
Addition (Basic)
Addition (Multi-Digit)
Algebra & Pre-Algebra
Comparing Numbers
Daily Math Review (Math Buzz)
Division (Basic)
Division (Long Division)
Hundreds Charts
Measurement
Multiplication (Basic)
Multiplication (Multi-Digit)
Order of Operations
Place Value
Probability
Skip Counting
Subtraction
Telling Time
Word Problems (Daily)
More Math Worksheets
Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension Gr. 1
Reading Comprehension Gr. 2
Reading Comprehension Gr. 3
Reading Comprehension Gr. 4
Reading Comprehension Gr. 5
Reading Comprehension Gr. 6

Reading & Writing
Reading Worksheets
Cause & Effect
Daily ELA Review (ELA Buzz)
Fact & Opinion
Fix the Sentences
Graphic Organizers
Synonyms & Antonyms
Writing Prompts
Writing Story Pictures
Writing Worksheets
More ELA Worksheets
Consonant Sounds
Vowel Sounds
Consonant Blends
Consonant Digraphs
Word Families
More Phonics Worksheets
Early Literacy
Build Sentences
Sight Word Units
Sight Words (Individual)
More Early Literacy
Punctuation
Subjects and Predicates
More Grammar Worksheets
Spelling Lists
Spelling Grade 1
Spelling Grade 2
Spelling Grade 3
Spelling Grade 4
Spelling Grade 5
Spelling Grade 6
More Spelling Worksheets
Chapter Books
Charlotte's Web
Magic Tree House #1
Boxcar Children
More Literacy Units
Animal (Vertebrate) Groups
Butterfly Life Cycle
Electricity
Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas)
Simple Machines
Space - Solar System
More Science Worksheets
Social Studies
Maps (Geography)
Maps (Map Skills)
More Social Studies
Columbus Day
Veterans Day
More Holiday Worksheets
Puzzles & Brain Teasers
Brain Teasers
Logic: Addition Squares
Mystery Graph Pictures
Number Detective
Lost in the USA
More Thinking Puzzles
Teacher Helpers
Teaching Tools
Award Certificates
More Teacher Helpers

Pre-K and Kindergarten
Alphabet (ABCs)
Numbers and Counting
Shapes (Basic)
More Kindergarten
Worksheet Generator
Word Search Generator
Multiple Choice Generator
Fill-in-the-Blanks Generator
More Generator Tools
Full Website Index
Transformations: Translation, Rotation, Reflection
A set of geometry worksheets for teaching students about different types of shape transformations: translation, rotation, and reflection.
See also: Flip, Slide, and Turn Worksheets .
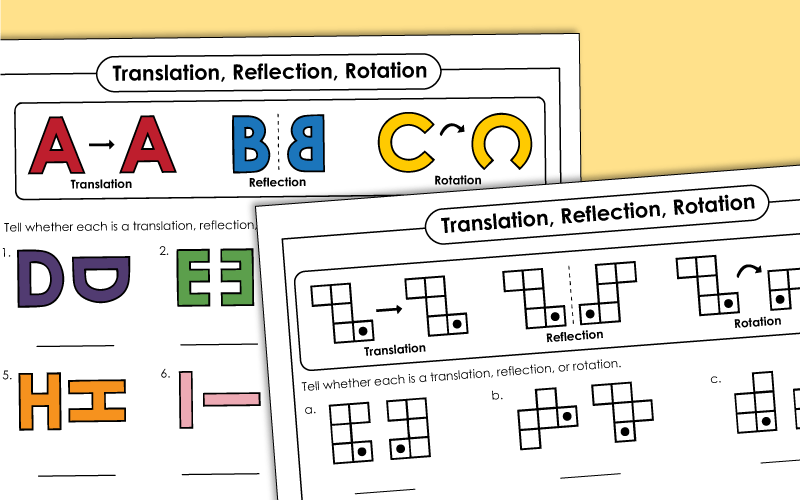
Translation, Rotation, Reflections (Mixed)

Logged in members can use the Super Teacher Worksheets filing cabinet to save their favorite worksheets.
Quickly access your most used files AND your custom generated worksheets!
Please login to your account or become a member and join our community today to utilize this helpful feature.

Translations Only

Reflections Only
These worksheets feature the same skills as translations, reflections, and rotations, but the vocabulary is suited for younger students
Worksheet Images
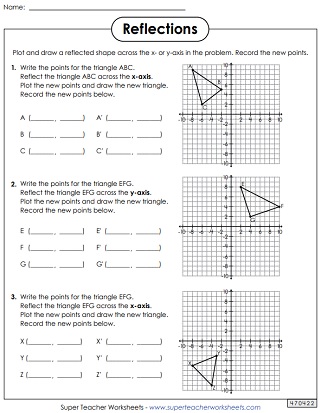
PDF with answer key:
PDF no answer key:

IMAGES