believe that to be critical thinkers, educators need to provide students with the strategies they need. And we need to ask more than just surface-level questions.
Questions to students must motivate them to dig up background knowledge. They should inspire them to make connections to real-world scenarios. These make the learning more memorable and meaningful.
Critical thinking is a general term. I believe this term means that students effectively identify, analyze, and evaluate content or skills. In this process, they (the students) will discover and present convincing reasons in support of their answers or thinking.
You can look up critical thinking and get many definitions like this one from Wikipedia: “ Critical thinking consists of a mental process of analyzing or evaluating information, particularly statements or propositions that people have offered as true. ”
Essential Skills for Critical Thinking
In my current role as director of curriculum and instruction, I work to promote the use of 21st-century tools and, more importantly, thinking skills. Some essential skills that are the basis for critical thinking are:
- Communication and Information skills
- Thinking and Problem-Solving skills
- Interpersonal and Self- Directional skills
- Collaboration skills
These four bullets are skills students are going to need in any field and in all levels of education. Hence my answer to the question. We need to teach our students to think critically and for themselves.
One of the goals of education is to prepare students to learn through discovery . Providing opportunities to practice being critical thinkers will assist students in analyzing others’ thinking and examining the logic of others.
Understanding others is an essential skill in collaboration and in everyday life. Critical thinking will allow students to do more than just memorize knowledge.
Ask Questions
So how do we do this? One recommendation is for educators to work in-depth questioning strategies into a lesson launch.
Ask thoughtful questions to allow for answers with sound reasoning. Then, word conversations and communication to shape students’ thinking. Quick answers often result in very few words and no eye contact, which are skills we don’t want to promote.
When you are asking students questions and they provide a solution, try some of these to promote further thinking:
- Could you elaborate further on that point?
- Will you express that point in another way?
- Can you give me an illustration?
- Would you give me an example?
- Will you you provide more details?
- Could you be more specific?
- Do we need to consider another point of view?
- Is there another way to look at this question?
Utilizing critical thinking skills could be seen as a change in the paradigm of teaching and learning. Engagement in education will enhance the collaboration among teachers and students. It will also provide a way for students to succeed even if the school system had to start over.
[scroll down to keep reading]
Promoting critical thinking into all aspects of instruction.
Engagement, application, and collaboration are skills that withstand the test of time. I also promote the integration of critical thinking into every aspect of instruction.
In my experience, I’ve found a few ways to make this happen.
Begin lessons/units with a probing question: It shouldn’t be a question you can answer with a ‘yes’ or a ‘no.’ These questions should inspire discovery learning and problem-solving.
Encourage Creativity: I have seen teachers prepare projects before they give it to their students many times. For example, designing snowmen or other “creative” projects. By doing the design work or by cutting all the circles out beforehand, it removes creativity options.
It may help the classroom run more smoothly if every child’s material is already cut out, but then every student’s project looks the same. Students don’t have to think on their own or problem solve.
Not having everything “glue ready” in advance is a good thing. Instead, give students all the supplies needed to create a snowman, and let them do it on their own.
Giving independence will allow students to become critical thinkers because they will have to create their own product with the supplies you give them. This might be an elementary example, but it’s one we can relate to any grade level or project.
Try not to jump to help too fast – let the students work through a productive struggle .
Build in opportunities for students to find connections in learning. Encouraging students to make connections to a real-life situation and identify patterns is a great way to practice their critical thinking skills. The use of real-world scenarios will increase rigor, relevance, and critical thinking.
A few other techniques to encourage critical thinking are:
- Use analogies
- Promote interaction among students
- Ask open-ended questions
- Allow reflection time
- Use real-life problems
- Allow for thinking practice
Critical thinking prepares students to think for themselves for the rest of their lives. I also believe critical thinkers are less likely to go along with the crowd because they think for themselves.

About Matthew X. Joseph, Ed.D.
Dr. Matthew X. Joseph has been a school and district leader in many capacities in public education over his 25 years in the field. Experiences such as the Director of Digital Learning and Innovation in Milford Public Schools (MA), elementary school principal in Natick, MA and Attleboro, MA, classroom teacher, and district professional development specialist have provided Matt incredible insights on how to best support teaching and learning. This experience has led to nationally publishing articles and opportunities to speak at multiple state and national events. He is the author of Power of Us: Creating Collaborative Schools and co-author of Modern Mentoring , Reimagining Teacher Mentorship (Due out, fall 2019). His master’s degree is in special education and his Ed.D. in Educational Leadership from Boston College.
Visit Matthew’s Blog

Connect with us to understand how we can help you.
State* Andhra Pradesh Chhattisgarh Delhi Gujarat Haryana Himachal Pradesh Karnataka Madhya Pradesh Maharashtra Odisha Punjab Rajasthan Tamil Nadu Telangana Uttar Pradesh Uttarakhand Others
- Solution Products* School Loans Smart Learning Maths and Science labs Digital Smart Classroom School ERP and Fee Management Integrated Curriculum Solution School Bus Insurance School Uniform
- I authorize Varthana to connect with me over call and WhatsApp overriding my registration with NDNC

- Board of Directors
- Our Investors
- School Solution
- VCARE – Varthana care for you

11 Tips For Teaching Critical Thinking Skills In The Classroom

- by Team Varthana
- Posted on December 26, 2023
- in Education
Critical thinking, often considered the cornerstone of education, empowers individuals to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to make informed decisions. Fostering critical thinking in the classroom is essential for preparing students to face the multifaceted challenges of the modern world. As an educator, cultivating an environment that encourages critical thinking is a primary goal. This article provides practical and effective tips to help teachers enhance critical thinking skills in their students, shaping them into informed, analytical, and thoughtful learners.
Create a Supportive Learning Environment
The fundamental pillar of nurturing critical thinking skills is establishing a supportive and inclusive learning environment. Students must feel safe and encouraged to express their thoughts and opinions without fear of judgment or ridicule. Open dialogue, active listening, and respect for diverse perspectives should be actively promoted within the classroom. When students feel comfortable, acknowledged, and respected, they are more likely to engage in critical discussions and share their viewpoints, fostering an atmosphere conducive to critical thinking.
Ask Thought-Provoking Questions
A crucial technique to stimulate critical thinking is the art of questioning. Teachers should pose questions that necessitate students to think critically and independently. It is essential to avoid yes/no questions or those that have simple factual answers. Instead, educators should frame open-ended questions that provoke analysis, interpretation, and evaluation. Encourage students to substantiate their answers with evidence and reasoning, cultivating a habit of more profound thought and analysis.

Promote Discussion and Debate
Engaging students in discussions and debates is an effective way to foster critical thinking. This encourages students to present evidence-based arguments, listen to opposing viewpoints, and construct counterarguments. Through this practice, students learn to analyze multiple perspectives and defend their own viewpoints using logical reasoning and evidence, thereby refining their critical thinking abilities.
Incorporate Real-World Examples
Connecting classroom content to real-life scenarios and examples is an excellent way to ignite critical thinking. When students can witness the practical application of what they are learning, it sparks their interest and curiosity. Encourage students to analyze these real-world examples, identify patterns, and draw conclusions based on their understanding. This practice helps students comprehend the relevance and significance of the knowledge they are acquiring.
Encourage Group Activities
Collaborative learning promotes critical thinking by providing a platform for students to share ideas and problem-solve together. Assigning group projects that require research, analysis, and synthesis of information encourages critical thinking. Each member brings a unique perspective, promoting diverse thinking and enhancing critical thought through collective efforts.
Also Read: 7 Tips for Teaching Financial Literacy to Children and Teenagers
Integrate Multimedia and Multisensory Learning
Integrating multimedia, videos, interactive simulations, or other interactive tools into the teaching process is an effective way to engage students. Different modalities of learning enhance critical thinking by providing diverse approaches to comprehend and analyze information. Encourage students to critique and evaluate the information presented in multimedia formats, fostering a well-rounded critical thinking experience.
Develop Information Literacy Skills
In the age of information, it’s crucial to teach students how to critically evaluate sources, assess credibility, and distinguish between reliable and biased information. Information literacy equips students with the ability to sift through vast amounts of data and determine what is trustworthy and relevant, a vital aspect of critical thinking. By honing these skills, students become adept at navigating the wealth of information available to them.
Assign Problem-Solving Tasks
Assigning problems that require students to apply knowledge, think critically, and devise solutions is an effective strategy. These problems can be related to the subject matter being taught or real-world challenges. Encourage students to brainstorm, analyze, and evaluate potential solutions, fostering their critical thinking abilities. Through this process, students learn to approach complex problems with a systematic and analytical mindset.
Foster a Growth Mindset
Promoting a growth mindset is paramount in enhancing critical thinking skills. Emphasize the belief that intelligence and abilities can be developed through effort and perseverance. Encourage students to embrace challenges, learn from failures, and view setbacks as opportunities for growth. A growth mindset cultivates resilience and enhances critical thinking skills by instilling the belief that abilities can be honed and improved over time.
Also Read: Importance of Teaching Kindergarten Kids about Sustainability
Encourage Reflection and Metacognition
Incorporating reflective exercises where students can ponder their learning experiences is essential. Encourage students to assess their thought processes, identify effective strategies, and recognize areas for improvement. Metacognitive practices help students become more aware of their thinking and learning strategies, enabling them to become more strategic and effective learners.
Provide Constructive Feedback
Offering constructive and specific feedback on assignments is a powerful tool to enhance critical thinking. Highlight the strengths and areas for improvement in a student’s work. Encourage students to reflect on this feedback and revise their work accordingly. Constructive feedback enhances critical thinking by guiding students to evaluate their own performance and make informed adjustments, promoting continuous improvement.
Creating a nurturing and encouraging learning environment lays the foundation for fostering critical thinking. It’s within this environment that thought-provoking questions, discussions, and real-world examples find their potency, encouraging students to delve into the realms of analysis and evaluation.
Educators, through their dedication and tireless efforts, can mold a generation of critical thinkers, preparing them to confront the multifaceted challenges of the 21st century. As the torchbearers of knowledge and insight, teachers play a pivotal role in ensuring a brighter and more informed future for all. Through their guidance, students are equipped with the indispensable skill of critical thinking, forming the bedrock of progress and enlightenment in society.
Latest Blogs
Beyond arts & crafts: unveiling the hidden academic benefits of summer camp, august 30, 2024, how is project-based learning helpful for students, july 11, 2024, building a brighter future: how parent involvement boosts student achievement, july 12, 2024, most viewed blogs, this software engineer from up now leads a school, bringing quality education to every village child, bloom’s taxonomy: your guide to designing powerful learning activities, july 17, 2024, level up learning: how to improve memory for studying, july 15, 2024.
- Activities (10)
- AI in Education (1)
- Announcement (1)
- Career Guidance (11)
- Classroom Management (35)
- Courses (2)
- Customer stories (131)
- Customer Story (3)
- Diversity in Education (14)
- Education (370)
- Education Awareness (6)
- Examination (3)
- Festive Learning (1)
- Financial Literacy (1)
- Mental health (15)
- Parent's Guide (13)
- Parents engagement (1)
- School finance (35)
- School Guide (20)
- School Infrastructure (11)
- School Leadership (19)
- School Loan (34)
- School Management (4)
- STEM Learning (11)
- Student Apps (1)
- Student loan (1)
- Student Productivity (11)
- teacher training (1)
- Teacher's Guide (27)
- Teachers training (2)
- Technology in Education (17)
- Uncategorized (7)
Dear Varthana Customer,
We have an information update regarding your loan/s with us.
Your details are submitted successfully.
You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/

Critical Thinking: A Guide For The Classroom And Beyond
“Clear, critical thinking should be at the heart of every discipline in school and a cultivated habit outside it too.” – Sir Ken Robinson

One of the great responsibilities for educators is to prepare students for the future in a complex and ever-changing world. As society and employment opportunities evolve, there is a greater need to develop 21st-century skills , such as critical thinking .
As an experienced educator, I understand the need to adapt to new challenges and equip students with the tools they need to navigate life beyond the classroom. This has become especially important during these uncertain times of the global pandemic.
The pandemic has placed further pressure on educators to adapt to new ways of working which also requires some critical thinking of their own.
This article will guide you through the fundamentals of Critical Thinking and provide tried and tested methods to use in your classroom and everyday life.
Critical Thinking Quick Guide:
- What is Critical Thinking?
Analytical Thinking vs Critical Thinking
Developing thinking skills, critical thinking in the classroom, critical thinking activities, critical thinking practice, barriers to critical thinking, food for thought, what is critical thinking.
“Critical thinking can be defined in a number of different ways consistent with each other, we should not put a lot of weight on any one definition. Definitions are at best scaffolding for the mind. With this qualification in mind, here is a bit of scaffolding: critical thinking is thinking about your thinking while you’re thinking in order to make your thinking better . ” – Richard Paul, author of Critical Thinking: How to Prepare Students for a Rapidly Changing World.
There is often a misconception that critical thinking is a negative process to disprove something. It would be more constructive to consider it as a means of putting an idea into perspective and seeing the bigger picture.
Critical thinking provides an opportunity to analyze and reflect on ideas. It also enables you to suspend past assumptions and self-doubt.
Analytical Thinking is a linear process which allows you to break down and review complex information. This type of thinking uses reasoning and logic to analyze the information presented, identify patterns and trends, and present facts and evidence.
Critical Thinking includes an element of analytical thinking but goes much further. It’s a more holistic process that results in a judgement of the validity of information using other sources. Critical thinking requires a detailed evaluation of the information. You should check for accuracy, any bias or assumptions, assess the conclusions and whether the evidence supports the conclusion.
Both of these skill sets should be developed to allow greater depth of thinking.

“We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them.” – Albert Einstein
When developing an academic curriculum, educators often refer to Bloom’s taxonomy – a model used to classify learning objectives. Within this model, thinking skills are categorized into lower and higher order thinking skills:
Lower order thinking skills – knowledge, comprehension and application Higher order thinking skills – analysis, synthesis and evaluation
The higher order thinking skills that students need for critical thinking can be assessed using a number of criteria:
- Use of information
- Questioning abilities
- Aptitude for communication and collaboration
- Ability to keep an open mind
- Ability to draw conclusions
- Self-awareness
Whilst this is not an exhaustive list, it is a good starting point for identifying learning outcomes and developing specific skills.
There are many tools that students can use to support their learning, such as interactive resources, social media and discussion groups to share thoughts and opinions. Connecting to others and the world around us can also help us to develop a greater understanding of ourselves.

“It is the mark of an educated mind to be able to entertain a thought without accepting it.” – Aristotle
“ How do you know that? ”
These two simple questions formed the basis of many interactions with students in my classroom, regardless of age or subject matter. When a student gave an answer to a question, I would ask one of these questions to encourage them to elaborate on their response. My students knew that I didn’t just want an answer but for them to demonstrate how they had arrived at the answer; I was interested in their critical thinking skills. Students would then consider if there were other ways to arrive at the same conclusion or whether there were alternative answers. They were also encouraged to ask their own questions to probe deeper into their thinking.
This simple resource can help students reflect and question their own thinking and ultimately develop their independent thinking skills for future learning.
Whilst this is just one anecdotal example to enhance critical thinking, there are many effective activities that you can use in the classroom with your students.

Continuum Line: Give students a key statement and a continuum line with ‘Always’ at one end and ‘Never’ at the other end. Students should determine where they would place themselves on the line and provide reasoning for their decisions. This task generates discussion and debate around the key statement. Some students may decide to change their position of the line throughout the course of the debate but persuasion is not the aim here. The purpose of the task is to elicit a range of viewpoints around the statement to support critical thinking.
Silent Debate: Set a number of written statements on large pieces of paper around the classroom. Students are then asked whether they agree or disagree with the statement. They should add their reasoning and also be encouraged to add to the ideas of others. This alternative to the traditional oral debate encourages everyone to contribute at the same time and promotes collaboration. It can be particularly effective for quieter class members.
Fact or Opinion?: Ask students to identify the facts and opinions within authentic articles or editorials. Encourage them to analyze the language and explain how they can distinguish the evidence from their beliefs.
All of these activities can be easily adapted from the classroom to online platforms such as Trello or Zoom breakouts rooms.
Check out this Critical Thinking Workbook for more examples.
“Everything we hear is an opinion, not a fact; everything we see is a perspective, not the truth.” – Marcus Aurelius.
In critical thinking, it is important not to willfully accept the all information presented. Question assumptions and ideas to determine whether or not you are seeing the bigger picture. ‘Fake News’ is a prime example of this.
Try these tips to hone your skills:
- Identify inconsistencies, errors, and omissions
- Find and understand links between ideas
- Develop systematic ways of solving problems
- Recognize problems before building any arguments
- Foster your curiosity – is there something else that hasn’t been explored?

A Closed Mind Everyone has opinions and their own perspective on some issues. If your bias is so strong that you are unwilling to consider any other perspectives, this leads to closed-mindedness. Your bias may be based on research outcomes that you consider unlikely to change. But critical thinkers know that even the basis of some knowledge can change over time. Check your assumptions to apply critical thinking.
Misunderstanding The Truth Or Facts We may occasionally accept beliefs presumed to be true but have little evidence to justify them. To demonstrate critical thinking, it’s crucial to distinguish facts from beliefs and to dig deeper by evaluating the "facts" and how much evidence there is to validate them.
Trusting Your Instincts When you trust your gut instincts, this is largely based on sensing or feeling. Using intuitive judgment is actually the last thing you should do if you want to demonstrate critical thinking, as you are less likely to question your assumptions or bias.
Lack Of Knowledge This barrier could be two-fold. Firstly, you may lack the knowledge and understanding of the higher-order skills required for critical thinking. Secondly, you may lack knowledge of the topic you need to evaluate. Recognizing this lack of understanding and carrying out research to close the knowledge gap will help to reduce the barrier.
Lack Of Effort Recognizing that critical thinking is not necessarily over-thinking is significant to removing this barrier. Even if you have developed the necessary skills, it is important to have the willingness to engage in the process of critical thinking.
Overcoming these barriers will help you to:
- Reinforce your problem-solving skills
- Boost your creativity
- Encourage curiosity
- Foster independence
- Develop your range of skills
- Provide you with a skill for life
Have you been evaluating the information presented in this guide?
Did you find yourself challenging or agreeing with points that have been raised?
Have you considered alternative ideas or new ways of thinking?
Are you think differently after reading this article?
If the answer is YES , you are already on the path to Critical Thinking!
Join us for more discussions at Aristotle’s Café .
Our Online Courses
- How to Use Zoom Like a Pro (And Look Good Doing It!)
- Online Authentic and Effective Communication (2021)
- Small Group Discussion Facilitation
- Persuasion, Sales, and Negotiation Skills for Life
Popular Posts
- 150+ Icebreaker Questions for Amazing Group Discussion (2023)
- How to Talk About Things That Matter – A Guide to Meaningful Conversations
- What Is Freedom, And How Can We Define It?
- Things I Learned From Article Writing For Aristotle’s Café
- Constructive Conflict vs Destructive Conflict: Managing Conflict Effectively
- Small Group Discussion Success: How to Super Engage Participants
- Topics to Talk About – 15 Experts Reveal Their Favorite Conversation Starters
- The Aristotle’s Cafe Definitive Guide to Toastmasters Table Topics (2021)
No products in the cart.

Critical thinking for teachers and students

What Do We Mean by the Term ‘Critical Thinking?’
Firstly, there is no single, commonly agreed definition of the term ‘critical thinking’.
However, most commonly as teachers, we use it to refer to what are known as the higher-order thinking skills.
These higher-order thinking skills are skills that require us to think in a deeper, more complex manner.
If you are familiar with Bloom’s taxonomy, think of the upper levels of the hierarchy – analyze, evaluate, create. We could also add infer to this list of critical thinking skills.
Put simply, critical thinking requires the student to engage in an objective analysis of a topic and evaluate the available information in order to form a judgment.
Critical thinking demands a systematic approach to evaluating new information. It encourages us to question and reflect on our own knowledge and how we arrive at the opinions we have and make the decisions we make.
THERE ARE NO FORMAL CRITICAL THINKING STANDARDS, BUT THESE ATTRIBUTES OUTLINED BY MONASH UNIVERSITY CAPTURE THE ESSENCE OF WHAT STUDENTS AND TEACHERS SHOULD ASPIRE TO IN THE CLASSROOM.
Why Is Critical Thinking Important?
Our students need to be able to think critically to make rational decisions on what to believe or what course of action to take.
An inability to think critically can leave students vulnerable to muddied thinking and the possibility of believing in unsound ideas.
Critical thinking helps students to filter the wheat from the chaff, intellectually speaking.
Developing strong critical thinking skills helps students to eliminate dubious data to leave only the strongest, most reliable information.
At its core, critical thinking is about having good reasons for our beliefs. It helps us to navigate through bias (our own and that of others) to avoid manipulation or becoming enslaved by our feelings. These are essential skills in an age of overwhelming information.
Helping our students to develop their critical thinking skills not only inoculates them against embracing flawed ideas, but these skills are also some of the most in-demand by employers and this looks set to continue to be so well into the future.
This is due to the ever-increasing pace of technological change. It is impossible to accurately predict the specific requirements of many future jobs. One thing is for sure though, so-called soft skills such as critical thinking will ensure students will be able to adapt to whatever shapes the workplace of the future will take.
Teaching Critical Thinking
There are any number of ways to introduce critical thinking into the classroom, either as discrete activities or interwoven into lessons with other stated objectives. However, it is helpful to students to take the time to teach a variety of strategies to help them think critically about the ideas they encounter which will help them form their own opinions.
An opinion based on critical thinking does not rely on gut feeling, but rather on rational reasoning which often requires some form of initial research.
Let’s start by taking a look at some ways you can encourage critical thinking in your classroom, especially in the research process.
THIS IS AN EXCELLENT GUIDE TO TEACHING CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS
A complete guide to teaching Critical Thinking
This 180 page e-book is an excellent resource for teachers looking to implement critical thinking in the classroom.
It is packed full of great content whether you are just starting out, or looking to go further.
It makes relevant connections to technology, STEM, and critical and creative thinking.
Teaching Strategies: A Step-by-Step Approach to Critical Thinking
The following process is a useful template for teaching students. When embarking on their research, this template provides a step-by-step process that they can use to structure their investigations.
1. Format the Question
In the age of the Internet, access to information is no longer the major hurdle facing the inquisitive student investigator. If anything, the real problem now is knowing how to appropriately sift through the almost inexhaustible amount of information out there.
The key to this filtration process is the formulation of the research question. How the question is composed and formatted will inform exactly what information the student is looking for and what information can be discarded.
The type of question formatted here will depend on the purpose of the research. For example, is the question intended to establish knowledge? Then, it may well be a straightforward What type question, for example, What are the consequences of a diet high in processed sugars?
If the question is geared more towards the use of that information or knowledge, then the question may be more of a Why type question, for example, Why do some commentators claim that a diet high in processed sugars is the greatest threat facing public health?
One extremely useful tool to assist in formatting questions that make demands on student critical thinking abilities is to employ Bloom’s taxonomy.
2. Gather the Information
Once the question has been clearly defined, then the process of gathering the information begins. Students should frequently refer back to their research questions to ensure they are maintaining their focus.
As they gather information concerning their question, reference to their initial question will help them to determine the relevance of the information in front of them. They can then weigh up whether or not the information helps move them further toward answering their initial research question.
3. Apply the Information
The ability to think critically about information is of no use unless the understanding gained can be applied in the real world.
The most practical application of this skill is seen when it is used to inform decision-making. When faced with making a decision, encourage students to reflect on the concepts at work in regard to the choice they face.
They must look at what assumptions exist and explore whether their interpretation of the issue is a logically sound one. To do this effectively, they will also need to consider the effects of that decision.

4. Consider the Implications
“The road to hell is paved with good intentions.”
As the old proverb suggests, our well-intended decisions can sometimes lead to unforeseen negative consequences. When considering paths of action, we need to encourage our students to reflect deeply on all possible outcomes of those actions: short, medium, and long-term.
Unintended consequences are outcomes that are unforeseen and can often undo much of the good of the original decision.
There are many fascinating examples of this phenomenon that are easily found online and can be interesting to share with the students.
One such example was uncovered by the economist Sam Peltzman. He found that when mandatory seat-belt legislation was passed in some of the US states the number of fatalities of drivers did go down as a result. However, he also found that this was offset by an increase in fatalities among pedestrians and cyclists as drivers felt safer wearing seat belts and many drove faster as a result.
5. Explore Other Points of View
This is the final testing ground of an opinion that has been forged in the fires of critical thinking. Though students will have been exposed to competing ideas earlier in the research stage, they should now take the time to measure their matured opinions against these other points of view.
Exploring alternative viewpoints helps us to evaluate our own choices and avoid stagnating in our own biases and innate preferences. Doing this helps us to make the most informed decisions possible.
Now that we’ve had a look at a step-by-step approach to critical thinking, let’s take a look at some creative ways to help students exercise those critical thinking muscles in the classroom. Getting critical doesn’t have to be boring!
Critical Thinking Games and Activities
The Barometer: Find Out Where You Stand
When considering where we stand on issues, it’s important to realise that things don’t always have to be a zero-sum game. Things don’t have to be all or nothing. Students need to learn that opinions can be nuanced and that often there exists a spectrum of opinions on any given issue.
In this activity, give the students a controversial issue to consider. Assign the extremes on the issue to opposite ends of the classroom and instruct students to arrange themselves along a continuum based on how strongly they feel about the issue.
They’ll likely need to engage in some free-flowing conversation to figure this out and setting a time limit will help ensure this discussion doesn’t go on endlessly.
Draw an Analogy: Making Lateral Links
This game encourages students to think creatively and indirectly about an idea or a subject and it can be used in practically any context. It encourages students to make comparisons between seemingly unconnected things by analyzing both for any underlying concepts that may link them together somehow – no matter how tenuously!
Start by asking your students a creative question based on the topic or idea you are exploring together in the classroom. The format of these questions should closely follow a similar pattern to the following examples:
● How is raising a child like building a house?
● Why is an egg like a hunk of marble?
● How is a bookshelf like a lunchbox?
The more inventive the elements in each question are, the more challenging it will be for the students to make links between the two of them.
This game can generate some interesting responses and is easy to differentiate for students of all ages. Younger students may enjoy a simpler question format such as ‘ Smell is to nose as sight is to… ’ where the links between the elements are much more obvious.
For older students, remember too that when devising the questions the links between the different elements do not have to be obvious. Indeed, as far as you’re concerned they do not even have to exist. That’s for the students to explore and create.
Build Critical Thinking Skills with Brain Teasers
Brain teasers are great fun and an enjoyable way to fill a few minutes of class time, but they also provide great exercise for students’ critical thinking abilities. Though they are often based on unlikely premises, the skills acquired in solving them can have real-world applications.
Let’s take an example to see how this works. Ask your students the following teaser – you might want to set a time limit and have them write their answers down to put some added pressure on:
A rooster sits on a barn and is facing west. The wind is blowing eastward at a speed of 15 kilometers per hour. The rooster lays an egg. Which cardinal direction does the egg roll?
The answer is, of course, that there is no egg. Roosters are male and therefore can’t lay eggs.
One of the reasons why so many will get this simple teaser wrong is that despite knowing that a rooster is a male chicken, they overlook it due to the casualness with which it’s thrown into the teaser.
The other reason is the misdirection caused by the quite meticulous detail provided. Students are likely to pay too much attention to the details such as the speed of the wind, its direction, and the direction of the rooster is facing.
All these irrelevant details distract the students from the fact that the only information required to solve this teaser is provided by the 2nd word of the riddle.
There are numerous brain teasers freely available on the Internet. Weaving them into your lessons gives students opportunities to sharpen their critical thinking skills by sorting relevant from irrelevant details and encouraging students to analyze closely the relevant details provided.
Build the Habit and Become a Critical Thinker

In this article, we have taken a look at some concrete ways to practice critical thinking skills in the classroom. However, becoming a critical thinker is much more about developing consistent critical thinking habits in our approach to ideas and opinions.
To help your students develop these habits, be sure to encourage intellectual curiosity in the classroom. Ask students to examine their own assumptions and evaluate these in light of opposing opinions and available evidence.
Create opportunities in your lessons to explore advertisements and even political statements together. Fight the urge to impart your own beliefs and biases in favor of allowing students to determine the credibility of the sources themselves. Encourage them to draw their own conclusions.
Consistently insist that your students provide evidence to support their conclusions when they express opinions in classroom discussions.
In time, the habit of critical thinking will inform how your students approach any new information that they come across. This will leave them better able to think clearly and systematically and better able to express themselves coherently too.
Create opportunities in your lessons to explore advertisements and even political statements together. Fight the urge to impart your own beliefs and biases in favor of allowing students to determine the credibility of the sources themselves. Encourage them to draw their conclusions.
Fostering Future Thinkers: 10 Dynamic Strategies for Cultivating Critical Thinking in the Classroom
- Socratic Questioning: Encourage students to engage in thoughtful discussions by employing Socratic questioning. This method involves asking open-ended questions that prompt deeper exploration of concepts, helping students develop analytical and reasoning skills.
- Real-World Problem-Solving: Integrate real-world problems into the curriculum, allowing students to apply critical thinking skills to authentic situations. This hands-on approach fosters practical problem-solving abilities and encourages creativity.
- Debate and Discussion: Organize debates and class discussions to expose students to diverse perspectives. This not only enhances their critical thinking but also teaches them how to construct persuasive arguments and consider alternative viewpoints.
- Case Studies: Utilize case studies from various fields to present complex scenarios. This challenges students to analyze information, identify key issues, and propose effective solutions, fostering critical thinking within specific contexts.
- Critical Reading and Writing: Emphasize critical reading and writing skills. Encourage students to analyze texts, identify main arguments, evaluate evidence, and express their thoughts coherently in writing. This enhances both analytical and communication skills.
- Concept Mapping: Introduce concept mapping as a visual tool to help students organize thoughts and relationships between ideas. This technique enhances their ability to see the bigger picture and understand the interconnectedness of concepts.
- Problem-Based Learning (PBL): Implement problem-based learning approaches, where students work collaboratively to solve complex problems. This method promotes critical thinking, teamwork, and the application of knowledge to real-world situations.
- Cognitive Dissonance Activities: Engage students in activities that provoke cognitive dissonance, challenging their existing beliefs or assumptions. This discomfort encourages critical examination and reflection, leading to intellectual growth.
- Metacognition Development: Foster metacognition by prompting students to reflect on their thinking processes. Encourage them to analyze how they approach problems, make decisions, and solve challenges, promoting self-awareness and self-correction.
- Role-Playing Scenarios: Create role-playing scenarios that require students to step into different perspectives or roles. This immersive approach encourages empathy, perspective-taking, and the ability to analyze situations from multiple viewpoints, enhancing overall critical thinking skills.
Similar Posts

Growth Mindset activities for teachers and students
Growth Mindset – What is it, and Why is it important? As educators, we are constantly advocating for the idea of…

Creative problem solving tools and skills for students and teachers
Creative Problem Solving: What Is It? Creative Problem Solving, or CPS, refers to the use of imagination and innovation to find…

An excellent collection of Fermi problems for your class
Enrico Fermi is the father of “solving maths problems we will never know the exact answer to.” Such as how many…
Five reasons why computational thinking is an essential tool for teachers and students.
Numerous countries and regions undertaking curriculum redesign within recent years have embraced computational thinking as an essential mindset for students and…

A Teacher’s Guide to Bloom’s Taxonomy
The purpose of this article is to develop a clear understanding of what Bloom’s Taxonomy is, and how you can apply…

Higher order thinking skills for students and teachers.
What Is Higher Order Thinking? In days gone by, rote learning was where it was at. Latin? Learn your grammar off…
Distance Learning
Using technology to develop students’ critical thinking skills.
by Jessica Mansbach
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a higher-order cognitive skill that is indispensable to students, readying them to respond to a variety of complex problems that are sure to arise in their personal and professional lives. The cognitive skills at the foundation of critical thinking are analysis, interpretation, evaluation, explanation, inference, and self-regulation.
When students think critically, they actively engage in these processes:
- Communication
- Problem-solving
To create environments that engage students in these processes, instructors need to ask questions, encourage the expression of diverse opinions, and involve students in a variety of hands-on activities that force them to be involved in their learning.
Types of Critical Thinking Skills
Instructors should select activities based on the level of thinking they want students to do and the learning objectives for the course or assignment. The chart below describes questions to ask in order to show that students can demonstrate different levels of critical thinking.
| Level of critical thinking | Skills students demonstrate | Questions to ask |
|---|---|---|
| Lower levels | ||
| Remembering | recognize, describe, list, identify, retrieve | |
| Understanding | explain, generalize, estimate, predict, describe | |
| Higher levels | ||
| Applying | carry out, use, implement, show, solve | |
| Analyzing | compare, organize, deconstruct | |
| Evaluating | check, judge, critique, conclude, explain | |
| Creating | construct, plan, design, produce | |
*Adapted from Brown University’s Harriet W Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning
Using Online Tools to Teach Critical Thinking Skills
Online instructors can use technology tools to create activities that help students develop both lower-level and higher-level critical thinking skills.
- Example: Use Google Doc, a collaboration feature in Canvas, and tell students to keep a journal in which they reflect on what they are learning, describe the progress they are making in the class, and cite course materials that have been most relevant to their progress. Students can share the Google Doc with you, and instructors can comment on their work.
- Example: Use the peer review assignment feature in Canvas and manually or automatically form peer review groups. These groups can be anonymous or display students’ names. Tell students to give feedback to two of their peers on the first draft of a research paper. Use the rubric feature in Canvas to create a rubric for students to use. Show students the rubric along with the assignment instructions so that students know what they will be evaluated on and how to evaluate their peers.
- Example: Use the discussions feature in Canvas and tell students to have a debate about a video they watched. Pose the debate questions in the discussion forum, and give students instructions to take a side of the debate and cite course readings to support their arguments.
- Example: Us e goreact , a tool for creating and commenting on online presentations, and tell students to design a presentation that summarizes and raises questions about a reading. Tell students to comment on the strengths and weaknesses of the author’s argument. Students can post the links to their goreact presentations in a discussion forum or an assignment using the insert link feature in Canvas.
- Example: Use goreact, a narrated Powerpoint, or a Google Doc and instruct students to tell a story that informs readers and listeners about how the course content they are learning is useful in their professional lives. In the story, tell students to offer specific examples of readings and class activities that they are finding most relevant to their professional work. Links to the goreact presentation and Google doc can be submitted via a discussion forum or an assignment in Canvas. The Powerpoint file can be submitted via a discussion or submitted in an assignment.
Pulling it All Together
Critical thinking is an invaluable skill that students need to be successful in their professional and personal lives. Instructors can be thoughtful and purposeful about creating learning objectives that promote lower and higher-level critical thinking skills, and about using technology to implement activities that support these learning objectives. Below are some additional resources about critical thinking.
Additional Resources
Carmichael, E., & Farrell, H. (2012). Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Online Resources in Developing Student Critical Thinking: Review of Literature and Case Study of a Critical Thinking Online Site. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice , 9 (1), 4.
Lai, E. R. (2011). Critical thinking: A literature review. Pearson’s Research Reports , 6 , 40-41.
Landers, H (n.d.). Using Peer Teaching In The Classroom. Retrieved electronically from https://tilt.colostate.edu/TipsAndGuides/Tip/180
Lynch, C. L., & Wolcott, S. K. (2001). Helping your students develop critical thinking skills (IDEA Paper# 37. In Manhattan, KS: The IDEA Center.
Mandernach, B. J. (2006). Thinking critically about critical thinking: Integrating online tools to Promote Critical Thinking. Insight: A collection of faculty scholarship , 1 , 41-50.
Yang, Y. T. C., & Wu, W. C. I. (2012). Digital storytelling for enhancing student academic achievement, critical thinking, and learning motivation: A year-long experimental study. Computers & Education , 59 (2), 339-352.
Insight Assessment: Measuring Thinking Worldwide
http://www.insightassessment.com/
Michigan State University’s Office of Faculty & Organizational Development, Critical Thinking: http://fod.msu.edu/oir/critical-thinking
The Critical Thinking Community
http://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766
Related Posts
Choosing a Web Conferencing Solution
Enter to Win an iRig Lavalier Microphone (by IK Multimedia)
Yellowdig: September 2015 Online Learning Webinar
Desktop Recording Tips & Tricks
9 responses to “ Using Technology To Develop Students’ Critical Thinking Skills ”
This is a great site for my students to learn how to develop critical thinking skills, especially in the STEM fields.
Great tools to help all learners at all levels… not everyone learns at the same rate.
Thanks for sharing the article. Is there any way to find tools which help in developing critical thinking skills to students?
Technology needs to be advance to develop the below factors:
Understand the links between ideas. Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas. Recognize, build and appraise arguments.
Excellent share! Can I know few tools which help in developing critical thinking skills to students? Any help will be appreciated. Thanks!
- Pingback: EDTC 6431 – Module 4 – Designing Lessons That Use Critical Thinking | Mr.Reed Teaches Math
- Pingback: Homepage
- Pingback: Magacus | Pearltrees
Brilliant post. Will be sharing this on our Twitter (@refthinking). I would love to chat to you about our tool, the Thinking Kit. It has been specifically designed to help students develop critical thinking skills whilst they also learn about the topics they ‘need’ to.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content

Developing critical thinking skills in the classroom
April 29, 2021
Critical thinking skills in the classroom: A teacher's guide to developing higher-order thinking and student reasoning.
Main, P (2021, April 29). Developing critical thinking skills in the classroom. Retrieved from https://www.structural-learning.com/post/what-is-critical-thinking
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is important in every aspect of our lives. It helps us make decisions, solve problems , and learn new information. But how do we develop these skills in school?
In order to become a well-rounded person who has developed critical thinking skills, students must first understand the importance of developing these skills. This means teaching students how to analyze data, evaluate arguments, and draw conclusions from evidence.
This article will help teachers teach critical thinking skills in the class room. We'll look at how to teach critical thinking skills using examples from history, science, math, literature, and art.
Critical thinking has been defined and re-defined by many teachers over the years and it's one of those essential abilities we want our students to develop. However, looking at the breakdown of the term as the two words that comprise it provides a simple, yet accurate definition.
The Critical Thinking process involves the use of the mind to incorporate prior experience and basic knowledge about a subject matter in order to reach conclusions. Critical thinking has a few definitions. In this article we are focused on what critical thinking looks like in the classroom.
We are interested in how we can make more logical and accurate thinking a classroom habit that every school can adopt. To examine the topic of critical thinking we have to look beyond the purely philosophical perspective and explore the latest cognitive science . For example, we now know the importance that knowledge plays in developing critical thinking, you can't have one without the other. Expert thinking is a domain specific skill and the subject disciplines act as a catalyst for enhancing this life long skill. We also know the importance of retrieval practice in developing higher order thinking.
Low stakes quizzing is not just rote learning, it plays an important part in freeing up our working memory to do more of the creative work. If we no longer have to strain to remember the facts and figures, our mental capacities can be put to work in more creative ways . Within the article we will also put forward some ideas about how to promote critical and creative thinking across your school.
Logical reasoning is one of the three main components of critical thinking. This component requires students to think critically about a problem and then apply logic to solve it. Students must understand the difference between logical and illogical arguments and recognize when someone is using logical fallacies.
Why critical thinking is important
Critical thinking is a process that is often viewed as a more intense version of just plain old thinking. In education, critical thinking is a disciplined process that has stuck around for a while now – but how is this coveted skill really different from just plain old thinking? Frankly, sometimes, it's not. The two terms can be used interchangeably, and often are.
Consider a teacher who is urging a student “think harder” or “think differently”. What the teacher is actually saying is: “think critically in order to reach a more complex solution”. We are not always conscious of the multitude of cognitive actions at our disposal, the Universal Thinking Framework addresses this issue by providing child-friendly explanations of the various ways in which we can think.
These can be chained together to create a logical inquiry that any student can follow. The idea being that over time, children begin to develop critical thinking dispositions that cause reflective thinking and advance the mental process. Increasing our repertoire of cognitive actions improves a students decision making process as they are simply more aware of the directions their learning could move in.

We have divided the various types of thinking using these key questions:
- How do I get started?
- How should I organise my ideas?
- How do I know this?
- How can I communicate my understanding?
- What can I do with my new knowledge and understanding?
All of the sections provide teachers with a systematic approach to encourage reflective thinking . The questions that are posed to the learner are designed to break down a complex process into basic skills. These thinking skills, over time can be mastered and understood. Having the different types of thinking available to both educators and students means that logical thinking can be achieved more readily and can eventually become an attitude of mind. The mental actions are accompanied by critical thinking questions . Teachers can use critical thinking questions to promote rational thinking.
Reflective thinking is employed when a solution is needed, or in school when there is a connection that needs to be drawn between two or more concepts. Therefore, critical thinking is, in essence, the thought processes that result from disapproval of the solutions and connections that already exist, or a lack thereof.

Mental skills or learning behaviours?
School leaders love to see and hear teachers incorporating the idea of crosscutting concepts into their daily instruction. That is, concepts and skills can be used and developed in more than one subject matter, and therefore more than one class. I don't think I have ever had an administrator who has not asked me how I plan to collaborate with my colleagues in order to make instruction more meaningful and applicable to my students' lives.
Upon further consideration of this popular interview question, there should really only ever be one acceptable response to such a question – “I will make it a priority to routinely engage my students in the practice of critical thinking so that they can grow that skill and use it in other classes as well as outside of the school” … or something along those lines.
It remains true that practice leads to confidence and increased ability. Therefore, as students learn what the process of thinking critically feels like for them, they will be able to replicate that feeling by replicating their actions in other classes. When critical thinking is used as a part of the daily routine, it becomes less scary to use that skill when faced with a problem, regardless of the subject matter .
Critical thinking is, therefore, a crosscutting concept to be planned for and incorporated into a teacher's daily lesson plans as well as the scope and sequence of a course. If you want a practical way of integrating critical thinking into your lessons, our mental modelling approach using the building block method might be a good place to start. The playful approach encourages children to organise their ideas and in doing so, engage in critical reasoning.
Principles of critical thinking
Despite its value in all subjects , one uncertainty that educators run into is the idea of what Daniel T. Willingham (2019) calls transfer. That is, whether or not the ability to think critically in one subject or in relation to one problem will automatically lead to similar abilities in other subjects or problems. As Willingham (2019) explains, the research on this idea is not necessarily all in agreement. Consequently, educators are faced with a task that seems to be in flux and altogether unanswered. While frustrating, this is not necessarily a new ask for educators.
Some scholars claim that the ability to think critically in one subject will naturally transfer to all other subjects , which is why it is so inherently valuable as a skill. Others argue that this is not the case, and that is why it is crucial to intentionally teach students how to think critically in all situations and across all subjects. With this quality still largely disagreed upon, it is difficult to know how best to proceed when attempting to teach and develop critical thinking skills.
Do students ever possess a true foundation of critical thinking skills and abilities, or do they regress back to a point of utter confusion with the introduction to each new problem? How can educators make these skills stick for their students ? What do students need to understand in order to be able approach problems from a critical thinking perspective regardless of the discipline or subject matter? How can we train students to recycle prior experience and previous solutions when faced with new problems?

Assessing students analytical thinking
Critical thinking is a high-level goal that educators everywhere strive toward for their students. Many “teacher moves” exist solely to work toward this purpose. However, repeatedly asking higher-order thinking questions in class and on tests, is merely the method that best demonstrates that the skill of thinking critically has already been developed. That is to say that just asking these types of questions as often as possible is not a sufficient method for the true development of this skill.
When we ask higher-order thinking questions in class or on assessments , we are ultimately trying to analyze whether or not students have that ability; or to what level they have mastered that ability. However, it stands to reason that the only way to develop this skill cannot be to simply ask more of these types of questions more often, since this is just the method of measurement. So, the question now becomes - what are the steps that lead up to a student being able to successfully encounter and respond to these higher-order thinking questions that show their ability to think critically? The answer is actually quite simple– continue to teach and prioritize critical thinking skills in every possible situation, regardless of how many times it has been reviewed.
What about critical thinking dispositions ? It has been argued that this ability is not a distinct cognitive skill but a set of critical thinking dispositions or habits of mind. Ron Ritchart talks through the argument here.
If your school is interested in implementing more critical thinking in your classrooms, you might want to start by sharing some key ideas with your staff. Our professional development approach gives staff access to the principles that underpinned critical thinking. We can help educators measure the impact of the interventions in the classroom.

How can we develop reasoning skills?
Notice that in the answer above, the onus is placed on the educator rather than the student. There is not necessarily a numbered universal list of steps to take when given a critical thinking problem that we can give to students as a road map and post as an anchor chart in the classroom. Quite the opposite, educators are charged with the vague task of teaching students how to access prior knowledge and experience and apply it in a way that will benefit them.
Ultimately, if students can manipulate their understanding and experience into a process and application that works for the task or question at hand, they are able to think critically . However, the ability to think critically in one situation does not predict with any real degree of certainty the same ability in a novel situation, especially one that seems more challenging to a student.
One characteristic that tends to make students believe that one situation is more difficult than another is subject matter. Students are not able to generalize solutions that they have already thought through because the subject matter is so different. Willingham (2019) refers to this as the surface structure of a problem and gives the example of an inability to derive the solution for a medical problem even though it is essentially the same as the solution to military/tactical problem that the group had just worked through.
However, since the surface structure of these problems seems so different, participants were not able to transfer the reasoning behind the solution to the tactical problem to the medical problem.Teachers see this difficulty with students all the time across subjects, which means that the real task for teachers to tackle is teaching students how to recognize the deep structure of a problem.

According to Willingham (2019), strong critical thinkers claim that they are able to recognize the deep structure of problems presented to them in their field of expertise, but not necessarily in other fields. This is both comforting and disconcerting for teachers. It is comforting because it shows that it is normal for it to be a challenge for students to be able to transfer critical thinking skills from one problem to another. However, it is disconcerting because it seems nearly impossible for teachers to be able to overcome this barrier if experts still encounter this barrier regularly.
All things considered, the seemingly realistic approach to the task of developing critical thinking skills in students through consistent practice seems to have a few clearly actionable approaches that are also memorable due to the alliteration they produce: collaboration , comparison and content knowledge. This form of knowledge is certainly important in everyday life.

Collaborative problem solving skills
Collaboration is the act of working with another person or other people in order to achieve a common goal or solve a common problem. In as many ways as possible, teachers should incorporate collaboration into their lessons. Initially, it may seem as though this practice takes away from the development of independent critical thinking since weaker thinkers can lean on stronger thinkers or just more dominant personalities. However, since subject-matter experts are easily able to identify the deep structure of problems within their area of expertise, it stands to reason that pairing experts together who excel in different areas and presenting them with a complex problem will yield the best results.
Of course, in any given group of students, there may not be identifiable “experts”, however, the idea is that the different perspectives and experiences that students bring with them will intuitively lead them to a problem from different angles . This type of natural exposure to different approaches serves to model for students how it is possible to think differently about a similar problem. With continued modelling and wider exposure, students will gradually learn to intentionally incorporate different ways of thinking and to continue to seek out differing perspectives when searching for a solution to a problem.
Logical thinking and careful thinking are often cited as being ways of thinking critically. The Cornell Critical Thinking Test and Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal both claim to be able to measure critical reasoning and critical thinking ability.
Comparisons and critical thinking
While telling students what the deep structure of a problem is might seem fairly simple, the fact is that telling does not equate to teaching, nor does it always result in learning, especially when a skill is involved . Therefore, one way to begin to lead students to be able to identify and extract the deep structure of a problem is to have them compare.
When asked to compare two (or more) problems with contrasting surface structures, students are forced to look harder for the similarities. While this may be met with resistance and frustration at first, when coupled with the practice of modelling these types of comparisons, students will begin to understand that there are similarities to be found after all, and how those comparisons can help lead to a practical and applicable solution.

Academic Arguments
Identification, construction , and evaluation of arguments are crucial parts of critical thinking.
People often use the term "argument" to refer to a quarrel between people in everyday life. To a logician or critical thinker, an argument is not a statement, it is a collection of statements , with one being the conclusion and the rest being premise or assumption.
The way students attain in subjects is by reading the views of the academic writing of others. The way students achieve in a formal exam setting is by writing the academic argument of their own. So without academic argument writing we cannot learn, or teach, or persuade. One way of promoting argumentation is by teaching students to create argument maps . This practical approach of developing an analysis of arguments means that students can visualise the main points in an easy-to-understand format.
Domain Knowledge and critical thinking
Sometimes, educators tend to avoid questions and practice activities that can be labelled as “ basic recall ” because they are said to be low in rigour. However, when attempting to develop critical thinking skills , it should be noted that domain knowledge expertise is achieved through extensive knowledge of the foundational aspects and facts of a topic. Willingham (2019) explains that effective critical thinking about a problem often comes from a place of confidence in the subject matter, which is born from extensive knowledge about it.
Being able to see alternative viewpoints, argument with evidence (and spot bad arguments) and avoid faulty reasoning can become habits of mind that are nurtured throughout a students career. Additionally, sometimes a complex solution is merely the sum of many smaller and more routine solutions. There is value in teaching and focusing on content in school , as it breeds experts. When paired with the challenge of critical thinking in order to solve real-world problems, new interest can also be bred for a subject that students may previously have seen little use for.

Five tips for improving critical thinking in your classroom
Critical thinking abilities are essential skills for students to develop. Here are five tips for improving critical thinking skills in your classroom :
1. Teach Students How to Think Critically
Teaching students how to think critically involves helping them understand the difference between facts and opinions. Facts are true statements that can be proven using evidence. Opinions are beliefs based on personal experiences, feelings, values, and preferences.
Students often confuse facts with opinions. For example, “I am going to the store to buy milk.” This statement contains no opinion. It is simply stating a fact. On the other hand, “Milk tastes good.” This statement expresses an opinion.
When teaching students how to think critically, focus on helping them distinguish between facts and opinions. Helping students learn how to think critically will improve their ability to analyze information and solve problems.
2. Encourage Critical Thinking
Encouraging students to think critically means encouraging them to question everything. If you ask students questions such as “Why did you write that?,” “What makes you say that?,” or “How would you prove that?,” you encourage them to think critically.
Asking questions helps students become better thinkers . Questions allow students to explore issues and come up with answers themselves. Asking questions encourages students to think deeply and analytically.
3. Use Real World Examples
Real world examples are helpful for teaching students how to think. Using real world examples allows students to apply concepts to situations outside of school.
For example, if you teach students how to identify logical fallacies, you can show them how to recognize these errors in arguments. Showing students how to identify logical fallacy gives them practice identifying common mistakes made by others.
4. Provide Feedback
Providing feedback is another effective method for teaching students how to improve their critical thinking skills. Giving students positive and constructive criticism improves their performance.
Giving students negative feedback does not improve their performance . Negative feedback may discourage students from trying again. Positive feedback motivates students to continue working toward success.
#5. Model Good Critical Thinking Skills
Modelling good critical thinking skills is one of the most effective methods for teaching students how to become better thinkers. Teaching students how to think critically requires modeling good critical thinking skills.
Good critical thinking skills include asking open-ended questions, analyzing data, evaluating sources, and recognizing logical fallacies.
By showing students how to think critically and model good critical thinking skills, you can help them develop into successful learners.
In a world where artificial intelligence is on the rise and continuously developing, a humanized value such as critical thinking is increasingly important. Reliance on technology makes life simpler in many ways, but simultaneously makes the possession of certain skills and abilities more attractive to potential employers and more beneficial for individuals who possess them.
Critical thinking allows for creativity when problem-solving and promotes independence and confidence. Should technology ever fail, those who are able to think critically in a variety of situations will be the ones who are valued the most.
Willingham, D. T. (2019). How to Teach Critical Thinking. Education: FutureFrontiers.
http://www.danielwillingham.com/uploads/5/0/0/7/5007325/willingham_2019_nsw_critical_thinking2.pdf

Enhance Learner Outcomes Across Your School
Download an Overview of our Support and Resources
We'll send it over now.
Please fill in the details so we can send over the resources.
What type of school are you?
We'll get you the right resource
Is your school involved in any staff development projects?
Are your colleagues running any research projects or courses?
Do you have any immediate school priorities?
Please check the ones that apply.

Download your resource
Thanks for taking the time to complete this form, submit the form to get the tool.
Educationise
11 Activities That Promote Critical Thinking In The Class
Ignite your child’s curiosity with our exclusive “Learning Adventures Activity Workbook for Kids” a perfect blend of education and adventure!
Critical thinking activities encourage individuals to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to develop informed opinions and make reasoned decisions. Engaging in such exercises cultivates intellectual agility, fostering a deeper understanding of complex issues and honing problem-solving skills for navigating an increasingly intricate world.
Through critical thinking, individuals empower themselves to challenge assumptions, uncover biases, and constructively contribute to discourse, thereby enriching both personal growth and societal progress.
Critical thinking serves as the cornerstone of effective problem-solving, enabling individuals to dissect challenges, explore diverse perspectives, and devise innovative solutions grounded in logic and evidence. For engaging problem solving activities, read our article problem solving activities that enhance student’s interest.
52 Critical Thinking Flashcards for Problem Solving
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a 21st-century skill that enables a person to think rationally and logically in order to reach a plausible conclusion. A critical thinker assesses facts and figures and data objectively and determines what to believe and what not to believe. Critical thinking skills empower a person to decipher complex problems and make impartial and better decisions based on effective information.
More Articles from Educationise
- 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
- How to Foster Critical Thinking Skills in Students? Creative Strategies and Real-World Examples
- 9 Must-Have AI Tools for Teachers to Create Interactive Learning Materials
- The Future of Education: 8 Predictions for the Next Decade
- The Latest in EdTech: 5 Innovative Tools and Technologies for the Classroom
- 8 Free Math Problem Solving Websites and Applications
Importance of Acquiring Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking skills cultivate habits of mind such as strategic thinking, skepticism, discerning fallacy from the facts, asking good questions and probing deep into the issues to find the truth. Acquiring critical thinking skills was never as valuable as it is today because of the prevalence of the modern knowledge economy.
Today, information and technology are the driving forces behind the global economy. To keep pace with ever-changing technology and new inventions, one has to be flexible enough to embrace changes swiftly.
Today critical thinking skills are one of the most sought-after skills by the companies. In fact, critical thinking skills are paramount not only for active learning and academic achievement but also for the professional career of the students.
The lack of critical thinking skills catalyzes memorization of the topics without a deeper insight, egocentrism, closed-mindedness, reduced student interest in the classroom and not being able to make timely and better decisions.
Incorporating critical thinking lessons into the curriculum equips students with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of the modern world, fostering a mindset that is adaptable, inquisitive, and capable of discerning truth from misinformation.
Benefits of Critical Thinking for Students
Certain strategies are more eloquent than others in teaching students how to think critically. Encouraging critical thinking in the classroom is indispensable for the learning and growth of the students. In this way, we can raise a generation of innovators and thinkers rather than followers. Some of the benefits offered by thinking critically in the classroom are given below:
- It allows a student to decipher problems and think through the situations in a disciplined and systematic manner
- Through a critical thinking ability, a student can comprehend the logical correlation between distinct ideas
- The student is able to rethink and re-justify his beliefs and ideas based on facts and figures
- Critical thinking skills make the students curious about things around them
- A student who is a critical thinker is creative and always strives to come up with out of the box solutions to intricate problems
Read our article: How to Foster Critical Thinking Skills in Students? Creative Strategies and Real-World Examples
- Critical thinking skills assist in the enhanced student learning experience in the classroom and prepares the students for lifelong learning and success
- The critical thinking process is the foundation of new discoveries and inventions in the world of science and technology
- The ability to think critically allows the students to think intellectually and enhances their presentation skills, hence they can convey their ideas and thoughts in a logical and convincing manner
- Critical thinking skills make students a terrific communicator because they have logical reasons behind their ideas
Critical Thinking Lessons and Activities
11 Activities that Promote Critical Thinking in the Class
We have compiled a list of 11 critical thinking activities for students that will facilitate you to promote critical thinking abilities in the students. By incorporating these activities, educators can introduce real-world examples of critical thinking in the classroom, empowering students to apply these skills in everyday situations.
We have also covered problem solving activities that enhance student’s interest in our another article. Click here to read it.
1. Worst Case Scenario
Divide students into teams and introduce each team with a hypothetical challenging scenario. Allocate minimum resources and time to each team and ask them to reach a viable conclusion using those resources.
The scenarios can include situations like stranded on an island or stuck in a forest. Students will come up with creative solutions to come out from the imaginary problematic situation they are encountering. Besides encouraging students to think critically, this activity will enhance teamwork, communication and problem-solving skills of the students.
This critical thinking activity not only pushes students to devise innovative solutions in challenging scenarios but also strengthens their teamwork, communication, and problem-solving abilities, making it an engaging and educational experience.
Read our article: 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
2. If You Build It
It is a very flexible game that allows students to think creatively. To start this activity, divide students into groups. Give each group a limited amount of resources such as pipe cleaners, blocks, and marshmallows etc.
Every group is supposed to use these resources and construct a certain item such as building, tower or a bridge in a limited time. You can use a variety of materials in the classroom to challenge the students. This activity is helpful in promoting teamwork and creative skills among the students.
Incorporating critical thinking games like this into your classroom not only promotes teamwork and creativity but also challenges students to think outside the box as they work together to build their structures.
It is also one of the classics which can be used in the classroom to encourage critical thinking. Print pictures of objects, animals or concepts and start by telling a unique story about the printed picture. The next student is supposed to continue the story and pass the picture to the other student and so on.
This engaging exercise is one of the most effective critical thinking activities for kids, as it encourages them to use their creativity and problem-solving skills while working together to construct innovative structures with limited resources.
4. Keeping it Real
In this activity, you can ask students to identify a real-world problem in their schools, community or city. After the problem is recognized, students should work in teams to come up with the best possible outcome of that problem.
5. Save the Egg
Make groups of three or four in the class. Ask them to drop an egg from a certain height and think of creative ideas to save the egg from breaking. Students can come up with diverse ideas to conserve the egg like a soft-landing material or any other device. Remember that this activity can get chaotic, so select the area in the school that can be cleaned easily afterward and where there are no chances of damaging the school property.
6. Start a Debate
In this activity, the teacher can act as a facilitator and spark an interesting conversation in the class on any given topic. Give a small introductory speech on an open-ended topic. The topic can be related to current affairs, technological development or a new discovery in the field of science. Encourage students to participate in the debate by expressing their views and ideas on the topic. Conclude the debate with a viable solution or fresh ideas generated during the activity through brainstorming.
7. Create and Invent
This project-based learning activity is best for teaching in the engineering class. Divide students into groups. Present a problem to the students and ask them to build a model or simulate a product using computer animations or graphics that will solve the problem. After students are done with building models, each group is supposed to explain their proposed product to the rest of the class. The primary objective of this activity is to promote creative thinking and problem-solving skills among the students.
8. Select from Alternatives
This activity can be used in computer science, engineering or any of the STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) classes. Introduce a variety of alternatives such as different formulas for solving the same problem, different computer codes, product designs or distinct explanations of the same topic.
Form groups in the class and ask them to select the best alternative. Each group will then explain its chosen alternative to the rest of the class with reasonable justification of its preference. During the process, the rest of the class can participate by asking questions from the group. This activity is very helpful in nurturing logical thinking and analytical skills among the students.
9. Reading and Critiquing
Present an article from a journal related to any topic that you are teaching. Ask the students to read the article critically and evaluate strengths and weaknesses in the article. Students can write about what they think about the article, any misleading statement or biases of the author and critique it by using their own judgments.
In this way, students can challenge the fallacies and rationality of judgments in the article. Hence, they can use their own thinking to come up with novel ideas pertaining to the topic.
10. Think Pair Share
In this activity, students will come up with their own questions. Make pairs or groups in the class and ask the students to discuss the questions together. The activity will be useful if the teacher gives students a topic on which the question should be based.
For example, if the teacher is teaching biology, the questions of the students can be based on reverse osmosis, human heart, respiratory system and so on. This activity drives student engagement and supports higher-order thinking skills among students.
11. Big Paper – Silent Conversation
Silence is a great way to slow down thinking and promote deep reflection on any subject. Present a driving question to the students and divide them into groups. The students will discuss the question with their teammates and brainstorm their ideas on a big paper.
After reflection and discussion, students can write their findings in silence. This is a great learning activity for students who are introverts and love to ruminate silently rather than thinking aloud.
Incorporating critical thinking activities for high school students, like silent reflection and group brainstorming, encourages deep thought and collaboration, making it an effective strategy for engaging both introverted and extroverted learners.
Finally, for students with critical thinking, you can go to GS-JJ.co m to customize exclusive rewards, which not only enlivens the classroom, but also promotes the development and training of students for critical thinking.
Share this:
Discover more from educationise.
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
4 thoughts on “ 11 Activities That Promote Critical Thinking In The Class ”
- Pingback: What is Growth Mindset? 50+ Motivational Quotes on Growth Mindset - Educationise
- Pingback: 6 Steps To Implement Project-Based Learning In The Classroom - Educationise
- Pingback: Engaging Problem-Solving Activities That Spark Student Interest - Educationise
Thanks for the great article! Especially with the post-pandemic learning gap, these critical thinking skills are essential! It’s also important to teach them a growth mindset. If you are interested in that, please check out The Teachers’ Blog!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Introducing TeachCatalystAI
TeachCatalystAI is a professional teaching assistant tool designed to help teachers create lesson plan, teaching materials, and many more with ease. Our AI-powered tool will help you streamline your classroom management, making it easier to keep track of students, assignments, and behavior. Our AI-powered tools and templates are great and configured to make you effective in teaching.
Lesson Objectives That Support Critical Thinking
The creation of lesson objectives that effectively promote critical thinking is crucial in education. Crafting objectives that stimulate analysis, evaluation, and synthesis enables educators to establish a learning environment that supports deeper cognitive engagement .
These objectives serve not only as a roadmap for student learning but also as tools for meaningful assessment and feedback. A thorough examination of the traits of effective objectives and their connection to critical thinking demonstrates that the strategies employed can significantly affect student outcomes.
To ensure these objectives are both impactful and measurable, educators can implement specific strategies. For instance, incorporating real-world problems into lesson plans encourages students to apply their knowledge in practical situations.
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy as a framework can help educators formulate objectives that target various levels of thinking, from basic knowledge recall to higher-order skills like analysis and creation. Additionally, setting clear criteria for success allows students to understand expectations and assess their progress effectively.
Understanding Critical Thinking
Analytical thinking involves the capacity to analyze, evaluate , and synthesize information with effectiveness. This skill set is crucial for navigating complex situations and making informed decisions . A thorough grasp of analytical thinking necessitates an understanding of its core components, such as critical analysis and cognitive skills .
Moreover, cognitive skills are vital in analytical thinking; they empower individuals to process information, establish connections, and apply knowledge in practical situations.
In summary, analytical thinking transcends mere techniques; it embodies a mindset that values inquiry and reflection. Cultivating these skills enhances an individual’s problem-solving capabilities and ability to assist others effectively.
Importance of Lesson Objectives
Establishing clear lesson objectives is crucial for directing students toward specific learning outcomes and encouraging a concentrated approach to critical thinking . These objectives should be shaped by insights into what motivates students and the obstacles they face in learning, ensuring that every student remains engaged.
For instance, if a lesson objective focuses on developing analytical writing skills , assessments should specifically evaluate students’ ability to construct coherent arguments and utilize evidence effectively. This connection between objectives and assessments helps educators identify areas where students may struggle and provide targeted support accordingly.
Clarity in Learning Goals
Clear learning goals act as a navigational guide for both educators and students, steering the educational journey and ensuring that everyone involved comprehends the intended outcomes. When educators define specific learning objectives, they enhance instructional clarity and create a direct connection between activities and desired learning results.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Goal Specificity | Well-defined objectives enhance focus. |
| Objective Transparency | Clear goals foster effective feedback mechanisms. |
| Educational Alignment | Aligning goals with assessments ensures coherence. |
Integrating these components into lesson planning fosters effective feedback mechanisms and facilitates the assessment of performance metrics. Ultimately, clear learning goals not only assist educators in delivering meaningful instruction but also empower students to take charge of their own educational paths.
Alignment With Assessments
This approach promotes an environment where both formative and summative assessments are intentional and interconnected. Such alignment not only adheres to educational standards but also fosters a deeper comprehension of the material, enabling students to meaningfully engage with the content.
When assessments are carefully designed to match lesson objectives, they offer valuable insights into student progress and highlight areas that require further attention. This connection empowers educators to modify their instructional strategies as needed, ensuring that all students receive adequate support to thrive.
Characteristics of Effective Objectives
Effective objectives provide a structured foundation for critical thinking instruction , ensuring that learning outcomes are both attainable and quantifiable. To nurture an environment that supports critical thinking, these objectives must be clear, specific , and aligned with the intended results of the lesson. This clarity empowers educators to design engaging activities that resonate with learners, leading to a more profound comprehension of the material.
Moreover, effective objectives should encourage higher-order thinking skills , prompting students to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information rather than simply recalling facts. Incorporating measurable outcomes allows educators to track student progress and adjust their teaching methods to better address individual needs. These measurable outcomes also provide clarity, enabling students to recognize the standards for achieving success.
In addition, effective objectives need to be inclusive , accommodating various learning styles and backgrounds. This inclusivity not only boosts engagement but also empowers students to take charge of their educational journey.
Aligning Objectives With Critical Thinking
Engaging students through activities that promote critical thinking, such as debates and role-playing, enhances their analytical skills. Including reflective thinking in lesson plans invites students to evaluate their own learning processes, which increases their metacognitive awareness and self-assessment abilities. This level of self-awareness is vital for enhancing decision-making skills, enabling students to make choices supported by evidence and logical reasoning.
Examples of Supportive Objectives
To create an environment that encourages critical thinking, educators can establish supportive objectives that challenge students while also guiding their cognitive development. These objectives prompt students to explore real-world applications and make interdisciplinary connections, enhancing their learning experiences and equipping them for future challenges.
| Objective Type | Example Objective |
|---|---|
| Knowledge Acquisition | Analyze how renewable energy influences local economies. |
| Application | Design a community project that tackles a local environmental issue. |
| Synthesis | Produce a multimedia presentation that combines concepts from science, economics, and ethics related to climate change. |
Assessment Techniques for Objectives
Assessment techniques are crucial for evaluating students’ attainment of critical thinking objectives . Employing a diverse range of strategies ensures that educators can effectively monitor student progress and modify their teaching approaches as necessary.
Formative assessment is particularly important for providing ongoing feedback , enabling educators to pinpoint areas needing improvement before final evaluations take place. This continuous process nurtures a growth mindset in students, allowing them to share their thoughts and disagreements constructively, which is essential for resolving conflicts in the classroom.
Observational methods are also beneficial, as they allow educators to assess students in real-time during collaborative tasks. Adaptive testing can further customize assessments to cater to individual student needs, while criterion-referenced assessments ensure that evaluations align with specific learning objectives.
Together, these assessment techniques form a comprehensive framework for evaluating critical thinking skills, creating an environment where students can flourish and make meaningful contributions to their communities.
Strategies for Implementation
Inquiry-based learning serves to ignite curiosity, prompting students to ask questions and seek answers. This process deepens their understanding of the subject matter. Metacognitive strategies play a crucial role here, as they enable students to reflect on their thought processes, improving their ability to self-regulate and evaluate their learning outcomes.
This guidance helps them become more thoughtful and informed individuals. Together, these strategies cultivate an environment that promotes the development of critical thinking skills essential for lifelong learning .
Continuous Improvement in Objectives
For instance, group discussions and project-based learning activities can motivate students to share different perspectives, fostering a deeper understanding of the material. Such active involvement not only supports objective clarity but also promotes a more dynamic and inclusive learning environment .
Objective Clarity Enhancement
Furthermore, well-defined rules and expectations create a structured environment that complements the clarity of objectives, ensuring students grasp not only what they are learning but also how they are expected to conduct themselves during the educational process.
Improving objective clarity significantly enhances the learning experience by helping students understand what is expected of them and align their efforts accordingly. When objectives are clearly communicated, learners are encouraged to engage meaningfully with the material, prompting them to ask questions and investigate concepts beyond superficial understanding. This method fosters critical thinking and empowers students to take charge of their educational journey.
For instance, a science teacher might establish a SMART objective such as “Students will be able to conduct a controlled experiment to test the effects of sunlight on plant growth within three weeks.” This objective not only provides clarity on what students are expected to achieve but also sets a timeline and measurable criteria for success.
Iterative Goal Refinement
Ongoing evaluation and adjustment of educational objectives are crucial for nurturing an environment that enhances critical thinking skills . Iterative goal refinement is a key strategy for educators committed to improving learning experiences for their students. Through continuous goal setting, educators can formulate clear and attainable objectives that adapt to the changing needs of their learners. This process highlights the significance of effective communication techniques in establishing expectations and facilitating constructive feedback.
Moreover, adopting an iterative mindset promotes a culture of continuous improvement among educators. By being flexible and open to feedback, they can cultivate a vibrant learning atmosphere where critical thinking thrives.
Latest Posts
Using bloom’s taxonomy for lesson objectives, curriculum alignment strategies for teachers, impact of reflection on teaching strategies.

- Health A to Z
- Alternative Medicine
- Blood Disorders
- Bone and Joint
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Child Health
- Coronavirus
- Dental Care
- Digestive System
- Disabilities
- Drug Center
- Ear, Nose, and Throat
- Environmental Health
- Exercise And Fitness
- First Aid and Emergencies
- General Health
- Health Technology
- Hearing Loss
- Hypertension
- Infectious Disease
- LGBTQ Health
- Liver Health
- Men's Health
- Mental Health
- Pain Management
- Public Health
- Pulmonology
- Senior Health
- Sexual Health
- Skin Health
- Women's Health
- News For Medical Professionals
- Our Products
- Consumer News
- Physician's Briefing
- HealthDay TV
- Wellness Library
- HealthDay Living
- Conference Coverage
- Custom Products
- Health Writing
- Health Editing
- Video Production
- Medical Review
Evidence Supports Classroom Cellphone Bans, Expert Says

Key Takeaways
Cellphone bans can help classroom learning
Students will be more focused and creative without their phones
They also will be more apt to learn better social skills
THURSDAY, Aug. 29, 2024 (HealthDay News) -- Classroom cellphone bans should help improve learning environments in schools, a child development expert says.
Keeping the devices out of classrooms would help focus attention, improve problem-solving and -- by allowing kids to occasionally lapse into boredom -- spur creativity, says Jon Piacentini , a child and adolescent psychologist at UCLA Health.
“There are more harms associated with cellphone use in school than the benefits,” Piacentini, a father of three, said in a UCLA news release.
As a new school year kicks in, school district officials across the United States are weighing cellphone restrictions, experts said.
Nearly 84% of teens ages 16 to 19 have a cellphone, making the devices as ubiquitous as backpacks, highlighters and three-ring binders, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
What’s more, U.S. children ages 8 to 12 spend about six hours a day on screens , sometimes while in class, the NIH said.
“We know that a lot of kids are spending time on their phone during class or during recess,” Piacentini said.
Dividing attention between class and a smartphone can make it tough for students to concentrate or problem-solve, he noted.
Students who can’t concentrate “do not have the ability to take multiple perspectives or see problems from multiple approaches,” Piacentini said.
Cellphones can also harm kids’ imagination and critical thinking skills by never allowing their minds to wander, and boredom actually stimulates creativity in kids, he explained.
“If kids are on their phones 24/7, it doesn’t help them develop a sense that they can create, understand and generate thoughts and ideas,” Piacentini said.
Smartphones can also stunt kids’ social development. Traditional forms of play and connection are being replaced by video games and online platforms, according to Piacentini. As a result, kids might not be prepared to engage socially in person with others they don’t know.
Social media algorithms also can increase a child’s anxiety by spreading misinformation or reinforcing biases, Piacentini said.
Young children without the capacity and context to understand and interpret such messages may come to believe “that the world is scary,” he said.
Parents can help schools that ban classroom cellphones by mirroring those restrictions at home.
For example, parents can require no cellphones at the dinner table or in the bedroom before sleep, Piacentini said. Parents also can create more opportunities for children to put away their phones and enjoy non-screen activities with family and friends.
More information
The National Education Association has more on classroom cellphone bans .
SOURCE: UCLA, news release, Aug. 12, 2024
What This Means For You
Parents can help support classroom cellphone bans by setting guidelines around phone use at home.
Related Stories

- Open access
- Published: 26 August 2024
Using a flipped teaching strategy in undergraduate nursing education: students’ perceptions and performance
- Shaherah Yousef Andargeery 1 ,
- Hibah Abdulrahim Bahri 2 ,
- Rania Ali Alhalwani 1 ,
- Shorok Hamed Alahmedi 1 &
- Waad Hasan Ali 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 926 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
81 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Flipped teaching is an interactive learning strategy that actively engages students in the learning process. Students have an active role in flipped teaching as they independently prepare for the class. Class time is dedicated to discussion and learning activities. Thus, it is believed that flipped teaching promotes students’ critical thinking, communication, application of knowledge in real-life situations, and becoming lifelong learners. The aim of this study was to describe the students’ perception of flipped teaching as an innovative learning strategy. And to assess if there was a difference in students’ academic performance between those who participated in a traditional teaching strategy compared to those who participated in flipped teaching intervention.
A quasi-experimental design with intervention and control groups. A purposive sampling technique of undergraduate nursing students was used.
A total of 355 students participated in both groups, and 70 out of 182 students in the intervention group completed the survey. The students perceived a moderate level of effectiveness of the flipped teaching classroom as a teaching strategy. The result revealed that there is a statistically significant difference in the mean students’ scores for the intervention group (M = 83.34, SD = 9.81) and control group (M = 75.57, SD = 9.82).
Flipped teaching proves its effectiveness in improving students’ learning experience and academic performance. Also, students had a positive perception about flipped teaching as it allowed them to develop essential nursing competencies. Future studies must consider measuring the influence of flipped teaching on students’ ability to acquire nursing competencies, such as critical thinking and clinical reasoning.
Peer Review reports
The successful outcome of individualized nursing care of each patient depends on effective communication between nurses and patients. Therapeutic communication consists of an exchange of verbal and non-verbal cues. It is a process in which the professional nurse uses specific techniques to help patients better understand their conditions and promote patients’ open communication of their thoughts and feelings in an environment of mutual respect and acceptance [ 1 ]. Effective educational preparation, continuing practice, and self-reflection about one’s communication skills are all necessary for becoming proficient in therapeutic communication. Teaching therapeutic communication to nursing students explains the principles of verbal and non-verbal communication that can be emphasized through classroom presentation, discussion, case studies and role-play. It also helps them develop their ability to communicate effectively with patients, families, and other health care professionals. Nursing students should be able to critically think, conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information generated by observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, and communication. Utilizing a traditional teaching strategy can be a challenge to meet the previously stated requirements [ 2 ]. Therefore, nurse educators should adapt unique teaching methods to help students learn and participate in their own education.
The “flipped classroom” is a pedagogical approach that has gained popularity worldwide to foster active learning. Active learning is defined as instructional strategies that actively engage students in their learning. It requires them to do meaningful learning activities and reflect on their actions [ 3 ]. Flipped teaching is a teaching strategy that promotes critical thinking and the application of information learned outside of the classroom to real-world situations and solves problems within the classroom. It is used in a way that allows educators to deliver lectures by using technologies such as video, audio files, PowerPoint or other media. Thus, the students can read or study those materials on their own at home before attending the class. As a result, discussions and debates about the materials take place throughout the lecture time. Some of the main principles of flipped teaching are increasing interaction and communication between students and educators, allocating more time for content mastery and understanding, granting opportunities for closing gaps and development, creating opportunities for active engagement, and providing immediate feedback [ 4 , 5 ]. This teaching/learning methodology is supported by constructivism learning theory. A “problem-solving approach to learning” is how constructivism is frequently described. In which, it requires a shift in the nurse educator’s epistemic assumptions about the teaching-learning process. Constructivism requires nursing educators to take on the role of a learning facilitator who encourages collaboration and teamwork as well as guides the students in building their knowledge. The underlying assumptions of constructivism include the idea that learning occurs as a result of social interaction in which the student actively creates their own knowledge, while prior experiences serve as the foundation for the learning process. The “flipping classroom” reflects that approach, which integrates student-centered learning [ 6 ].
Flipped teaching approach has students learning before lectures, teaching the material to better use classroom time for cooperative learning. The discussed herein represents studies and case studies from primary through graduate schools. The literature indicated students did see value in this pedagogical approach. Most of the studies found that flipped teaching was associated with better understanding of the material learned, higher academic achievement/performance, and potentially improved psychosocial factors (self-esteem, self-efficacy) that are associated with learning. Interestingly, one article pointed out that non-didactic material used in flipped-teaching lead to an increase in performance and this did not happen with didactic material.
According to Jordan et al. [ 7 ], a flipped teaching is a methodology that was developed as a response to advancements and changes in society, pedagogical approaches, and rapid growth and advancement of technology; The flipped teaching was evolved from the peer instruction and just in time teaching approaches. Jordan and colleagues [ 7 ] state that independent learning happens outside the classroom prior to the lesson through instructional materials while classroom time is maximized to fosters an environment of collaborative learning. Qutob [ 8 ] states that flipped teaching enhances student learning and engagement and promotes greater independence for students.
Jordan et al. [ 7 ] studied the use of flipped teaching on the teaching of first- and fourth-year students’ discrete mathematics and graphs, models, and applications. Across all the classes studied (pilot, graph, model and application, practices, computer and business administration), students preferred flipped teaching compared to traditional teaching. According to Jordan et al. [ 7 ], the quality of the materials and exercises, and perceived difficulty of the course and material are important to student satisfaction with this method. Additionally, it was found that interactions with teachers and collaborative learning were positive. Likewise, Nguyen et al. [ 9 ] found students favorably perceive flipped teaching. This is especially true for those students who have an understanding that the method involves preparation and interaction and how these affect the outcomes. Vazquez and Chiang [ 10 ] discuss the lessons learned from observing two large Principles of Economics Classes at the University of Illinois; each class held 900 students. Vazquez and Chiang [ 10 ] found that the students preferred watching videos over reading the textbook. Secondly, students were better prepared after they watched pre-lecture videos compared to reading the textbook beforehand. The third finding involved the length of time pre-lecture work should take; the authors state pre-lecture work should be approximately 15 to 20 min of work ahead of each in-class session. The fourth finding is that the flipped teaching is a costly endeavor. Finally, it was found that having the students watch videos before the lectures reduced the time spent in class covering the material; the end result of this is students spend more time engaging in active learning than reviewing the material.
Qutob [ 8 ] studied the effects of flip teaching using two hematology courses. One of the courses was delivered using traditional teaching and the other course was flipped teaching. Qutob [ 8 ] found that students in the flipped course not only performed better on academic tasks, but also they had more knowledge and understanding of the material covered compared to those in the traditional format class. Additionally, Qutob [ 8 ] revealed that students in the flipped classroom found this style of learning is more beneficial than traditional teaching. Moreover, Florence and Kolski [ 11 ] found an improvement in high school students’ writing post-intervention. The authors further found that students were more engaged with the material and had a positive perception of the flipped model. Bahadur and Akhtar [ 12 ] conducted a meta-analysis of twelve research articles on flipped teaching; the studies demonstrated that students taught in the flip teaching classroom performed better academically and were more interactive and engaged in the material than students taught through traditional methods. Galindo-Dominguez [ 13 ] conducted a systematic review using 61 studies and found evidence for the effectiveness of this approach compared to other pedagogical approaches with regards to academic achievement, improved self-efficacy, motivation, engagement, and cooperativeness. Webb et al. [ 14 ] studied 127 students taking microeconomics and found the delivery of flipped material (didactic vs. non-didactic) influenced students’ improvements. They further found performance improvements for the students who attended flipped classes using non-didactic pre-class material. At the same time, Webb et al. [ 14 ] further found non-improvement associated with flipped classes that used didactic pre-class materials; these materials are akin to traditional lectures.
In the context of nursing education, flipped teaching strategy has demonstrated promising and effective results in enhancing student motivation, performance, critical thinking skills, and learning quality. The flipped teaching classrooms were associated with high ratings in teaching evaluations, increased course satisfaction, improved critical thinking skills [ 15 ], improved exam results and learning quality [ 16 ] and high levels of personal, teaching, and pedagogical readiness [ 17 ]. Another study showed that student performance motivation scores especially in extrinsic goal orientation, control beliefs, and self-efficacy for learning and performance were significantly higher in the flipped teaching classroom when compared to the traditional classroom strategy [ 16 ].
Regardless of these important findings, there have been limited studies published about the flipped teaching strategy in Saudi Arabia, particularly among nursing students. Therefore, implementing the flipped teaching strategy in a therapeutic communication course would be effective in academic performance and retention of knowledge. The flipped teaching method will fit best with the goals of a therapeutic communication course as both focus on active learning and student engagement. This approach is well-matched for a therapeutic communication course as it allows students to apply and practice the communication techniques and strategies, they have learned outside of class from the flipped teaching materials and freeing up class time for interactive and experiential activities. The filliped teaching method can provide opportunities for students to apply effective interpersonal communication skills in classes, provide more time to observe students practicing therapeutic communication techniques through role-play, group discussions, and case studies. It also allows instructors to refine and provide individualized feedback and offer real-time guidance to help students improve their interpersonal communication skills.
The current study aims to examine the students’ perception of a teaching innovation based on the use of the flipped teaching strategy in the therapeutic communication course. Further, to compare if there is a difference in students’ academic performance of students who participate in a traditional teaching strategy when compared with students who participate in flipped teaching intervention.
Students who participated in the intervention group perceived a high level of effectiveness of the flipped teaching classroom as a teaching/learning strategy.
There is a significant difference in the mean scores of students’ academic performance between students who participate in a traditional teaching strategy (control group) when compared with those students who participate in flipped teaching classroom (intervention group).
Design of the study
Quantitative method, quasi-experimental design was used in this study. This research study involves implementing a flipped teaching strategy (intervention) to examine the effectiveness of the flipped teaching among the participants in the intervention group and to examine the significant difference in the mean scores of the students’ performance between the intervention and control group.
College of Nursing at one of the educational universities located in Saudi Arabia.
A purposive sampling technique was conducted in this study. This sampling technique allows the researcher to target specific participants who have certain characteristics that are most relevant and informative for addressing the research questions. The advantages of the purposive sampling lie in gathering in-depth, detailed and contextual data from the most appropriate sources and ensure that the study captures a more comprehensive understanding of the concept of interest by considering different viewpoints [ 18 ]. Participants were eligible to participate in this study if they were (1) Enrolled in the undergraduate nursing programs (Nursing or Midwifery Programs) in the College Nursing; (2) Enrolled in Therapeutic Communication Course; (3) at least 18 years old or older. Participant’s data was excluded if 50% of the responses were incomplete. The sample size was calculated using G-Power. The required participants for recruitment to implement this study is 152 participants to reach a confidence level of 95% and a margin error of 5%.
Measurement
Demographic data including the participants’ age and GPA were collected from all the participants. Educational characteristics related to the flipped teaching were collected from the participants in the intervention group including the level of English proficiency, program enrollment, attending previous, attending previous course(s) that used flipped teaching strategy, time spent each week preparing for the lectures, time spent preparing for the course exams, and recommendation for applying flipped teaching in other classes.
The student’s perception of the effectiveness of the flipped teaching strategy was measured by a survey that focused on the effectiveness of flipped teaching. This data was collected only from the participants in the intervention group. The survey involves 14 items that used 5-point Likert-type scale (5 = strongly agree, 4 = agree, 3 = neutral, 2 = disagree and 1 = strongly disagree). The sum of the scores was calculated for the item, a high score indicates a high effectiveness of flipped teaching. The survey was developed by Neeli et al. [ 19 ] and the author was contacted to obtain permission to use the survey. The reliability of the scale was tested using Cronbach alpha, which was 0.91, indicating that the scale has an excellent reliability.
Also, student academic performance was measured for both the intervention and control groups though the average cumulative scores of the assessment methods of students who were enrolled in the Therapeutic Communication Course, given a total of 100. The students’ grades obtained in the course were calculated based grading structure of the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia (The Rules and Regulations of Undergraduate Study and Examination).
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval (No. 22-0860) was received before conducting the study. Participants were provided with information about the study and informed about the consent process. Informed consent to participate was obtained from all the participants in the study.
Intervention
Therapeutic communication course was taught face-to-face for students enrolled in the second year in the Bachelor of Science in Midwifery and Bachelor of Science in Nursing Programs. There were eight sections for the therapeutic communication course, two of them were under the midwifery program and the remaining (six sections) were under the nursing program. Each section was held once a week in a two-hour length for 10 weeks during the second semester of 2022. Students in all sections received the same materials, contents, and assessment methods, which is considered the traditional teaching strategy. The contents of the course included the following topics: introduction of communication, verbal and written communication, listening skills, non-verbal communication, nurse-patient relationship, professional boundaries, communication styles, effective communication skills for small groups, communication through nursing process, communication with special needs patient, health education and principles for empowering individuals, communication through technology, and trends and issues in therapeutic communication. The course materials, course objectives and learning outcomes, learning resources, and other supporting materials were uploaded to the electronic platform “Blackboard” (A Learning Management System) for all sections to facilitate students’ preparation during classes. The assessment methods include written mid-term examination, case studies, group presentation, and final written examination. The grading scores for each assessment method were also the same for all sections.
The eight course sections were randomly assigned into traditional teaching strategy (control group) or flipped teaching strategy (intervention group). Figure 1 shows random distribution of the course sections. The intervention group ( n = 182) included one section of the Bachelor of Science in Midwifery program ( n = 55 students) and three sections of Bachelor of Science in Nursing program ( n = 127 students). The control group ( n = 173) included one section of the Bachelor of Science in Midwifery program ( n = 50 students) and three sections of Bachelor of Science in Nursing program ( n = 123 students). Although randomization of the participants is not possible, we were able to create comparison groups between participants who received the flipped teaching and traditional teaching strategy. To ensure the consistency of the information given to the students and reduce the variability, the instructors were meeting periodically and reviewed the materials together. More importantly, all students received the same topics and assessment methods as stated in the course syllabus and as mentioned above. The instructors in all sections were required to answer students’ questions, provide clarification to the points raised throughout the semester, and give constructive feedback after the evaluation of each assessment method. Students were encouraged to freely express their opinions on the issues discussed and to share their thoughts when the opinions were inconsistent.

Random Distribution of the Course Sections
The intervention group were taught the course contents by using the flipped teaching strategy. The participants in the intervention group were asked to read the lectures and watch short videos from online sources before coming to classes. Similar materials and links were uploaded by the course instructors into the Blackboard system. During the classes, participants were divided into groups and were given time to appraise research articles and case scenarios related to the topics of the course. During the discussion time, each group presented their answers, and the course instructors encouraged the students to share their thoughts and provided constructive feedback. Questions corresponded to the intended objectives and learning outcomes were posted during the class time in Kahoot and Nearpod platforms as a competition to enhance students’ engagement. By the end of the semester, the flipped teaching survey was electronically distributed to students who were involved in the intervention group to examine the educational characteristics and assess the students’ perceptions about the flipped teaching.
Data collection procedure
After obtaining the IRB approval, the PI sent invitation letters to the potential participants using their official university email accounts. The invitation letter included a Microsoft Forms’ link with the description about the study, aim, research question, and sample size required to conduct the study. All students gave their permission to participate, and informed consent was obtained from them ( N = 355). The link also included questions related to age, GPA, and approval to use their scores from assessment methods for research purposes. The first part of data collection was obtained immediately after the therapeutic communication course was over. The average cumulative scores of all the assessment methods (out of 100) were calculated to measure the students’ academic performance for both the intervention and control groups.
The second part of data collection was conducted after the final exam of the therapeutic communication course ( n = 182). A Microsoft Forms link was sent to the participants in the intervention group only. It included questions related to educational characteristics and students’ perception of the effectiveness of flipped teaching. Students needed a maximum of 10 min to complete the study survey.
Data analysis
Data was analyzed using the SPSS version 27. Descriptive analysis was used to analyze the demographic and educational characteristics and perception of flipped teaching strategy. An independent t-test was implemented to compare the mean scores of the intervention and control groups to examine whether there is a statistically significance difference between both groups. A significance level of p < 0.05 was determined as statistical significance in this study.
The total number of students who enrolled in therapeutic communication course was 355 students. The intervention group included 182 students and the control group included 173 students. The mean age of all participants in the study was 19 years old (M = 19.56, SD = 1.19). The mean GPA was 3.53 (SD = 1.43). Of those enrolled in the intervention group, only 70 out of 182 students completed the survey. Table 1 represents the description of the educational characteristics of the participants in intervention group ( n = 70). Around 65% of the participants reported that their level of English proficiency is intermediate, and they were enrolled in the nursing program. Half of the students had precious courses that used flipped teaching strategy. About one-third of the students indicated that they spent less than 15 min each week preparing for lectures. Around 65% of the students stated that they spent more than 120 min preparing for the course exam. Half of the students gave their recommendation for applying flipped teaching strategy in other courses. The mean score of the students’ performance in Therapeutic Communication course who enrolled in the intervention group is 83.34 (SD = 9.81) and for those who were enrolled in the control group is 75.57 (SD = 9.82).
The students perceived a moderate level of effectiveness of the flipped teaching classroom as a teaching strategy (M = 3.49, SD = 0.69) (Table 2 ). The three highest items that improved students’ perception about the flipped teaching strategy were: flipped classroom session develops logical thinking (M = 3.77, SD = 0.99), followed by flipped classroom session provides extra information (M = 3.68, SD = 1.02), then flipped classroom session improves the application of knowledge (M = 3.64, SD = 1.04). The three lowest items perceived by the students were: Flipped classroom session should have allotted more time for each topic (M = 3.11, SD = 1.07), flipped classroom session requires a long time for preparation and conduction (M = 3.23, SD = 1.04), and flipped classroom session reduces the amount of time needed for study when compared to lectures (M = 3.26, SD = 1.07).
An independent sample T-test was implemented to compare the mean scores of the students’ academic performance between the intervention group ( n = 182) and control group ( n = 173) (Table 3 ). The results of Levene’s test for equality of variances ( p = 0.801) indicated that equal variances assumed, and the assumption of equal variances has not been violated. The significant level value (2-tailed) is p ≤ 0.001, indicating that there is a statistically significant difference in the mean scores of students’ academic performance for the intervention group (M = 83.34, SD = 9.81) and control group (M = 75.57, SD = 9.82). The magnitude of the differences in the means (Mean difference= -7.77%, CI: -10.02 to -5.52) is very small (Eta squared = 0.00035).
Flipped teaching is a learning strategy that engages students in the learning process allowing them to improve their academic performance and develop cognitive skills [ 20 ]. This study investigated the effect of implementing flipped teaching as an interactive learning strategy on nursing students’ performance. Also, the study examined students’ perceptions of integrating flipped teaching into their learning process. Flipped teaching is identified as an interactive teaching strategy that provides an engaging learning environment with immediate feedback allowing students to master the learning content [ 4 , 5 ]. Improvement in the student’s academic performance and development of learning competencies were expected outcomes. The flipped classroom approach aligns with the constructivist theory of education, which posits that students actively construct their own knowledge and understanding through engaging with the content and applying it in meaningful contexts. By providing pre-class materials (e.g., videos, readings) for students to engage with independently, the flipped classroom allows them to build a foundational understanding of the concepts before class, enabling them to actively participate in discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative activities during the class. By shifting the passive acquisition of knowledge to the pre-class phase and dedicating in-class time to active, collaborative, and problem-based learning, the flipped classroom approach creates an environment that fosters deeper understanding, the development of critical thinking and clinical reasoning skills as well as the ability to apply knowledge in clinical practice [ 21 ].
Effectiveness of the flipped teaching on students’ academic performance
The influence of flipped teaching on students’ academic performance was identified by evaluating students’ examination scores. The results of this study indicated that flipped teaching had a significant influence on students’ academic performance ( p = 0.000). This significant influence implies the positive effectiveness of flipped teaching on students’ academic performance (M = 83.34, SD = 9.81) compared to traditional classroom (M = 75.57, SD = 9.82). These results are in line with other researchers regarding improving students’ academic performance [ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Qutob’s [ 8 ] study shows that flipped teaching positively influences students’ performance. Preparation for class positively influenced students’ academic performance. The flipped classroom approach is underpinned by the principles of constructivism. These principles emphasize the active role of students in constructing their own understanding of concepts and ideas, rather than passively receiving information [ 21 ].
In a traditional classroom, the teacher typically delivers content through lectures, and students are tasked with applying that knowledge through homework or in-class activities. However, this model often fails to engage students actively in the learning process. In contract,
Flipped classroom requires students to prepare for the class which allows them to be exposed to the learning material before the class. During class time, students are giving opportunities to interact with their classmates and instructors to discuss the learning topic which can positively influencing their academic performance later [ 7 , 9 ]. Furthermore, the flipped classroom approach aligns perfectly with the core tenets of constructivism. Its adherence to the constructivist 5E Instructional Model further demonstrates its grounding in this learning theory. The 5E model, which includes the phases of engagement, exploration, explanation, elaboration, and evaluation, provides a framework for facilitating the active construction of knowledge [ 22 ].
It first sparks student interest and curiosity about the concepts (engagement), then enables students to investigate and experiment with the ideas through hands-on activities and investigations (exploration). This is followed by opportunities for students to make sense of their explorations and construct their own explanations (explanation). The flipped classroom then allows students to apply their knowledge in new contexts, deepening their understanding (elaboration). Finally, the evaluation phase assesses student learning and provides feedback, completing the cycle of constructivist learning [ 22 ]. This alignment with the 5E model, along with the flipped classroom’s emphasis on active learning and create environment that nurtures deeper understanding, the development of higher-order thinking skills, and the ability to transfer learning to real-world contexts.
In this study, one third of the students indicated that the preparation time was less than fifteen minutes a week. According to Vazquez and Chiang [ 10 ], preparation time for classroom should be about 15 to 20 min for each topic. Preparation for class did not take much time but positively influenced students’ academic performance. Furthermore, preparation for class allows students to develop the skills to be independent learners [ 8 ]. Independence in learning develops continuous learning skills, such as long-life learning which is a required competency for nursing. Garcia et al. [ 22 ] found out that focusing on shifting teachers’ practices towards active learning approaches, such as the 5E Instructional Model, can have lasting, positive impacts on students’ conceptual understanding and learning.
Students’ perception of flipped teaching as a teaching strategy
Students’ perception of flipped teaching as a learning strategy was examined using a survey developed by Neeli et al. [ 19 ]. Students recognize flipped teaching as an effective teaching strategy (M = 3.49, SD = 0.69) that had a positive influence on their learning processes and outcomes. Several studies identified the positive influence of flipped teaching on students’ learning process and learning outcomes [ 8 , 19 ]. Flipped teaching provides a problem-based learning environment allowing students to develop clinical reasoning, critical thinking, and a deeper understanding of the subject [ 5 , 8 , 19 , 23 ]. The flipped teaching approach introduces students to the learning materials before class. Class time is then utilized for discussion, hands-on, and problem-solving activities to foster a deeper understanding of the studied subject [ 5 ]. Consequently, flipped teaching provides a problem-based learning environment as it encourages students to be actively engaged in the learning process, work collaboratively with their classmates, and apply previously learned knowledge and skills to solve a problem. The result of this study is consistent with the results from a systematic review conducted by Youhasan et al. [ 5 ]. Implementing flipped teaching in undergraduate nursing education provides positive outcomes on students’ learning experiences and outcomes and prepares them to deal with future challenges in their academic and professional activities [ 5 ].
Implications
The results from this study identified that flipped teaching has a significant influence on students’ academic performance. The results also indicated that students have positive perception of flipped teaching as an interactive learning strategy. Flipped teaching pedagogy could be integrated in nursing curriculum to improve the quality of education process and outcomes which will result in improving the students’ performance. Flipped teaching provides an interactive learning environment that enhances the development of essential nursing competencies, such as communication, teamwork, collaboration, life-long learning, clinical reasoning, and critical thinking. For example, flipped teaching allows students to develop communication skills throughout discussion in the classroom, and collaboration skills by working with their classmate and instructor. In this study, flipped teaching was implemented in a theoretical course (therapeutic communication course). This interactive learning strategy could also be applied in clinical and practice setting for effective and meaningful learning process and outcomes.
Strengths and limitations
This research study reveals the effectiveness of flipped teaching on students’ academic performance. This study used a quasi-experimental design with control and intervention groups to investigate the influence of flipped teaching on nursing education. Nevertheless, this study has limitations. One of the study’s limitations is the lack of randomization, thus causal association between the variables cannot be investigated. In addition, this study used a self-administered survey which may include respondents’ bias; thus, it may affect the results. Also, this study investigated students’ perceptions of flipped teaching as a learning strategy. The results from examining students’ perceptions indicated that students had a positive perception of flipped teaching as it allowed them to develop essential nursing competencies. This study did not focus on identifying and measuring competencies. Therefore, future studies must consider measuring the influence of flipped teaching on students’ ability to acquire nursing competencies, such as critical thinking and clinical reasoning.
Flipped teaching is an interactive learning strategy that depends on students’ preparation of the topic to be interactive learners in the learning environment. Interactive learning environment improves learning process and outcomes. This study indicated that flipped teaching has significant influence on students’ academic performance. Students perceived flipped teaching as a learning strategy that allowed them to acquire learning skills, such as logical thinking and application of knowledge. These skills allow students to have meaningful learning experience. Also, students could apply these skills in other learning content and/or environments, for example, in clinical. Thus, we believe that flipped teaching is an effective learning approach to be integrated in the nursing curriculum to enhance students’ learning experience.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to data privacy but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Institutional Review Board
Standard deviation
The level of marginal significance within a statistical test
Confidence Interval of the Difference
Figueiredo AR, Potra TS. Effective communication transitions in nursing care: a scoping review. Ann Med. 2019;51(sup1):201–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2018.1560159 .
Article Google Scholar
O’Rae A, Ferreira C, Hnatyshyn T, Krut B. Family nursing telesimulation: teaching therapeutic communication in an authentic way. Teach Learn Nurs. 2021;16(4):404–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teln.2021.06.013 .
Thai NTT, De Wever B, Valcke M. The impact of a flipped classroom design on learning performance in higher education: looking for the best blend of lectures and guiding questions with feedback. Computers Educ. 2017;107:113–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.01.003 .
Özbay Ö, Çınar S. Effectiveness of flipped classroom teaching models in nursing education: a systematic review. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;104922–104922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104922 . 102 (n. Issue).
Youhasan P, Chen Y, Lyndon M, Henning MA. Exploring the pedagogical design features of the flipped classroom in undergraduate nursing education: a systematic review. BMC Nurs. 2021;20(1):50–50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00555-w .
Barbour C, Schuessler JB. A preliminary framework to guide implementation of the flipped classroom method in nursing education. Nurse Educ Pract. 2019;34:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2018.11.001 .
Jordan C, Magrenan A, Orcos L. Considerations about flip education in the teaching of advanced mathematics. Educational Sci. 2019;9(3):227.
Qutob H. Effect of flipped classroom approach in the teaching of a hematology course. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(4):1–8.
Nguyen B, Yu X, Japutra A, Chen C. Reverse teaching: exploring student perceptions of flip teaching. Act Learn High Educ. 2016;17(1):51–61.
Vazquez J, Chiang E. Flipping out! A case study on how to flip the principles of economics classroom. Int Adv Econ Res. 2015;21(4):379–90.
Florence E, Kolski T. Investigating the flipped classroom model in a high school writing course: action research to impact student writing achievement and engagement. TechTrends: Link Res Pract Improve Learn. 2021;65(6):1042–52.
Bahadur G, Akhtar Z. Effect of teaching with flipped classroom model: a meta-analysis. Adv Social Sci Educ Humanit Res. 2021;15(3):191–7.
Google Scholar
Galindo-Dominguez H. Flipped classroom in the educational system: Trend or effective pedagogical model compared to other methodologies? J Educational Technol Soc. 2021;24(3):44–60.
Webb R, Watson D, Shepherd C, Cook S. Flipping the classroom: is it the type of flipping that adds value? Stud High Educ. 2021;46(8):1649–63.
Barranquero-Herbosa M, Abajas-Bustillo R, Ortego-Maté C. Effectiveness of flipped classroom in nursing education: a systematic review of systematic and integrative reviews. Int J Nurs Stud. 2022;135:104327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2022.104327 .
Lelean H, Edwards F. The impact of flipped classrooms in nurse education. Waikato J Educ. 2020;25:145–57.
Youhasan P, Chen Y, Lyndon M, Henning MA. Assess the feasibility of flipped classroom pedagogy in undergraduate nursing education in Sri Lanka: a mixed-methods study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(11):e0259003. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259003 .
Harris AD, McGregor JC, Perencevich EN, Furuno JP, Zhu J, Peterson DE, Finkelstein J. The use and interpretation of quasi-experimental studies in medical informatics. J Am Med Inf Association: JAMIA. 2006;13(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1197/jamia.M1749 .
Neeli D, Prasad U, Atla B, Kukkala SSS, Konuku VBS, Mohammad A. (2019). Integrated teaching in medical education: undergraduate student’s perception.
Baloch MH, Shahid S, Saeed S, Nasir A, Mansoor S. Does the implementation of flipped Classroom Model improve the Learning Outcomes of Medical College Students? A single centre analysis. J Coll Physicians Surgeons–pakistan: JCPSP. 2022;32(12):1544–7.
Robertson WH. The Constructivist flipped Classroom. J Coll Sci Teach. 2022;52(2):17–22.
Garcia I, Grau F, Valls C, Piqué N, Ruiz-Martín H. The long-term effects of introducing the 5E model of instruction on students’ conceptual learning. Int J Sci Educ. 2021;43(9):1441–58.
Chu TL, Wang J, Monrouxe L, Sung YC, Kuo CL, Ho LH, Lin YE. The effects of the flipped classroom in teaching evidence based nursing: a quasi-experimental study. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(1):e0210606.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the facilities and other support given by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R447), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
This research was funded by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R447), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nursing Management and Education Department, College of Nursing, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, P.O. Box 84428, Riyadh, 11671, Saudi Arabia
Shaherah Yousef Andargeery, Rania Ali Alhalwani, Shorok Hamed Alahmedi & Waad Hasan Ali
Medical-Surgical Nursing Department, College of Nursing, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, P.O. Box 84428, Riyadh, 11671, Saudi Arabia
Hibah Abdulrahim Bahri
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, H.B, S.Y.A, W.A.; methodology, S.Y.A., S.H.A.; validation, S.Y.A.; formal analysis, S.Y.A.; resources, H.B, S.Y.A, W.A, R. A.; data curation, S.Y.A, S.H.A.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A, H.B, S.Y.A., S.H.A, W.A; writing—review and editing, R.A, H.B, S.Y.A, S.H.A, W.A; supervision, R.A, H.B, S.Y.A, S.H.A.; project administration, R.A, S.Y.A, S.H.A.; funding acquisition, S.Y.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hibah Abdulrahim Bahri .
Ethics declarations
Institutional review board.
Institutional Review Board (IRB) in Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, approval No. (22-0860).
Informed consent
Informed consents were obtained from all study participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Andargeery, S.Y., Bahri, H.A., Alhalwani, R.A. et al. Using a flipped teaching strategy in undergraduate nursing education: students’ perceptions and performance. BMC Med Educ 24 , 926 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05749-9
Download citation
Received : 26 February 2024
Accepted : 05 July 2024
Published : 26 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05749-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Flipped teaching
- Active learning
- Teaching strategy
- Nursing education
- Undergraduate nursing education
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Trends in Medicine
The benefits of the latest ai technologies for patients and clinicians.

Today, artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the trajectory of health care—from automating routine tasks and increasing efficiency to improving diagnoses, accelerating the discovery of more effective treatments, and so much more.
“When we talk about the application of AI, we can think of applying it across the entire spectrum of health care specialties, from the administrative side through to clinical care,” explains Samir Kendale, MD, FASA, medical director of Anaesthesia Informatics at Beth Israel Lahey Health, assistant professor of Anaesthesia at Harvard Medical School, and course director of the Harvard Medical School Continuing Education course, AI in Clinical Medicine .
The Need for Clinicians to Get Up to Speed on AI
Despite the potential AI brings, Kendale points out that many health care providers are not yet familiar with this technology. “AI wasn’t introduced in medical school until recently,” he says. This means that generations of doctors have not been trained on how AI works or how to use it. But, with changing times comes the need for clinicians to fill in their skill gaps in this area.
“It’s prime time for clinicians to learn how to incorporate AI into their jobs,” agrees Maha Farhat, MD, MSc, associate physician of Pulmonary and Critical Care at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Gil Omenn, Associate Professor of Biomedical Informatics at Harvard Medical School. Farhat also joins Kendale and Isaac Kohane, MD, PhD, as a course director of AI in Clinical Medicine.
When clinicians get up to speed on AI, Farhat says that they will be able to use the latest tools strategically to benefit their practices, their health systems, and the patients they serve. “AI can help us learn new approaches to treatment and diagnostic testing for some cases that can reduce uncertainty in medicine,” she says.
Exploring AI Use Cases
Here are several examples Kendale and Farhat share that illustrate the benefits AI can bring:
- AI can automate tasks to free up a clinician’s time to focus more on their patients, “humanizing” care in new ways . With many health care providers feeling overworked today, tools like medical scribe technology can automatically capture visit notes and store them in a patient’s medical record, even flagging key details and insights. This can increase efficiency and free up clinicians to focus more on face-to-face time with their patients. “Doctors can also use AI algorithms to write letters to patients, to collect past history and summarize it to support medical decision making, and to select the best medicine for each patient’s specific case,” Kendale says. All of this can reduce the manual and cognitive burden that many clinicians are feeling. Ultimately, this can help prevent clinician burnout while improving the patient experience.
- AI can help clinicians better interpret imaging results. For instance, in gastroenterology, AI can improve the process of getting colonoscopy results, using image recognition to detect and identify polyps on the imaging files. AI can also be used to interpret EKG and CAT scan results and to identify irregularities. While this doesn’t replace the need for specialists in pathology, histology, or radiology, Kendale points out that it can help these experts put their time to better use. Additionally, AI can clear those imaging tests with normal results and flag those that need to be reviewed more closely by the experts, helping them focus their time in the very best way. AI can also help clinicians hone in on the top four or five possible diagnoses to consider. This means that patients can get their results sooner, and clinicians can spend more time focused on patient care.
- AI can help health care organizations improve quality and safety. One example is using AI software to review a large amount of data quickly and easily to identify people at high risk of developing sepsis. This can enable a health system to respond proactively to try to prevent this problem, such as moving a high-risk patient to a unit with higher acuity staffing. AI can also identify people who have a higher likelihood of developing opioid dependency after surgery to monitor them closely and wean them off the drugs as soon as possible. In addition, it can be used to identify areas where drug errors are most likely to occur in a health system so the staff can implement stronger safety protocols. These are just a few of the many ways that AI can be used to help achieve value-based care.
- AI can be an important source of data and expertise for clinicians. In the past, clinicians had to do extensive research to help zero in on a case that was difficult to diagnose or treat. Today, clinicians can ask AI chatbots diagnostic questions and gain immediate access to a wealth of information and advice, saving hours or even days of searching for similar cases. AI can also support clinical decision-making. When clinicians are looking at similar cases to predict who will best respond to certain treatment options, AI can help them better personalize their treatment regimens.
- AI can aid in the diagnosis and treatment of rare diseases. One of the challenges of diagnosing and treating someone with a rare disease has traditionally been that clinicians may not recognize the signs of a condition they have not personally encountered. Finding other cases of rare diseases online can also be challenging. By scanning large data sets to find similar cases, AI can help clinicians not only get to a diagnosis more quickly but also find examples of treatments that have been effective in people with this condition.
How to Leverage AI
For clinicians looking to boost their AI IQ within their own organizations, Kendale stresses the need to look for the person or team in the health system who oversees informatics. They will be well positioned to explain the options that exist and share the process to integrate these tools into existing workflows or use them to improve processes.
Clinicians can also connect with local, state, and national professional organizations to learn more about using AI and explore the wealth of ways it can benefit their practices and their patients.
Related Articles

A Physician’s Journey in Clinical Research Training

Becoming a Well-Rounded Researcher in Global Clinical Scholars Research Training

Incorporating Critical Thinking Skills in Medical Education
Clinicians today need strong critical thinking skills in order to properly diagnose and treat…
© 2024 by the President and Fellows of Harvard College

COMMENTS
Critical thinking blasts through the surface level of a topic. It reaches beyond the who and the what and launches students on a learning journey that ultimately unlocks a deeper level of ...
Critical thinking is a key skill that goes far beyond the four walls of a classroom. It equips students to better understand and interact with the world around them. Here are some reasons why fostering critical thinking is important: Making Informed Decisions: Critical thinking enables students to evaluate the pros and cons of a situation ...
Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care ...
Critical thinking in the classroom is a common term used by educators. Critical thinking has been called "the art of thinking about thinking" (Ruggiero, V.R., 2012) with the intent to improve one's thinking. The challenge, of course, is to create learning environments that promote critical thinking both in the classroom and beyond.
You can encourage students to emulate this by using them in demonstrations, asking them to "think out loud" in order for classmates to observe how they reason through a problem. Develop the habit of asking questions that require students to think critically, and tell students that you really expect them to give answers!
26. Compare/contrast. Compare and contrast are important critical thinking strategies. Students can create a Venn diagram to show similarities or differences, or they could write a good old-fashioned compare/contrast essay about the characters of Romeo and Juliet. 27. Pick a word, find a related word.
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
The Critical Thinking Framework presents ways to approach all kinds of knowledge in a way that presses students toward deeper processing of the content they are learning. If we can raise the bar for student work and thinking in our classrooms, the question of how students perform on standardized tests will become secondary to helping them ...
Questioning Techniques. One of the most effective ways to promote critical thinking is through questioning. Teachers can employ various questioning techniques to stimulate thought, such as Socratic questioning. By asking open-ended questions that require students to think deeply, analyze, and evaluate, teachers can guide students to explore ...
By promoting critical thinking in the classroom, educators can foster intellectual curiosity, enhance problem-solving abilities, and prepare students for success in an ever-evolving world. This article explores effective strategies and engaging activities to promote critical thinking among students. 1. Ask Thought-Provoking Questions.
The fourteen principles of a Thinking Classroom are designed to promote a classroom environment that encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration. Here's a summary of each principle to help teachers create an engaging and effective learning environment: 1. Classroom Culture of Thinking. Create a classroom culture that ...
Critical thinking isn't about acting on your beliefs. It extends to reasoning, communication, reflection, and action. With roots dating back to the mid-late 20th century, the term "critical thinking" has evolved through the years. It takes discipline to critically think because it requires questioning, open-mindedness, and problem-solving skills.
Despite the wealth of research, there is still little evidence regarding what teachers are effectively doing in the classroom in order to teach critical thinking (Abrami et al., 2014; Larsson, 2017). This is especially true in school settings, even though it has been proven that critical thinking can be developed from a young age (Kuhn, 1999).
Provide students with a Critical Thinking rubric. (Have them look at the rubric before a critical thinking activity, and once again when they are finished) Make assessment of Critical Thinking an ongoing effort. (While the teacher can assess, have students assess themselves. Self assessment can be powerful) Concentrate on specific indicators in ...
Some essential skills that are the basis for critical thinking are: Communication and Information skills. Thinking and Problem-Solving skills. Interpersonal and Self- Directional skills. Collaboration skills. These four bullets are skills students are going to need in any field and in all levels of education.
Foster a Growth Mindset. Promoting a growth mindset is paramount in enhancing critical thinking skills. Emphasize the belief that intelligence and abilities can be developed through effort and perseverance. Encourage students to embrace challenges, learn from failures, and view setbacks as opportunities for growth.
Analytical Thinking is a linear process which allows you to break down and review complex information. This type of thinking uses reasoning and logic to analyze the information presented, identify patterns and trends, and present facts and evidence. Critical Thinking includes an element of analytical thinking but goes much further.
A complete guide to teaching Critical Thinking. This 180 page e-book is an excellent resource for teachers looking to implement critical thinking in the classroom. It is packed full of great content whether you are just starting out, or looking to go further. It makes relevant connections to technology, STEM, and critical and creative thinking.
The cognitive skills at the foundation of critical thinking are analysis, interpretation, evaluation, explanation, inference, and self-regulation. When students think critically, they actively engage in these processes: To create environments that engage students in these processes, instructors need to ask questions, encourage the expression of ...
Teachers can use critical thinking questions to promote rational thinking. Reflective thinking is employed when a solution is needed, or in school when there is a connection that needs to be drawn between two or more concepts. Therefore, critical thinking is, in essence, the thought processes that result from disapproval of the solutions and ...
In recent decades, approaches to critical thinking have generally taken a practical turn, pivoting away from more abstract accounts - such as emphasizing the logical relations that hold between statements (Ennis, 1964) - and moving toward an emphasis on belief and action.According to the definition that Robert Ennis (2018) has been advocating for the last few decades, critical thinking is ...
Discover how to use critical thinking in the classroom with some practical tips from teacher and author Kathleen Kampa. Learn more at: https://elt.oup.com/fe...
6. Start a Debate. In this activity, the teacher can act as a facilitator and spark an interesting conversation in the class on any given topic. Give a small introductory speech on an open-ended topic. The topic can be related to current affairs, technological development or a new discovery in the field of science.
Educational theories enhance this comprehension by shedding light on the mechanisms that drive effective learning and motivation. This insight can refine analytical thinking abilities through customized teaching approaches.. Critical analysis entails breaking down arguments, identifying biases, and evaluating the credibility of sources.Engaging in this process deepens one's understanding of ...
Cellphones can also harm kids' imagination and critical thinking skills by never allowing their minds to wander, and boredom actually stimulates creativity in kids, he explained. "If kids are on their phones 24/7, it doesn't help them develop a sense that they can create, understand and generate thoughts and ideas," Piacentini said.
Flipped teaching is a teaching strategy that promotes critical thinking and the application of information learned outside of the classroom to real-world situations and solves problems within the classroom. It is used in a way that allows educators to deliver lectures by using technologies such as video, audio files, PowerPoint or other media.
In addition, it can be used to identify areas where drug errors are most likely to occur in a health system so the staff can implement stronger safety protocols. These are just a few of the many ways that AI can be used to help achieve value-based care. AI can be an important source of data and expertise for clinicians.