
- Pregnancy Classes


Breech Births
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3–4% of full-term births.
What are the different types of breech birth presentations?
- Complete breech: Here, the buttocks are pointing downward with the legs folded at the knees and feet near the buttocks.
- Frank breech: In this position, the baby’s buttocks are aimed at the birth canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of his or her body and the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: In this position, one or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of the body.
What causes a breech presentation?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common when:
- You have been pregnant before
- In pregnancies of multiples
- When there is a history of premature delivery
- When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid
- When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids
- The placenta covers all or part of the opening of the uterus placenta previa
How is a breech presentation diagnosed?
A few weeks prior to the due date, the health care provider will place her hands on the mother’s lower abdomen to locate the baby’s head, back, and buttocks. If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound or pelvic exam to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong?
Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Can a breech presentation be changed?
It is preferable to try to turn a breech baby between the 32nd and 37th weeks of pregnancy . The methods of turning a baby will vary and the success rate for each method can also vary. It is best to discuss the options with the health care provider to see which method she recommends.
Medical Techniques
External Cephalic Version (EVC) is a non-surgical technique to move the baby in the uterus. In this procedure, a medication is given to help relax the uterus. There might also be the use of an ultrasound to determine the position of the baby, the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
Gentle pushing on the lower abdomen can turn the baby into the head-down position. Throughout the external version the baby’s heartbeat will be closely monitored so that if a problem develops, the health care provider will immediately stop the procedure. ECV usually is done near a delivery room so if a problem occurs, a cesarean delivery can be performed quickly. The external version has a high success rate and can be considered if you have had a previous cesarean delivery.
ECV will not be tried if:
- You are carrying more than one fetus
- There are concerns about the health of the fetus
- You have certain abnormalities of the reproductive system
- The placenta is in the wrong place
- The placenta has come away from the wall of the uterus ( placental abruption )
Complications of EVC include:
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
- Changes in the fetus’s heart rate
- Placental abruption
- Preterm labor
Vaginal delivery versus cesarean for breech birth?
Most health care providers do not believe in attempting a vaginal delivery for a breech position. However, some will delay making a final decision until the woman is in labor. The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth:
- The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation
- The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored.
- The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
- The health care provider estimates that the baby is not too big or the mother’s pelvis too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- Anesthesia is available and a cesarean delivery possible on short notice
What are the risks and complications of a vaginal delivery?
In a breech birth, the baby’s head is the last part of its body to emerge making it more difficult to ease it through the birth canal. Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby’s head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse . In this situation the umbilical cord is squeezed as the baby moves toward the birth canal, thus slowing the baby’s supply of oxygen and blood. In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor. Cesarean delivery may be an option if signs develop that the baby may be in distress.
When is a cesarean delivery used with a breech presentation?
Most health care providers recommend a cesarean delivery for all babies in a breech position, especially babies that are premature. Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
Want to Know More?
- Creating Your Birth Plan
- Labor & Birth Terms to Know
- Cesarean Birth After Care
Compiled using information from the following sources:
- ACOG: If Your Baby is Breech
- William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 24.
- Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. Scott, James R., et al, Ch. 21.
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Paternity Tests 2
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Multiple Births 10
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Cord Blood 4
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Labor and Birth 65
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Breastfeeding 29
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 55
- The First Year 41
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Uncategorized 4
- Women's Health 34
- Prenatal Testing 16
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
- Pregnancy Questions Center
Share this post:
Similar post.

Episiotomy: Advantages & Complications

Retained Placenta

What is Dilation in Pregnancy?
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
Head down, face up
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
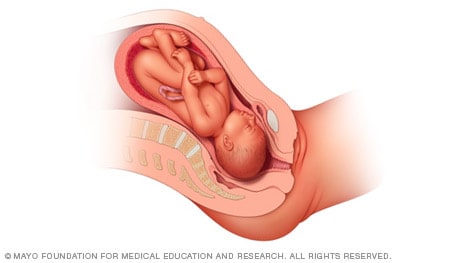
Frank breech
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

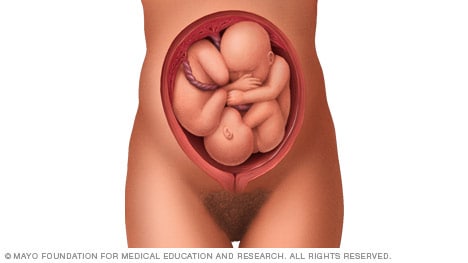
Complete and incomplete breech
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
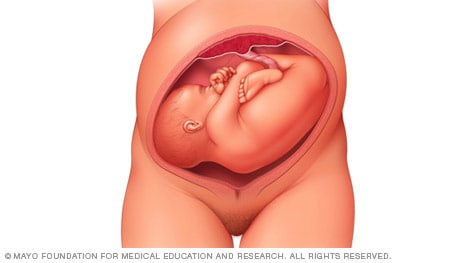
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: Third trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Help transform healthcare
Your donation can make a difference in the future of healthcare. Give now to support Mayo Clinic's research.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Is Breech?
When a fetus is delivered buttocks or feet first
- Types of Presentation
Risk Factors
Complications.
Breech concerns the position of the fetus before labor . Typically, the fetus comes out headfirst, but in a breech delivery, the buttocks or feet come out first. This type of delivery is risky for both the pregnant person and the fetus.
This article discusses the different types of breech presentations, risk factors that might make a breech presentation more likely, treatment options, and complications associated with a breech delivery.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
Types of Breech Presentation
During the last few weeks of pregnancy, a fetus usually rotates so that the head is positioned downward to come out of the vagina first. This is called the vertex position.
In a breech presentation, the fetus does not turn to lie in the correct position. Instead, the fetus’s buttocks or feet are positioned to come out of the vagina first.
At 28 weeks of gestation, approximately 20% of fetuses are in a breech position. However, the majority of these rotate to the proper vertex position. At full term, around 3%–4% of births are breech.
The different types of breech presentations include:
- Complete : The fetus’s knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Frank : The fetus’s legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Footling : The fetus’s foot is showing first.
Signs of Breech
There are no specific symptoms associated with a breech presentation.
Diagnosing breech before the last few weeks of pregnancy is not helpful, since the fetus is likely to turn to the proper vertex position before 35 weeks gestation.
A healthcare provider may be able to tell which direction the fetus is facing by touching a pregnant person’s abdomen. However, an ultrasound examination is the best way to determine how the fetus is lying in the uterus.
Most breech presentations are not related to any specific risk factor. However, certain circumstances can increase the risk for breech presentation.
These can include:
- Previous pregnancies
- Multiple fetuses in the uterus
- An abnormally shaped uterus
- Uterine fibroids , which are noncancerous growths of the uterus that usually appear during the childbearing years
- Placenta previa, a condition in which the placenta covers the opening to the uterus
- Preterm labor or prematurity of the fetus
- Too much or too little amniotic fluid (the liquid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy)
- Fetal congenital abnormalities
Most fetuses that are breech are born by cesarean delivery (cesarean section or C-section), a surgical procedure in which the baby is born through an incision in the pregnant person’s abdomen.
In rare instances, a healthcare provider may plan a vaginal birth of a breech fetus. However, there are more risks associated with this type of delivery than there are with cesarean delivery.
Before cesarean delivery, a healthcare provider might utilize the external cephalic version (ECV) procedure to turn the fetus so that the head is down and in the vertex position. This procedure involves pushing on the pregnant person’s belly to turn the fetus while viewing the maneuvers on an ultrasound. This can be an uncomfortable procedure, and it is usually done around 37 weeks gestation.
ECV reduces the risks associated with having a cesarean delivery. It is successful approximately 40%–60% of the time. The procedure cannot be done once a pregnant person is in active labor.
Complications related to ECV are low and include the placenta tearing away from the uterine lining, changes in the fetus’s heart rate, and preterm labor.
ECV is usually not recommended if the:
- Pregnant person is carrying more than one fetus
- Placenta is in the wrong place
- Healthcare provider has concerns about the health of the fetus
- Pregnant person has specific abnormalities of the reproductive system
Recommendations for Previous C-Sections
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) says that ECV can be considered if a person has had a previous cesarean delivery.
During a breech delivery, the umbilical cord might come out first and be pinched by the exiting fetus. This is called cord prolapse and puts the fetus at risk for decreased oxygen and blood flow. There’s also a risk that the fetus’s head or shoulders will get stuck inside the mother’s pelvis, leading to suffocation.
Complications associated with cesarean delivery include infection, bleeding, injury to other internal organs, and problems with future pregnancies.
A healthcare provider needs to weigh the risks and benefits of ECV, delivering a breech fetus vaginally, and cesarean delivery.
In a breech delivery, the fetus comes out buttocks or feet first rather than headfirst (vertex), the preferred and usual method. This type of delivery can be more dangerous than a vertex delivery and lead to complications. If your baby is in breech, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a C-section.
A Word From Verywell
Knowing that your baby is in the wrong position and that you may be facing a breech delivery can be extremely stressful. However, most fetuses turn to have their head down before a person goes into labor. It is not a cause for concern if your fetus is breech before 36 weeks. It is common for the fetus to move around in many different positions before that time.
At the end of your pregnancy, if your fetus is in a breech position, your healthcare provider can perform maneuvers to turn the fetus around. If these maneuvers are unsuccessful or not appropriate for your situation, cesarean delivery is most often recommended. Discussing all of these options in advance can help you feel prepared should you be faced with a breech delivery.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
TeachMeObGyn. Breech presentation .
MedlinePlus. Breech birth .
Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term . Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Apr 1;2015(4):CD000083. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000083.pub3
By Christine Zink, MD Dr. Zink is a board-certified emergency medicine physician with expertise in the wilderness and global medicine.
When viewing this topic in a different language, you may notice some differences in the way the content is structured, but it still reflects the latest evidence-based guidance.
Breech presentation
- Overview
- Theory
- Diagnosis
- Management
- Follow up
- Resources
Breech presentation refers to the baby presenting for delivery with the buttocks or feet first rather than head.
Associated with increased morbidity and mortality for the mother in terms of emergency cesarean section and placenta previa; and for the baby in terms of preterm birth, small fetal size, congenital anomalies, and perinatal mortality.
Incidence decreases as pregnancy progresses and by term occurs in 3% to 4% of singleton term pregnancies.
Treatment options include external cephalic version to increase the likelihood of vaginal birth or a planned cesarean section, the optimal gestation being 37 and 39 weeks, respectively.
Planned cesarean section is considered the safest form of delivery for infants with a persisting breech presentation at term.
Breech presentation in pregnancy occurs when a baby presents with the buttocks or feet rather than the head first (cephalic presentation) and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality for both the mother and the baby. [1] Cunningham F, Gant N, Leveno K, et al. Williams obstetrics. 21st ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1997. [2] Kish K, Collea JV. Malpresentation and cord prolapse. In: DeCherney AH, Nathan L, eds. Current obstetric and gynecologic diagnosis and treatment. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional; 2002. There is good current evidence regarding effective management of breech presentation in late pregnancy using external cephalic version and/or planned cesarean section.
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors.
- buttocks or feet as the presenting part
- fetal head under costal margin
- fetal heartbeat above the maternal umbilicus
Other diagnostic factors
- subcostal tenderness
- pelvic or bladder pain
Risk factors
- premature fetus
- small for gestational age fetus
- nulliparity
- fetal congenital anomalies
- previous breech delivery
- uterine abnormalities
- abnormal amniotic fluid volume
- placental abnormalities
- female fetus
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order.
- transabdominal/transvaginal ultrasound
Treatment algorithm
<37 weeks' gestation and in labor, ≥37 weeks' gestation not in labor, ≥37 weeks' gestation in labor: no imminent delivery, ≥37 weeks' gestation in labor: imminent delivery, contributors, natasha nassar, phd.
Associate Professor
Menzies Centre for Health Policy
Sydney School of Public Health
University of Sydney
Disclosures
NN has received salary support from Australian National Health and a Medical Research Council Career Development Fellowship; she is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Christine L. Roberts, MBBS, FAFPHM, DrPH
Research Director
Clinical and Population Health Division
Perinatal Medicine Group
Kolling Institute of Medical Research
CLR declares that she has no competing interests.
Jonathan Morris, MBChB, FRANZCOG, PhD
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of Department
JM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
John w. bachman, md.
Consultant in Family Medicine
Department of Family Medicine
Mayo Clinic
JWB declares that he has no competing interests.
Rhona Hughes, MBChB
Lead Obstetrician
Lothian Simpson Centre for Reproductive Health
The Royal Infirmary
RH declares that she has no competing interests.
Brian Peat, MD
Director of Obstetrics
Women's and Children's Hospital
North Adelaide
South Australia
BP declares that he has no competing interests.
Lelia Duley, MBChB
Professor of Obstetric Epidemiology
University of Leeds
Bradford Institute of Health Research
Temple Bank House
Bradford Royal Infirmary
LD declares that she has no competing interests.
Justus Hofmeyr, MD
Head of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
East London Private Hospital
East London
South Africa
JH is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Differentials
- Transverse lie
- Caesarean birth
- Mode of term singleton breech delivery
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer
Log in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Log in to access all of bmj best practice, help us improve bmj best practice.
Please complete all fields.
I have some feedback on:
We will respond to all feedback.
For any urgent enquiries please contact our customer services team who are ready to help with any problems.
Phone: +44 (0) 207 111 1105
Email: [email protected]
Your feedback has been submitted successfully.

Breech Presentation
- 📖 Geeky Medics OSCE Book
- ⚡ Geeky Medics Bundles
- ✨ 1300+ OSCE Stations
- ✅ OSCE Checklist PDF Booklet
- 🧠 UKMLA AKT Question Bank
- 💊 PSA Question Bank
- 💉 Clinical Skills App
- 🗂️ Flashcard Collections | OSCE , Medicine , Surgery , Anatomy
- 💬 SCA Cases for MRCGP
To be the first to know about our latest videos subscribe to our YouTube channel 🙌
Table of Contents
Suggest an improvement
- Hidden Post Title
- Hidden Post URL
- Hidden Post ID
- Type of issue * N/A Fix spelling/grammar issue Add or fix a link Add or fix an image Add more detail Improve the quality of the writing Fix a factual error
- Please provide as much detail as possible * You don't need to tell us which article this feedback relates to, as we automatically capture that information for you.
- Your Email (optional) This allows us to get in touch for more details if required.
- Which organ is responsible for pumping blood around the body? * Enter a five letter word in lowercase
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Introduction
Breech presentation is a type of malpresentation and occurs when the fetal head lies over the uterine fundus and fetal buttocks or feet present over the maternal pelvis (instead of cephalic/head presentation).
The incidence in the United Kingdom of breech presentation is 3-4% of all fetuses. 1
Breech presentation is most commonly idiopathic .
Types of breech presentation
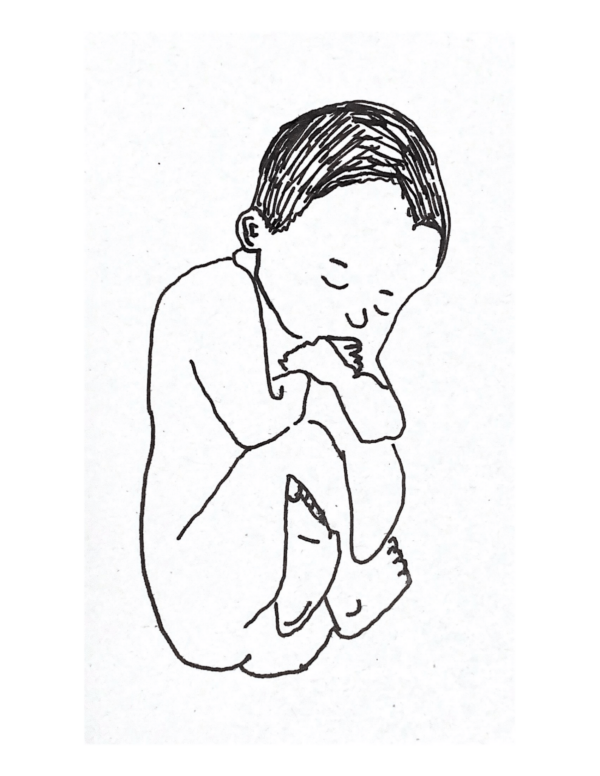
The three types of breech presentation are:
- Complete (flexed) breech : one or both knees are flexed (Figure 1)
- Footling (incomplete) breech : one or both feet present below the fetal buttocks, with hips and knees extended (Figure 2)
- Frank (extended) breech : both hips flexed and both knees extended. Babies born in frank breech are more likely to have developmental dysplasia of the hip (Figure 3)
Risk factors
Risk factors for breech presentation can be divided into maternal , fetal and placental risk factors:
- Maternal : multiparity, fibroids, previous breech presentation, Mullerian duct abnormalities
- Fetal : preterm, macrosomia, fetal abnormalities (anencephaly, hydrocephalus, cystic hygroma), multiple pregnancy
- Placental : placenta praevia , polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios , amniotic bands
Clinical features
Before 36 weeks , breech presentation is not significant, as the fetus is likely to revert to a cephalic presentation. The mother will often be asymptomatic with the diagnosis being incidental.
The incidence of breech presentation is approximately 20% at 28 weeks gestation, 16% at 32 weeks gestation and 3-4% at term . Therefore, breech presentation is more common in preterm labour . Most fetuses with breech presentation in the early third trimester will turn spontaneously and be cephalic at term.
However, spontaneous version rates for nulliparous women with breech presentation at 36 weeks of gestation are less than 10% .

Clinical examination
Typical clinical findings of a breech presentation include:
- Longitudinal lie
- Head palpated at the fundus
- Irregular mass over pelvis (feet, legs and buttocks)
- Fetal heart auscultated higher on the maternal abdomen
- Palpation of feet or sacrum at the cervical os during vaginal examination
For more information, see the Geeky Medics guide to obstetric abdominal examination .
Positions in breech presentation
There are multiple fetal positions in breech presentation which are described according to the relation of the fetal sacrum to the maternal pelvis .
These are: direct sacroanterior, left sacroanterior, right sacroanterior, direct sacroposterior, right sacroposterior, left sacroposterior, left sacrotransverse and right sacrotranverse. 5
Investigations
An ultrasound scan is diagnostic for breech presentation. Growth, amniotic fluid volume and anatomy should be assessed to check for abnormalities.
There are three management options for breech presentation at term, with consideration of maternal choice: external cephalic version , vaginal delivery and Caesarean section .
External cephalic version
External cephalic version (ECV) involves manual rotation of the fetus into a cephalic presentation by applying pressure to the maternal abdomen under ultrasound guidance. Entonox and subcutaneous terbutaline are used to relax the uterus.
ECV has a 40% success rate in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women . It should be offered to nulliparous women at 36 weeks and multiparous women at 37 weeks gestation.
If ECV is unsuccessful, then delivery options include elective caesarean section or vaginal delivery.
Contraindications for undertaking external cephalic version include:
- Antepartum haemorrhage
- Ruptured membranes
- Previous caesarean section
- Major uterine abnormality
- Multiple pregnancy
- Abnormal cardiotocography (CTG)
Vaginal delivery
Vaginal delivery is an option but carries risks including head entrapment, birth asphyxia, intracranial haemorrhage, perinatal mortality, cord prolapse and fetal and/or maternal trauma.
The preference is to deliver the baby without traction and with an anterior sacrum during delivery to decrease the risk of fetal head entrapment .
The mother may be offered an epidural , as vaginal breech delivery can be very painful. 6
Contraindications for vaginal delivery in a breech presentation include:
- Footling breech: the baby’s head and trunk are more likely to be trapped if the feet pass through the dilated cervix too soon
- Macrosomia: usually defined as larger than 3800g
- Growth restricted baby: usually defined as smaller than 2000g
- Other complications of vaginal birth: for example, placenta praevia and fetal compromise
- Lack of clinical staff trained in vaginal breech delivery
Caesarean section
A caesarian section booked as an elective procedure at term is the most common management for breech presentation.
Caesarean section is preferred for preterm babies (due to an increased head to abdominal circumference ratio in preterm babies) and is used if the external cephalic version is unsuccessful or as a maternal preference. This option has fewer risks than a vaginal delivery.
Complications
Fetal complications of breech presentation include:
- Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
- Cord prolapse
- Fetal head entrapment
- Birth asphyxia
- Intracranial haemorrhage
- Perinatal mortality
Complications of external cephalic version include:
- Transient fetal heart abnormalities (common)
- Fetomaternal haemorrhage
- Placental abruption (rare)
- There are three types of breech presentation: complete, incomplete and frank breech
- The most common clinical findings include: longitudinal lie, smooth fetal head-shape at the fundus, irregular masses over the pelvis and abnormal placement being required for fetal hear auscultation
- The diagnostic investigation is an ultrasound scan
- Breech presentation can be managed in three ways: external cephalic version , vaginal delivery or elective caesarean section
- Complications are more common in vaginal delivery , such as cord prolapse, fetal head entrapment, intracranial haemorrhage and birth asphyxia
Miss Saba Al Juboori
Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Miss Neeraja Kuruba
Dr chris jefferies.
- Oxford Handbook of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Breech Presentation: Overview. Published in 2011.
- Jemimah Thomas. Image: Complete breech.
- Bonnie Urquhart Gruenberg. Footling breech. Licence: [ CC BY-SA ]
- Bonnie Urquhart Gruenberg. Frank breech . Licence: [ CC BY-SA ]
- A Comprehensive Textbook of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Chapter 50: Malpresentation and Malposition: Breech Presentation. Published in 2011.
- Diana Hamilton Fairley. Lecture Notes: Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Malpresentation, Breech Presentation. Published in 2009.

Other pages
- Product Bundles 🎉
- Join the Team 🙌
- Institutional Licence 📚
- OSCE Station Creator Tool 🩺
- Create and Share Flashcards 🗂️
- OSCE Group Chat 💬
- Newsletter 📰
- Advertise With Us
Join the community
Warning: The NCBI web site requires JavaScript to function. more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Breech presentation.
Caron J. Gray ; Meaghan M. Shanahan .
Affiliations
Last Update: November 6, 2022 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. This activity reviews the cause and pathophysiology of breech presentation and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
- Describe the pathophysiology of breech presentation.
- Review the physical exam of a patient with a breech presentation.
- Summarize the treatment options for breech presentation.
- Explain the importance of improving care coordination among interprofessional team members to improve outcomes for patients affected by breech presentation.
- Introduction
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the fetus sitting with flexion of both hips and both legs in a tuck position. Finally, the incomplete breech can have any combination of one or both hips extended, also known as footling (one leg extended) breech, or double footling breech (both legs extended). [1] [2] [3]
Clinical conditions associated with breech presentation include those that may increase or decrease fetal motility, or affect the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. Prematurity, multiple gestations, aneuploidies, congenital anomalies, Mullerian anomalies, uterine leiomyoma, and placental polarity as in placenta previa are most commonly associated with a breech presentation. Also, a previous history of breech presentation at term increases the risk of repeat breech presentation at term in subsequent pregnancies. [4] [5] These are discussed in more detail in the pathophysiology section.
- Epidemiology
Breech presentation occurs in 3% to 4% of all term pregnancies. A higher percentage of breech presentations occurs with less advanced gestational age. At 32 weeks, 7% of fetuses are breech, and 28 weeks or less, 25% are breech.
Specifically, following one breech delivery, the recurrence rate for the second pregnancy was nearly 10%, and for a subsequent third pregnancy, it was 27%. Prior cesarean delivery has also been described by some to increase the incidence of breech presentation two-fold.
- Pathophysiology
As mentioned previously, the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation are those that affect fetal motility or the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. [6] [7]
Conditions that change the vertical polarity or the uterine cavity, or affect the ease or ability of the fetus to turn into the vertex presentation in the third trimester include:
- Mullerian anomalies: Septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, and didelphys uterus
- Placentation: Placenta previa as the placenta is occupying the inferior portion of the uterine cavity. Therefore, the presenting part cannot engage
- Uterine leiomyoma: Mainly larger myomas located in the lower uterine segment, often intramural or submucosal, that prevent engagement of the presenting part.
- Prematurity
- Aneuploidies and fetal neuromuscular disorders commonly cause hypotonia of the fetus, inability to move effectively
- Congenital anomalies: Fetal sacrococcygeal teratoma, fetal thyroid goiter
- Polyhydramnios: Fetus is often in unstable lie, unable to engage
- Oligohydramnios: Fetus is unable to turn to vertex due to lack of fluid
- Laxity of the maternal abdominal wall: Uterus falls forward, the fetus is unable to engage in the pelvis.
The risk of cord prolapse varies depending on the type of breech. Incomplete or footling breech carries the highest risk of cord prolapse at 15% to 18%, while complete breech is lower at 4% to 6%, and frank breech is uncommon at 0.5%.
- History and Physical
During the physical exam, using the Leopold maneuvers, palpation of a hard, round, mobile structure at the fundus and the inability to palpate a presenting part in the lower abdomen superior to the pubic bone or the engaged breech in the same area, should raise suspicion of a breech presentation.
During a cervical exam, findings may include the lack of a palpable presenting part, palpation of a lower extremity, usually a foot, or for the engaged breech, palpation of the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be noted. If the patient has been laboring, caution is warranted as the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be interpreted as caput of the fetal vertex.
Any of these findings should raise suspicion and ultrasound should be performed.
Diagnosis of a breech presentation can be accomplished through abdominal exam using the Leopold maneuvers in combination with the cervical exam. Ultrasound should confirm the diagnosis.
On ultrasound, the fetal lie and presenting part should be visualized and documented. If breech presentation is diagnosed, specific information including the specific type of breech, the degree of flexion of the fetal head, estimated fetal weight, amniotic fluid volume, placental location, and fetal anatomy review (if not already done previously) should be documented.
- Treatment / Management
Expertise in the delivery of the vaginal breech baby is becoming less common due to fewer vaginal breech deliveries being offered throughout the United States and in most industrialized countries. The Term Breech Trial (TBT), a well-designed, multicenter, international, randomized controlled trial published in 2000 compared planned vaginal delivery to planned cesarean delivery for the term breech infant. The investigators reported that delivery by planned cesarean resulted in significantly lower perinatal mortality, neonatal mortality, and serious neonatal morbidity. Also, there was no significant difference in maternal morbidity or mortality between the two groups. Since that time, the rate of term breech infants delivered by planned cesarean has increased dramatically. Follow-up studies to the TBT have been published looking at maternal morbidity and outcomes of the children at two years. Although these reports did not show any significant difference in the risk of death and neurodevelopmental, these studies were felt to be underpowered. [8] [9] [10] [11]
Since the TBT, many authors since have argued that there are still some specific situations that vaginal breech delivery is a potential, safe alternative to planned cesarean. Many smaller retrospective studies have reported no difference in neonatal morbidity or mortality using these specific criteria.
The initial criteria used in these reports were similar: gestational age greater than 37 weeks, frank or complete breech presentation, no fetal anomalies on ultrasound examination, adequate maternal pelvis, and estimated fetal weight between 2500 g and 4000 g. In addition, the protocol presented by one report required documentation of fetal head flexion and adequate amniotic fluid volume, defined as a 3-cm vertical pocket. Oxytocin induction or augmentation was not offered, and strict criteria were established for normal labor progress. CT pelvimetry did determine an adequate maternal pelvis.
Despite debate on both sides, the current recommendation for the breech presentation at term includes offering external cephalic version (ECV) to those patients that meet criteria, and for those whom are not candidates or decline external cephalic version, a planned cesarean section for delivery sometime after 39 weeks.
Regarding the premature breech, gestational age will determine the mode of delivery. Before 26 weeks, there is a lack of quality clinical evidence to guide mode of delivery. One large retrospective cohort study recently concluded that from 28 to 31 6/7 weeks, there is a significant decrease in perinatal morbidity and mortality in a planned cesarean delivery versus intended vaginal delivery, while there is no difference in perinatal morbidity and mortality in gestational age 32 to 36 weeks. Of note, due to lack of recruitment, no prospective clinical trials are examining this issue.
- Differential Diagnosis
- Face and brow presentation
- Fetal anomalies
- Fetal death
- Grand multiparity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Oligohydramnios
- Pelvis Anatomy
- Preterm labor
- Primigravida
- Uterine anomalies
- Pearls and Other Issues
In light of the decrease in planned vaginal breech deliveries, thus the decrease in expertise in managing this clinical scenario, it is prudent that policies requiring simulation and instruction in the delivery technique for vaginal breech birth are established to care for the emergency breech vaginal delivery.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A breech delivery is usually managed by an obstetrician, labor and delivery nurse, anesthesiologist and a neonatologist. The ultimate decison rests on the obstetrician. To prevent complications, today cesarean sections are performed and experienced with vaginal deliveries of breech presentation is limited. For healthcare workers including the midwife who has no experience with a breech delivery, it is vital to communicate with an obstetrician, otherwise one risks litigation if complications arise during delivery. [12] [13] [14]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Caron Gray declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Meaghan Shanahan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. Breech Presentation. [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. [Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997] [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. Krause M, Fischer T, Feige A. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997 Jul-Aug; 201(4):128-35.
- The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. [Early Hum Dev. 1993] The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. Sival DA, Prechtl HF, Sonder GH, Touwen BC. Early Hum Dev. 1993 Mar; 32(2-3):161-76.
- The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. [PLoS One. 2019] The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. Jennewein L, Allert R, Möllmann CJ, Paul B, Kielland-Kaisen U, Raimann FJ, Brüggmann D, Louwen F. PLoS One. 2019; 14(12):e0225546. Epub 2019 Dec 2.
- Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. [Semin Perinatol. 2003] Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. Tunde-Byass MO, Hannah ME. Semin Perinatol. 2003 Feb; 27(1):34-45.
- Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. [Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2...] Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. Mattuizzi A. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2020 Jan; 48(1):70-80. Epub 2019 Nov 1.
Recent Activity
- Breech Presentation - StatPearls Breech Presentation - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
- AI Generator
breech birth
31 breech presentation stock photos & high-res pictures.
Browse 31 breech presentation photos and images available, or search for breech birth to find more great photos and pictures.


Breech Presentation
- Author: Richard Fischer, MD; Chief Editor: Ronald M Ramus, MD more...
- Sections Breech Presentation
- Vaginal Breech Delivery
- Cesarean Delivery
- Comparative Studies
- External Cephalic Version
- Conclusions
- Media Gallery
Breech presentation is defined as a fetus in a longitudinal lie with the buttocks or feet closest to the cervix. This occurs in 3-4% of all deliveries. The percentage of breech deliveries decreases with advancing gestational age from 22-25% of births prior to 28 weeks' gestation to 7-15% of births at 32 weeks' gestation to 3-4% of births at term. [ 1 ]
Predisposing factors for breech presentation include prematurity , uterine malformations or fibroids, polyhydramnios , placenta previa , fetal abnormalities (eg, CNS malformations, neck masses, aneuploidy), and multiple gestations . Fetal abnormalities are observed in 17% of preterm breech deliveries and in 9% of term breech deliveries.
Perinatal mortality is increased 2- to 4-fold with breech presentation, regardless of the mode of delivery. Deaths are most often associated with malformations, prematurity, and intrauterine fetal demise .
Types of breeches
The types of breeches are as follows:
Frank breech (50-70%) - Hips flexed, knees extended (pike position)
Complete breech (5-10%) - Hips flexed, knees flexed (cannonball position)
Footling or incomplete (10-30%) - One or both hips extended, foot presenting
Historical considerations
Vaginal breech deliveries were previously the norm until 1959 when it was proposed that all breech presentations should be delivered abdominally to reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality. [ 2 ]
Vaginal breech delivery
Three types of vaginal breech deliveries are described, as follows:
Spontaneous breech delivery: No traction or manipulation of the infant is used. This occurs predominantly in very preterm, often previable, deliveries.
Assisted breech delivery: This is the most common type of vaginal breech delivery. The infant is allowed to spontaneously deliver up to the umbilicus, and then maneuvers are initiated to assist in the delivery of the remainder of the body, arms, and head.
Total breech extraction: The fetal feet are grasped, and the entire fetus is extracted. Total breech extraction should be used only for a noncephalic second twin; it should not be used for a singleton fetus because the cervix may not be adequately dilated to allow passage of the fetal head. Total breech extraction for the singleton breech is associated with a birth injury rate of 25% and a mortality rate of approximately 10%. Total breech extractions are sometimes performed by less experienced accoucheurs when a foot unexpectedly prolapses through the vagina. As long as the fetal heart rate is stable in this situation, it is permissible to manage expectantly to allow the cervix to completely dilate around the breech (see the image below).
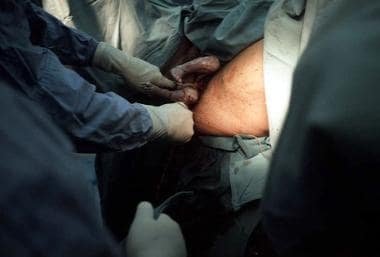
Technique and tips for assisted vaginal breech delivery
The fetal membranes should be left intact as long as possible to act as a dilating wedge and to prevent overt cord prolapse .
Oxytocin induction and augmentation are controversial. In many previous studies, oxytocin was used for induction and augmentation, especially for hypotonic uterine dysfunction. However, others are concerned that nonphysiologic forceful contractions could result in an incompletely dilated cervix and an entrapped head.
An anesthesiologist and a pediatrician should be immediately available for all vaginal breech deliveries. A pediatrician is needed because of the higher prevalence of neonatal depression and the increased risk for unrecognized fetal anomalies. An anesthesiologist may be needed if intrapartum complications develop and the patient requires general anesthesia .
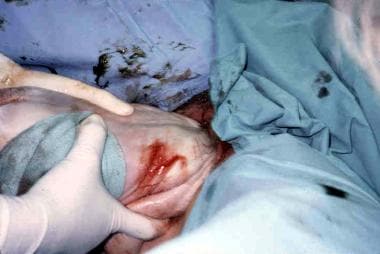
Some clinicians perform an episiotomy when the breech delivery is imminent, even in multiparas, as it may help prevent soft tissue dystocia for the aftercoming head (see the images below).
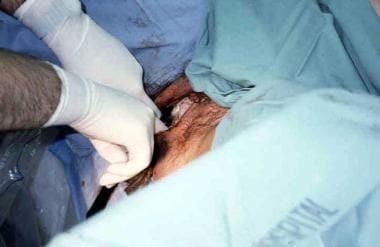
The Pinard maneuver may be needed with a frank breech to facilitate delivery of the legs but only after the fetal umbilicus has been reached. Pressure is exerted in the popliteal space of the knee. Flexion of the knee follows, and the lower leg is swept medially and out of the vagina.
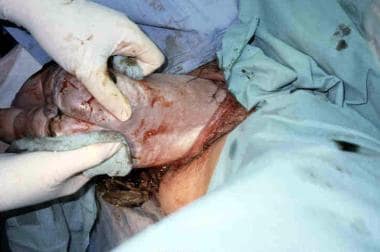
No traction should be exerted on the infant until the fetal umbilicus is past the perineum, after which time maternal expulsive efforts should be used along with gentle downward and outward traction of the infant until the scapula and axilla are visible (see the image below).
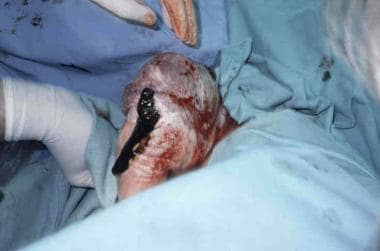
Use a dry towel to wrap around the hips (not the abdomen) to help with gentle traction of the infant (see the image below).
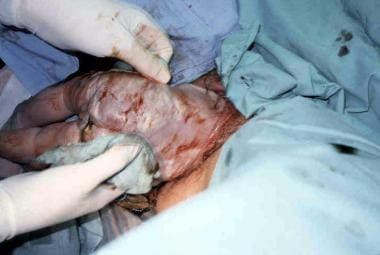
An assistant should exert transfundal pressure from above to keep the fetal head flexed.
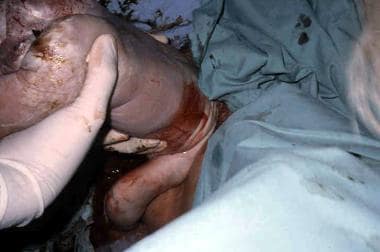
Once the scapula is visible, rotate the infant 90° and gently sweep the anterior arm out of the vagina by pressing on the inner aspect of the arm or elbow (see the image below).
Rotate the infant 180° in the reverse direction, and sweep the other arm out of the vagina. Once the arms are delivered, rotate the infant back 90° so that the back is anterior (see the image below).
The fetal head should be maintained in a flexed position during delivery to allow passage of the smallest diameter of the head. The flexed position can be accomplished by using the Mauriceau Smellie Veit maneuver, in which the operator's index and middle fingers lift up on the fetal maxillary prominences, while the assistant applies suprapubic pressure (see the image below).
Alternatively, Piper forceps can be used to maintain the head in a flexed position (see the image below).
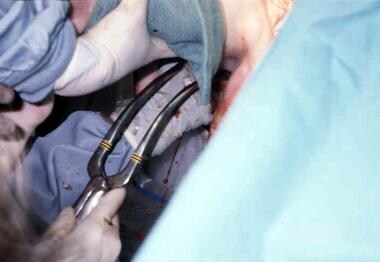
In many early studies, routine use of Piper forceps was recommended to protect the head and to minimize traction on the fetal neck. Piper forceps are specialized forceps that are placed from below the infant and, unlike conventional forceps, are not tailored to the position of the fetal head (ie, it is a pelvic, not cephalic, application). The forceps are applied while the assistant supports the fetal body in a horizontal plane.
During delivery of the head, avoid extreme elevation of the body, which may result in hyperextension of the cervical spine and potential neurologic injury (see the images below).
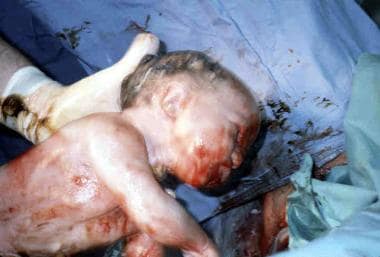
Lower Apgar scores, especially at 1 minute, are more common with vaginal breech deliveries. Many advocate obtaining an umbilical cord artery and venous pH for all vaginal breech deliveries to document that neonatal depression is not due to perinatal acidosis.
Fetal head entrapment may result from an incompletely dilated cervix and a head that lacks time to mold to the maternal pelvis. This occurs in 0-8.5% of vaginal breech deliveries. [ 3 ] This percentage is higher with preterm fetuses (< 32 wk), when the head is larger than the body. Dührssen incisions (ie, 1-3 cervical incisions made to facilitate delivery of the head) may be necessary to relieve cervical entrapment. However, extension of the incision can occur into the lower segment of the uterus, and the operator must be equipped to deal with this complication. The Zavanelli maneuver has been described, which involves replacement of the fetus into the abdominal cavity followed by cesarean delivery. While success has been reported with this maneuver, fetal injury and even fetal death have occurred.
Nuchal arms, in which one or both arms are wrapped around the back of the neck, are present in 0-5% of vaginal breech deliveries and in 9% of breech extractions. [ 3 ] Nuchal arms may result in neonatal trauma (including brachial plexus injuries) in 25% of cases. Risks may be reduced by avoiding rapid extraction of the infant during delivery of the body. To relieve nuchal arms when it is encountered, rotate the infant so that the fetal face turns toward the maternal symphysis pubis (in the direction of the impacted arm); this reduces the tension holding the arm around the back of the fetal head, allowing for delivery of the arm.
Cervical spine injury is predominantly observed when the fetus has a hyperextended head prior to delivery. Ballas and Toaff (1976) reported 20 cases of hyperextended necks, defined as an angle of extension greater than 90° ("star-gazing"), discovered on antepartum radiographs. [ 4 ] Of the 11 fetuses delivered vaginally, 8 (73%) sustained complete cervical spinal cord lesions, defined as either transection or nonfunction.
Cord prolapse may occur in 7.4% of all breech labors. This incidence varies with the type of breech: 0-2% with frank breech, 5-10% with complete breech, and 10-25% with footling breech. [ 3 ] Cord prolapse occurs twice as often in multiparas (6%) than in primigravidas (3%). Cord prolapse may not always result in severe fetal heart rate decelerations because of the lack of presenting parts to compress the umbilical cord (ie, that which predisposes also protects).
Prior to the 2001 recommendations by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), approximately 50% of breech presentations were considered candidates for vaginal delivery. Of these candidates, 60-82% were successfully delivered vaginally.
Candidates can be classified based on gestational age. For pregnancies prior to 26 weeks' gestation, prematurity, not mode of delivery, is the greatest risk factor. Unfortunately, no randomized clinical trials to help guide clinical management have been reported. Vaginal delivery can be considered, but a detailed discussion of the risks from prematurity and the lack of data regarding the ideal mode of delivery should take place with the parent(s). For example, intraventricular hemorrhage, which can occur in an infant of extremely low birth weight, should not be misinterpreted as proof of a traumatic vaginal breech delivery.
For pregnancies between 26 and 32 weeks, retrospective studies suggest an improved outcome with cesarean delivery, although these reports are subject to selection bias. In contrast, between 32 and 36 weeks' gestation, vaginal breech delivery may be considered after a discussion of risks and benefits with the parent(s).
After 37 weeks' gestation, parents should be informed of the results of a multicenter randomized clinical trial that demonstrated significantly increased perinatal mortality and short-term neonatal morbidity associated with vaginal breech delivery (see Comparative Studies). For those attempting vaginal delivery, if estimated fetal weight (EFW) is more than 4000 g, some recommend cesarean delivery because of concern for entrapment of the unmolded head in the maternal pelvis, although data to support this practice are limited.
A frank breech presentation is preferred when vaginal delivery is attempted. Complete breeches and footling breeches are still candidates, as long as the presenting part is well applied to the cervix and both obstetrical and anesthesia services are readily available in the event of a cord prolapse.
The fetus should show no neck hyperextension on antepartum ultrasound imaging (see the image below). Flexed or military position is acceptable.
Regarding prior cesarean delivery, a retrospective study by Ophir et al of 71 women with one prior low transverse cesarean delivery who subsequently delivered a breech fetus found that 24 women had an elective repeat cesarean and 47 women had a trial of labor. [ 5 ] In the 47 women with a trial of labor, 37 (78.7%) resulted in a vaginal delivery. Two infants in the trial of labor group had nuchal arms (1 with a transient brachial plexus injury) and 1 woman required a hysterectomy for hemorrhage due to a uterine dehiscence discovered after vaginal delivery. Vaginal breech delivery after one prior cesarean delivery is not contraindicated, though larger studies are needed.
Primigravida versus multiparous
It had been commonly believed that primigravidas with a breech presentation should have a cesarean delivery, although no data (prospective or retrospective) support this view. The only documented risk related to parity is cord prolapse, which is 2-fold higher in parous women than in primigravid women.
Radiographic and CT pelvimetry
Historically, radiograph pelvimetry was believed to be useful to quantitatively assess the inlet and mid pelvis. Recommended pelvimetry criteria included a transverse inlet diameter larger than 11.5 cm, anteroposterior inlet diameter larger than 10.5 cm, transverse midpelvic diameter (between the ischial spines) larger than 10 cm, and anteroposterior midpelvic diameter larger than 11.5 cm. However, radiographic pelvimetry is rarely, if ever, used in the United States.
CT pelvimetry , which is associated with less fetal radiation exposure than conventional radiographic pelvimetry, was more recently advocated by some investigators. It, too, is rarely used today.
Ultimately, if the obstetrical operator is not experienced or comfortable with vaginal breech deliveries, cesarean delivery may be the best choice. Unfortunately, with the dwindling number of experienced obstetricians who still perform vaginal breech deliveries and who can teach future generations of obstetricians, this technique may soon be lost due to attrition.
In 1970, approximately 14% of breeches were delivered by cesarean delivery. By 1986, that rate had increased to 86%. In 2003, based on data from the National Center for Health Statistics, the rate of cesarean delivery for all breech presentations was 87.2%. Most of the remaining breeches delivered vaginally were likely second twins, fetal demises, and precipitous deliveries. However, the rise in cesarean deliveries for breeches has not necessarily equated with an improvement in perinatal outcome. Green et al compared the outcome for term breeches prior to 1975 (595 infants, 22% cesarean delivery rate for breeches) with those from 1978-1979 (164 infants, 94% cesarean delivery rate for breeches). [ 6 ] Despite the increase in rates of cesarean delivery, the differences in rates of asphyxia, birth injury, and perinatal deaths were not significant.
Maneuvers for cesarean delivery are similar to those for vaginal breech delivery, including the Pinard maneuver, wrapping the hips with a towel for traction, head flexion during traction, rotation and sweeping out of the fetal arms, and the Mauriceau Smellie Veit maneuver.
An entrapped head can still occur during cesarean delivery as the uterus contracts after delivery of the body, even with a lower uterine segment that misleadingly appears adequate prior to uterine incision. Entrapped heads occur more commonly with preterm breeches, especially with a low transverse uterine incision. As a result, some practitioners opt to perform low vertical uterine incisions for preterm breeches prior to 32 weeks' gestation to avoid head entrapment and the kind of difficult delivery that cesarean delivery was meant to avoid. Low vertical incisions usually require extension into the corpus, resulting in cesarean delivery for all future deliveries.
If a low transverse incision is performed, the physician should move quickly once the breech is extracted in order to deliver the head before the uterus begins to contract. If any difficulty is encountered with delivery of the fetal head, the transverse incision can be extended vertically upward (T incision). Alternatively, the transverse incision can be extended laterally and upward, taking great care to avoid trauma to the uterine arteries. A third option is the use of a short-acting uterine relaxant (eg, nitroglycerin) in an attempt to facilitate delivery.
Only 3 randomized studies have evaluated the mode of delivery of the term breech. All other studies were nonrandomized or retrospective, which may be subject to selection bias.
In 1980, Collea et al randomized 208 women in labor with term frank breech presentations to either elective cesarean delivery or attempted vaginal delivery after radiographic pelvimetry. [ 7 ] Oxytocin was allowed for dysfunctional labor. Of the 60 women with adequate pelves, 49 delivered vaginally. Two neonates had transient brachial plexus injuries. Women randomized to elective cesarean delivery had higher postpartum morbidity rates (49.3% vs 6.7%).
In 1983, Gimovsky et al randomized 105 women in labor with term nonfrank breech presentations to a trial of labor versus elective cesarean delivery. [ 8 ] In this group of women, 47 had complete breech presentations, 16 had incomplete breech presentations (hips flexed, 1 knee extended/1 knee flexed), 32 had double-footling presentations, and 10 had single-footling presentations. Oxytocin was allowed for dysfunctional labor. Of the labor group, 44% had successful vaginal delivery. Most cesarean deliveries were performed for inadequate pelvic dimensions on radiographic pelvimetry. The rate of neonatal morbidity did not differ between neonates delivered vaginally and those delivered by cesarean delivery, although a higher maternal morbidity rate was noted in the cesarean delivery group.
In 2000, Hannah and colleagues completed a large, multicenter, randomized clinical trial involving 2088 term singleton fetuses in frank or complete breech presentations at 121 institutions in 26 countries. [ 9 ] In this study, popularly known as the Term Breech Trial, subjects were randomized into a planned cesarean delivery group or a planned vaginal birth group. Exclusion criteria were estimated fetal weight (EFW) more than 4000 g, hyperextension of the fetal head, lethal fetal anomaly or anomaly that might result in difficulty with delivery, or contraindication to labor or vaginal delivery (eg, placenta previa ).
Subjects randomized to cesarean delivery were scheduled to deliver after 38 weeks' gestation unless conversion to cephalic presentation had occurred. Subjects randomized to vaginal delivery were treated expectantly until labor ensued. Electronic fetal monitoring was either continuous or intermittent. Inductions were allowed for standard obstetrical indications, such as postterm gestations. Augmentation with oxytocin was allowed in the absence of apparent fetopelvic disproportion, and epidural analgesia was permitted.
Adequate labor was defined as a cervical dilation rate of 0.5 cm/h in the active phase of labor and the descent of the breech fetus to the pelvic floor within 2 hours of achieving full dilation. Vaginal delivery was spontaneous or assisted and was attended by an experienced obstetrician. Cesarean deliveries were performed for inadequate progress of labor, nonreassuring fetal heart rate, or conversion to footling breech. Results were analyzed by intent-to-treat (ie, subjects were analyzed by randomization group, not by ultimate mode of delivery).
Of 1041 subjects in the planned cesarean delivery group, 941 (90.4%) had cesarean deliveries. Of 1042 subjects in the planned vaginal delivery group, 591 (56.7%) had vaginal deliveries. Indications for cesarean delivery included: fetopelvic disproportion or failure to progress in labor (226), nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracing (129), footling breech (69), request for cesarean delivery (61), obstetrical or medical indications (45), or cord prolapse (12).
The composite measurement of either perinatal mortality or serious neonatal morbidity by 6 weeks of life was significantly lower in the planned cesarean group than in the planned vaginal group (5% vs 1.6%, P < .0001). Six of 16 neonatal deaths were associated with difficult vaginal deliveries, and 4 deaths were associated with fetal heart rate abnormalities. The reduction in risk in the cesarean group was even greater in participating countries with overall low perinatal mortality rates as reported by the World Health Organization. The difference in perinatal outcome held after controlling for the experience level of the obstetrician. No significant difference was noted in maternal mortality or serious maternal morbidity between the 2 groups within the first 6 weeks of delivery (3.9% vs 3.2%, P = .35).
A separate analysis showed no difference in breastfeeding, sexual relations, or depression at 3 months postpartum, though the reported rate of urinary incontinence was higher in the planned vaginal group (7.3% vs 4.5%).
Based on the multicenter trial, the ACOG published a Committee Opinion in 2001 that stated "planned vaginal delivery of a singleton term breech may no longer be appropriate." This did not apply to those gravidas presenting in advanced labor with a term breech and imminent delivery or to a nonvertex second twin.
A follow-up study by Whyte et al was conducted in 2004 on 923 children who were part of the initial multicenter study. [ 10 ] The authors found no differences between the planned cesarean delivery and planned vaginal breech delivery groups with regards to infant death rates or neurodevelopmental delay by age 2 years. Similarly, among 917 participating mothers from the original trial, no substantive differences were apparent in maternal outcome between the 2 groups. [ 11 ] No longer-term maternal effects, such as the impact of a uterine scar on future pregnancies, have yet been reported.
A meta-analysis of the 3 above mentioned randomized trials was published in 2015. The findings included a reduction in perinatal/neonatal death, reduced composite short-term outcome of perinatal/neonatal death or serious neonatal morbidity with planned cesarean delivery versus planned vaginal delivery. [ 12 ] However, at 2 years of age, there was no significant difference in death or neurodevelopmental delay between the two groups. Maternal outcomes assessed at 2 years after delivery were not significantly different.
With regard to preterm breech deliveries, only one prospective randomized study has been performed, which included only 38 subjects (28-36 wk) with preterm labor and breech presentation. [ 13 ] Of these subjects, 20 were randomized to attempted vaginal delivery and 18 were randomized to immediate cesarean delivery. Of the attempted vaginal delivery group, 25% underwent cesarean delivery for nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracings. Five neonatal deaths occurred in the vaginal delivery group, and 1 neonatal death occurred in the cesarean delivery group. Two neonates died from fetal anomalies, 3 from respiratory distress, and 1 from sepsis.
Nonanomalous infants who died were not acidotic at delivery and did not have birth trauma. Differences in Apgar scores were not significant, although the vaginal delivery group had lower scores. The small number of enrolled subjects precluded any definitive conclusions regarding the safety of vaginal breech delivery for a preterm breech.
Retrospective analyses showed a higher mortality rate in vaginal breech neonates weighing 750-1500 g (26-32 wk), but less certain benefit was shown with cesarean delivery if the fetal weight was more than 1500 g (approximately 32 wk). Therefore, this subgroup of very preterm infants (26-32 wk) may benefit from cesarean delivery, although this recommendation is based on potentially biased retrospective data.
A large cohort study was published in 2015 from the Netherlands Perinatal Registry, which included 8356 women with a preterm (26-36 6/7 weeks) breech from 2000 to 2011, over three quarters of whom intended to deliver vaginally. In this overall cohort, there was no significant difference in perinatal mortality between the planned vaginal delivery and planned cesarean delivery groups (adjusted odds ratio 0.97, 95% confidence interval 0.60 – 1.57). However, the subgroup delivering at 28 to 32 weeks had a lower perinatal mortality with planned cesarean section (aOR 0.27, 95% CI 0.10 – 0.77). After adding a composite of perinatal morbidity, planned cesarean delivery was associated with a better outcome than a planned vaginal delivery (aOR 0.77, 95% CI 0.63 – 0.93. [ 14 ]
A Danish study found that nulliparous women with a singleton breech presentation who had a planned vaginal delivery were at significantly higher risk for postoperative complications, such as infection, compared with women who had a planned cesarean delivery. This increased risk was due to the likelihood of conversion to an emergency cesarean section, which occurred in over 69% of the planned vaginal deliveries in the study. [ 15 ]
The Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network of the US National Institute of Child Health and Human Development considered a multicenter randomized clinical trial of attempted vaginal delivery versus elective cesarean delivery for 24- to 28-week breech fetuses. [ 16 ] However, it was not initiated because of anticipated difficulty with recruitment, inadequate numbers to show statistically significant differences, and medicolegal concerns. Therefore, this study is not likely to be performed.
External cephalic version (ECV) is the transabdominal manual rotation of the fetus into a cephalic presentation.
Initially popular in the 1960s and 1970s, ECV virtually disappeared after reports of fetal deaths following the procedure. Reintroduced to the United States in the 1980s, it became increasingly popular in the 1990s.
Improved outcome may be related to the use of nonstress tests both before and after ECV, improved selection of low-risk fetuses, and Rh immune globulin to prevent isoimmunization.
Prepare for the possibility of cesarean delivery. Obtain a type and screen as well as an anesthesia consult. The patient should have nothing by mouth for at least 8 hours prior to the procedure. Recent ultrasonography should have been performed for fetal position, to check growth and amniotic fluid volume, to rule out a placenta previa, and to rule out anomalies associated with breech. Another sonogram should be performed on the day of the procedure to confirm that the fetus is still breech.
A nonstress test (biophysical profile as backup) should be performed prior to ECV to confirm fetal well-being.
Perform ECV in or near a delivery suite in the unlikely event of fetal compromise during or following the procedure, which may require emergent delivery.
ECV can be performed with 1 or 2 operators. Some prefer to have an assistant to help turn the fetus, elevate the breech out of the pelvis, or to monitor the position of the baby with ultrasonography. Others prefer a single operator approach, as there may be better coordination between the forces that are raising the breech and moving the head.
ECV is accomplished by judicious manipulation of the fetal head toward the pelvis while the breech is brought up toward the fundus. Attempt a forward roll first and then a backward roll if the initial attempts are unsuccessful. No consensus has been reached regarding how many ECV attempts are appropriate at one time. Excessive force should not be used at any time, as this may increase the risk of fetal trauma.
Following an ECV attempt, whether successful or not, repeat the nonstress test (biophysical profile if needed) prior to discharge. Also, administer Rh immune globulin to women who are Rh negative. Some physicians traditionally induce labor following successful ECV. However, as virtually all of these recently converted fetuses are unengaged, many practitioners will discharge the patient and wait for spontaneous labor to ensue, thereby avoiding the risk of a failed induction of labor. Additionally, as most ECV’s are attempted prior to 39 weeks, as long as there are no obstetrical or medical indications for induction, discharging the patient to await spontaneous labor would seem most prudent.
In those with an unsuccessful ECV, the practitioner has the option of sending the patient home or proceeding with a cesarean delivery. Expectant management allows for the possibility of spontaneous version. Alternatively, cesarean delivery may be performed at the time of the failed ECV, especially if regional anesthesia is used and the patient is already in the delivery room (see Regional anesthesia). This would minimize the risk of a second regional analgesia.
In those with an unsuccessful ECV, the practitioner may send the patient home, if less than 39 weeks, with plans for either a vaginal breech delivery or scheduled cesarean after 39 weeks. Expectant management allows for the possibility of a spontaneous version. Alternatively, if ECV is attempted after 39 weeks, cesarean delivery may be performed at the time of the failed ECV, especially if regional anesthesia is used and the patient is already in the delivery room (see Regional anesthesia). This would minimize the risk of a second regional analgesia.
Success rate
Success rates vary widely but range from 35% to 86% (average success rate in the 2004 National Vital Statistics was 58%). Improved success rates occur with multiparity, earlier gestational age, frank (versus complete or footling) breech presentation, transverse lie, and in African American patients.
Opinions differ regarding the influence of maternal weight, placental position, and amniotic fluid volume. Some practitioners find that thinner patients, posterior placentas, and adequate fluid volumes facilitate successful ECV. However, both patients and physicians need to be prepared for an unsuccessful ECV; version failure is not necessarily a reflection of the skill of the practitioner.
Zhang et al reviewed 25 studies of ECV in the United States, Europe, Africa, and Israel. [ 17 ] The average success rate in the United States was 65%. Of successful ECVs, 2.5% reverted back to breech presentation (other estimates range from 3% to 5%), while 2% of unsuccessful ECVs had spontaneous version to cephalic presentation prior to labor (other estimates range from 12% to 26%). Spontaneous version rates depend on the gestational age when the breech is discovered, with earlier breeches more likely to undergo spontaneous version.
A prospective study conducted in Germany by Zielbauer et al demonstrated an overall success rate of 22.4% for ECV among 353 patients with a singleton fetus in breech presentation. ECV was performed at 38 weeks of gestation. Factors found to increase the likelihood of success were a later week of gestation, abundant amniotic fluid, fundal and anterior placental location, and an oblique lie. [ 18 ]
A systematic review in 2015 looked at the effectiveness of ECV with eight randomized trials of ECV at term. Compared to women with no attempt at ECV, ECV reduced non-cephalic presentation at birth by 60% and reduced cesarean sections by 40% in the same group. [ 19 ] Although the rate of cesarean section is lower when ECV is performed than if not, the overall rate of cesarean section remains nearly twice as high after successful ECV due to both dystocia and non-reassuring fetal heart rate patterns. [ 20 ] Nulliparity was the only factor shown in follow-up to increase the risk of instrumental delivery following successful ECV. [ 21 ]
While most studies of ECV have been performed in university hospitals, Cook showed that ECV has also been effective in the private practice setting. [ 22 ] Of 65 patients with term breeches, 60 were offered ECV. ECV was successful in 32 (53%) of the 60 patients, with vaginal delivery in 23 (72%) of the 32 patients. Of the remaining breech fetuses believed to be candidates for vaginal delivery, 8 (80%) had successful vaginal delivery. The overall vaginal delivery rate was 48% (31 of 65 patients), with no significant morbidity.
Cost analysis
In 1995, Gifford et al performed a cost analysis of 4 options for breech presentations at term: (1) ECV attempt on all breeches, with attempted vaginal breech delivery for selected persistent breeches; (2) ECV on all breeches, with cesarean delivery for persistent breeches; (3) trial of labor for selected breeches, with scheduled cesarean delivery for all others; and (4) scheduled cesarean delivery for all breeches prior to labor. [ 23 ]
ECV attempt on all breeches with attempted vaginal breech delivery on selected persistent breeches was associated with the lowest cesarean delivery rate and was the most cost-effective approach. The second most cost-effective approach was ECV attempt on all breeches, with cesarean delivery for persistent breeches.
Uncommon risks of ECV include fractured fetal bones, precipitation of labor or premature rupture of membranes , abruptio placentae , fetomaternal hemorrhage (0-5%), and cord entanglement (< 1.5%). A more common risk of ECV is transient slowing of the fetal heart rate (in as many as 40% of cases). This risk is believed to be a vagal response to head compression with ECV. It usually resolves within a few minutes after cessation of the ECV attempt and is not usually associated with adverse sequelae for the fetus.
Trials have not been large enough to determine whether the overall risk of perinatal mortality is increased with ECV. The Cochrane review from 2015 reported perinatal death in 2 of 644 in ECV and 6 of 661 in the group that did not attempt ECV. [ 19 ]
A 2016 Practice Bulletin by ACOG recommended that all women who are near term with breech presentations should be offered an ECV attempt if there are no contraindications (see Contraindications below). [ 24 ] ACOG guidelines issued in 2020 recommend that ECV should be performed starting at 37+0 weeks, in order to reduce the likelihood of reversion and to increase the rate of spontaneous version. [ 25 ]
ACOG recommends that ECV be offered as an alternative to a planned cesarean section for a patient who has a term singleton breech fetus, wishes to have a planned vaginal delivery of a vertex-presenting fetus, and has no contraindications. ACOG also advises that ECV be attempted only in settings where cesarean delivery services are available. [ 26 ]
ECV is usually not performed on preterm breeches because they are more likely to undergo spontaneous version to cephalic presentation and are more likely to revert to breech after successful ECV (approximately 50%). Earlier studies of preterm ECV did not show a difference in the rates of breech presentations at term or overall rates of cesarean delivery. Additionally, if complications of ECV were to arise that warranted emergent delivery, it would result in a preterm neonate with its inherent risks. The Early External Cephalic Version (ECV) 2 trial was an international, multicentered, randomized clinical trial that compared ECV performed at 34-35 weeks’ gestation compared with 37 weeks’ gestation or more. [ 27 ] Early ECV increased the chance of cephalic presentation at birth; however, no difference in cesarean delivery rates was noted, along with a nonstatistical increase in preterm births.
A systematic review looked at 5 studies of ECV completed prior to 37 weeks and concluded that compared with no ECV attempt, ECV commenced before term reduces the non-cephalic presentation at birth, however early ECV may increase the risk of late preterm birth. [ 28 ]
Given the increasing awareness of the risks of late preterm birth and early term deliveries, the higher success of earlier ECV should be weighed against the risks of iatrogenic prematurity should a complication arise necessitating delivery.
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications for ECV include multiple gestations with a breech presenting fetus, contraindications to vaginal delivery (eg, herpes simplex virus infection, placenta previa), and nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracing.
Relative contraindications include polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios , fetal growth restriction , uterine malformation , and major fetal anomaly.
Controversial candidates
Women with prior uterine incisions may be candidates for ECV, but data are scant. In 1991, Flamm et al attempted ECV on 56 women with one or more prior low transverse cesarean deliveries. [ 29 ] The success rate of ECV was 82%, with successful vaginal births in 65% of patients with successful ECVs. No uterine ruptures occurred during attempted ECV or subsequent labor, and no significant fetal complications occurred.
In 2010 ACOG acknowledged that although there is limited data in both the above study and one more recently, [ 30 ] no serious adverse events occurred in these series. A larger prospective cohort study that was published in 2014 reported similar success rates of ECV among women with and without prior cesarean section, although lower vaginal birth rates. There were, however, no cases of uterine rupture or other adverse outcomes. [ 31 ]
Another controversial area is performing ECV on a woman in active labor. In 1985, Ferguson and Dyson reported on 15 women in labor with term breeches and intact membranes. [ 32 ] Four patients were dilated greater than 5 cm (2 women were dilated 8 cm). Tocolysis was administered, and intrapartum ECV was attempted. ECV was successful in 11 of 15 patients, with successful vaginal births in 10 patients. No adverse effects were noted. Further studies are needed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of intrapartum ECV.
Data regarding the benefit of intravenous or subcutaneous beta-mimetics in improving ECV rates are conflicting.
In 1996, Marquette et al performed a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study on 283 subjects with breech presentations between 36 and 41 weeks' gestation. [ 33 ] Subjects received either intravenous ritodrine or placebo. The success rate of ECV was 52% in the ritodrine group versus 42% in the placebo group ( P = .35). When only nulliparous subjects were analyzed, significant differences were observed in the success of ECV (43% vs 25%, P < .03). ECV success rates were significantly higher in parous versus nulliparous subjects (61% vs 34%, P < .0001), with no additional improvement with ritodrine.
A systematic review published in 2015 of six randomized controlled trials of ECV that compared the use of parenteral beta-mimetic tocolysis during ECV concluded that tocolysis was effective in increasing the rate of cephalic presentation in labor and reducing the cesarean delivery rate by almost 25% in both nulliparous and multiparous women. [ 34 ] Data on adverse effects and other tocolytics was insufficient. A review published in 2011 on Nifedipine did not show an improvement in ECV success. [ 35 ]
Regional anesthesia
Regional analgesia, either epidural or spinal, may be used to facilitate external cephalic version (ECV) success. When analgesia levels similar to that for cesarean delivery are given, it allows relaxation of the anterior abdominal wall, making palpation and manipulation of the fetal head easier. Epidural or spinal analgesia also eliminates maternal pain that may cause bearing down and tensing of the abdominal muscles. If ECV is successful, the epidural can be removed and the patient sent home to await spontaneous labor. If ECV is unsuccessful, a patient can proceed to cesarean delivery under her current anesthesia, if the gestational age is more than 39 weeks.
The main disadvantage is the inherent risk of regional analgesia, which is considered small. Additionally, lack of maternal pain could potentially result in excessive force being applied to the fetus without the knowledge of the operator.
In 1994, Carlan et al retrospectively analyzed 61 women who were at more than 36 weeks' gestation and had ECV with or without epidural. [ 36 ] The success rate of ECV was 59% in the epidural group and 24% in the nonepidural group ( P < .05). In 7 of 8 women with unsuccessful ECV without epidural, a repeat ECV attempt after epidural was successful. No adverse effects on maternal or perinatal morbidity or mortality occurred.
In 1997, Schorr et al randomized 69 subjects who were at least 37 weeks' gestation to either epidural or control groups prior to attempted ECV. [ 37 ] Those in whom ECV failed underwent cesarean delivery. The success rate of ECV was 69% in the epidural group and 32% in the control group (RR, 2.12; 95% CI, 1.24-3.62). The cesarean delivery rate was 79% in the control group and 34% in the epidural group ( P = .001). No complications of epidural anesthesia and no adverse fetal effects occurred.
In 1999, Dugoff et al randomized 102 subjects who were at more than 36 weeks' gestation with breech presentations to either spinal anesthesia or a control group. [ 38 ] All subjects received 0.25 mg terbutaline subcutaneously. The success rate of ECV was 44% in the spinal group and 42% in the nonspinal group, which was not statistically significant.
In contrast, a 2007 randomized clinical trial of spinal analgesia versus no analgesia in 74 women showed a significant improvement in ECV success (66.7% vs 32.4%, p = .004), with a significantly lower pain score by the patient. [ 39 ]
The 2015 systematic review asserted that regional analgesia in combination with a tocolytic was more effective than the tocolytic alone for increasing ECV success; however there was no difference in cephalic presentation in labor. Data from the same review was insufficient to assess regional analgesia without tocolysis [ 34 ]
Acoustic stimulation
Johnson and Elliott performed a randomized, blinded trial on 23 subjects to compare acoustic stimulation prior to ECV with a control group when the fetal spine was in the midline (directly back up or back down). [ 40 ] Of those who received acoustic stimulation, 12 of 12 fetuses shifted to a spine-lateral position after acoustic stimulation, and 11 (91%) underwent successful ECV. In the control group, 0 of 11 shifts and 1 (9%) successful ECV ( P < .0001) occurred. Additional studies are needed.
Amnioinfusion
Although an earlier study reported on the utility of amnioinfusion to successfully turn 6 fetuses who initially failed ECV, [ 41 ] a subsequent study was published of 7 women with failed ECV who underwent amniocentesis and amnioinfusion of up to 1 liter of crystalloid. [ 42 ] Repeat attempts of ECV were unsuccessful in all 7 cases. Amnioinfusion to facilitate ECV cannot be recommended at this time.
Vaginal delivery rates after successful version
The rate of cesarean delivery ranges from 0-31% after successful external cephalic version (ECV). Controversy has existed on whether there is a higher rate of cesarean delivery for labor dystocia following ECV. In 1994, a retrospective study by Egge et al of 76 successful ECVs matched with cephalic controls by delivery date, parity, and gestational age failed to note any significant difference in the cesarean delivery rate (8% in ECV group, 6% in control group). [ 43 ]
However, in 1997, Lau et al compared 154 successful ECVs to 308 spontaneously occurring cephalic controls (matched for age, parity, and type of labor onset) with regard to the cesarean delivery rate. [ 44 ] Cesarean delivery rates were higher after ECV (16.9% vs 7.5%, P < .005) because of higher rates of cephalopelvic disproportion and nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracings. This may be related to an increased frequency of compound presentations after ECV. Immediate induction of labor after successful ECV may also contribute to an increase in the cesarean delivery rate due to failed induction in women with unripe cervices and unengaged fetal heads.
Further, in another cohort study from 2015, factors were described which decreased the vaginal delivery rate after successful ECV including labor induction, less than 2 weeks between ECV and delivery, high body mass index, and previous cesarean. [ 45 ] The overall caesarean delivery rate in this cohort was 15%.
Vaginal breech delivery requires an experienced obstetrician and careful counseling of the parents. Although studies on the delivery of the preterm breech are limited, the multicenter Term Breech Trial found an increased rate of perinatal mortality and serious immediate perinatal morbidity, though no differences were seen in infant outcome at 2 years of age.
Parents must be informed about potential risks and benefits to the mother and neonate for both vaginal breech delivery and cesarean delivery. Discussion of risks should not be limited only to the current pregnancy. The risks of a cesarean on subsequent pregnancies, including uterine rupture and placental attachment abnormalities ( placenta previa , abruption , accreta), as well as maternal and perinatal sequelae from these complications, should be reviewed as well.
It remains concerning that the dearth of experienced physicians to teach younger practitioners will lead to the abandonment of vaginal breeches altogether. For those wishing to learn the art of vaginal breech deliveries, simulation training with pelvic models has been advocated to familiarize trainees with the procedure in a nonthreatening environment. [ 46 ] Once comfortable with the appropriate maneuvers, vaginal delivery of the second, noncephalic twin, may be attempted under close supervision by an experienced physician. The cervix will already be fully dilated, and, assuming the second twin is not significantly larger, the successful vaginal delivery rate has been quoted to be as high as 96%.
External cephalic version (ECV) is a safe alternative to vaginal breech delivery or cesarean delivery, reducing the cesarean delivery rate for breech by 50%. ACOG recommends offering ECV to all women with a breech fetus near term. [ 24 ] Adjuncts such as tocolysis, regional anesthesia, and acoustic stimulation when appropriate may improve ECV success rates.
Hickok DE, Gordon DC, Milberg JA, Williams MA, Daling JR. The frequency of breech presentation by gestational age at birth: a large population-based study. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1992 Mar. 166(3):851-2. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Wright RC. Reduction of perinatal mortality and morbidity in breech delivery through routine use of cesarean section. Obstet Gynecol . 1959. 14:758-63.
Cheng M, Hannah M. Breech delivery at term: a critical review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol . 1993 Oct. 82(4 Pt 1):605-18. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Ballas S, Toaff R. Hyperextension of the fetal head in breech presentation: radiological evaluation and significance. Br J Obstet Gynaecol . 1976 Mar. 83(3):201-4. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Ophir E, Oettinger M, Yagoda A, Markovits Y, Rojansky N, Shapiro H. Breech presentation after cesarean section: always a section?. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1989 Jul. 161(1):25-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Green JE, McLean F, Smith LP, Usher R. Has an increased cesarean section rate for term breech delivery reduced in incidence of birth asphyxia, trauma, and death?. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1982 Mar 15. 142(6 Pt 1):643-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Collea JV, Chein C, Quilligan EJ. The randomized management of term frank breech presentation: a study of 208 cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1980 May 15. 137(2):235-44. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Gimovsky ML, Wallace RL, Schifrin BS, Paul RH. Randomized management of the nonfrank breech presentation at term: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1983 May 1. 146(1):34-40. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Hannah ME, Hannah WJ, Hewson SA, Hodnett ED, Saigal S, Willan AR. Planned caesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: a randomised multicentre trial. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group. Lancet . 2000 Oct 21. 356(9239):1375-83. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Whyte H, Hannah ME, Saigal S, et al. Outcomes of children at 2 years after planned cesarean birth versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: the International Randomized Term Breech Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 2004 Sep. 191(3):864-71. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Hannah ME, Whyte H, Hannah WJ, Hewson S, Amankwah K, Cheng M. Maternal outcomes at 2 years after planned cesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: the international randomized Term Breech Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 2004 Sep. 191(3):917-27. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Hofmeyr GJ, Hannah M, Lawrie TA. Planned caesarean section for term breech delivery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Jul 21. 7:CD000166. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Zlatnik FJ. The Iowa premature breech trial. Am J Perinatol . 1993 Jan. 10(1):60-3. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Bergenhenegouwen L, Vlemmix F, Ensing S, Schaaf J, van der Post J, Abu-Hanna A, et al. Preterm Breech Presentation: A Comparison of Intended Vaginal and Intended Cesarean Delivery. Obstet Gynecol . 2015 Dec. 126 (6):1223-30. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Caning MM, Rasmussen SC, Krebs L. Maternal outcomes of planned mode of delivery for term breech in nulliparous women. PLoS One . 2024. 19 (4):e0297971. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] . [Full Text] .
Eller DP, VanDorsten JP. Route of delivery for the breech presentation: a conundrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1995 Aug. 173(2):393-6; discussion 396-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Zhang J, Bowes WA Jr, Fortney JA. Efficacy of external cephalic version: a review. Obstet Gynecol . 1993 Aug. 82(2):306-12. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Zielbauer AS, Louwen F, Jennewein L. External cephalic version at 38 weeks' gestation at a specialized German single center. PLoS One . 2021. 16 (8):e0252702. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] . [Full Text] .
Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Apr 1. 4:CD000083. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
de Hundt M, Velzel J, de Groot CJ, Mol BW, Kok M. Mode of delivery after successful external cephalic version: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol . 2014 Jun. 123 (6):1327-34. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
de Hundt M, Vlemmix F, Bais JM, de Groot CJ, Mol BW, Kok M. Risk factors for cesarean section and instrumental vaginal delivery after successful external cephalic version. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med . 2016 Jun. 29 (12):2005-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Cook HA. Experience with external cephalic version and selective vaginal breech delivery in private practice. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1993 Jun. 168(6 Pt 1):1886-9; discussion 1889-90. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Gifford DS, Keeler E, Kahn KL. Reductions in cost and cesarean rate by routine use of external cephalic version: a decision analysis. Obstet Gynecol . 1995 Jun. 85(6):930-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Practice Bulletin No. 161 Summary: External Cephalic Version. Obstet Gynecol . 2016 Feb. 127 (2):412-3. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
[Guideline] External Cephalic Version: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 221. Obstet Gynecol . 2020 May. 135 (5):e203-e212. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
[Guideline] ACOG Committee Opinion No. 745: Mode of Term Singleton Breech Delivery. Obstet Gynecol . 2018 Aug; reaffirmed 2023. 132 (2):e60-e63. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] . [Full Text] .
Hutton E, Hannah M, Ross S, Delisle MF, Carson G, Windrim R, et al. The Early External Cephalic Version (ECV) 2 Trial: an international multicentre randomised controlled trial of timing of ECV for breech pregnancies. BJOG . 2011 Apr. 118(5):564-577. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Hutton EK, Hofmeyr GJ, Dowswell T. External cephalic version for breech presentation before term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Jul 29. 7:CD000084. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Flamm BL, Fried MW, Lonky NM, Giles WS. External cephalic version after previous cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1991 Aug. 165(2):370-2. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
de Meeus JB, Ellia F, Magnin G. External cephalic version after previous cesarean section: a series of 38 cases. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol . 1998 Oct. 81 (1):65-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Burgos J, Cobos P, Rodríguez L, Osuna C, Centeno MM, Martínez-Astorquiza T, et al. Is external cephalic version at term contraindicated in previous caesarean section? A prospective comparative cohort study. BJOG . 2014 Jan. 121 (2):230-5; discussion 235. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Ferguson JE 2nd, Dyson DC. Intrapartum external cephalic version. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1985 Jun 1. 152(3):297-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Marquette GP, Boucher M, Theriault D, Rinfret D. Does the use of a tocolytic agent affect the success rate of external cephalic version?. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1996 Oct. 175(4 Pt 1):859-61. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Cluver C, Gyte GM, Sinclair M, Dowswell T, Hofmeyr GJ. Interventions for helping to turn term breech babies to head first presentation when using external cephalic version. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Feb 9. 2:CD000184. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Wilcox CB, Nassar N, Roberts CL. Effectiveness of nifedipine tocolysis to facilitate external cephalic version: a systematic review. BJOG . 2011 Mar. 118 (4):423-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Carlan SJ, Dent JM, Huckaby T, Whittington EC, Shaefer D. The effect of epidural anesthesia on safety and success of external cephalic version at term. Anesth Analg . 1994 Sep. 79(3):525-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Schorr SJ, Speights SE, Ross EL, et al. A randomized trial of epidural anesthesia to improve external cephalic version success. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1997 Nov. 177(5):1133-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Dugoff L, Stamm CA, Jones OW 3rd, Mohling SI, Hawkins JL. The effect of spinal anesthesia on the success rate of external cephalic version: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol . 1999 Mar. 93(3):345-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Weiniger CF, Ginosar Y, Elchalal U, Sharon E, Nokrian M, Ezra Y. External cephalic version for breech presentation with or without spinal analgesia in nulliparous women at term: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol . 2007 Dec. 110(6):1343-50. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Johnson RL, Elliott JP. Fetal acoustic stimulation, an adjunct to external cephalic version: a blinded, randomized crossover study. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1995 Nov. 173(5):1369-72. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Benifla JL, Goffinet F, Darai E, Madelenat P. Antepartum transabdominal amnioinfusion to facilitate external cephalic version after initial failure. Obstet Gynecol . 1994 Dec. 84(6):1041-2. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Adama van Scheltema PN, Feitsma AH, Middeldorp JM, Vandenbussche FP, Oepkes D. Amnioinfusion to facilitate external cephalic version after initial failure. Obstet Gynecol . 2006 Sep. 108(3 Pt 1):591-2. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Egge T, Schauberger C, Schaper A. Dysfunctional labor after external cephalic version. Obstet Gynecol . 1994 May. 83(5 Pt 1):771-3. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Lau TK, Lo KW, Rogers M. Pregnancy outcome after successful external cephalic version for breech presentation at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 1997 Jan. 176(1 Pt 1):218-23. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Burgos J, Iglesias M, Pijoan JI, Rodriguez L, Fernández-Llebrez L, Martínez-Astorquiza T. Probability of cesarean delivery after successful external cephalic version. Int J Gynaecol Obstet . 2015 Nov. 131 (2):192-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
Deering S, Brown J, Hodor J, Satin AJ. Simulation training and resident performance of singleton vaginal breech delivery. Obstet Gynecol . 2006 Jan. 107(1):86-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link] .
- Footling breech presentation. Once the feet have delivered, one may be tempted to pull on the feet. However, a singleton gestation should not be pulled by the feet because this action may precipitate head entrapment in an incompletely dilated cervix or may precipitate nuchal arms. As long as the fetal heart rate is stable and no physical evidence of a prolapsed cord is evident, management may be expectant while awaiting full cervical dilation.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. Thick meconium passage is common as the breech is squeezed through the birth canal. This is usually not associated with meconium aspiration because the meconium passes out of the vagina and does not mix with the amniotic fluid.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. The Ritgen maneuver is applied to take pressure off the perineum during vaginal delivery. Episiotomies are often performed for assisted vaginal breech deliveries, even in multiparous women, to prevent soft tissue dystocia.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. No downward or outward traction is applied to the fetus until the umbilicus has been reached.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. With a towel wrapped around the fetal hips, gentle downward and outward traction is applied in conjunction with maternal expulsive efforts until the scapula is reached. An assistant should be applying gentle fundal pressure to keep the fetal head flexed.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. After the scapula is reached, the fetus should be rotated 90° in order to deliver the anterior arm.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. The anterior arm is followed to the elbow, and the arm is swept out of the vagina.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. The fetus is rotated 180°, and the contralateral arm is delivered in a similar manner as the first. The infant is then rotated 90° to the backup position in preparation for delivery of the head.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. The fetal head is maintained in a flexed position by using the Mauriceau maneuver, which is performed by placing the index and middle fingers over the maxillary prominence on either side of the nose. The fetal body is supported in a neutral position, with care to not overextend the neck.
- Piper forceps application. Piper forceps are specialized forceps used only for the after-coming head of a breech presentation. They are used to keep the fetal head flexed during extraction of the head. An assistant is needed to hold the infant while the operator gets on one knee to apply the forceps from below.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. Low 1-minute Apgar scores are not uncommon after a vaginal breech delivery. A pediatrician should be present for the delivery in the event that neonatal resuscitation is needed.
- Assisted vaginal breech delivery. The neonate after birth.
- Ultrasound demonstrating a fetus in breech presentation with a hyperextended head (ie, "star gazing").

Contributor Information and Disclosures
Richard Fischer, MD Professor, Division Head, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Cooper University Hospital Richard Fischer, MD is a member of the following medical societies: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists , American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine , Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics , Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Disclosure: Stock ownership for: Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (< 5% of portfolio); Johnson & Johnson (< 5% of portfolio).
Alisa B Modena, MD, FACOG Assistant Professor, Cooper Medical School of Rowan University; Attending Physician, Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Cooper University Hospital Alisa B Modena, MD, FACOG is a member of the following medical societies: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists , American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine , Philadelphia Perinatal Society, Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Disclosure: Nothing to disclose.
Francisco Talavera, PharmD, PhD Adjunct Assistant Professor, University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Pharmacy; Editor-in-Chief, Medscape Drug Reference Disclosure: Received salary from Medscape for employment. for: Medscape.
Richard S Legro, MD Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Reproductive Endocrinology, Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine; Consulting Staff, Milton S Hershey Medical Center Richard S Legro, MD is a member of the following medical societies: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists , Society of Reproductive Surgeons , American Society for Reproductive Medicine , Endocrine Society , Phi Beta Kappa Disclosure: Received honoraria from Korea National Institute of Health and National Institute of Health (Bethesda, MD) for speaking and teaching; Received honoraria from Greater Toronto Area Reproductive Medicine Society (Toronto, ON, CA) for speaking and teaching; Received honoraria from American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists (Washington, DC) for speaking and teaching; Received honoraria from National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology Research Thi.
Ronald M Ramus, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Director, Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine Ronald M Ramus, MD is a member of the following medical societies: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists , American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine , Medical Society of Virginia , Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Disclosure: Nothing to disclose.
What would you like to print?
- Print this section
- Print the entire contents of
- Print the entire contents of article

- HIV in Pregnancy
- Cardiovascular Disease and Pregnancy
- Pulmonary Disease and Pregnancy
- Kidney Disease and Pregnancy
- Multifetal Pregnancy
- Vaccinations/Immunizations During Pregnancy
- Anemia and Thrombocytopenia in Pregnancy
- Is immunotherapy for cancer safe in pregnancy?
- Olympic Moms Are Redefining Exercise in Pregnancy
- Labetalol, Nifedipine: Outcome on Pregnancy Hypertension

- Drug Interaction Checker
- Pill Identifier
- Calculators

- 2020/viewarticle/immunotherapy-cancer-safe-pregnancy-2024a100083dnews news Is immunotherapy for cancer safe in pregnancy?

- 2002261369-overviewDiseases & Conditions Diseases & Conditions Postterm Pregnancy

- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Pregnancy Complications
What Does It Mean to Have a Frank Breech Baby?
Frank breech is the most common type of breech position. Learn what this position means for you and your baby.
- Types of Breech Positions
How To Tell If Your Baby Is Breech
Causes of breech presentations, treatment for breech presentations, complications of a breech birth, what happens if my baby is breech.
If your baby is in a frank breech position, that means that their bottom is facing down towards the birth canal instead of their head. The part of the baby that is nearest to the cervix is called the presenting part. The presenting part, which is the part of the baby's body that is born first in a vaginal delivery , is usually the baby's head (known as vertex presentation).
In a small number of deliveries, however, a baby’s bottom or feet are in a position to be born first. This is called a breech presentation, and frank breech (bottom first, with feet up near the head) is the most common type.
Learn about the types of breech presentation including frank breech, what causes a baby to be breech, how it's treated, and what to expect with a breech delivery.
Jamie Grill / Getty Images
Frank Breech and Other Types of Breech Positions
Babies can be in all sorts of positions during pregnancy, but most babies eventually turn head down in late pregnancy. As pregnancy progresses, the more likely it is that the baby will turn and the head will be down near the cervix when it's time for delivery.
Breech Presentation Statistics
- Before the 28th week of pregnancy, about 20% to 25% of babies are breech.
- By the 34th week of pregnancy, most babies will turn and approximately 5% to 7% will be breech.
- By full term, only 3% to 4% of babies (3 or 4 out of every 100 births) are breech.
Sometimes, however, babies are in a breech (bottom or leg down) position when labor begins. There are several types of breech positions.
Frank breech
A frank breech position is when the baby’s bottom is down, but their legs are straight up with their feet near their head. The presenting part is the buttocks.
A frank breech is the most common breech presentation, especially when a baby is born at full term. Of the 3% to 4% of term breech births, babies are in the frank breech position 50% to 70% of the time.
Complete breech
In this position, the bottom is down, but the baby's knees are also bent, so the feet are also down near the buttocks. The presenting part is not only the bottom but both feet as well. At delivery, about 10% of breech babies are in a complete breech position.
Incomplete (footling) breech
A footling breech position is when the baby’s legs are extended and facing straight down. Instead of the bottom, the presenting part is one foot (a single footling) or both feet (a double footling). Approximately 25% of breech deliveries are incomplete.
As your pregnancy progresses, your prenatal health care provider will examine you and keep track of your baby’s position . You might even be able to figure out how your baby is positioned on your own.
Here are some of the techniques you and your health care provider can use to tell which way your baby is facing.
- Kicks : You can feel where your baby is kicking you and judge their general position. If you feel kicks in your lower pelvis, then the baby hasn’t turned head down yet. But if the kicks are up toward your ribs and the top of your uterus, then the baby’s head is most likely facing down.
- Palpation : At your prenatal visits, your doctor or midwife will check your baby's position by palpating or feeling your belly to find the baby’s head, back, and bottom.
- Heartbeat : Listening to the baby’s heartbeat is another way to tell where your baby is in the uterus. By finding the heartbeat's location, the doctor or midwife can get a better idea of the baby’s position.
- Ultrasound : An ultrasound provides the best position information. It shows you and your health care team a picture of the baby and their exact position in your uterus. If your baby is breech, the ultrasound can determine the type of breech position your baby is in, such as frank breech or complete breech.
- Pelvic exam : During labor, your health care provider can perform a pelvic examination . They will be able to feel whether the baby’s head or their bottom and feet are in the birth canal.
The size of the baby, amount of amniotic fluid , and amount of space inside the uterus are all factors that can contribute to a baby’s ability to move around.
The most common reason for a breech presentation is prematurity, but other factors could lead to a baby in a breech position:
- Premature delivery : A premature baby is smaller and has more room inside the uterus to move around, which increases the chances that they will be in a breech presentation if you go into preterm labor .
- Multiples : Twins or other multiples have less room in the uterus to move around and get into the head-down position for delivery.
- Uterine issues : Fibroids or a heart-shaped uterus can get in the way of the baby’s ability to turn.
- Shortened umbilical cord : If the umbilical cord is very short, the baby may not be able to move and turn.
- Too much or too little amniotic fluid : Too much amniotic fluid gives the baby the ability to move around freely in the uterus. As they grow, they may still be able to flip and turn rather than turning head down and staying head down. Too little amniotic fluid , on the other hand, may prevent a baby from moving into the head-down position as they get closer to full-term.
- Location of the placenta : When the placenta is low and covers all or part of the cervix, it’s called placenta previa . When the placenta is in this position, it takes up the room at the bottom of the uterus and can make it difficult for the baby to turn head down.
- Congenital abnormalities in the baby : Some congenital abnormalities can affect the baby’s ability to move into the head-down position. These conditions are usually not a surprise at delivery since they are typically seen during prenatal ultrasound examinations .
If your baby is breech, you will face four possible outcomes to your pregnancy:
- Your baby may turn on its own . Especially if it's early in your pregnancy, there is a chance your baby will turn from a breech position to a head-down position. Many prenatal health care providers will take a wait-and-see approach early on.
- Your doctor may attempt to manually turn your baby . If there are no complications in your pregnancy and the baby has not yet turned on its own by the 36th or 37th week, your doctor may attempt to turn the baby using a manual procedure called external cephalic version (ECV). ECV works approximately 60% of the time.
- Your doctor may schedule a C-section . For a baby that remains in a breech position in late pregnancy, most doctors will recommend a surgical birth via a C-section .
- Your doctor may agree to help you attempt a vaginal delivery . The majority of pregnancy care providers will not deliver a breech baby vaginally, but a small percentage of doctors may be willing to work with you having a vaginal delivery with a breech baby.
You can also do some things to encourage your baby to turn head down , such as acupuncture and exercises like pelvic tilts and even walking.
Most babies who are born breech are healthy. But when a baby is frank breech or in any other breech position, there is a higher chance of a complicated labor and delivery. Here are some of the complications associated with breech birth.
Umbilical cord prolapse
During a vaginal breech delivery, there is a chance that the umbilical cord will come down through the cervix before the baby is born. As the baby comes through the birth canal, their body and head can press on the cord and cut off the supply of blood and oxygen that the cord is carrying.
This can affect the baby’s heart rate and the flow of oxygen and blood to the baby’s brain. The danger of a prolapsed cord is greater with a footling breech and a complete breech.
The risk of cord prolapse is less when the baby is in the frank breech position.
Head entrapment
The baby’s head can get stuck during the delivery if the baby’s body is born before the cervix fully dilates. This situation is dangerous since the head can press against the umbilical cord and cause asphyxia or a lack of oxygen.
Head entrapment is more common in premature deliveries because the baby’s head is typically bigger than their body.
Physical injuries to the baby
The risk of injury to the baby during delivery is higher when the baby is breech compared to when the baby is not breech. Preemies are more likely to injure their head and skull. Bruising, broken bones, and dislocated joints can also occur depending on the baby's position during birth.
Additionally, after a baby is born, breech newborns have a higher incidence of neonatal hip instability, also called developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). This complication occurs in between 12% to 24% of breech babies.
Physical injury to the gestational parent
The vaginal delivery of a breech baby can require an episiotomy and the use of forceps, which can cause injury to the birthing person's genital area.
Many babies will turn to the head-down position before labor begins. However, if your baby is still breech when labor begins, you and your doctor will have to decide between having a C-section or trying a vaginal birth.
Whenever possible, the standard choice is to deliver any breech baby who is premature or in distress via cesarean section. Since vaginal deliveries, even when all the above criteria are met, come with a higher risk of a difficult birth and birth injuries, most doctors prefer to deliver all breech presentations by C-section.
However, when there are no other complications, a baby in the frank breech position may be delivered vaginally if the doctor agrees to it and certain conditions are met:
- Emergency resources are available
- The baby is at least 36 weeks
- The baby is not too big or too small
- The baby’s head is in the right position (flexed)
- The health care team has experience with breech deliveries
- The size of your pelvis is large enough
- There is continuous monitoring of the baby
- You have delivered vaginally before
If any complications arise during the delivery, you may still need an emergency C-section .
If Your Baby Is Breech . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists . 2024.
A comparison of risk factors for breech presentation in preterm and term labor: A nationwide, population-based case-control study . Arch Gynecol Obstet . 2020.
Breech presentation: Vaginal versus cesarean delivery, which intervention leads to the best outcomes? . Acta Med Port. 2017.
Breech presentation . Medscape . 2022.
Breech presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Information and management . Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2020.
Mode of Term Singleton Breech Delivery . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists . 2023.
Umbilical Cord Prolapse . StatPearls . 2023.
Incidence of acetabular dysplasia in breech infants following initially normal ultrasound: the effect of variable diagnostic criteria . J Child Orthop . 2017.
Related Articles
- AI Generator
breech birth
31 breech presentation stock photos & high-res pictures.
Browse 31 breech presentation photos and images available, or search for breech birth to find more great photos and pictures.

- AI Generator
31 Breech Presentation Stock Photos and High-res Pictures
Browse 31 breech presentation photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more photos and images.

Breech presentation
Highlights & basics.
- Diagnostic Approach
- Risk Factors
History & Exam
- Differential Diagnosis
- Tx Approach
- Emerging Tx
- Complications
PATIENT RESOURCES
- Patient Instructions
Breech presentation refers to the baby presenting for delivery with the buttocks or feet first rather than head.
Associated with increased morbidity and mortality for the mother in terms of emergency cesarean section and placenta previa; and for the baby in terms of preterm birth, small fetal size, congenital anomalies, and perinatal mortality.
Incidence decreases as pregnancy progresses and by term occurs in 3% to 4% of singleton term pregnancies.
Treatment options include external cephalic version to increase the likelihood of vaginal birth or a planned cesarean section, the optimal gestation being 37 and 39 weeks, respectively.
Planned cesarean section is considered the safest form of delivery for infants with a persisting breech presentation at term.
Quick Reference
Key Factors
Other Factors
Diagnostics Tests
Treatment Options
Epidemiology
Pathophysiology.

Key Articles
Impey LWM, Murphy DJ, Griffiths M, et al; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Management of breech presentation: green-top guideline no. 20b. BJOG. 2017 Jun;124(7):e151-77. [Full Text]
Hofmeyr GJ, Hannah M, Lawrie TA. Planned caesarean section for term breech delivery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 21;(7):CD000166. [Abstract] [Full Text]
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. External cephalic version and reducing the incidence of term breech presentation. Mar 2017 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
Cluver C, Gyte GM, Sinclair M, et al. Interventions for helping to turn term breech babies to head first presentation when using external cephalic version. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 9;(2):CD000184. [Abstract] [Full Text]
de Hundt M, Velzel J, de Groot CJ, et al. Mode of delivery after successful external cephalic version: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123(6):1327-34. [Abstract]
Referenced Articles
1. Cunningham F, Gant N, Leveno K, et al. Williams obstetrics. 21st ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1997.
2. Kish K, Collea JV. Malpresentation and cord prolapse. In: DeCherney AH, Nathan L, eds. Current obstetric and gynecologic diagnosis and treatment. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional; 2002.
3. Scheer K, Nubar J. Variation of fetal presentation with gestational age. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 May 15;125(2):269-70. [Abstract]
4. Nassar N, Roberts CL, Cameron CA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical examination for detection of non-cephalic presentation in late pregnancy: cross sectional analytic study. BMJ. 2006 Sep 16;333(7568):578-80. [Abstract] [Full Text]
5. Roberts CL, Peat B, Algert CS, et al. Term breech birth in New South Wales, 1990-1997. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2000 Feb;40(1):23-9. [Abstract]
6. Roberts CL, Algert CS, Peat B, et al. Small fetal size: a risk factor for breech birth at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1999 Oct;67(1):1-8. [Abstract]
7. Brar HS, Platt LD, DeVore GR, et al. Fetal umbilical velocimetry for the surveillance of pregnancies complicated by placenta previa. J Reprod Med. 1988 Sep;33(9):741-4. [Abstract]
8. Kian L. The role of the placental site in the aetiology of breech presentation. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1963 Oct;70:795-7. [Abstract]
9. Rayl J, Gibson PJ, Hickok DE. A population-based case-control study of risk factors for breech presentation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Jan;174(1 Pt 1):28-32. [Abstract]
10. Westgren M, Edvall H, Nordstrom L, et al. Spontaneous cephalic version of breech presentation in the last trimester. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Jan;92(1):19-22. [Abstract]
11. Brenner WE, Bruce RD, Hendricks CH. The characteristics and perils of breech presentation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Mar 1;118(5):700-12. [Abstract]
12. Hall JE, Kohl S. Breech presentation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1956 Nov;72(5):977-90. [Abstract]
13. Morgan HS, Kane SH. An analysis of 16,327 breech births. JAMA. 1964 Jan 25;187:262-4. [Abstract]
14. Luterkort M, Persson P, Weldner B. Maternal and fetal factors in breech presentation. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Jul;64(1):55-9. [Abstract]
15. Braun FH, Jones KL, Smith DW. Breech presentation as an indicator of fetal abnormality. J Pediatr. 1975 Mar;86(3):419-21. [Abstract]
16. Albrechtsen S, Rasmussen S, Dalaker K, et al. Reproductive career after breech presentation: subsequent pregnancy rates, interpregnancy interval, and recurrence. Obstet Gynecol. 1998 Sep;92(3):345-50. [Abstract]
17. Zlopasa G, Skrablin S, Kalafatić D, et al. Uterine anomalies and pregnancy outcome following resectoscope metroplasty. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2007 Aug;98(2):129-33. [Abstract]
18. Acién P. Breech presentation in Spain, 1992: a collaborative study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1995 Sep;62(1):19-24. [Abstract]
19. Michalas SP. Outcome of pregnancy in women with uterine malformation: evaluation of 62 cases. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1991 Jul;35(3):215-9. [Abstract]
20. Fianu S, Vaclavinkova V. The site of placental attachment as a factor in the aetiology of breech presentation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1978;57(4):371-2. [Abstract]
21. Haruyama Y. Placental implantation as the cause of breech presentation [in Japanese]. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1987 Jan;39(1):92-8. [Abstract]
22. Filipov E, Borisov I, Kolarov G. Placental location and its influence on the position of the fetus in the uterus [in Bulgarian]. Akush Ginekol (Sofiia). 2000;40(4):11-2. [Abstract]
23. Waterstone M, Bewley S, Wolfe C. Incidence and predictors of severe obstetric morbidity: case-control study. BMJ. 2001 May 5;322(7294):1089-93. [Abstract] [Full Text]
24. Beischer NA, Mackay EV, Colditz P, eds. Obstetrics and the newborn: an illustrated textbook. 3rd ed. London: W.B. Saunders; 1997.
25. Impey LWM, Murphy DJ, Griffiths M, et al; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Management of breech presentation: green-top guideline no. 20b. BJOG. 2017 Jun;124(7):e151-77. [Full Text]
26. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Antepartum haemorrhage: green-top guideline no. 63. November 2011 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
27. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 175: ultrasound in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Dec;128(6):e241-56. [Abstract]
28. Enkin M, Keirse MJNC, Neilson J, et al. Guide to effective care in pregnancy and childbirth. 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2000.
29. Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;(10):CD000083. [Abstract] [Full Text]
30. Hofmeyr GJ, Hannah M, Lawrie TA. Planned caesarean section for term breech delivery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 21;(7):CD000166. [Abstract] [Full Text]
31. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. External cephalic version and reducing the incidence of term breech presentation. Mar 2017 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
32. Rosman AN, Guijt A, Vlemmix F, et al. Contraindications for external cephalic version in breech position at term: a systematic review. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013 Feb;92(2):137-42. [Abstract]
33. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 221: external cephalic version. May 2020 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
34. Bogner G, Xu F, Simbrunner C, et al. Single-institute experience, management, success rate, and outcome after external cephalic version at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2012 Feb;116(2):134-7. [Abstract]
35. Hofmeyr GJ. Effect of external cephalic version in late pregnancy on breech presentation and caesarean section rate: a controlled trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1983 May;90(5):392-9. [Abstract]
36. Beuckens A, Rijnders M, Verburgt-Doeleman GH, et al. An observational study of the success and complications of 2546 external cephalic versions in low-risk pregnant women performed by trained midwives. BJOG. 2016 Feb;123(3):415-23. [Abstract]
37. Nassar N, Roberts CL, Barratt A, et al. Systematic review of adverse outcomes of external cephalic version and persisting breech presentation at term. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2006 Mar;20(2):163-71. [Abstract]
38. Sela HY, Fiegenberg T, Ben-Meir A, et al. Safety and efficacy of external cephalic version for women with a previous cesarean delivery. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009 Feb;142(2):111-4. [Abstract]
39. Pichon M, Guittier MJ, Irion O, et al. External cephalic version in case of persisting breech presentation at term: motivations and women's experience of the intervention [in French]. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2013 Jul-Aug;41(7-8):427-32. [Abstract]
40. Nassar N, Roberts CL, Raynes-Greenow CH, et al. Evaluation of a decision aid for women with breech presentation at term: a randomised controlled trial [ISRCTN14570598]. BJOG. 2007 Mar;114(3):325-33. [Abstract] [Full Text]
41. Cluver C, Gyte GM, Sinclair M, et al. Interventions for helping to turn term breech babies to head first presentation when using external cephalic version. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 9;(2):CD000184. [Abstract] [Full Text]
42. US Food & Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: new warnings against use of terbutaline to treat preterm labor. Feb 2011 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
43. European Medicines Agency. Restrictions on use of short-acting beta-agonists in obstetric indications - CMDh endorses PRAC recommendations. October 2013 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
44. Magro-Malosso ER, Saccone G, Di Tommaso M, et al. Neuraxial analgesia to increase the success rate of external cephalic version: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep;215(3):276-86. [Abstract]
45. de Hundt M, Velzel J, de Groot CJ, et al. Mode of delivery after successful external cephalic version: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123(6):1327-34. [Abstract]
46. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion no. 745: mode of term singleton breech delivery. Aug 2018 (reaffirmed 2023) [internet publication]. [Full Text]
47. Berhan Y, Haileamlak A. The risks of planned vaginal breech delivery versus planned caesarean section for term breech birth: a meta-analysis including observational studies. BJOG. 2016 Jan;123(1):49-57. [Abstract] [Full Text]
48. Lydon-Rochelle M, Holt VL, Martin DP, et al. Association between method of delivery and maternal rehospitalisation. JAMA. 2000 May 10;283(18):2411-6. [Abstract]
49. Yokoe DS, Christiansen CL, Johnson R, et al. Epidemiology of and surveillance for postpartum infections. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001 Sep-Oct;7(5):837-41. [Abstract]
50. van Ham MA, van Dongen PW, Mulder J. Maternal consequences of caesarean section. A retrospective study of intra-operative and postoperative maternal complications of caesarean section during a 10-year period. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1997 Jul;74(1):1-6. [Abstract]
51. Murphy DJ, Liebling RE, Verity L, et al. Early maternal and neonatal morbidity associated with operative delivery in second stage of labour: a cohort study. Lancet. 2001 Oct 13;358(9289):1203-7. [Abstract]
52. Lydon-Rochelle MT, Holt VL, Martin DP. Delivery method and self-reported postpartum general health status among primiparous women. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2001 Jul;15(3):232-40. [Abstract]
53. Wilson PD, Herbison RM, Herbison GP. Obstetric practice and the prevalence of urinary incontinence three months after delivery. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1996 Feb;103(2):154-61. [Abstract]
54. Persson J, Wolner-Hanssen P, Rydhstroem H. Obstetric risk factors for stress urinary incontinence: a population-based study. Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Sep;96(3):440-5. [Abstract]
55. MacLennan AH, Taylor AW, Wilson DH, et al. The prevalence of pelvic disorders and their relationship to gender, age, parity and mode of delivery. BJOG. 2000 Dec;107(12):1460-70. [Abstract]
56. Thompson JF, Roberts CL, Currie M, et al. Prevalence and persistence of health problems after childbirth: associations with parity and method of birth. Birth. 2002 Jun;29(2):83-94. [Abstract]
57. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Australia's mothers and babies 2015 - in brief. October 2017 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
58. Mutryn CS. Psychosocial impact of cesarean section on the family: a literature review. Soc Sci Med. 1993 Nov;37(10):1271-81. [Abstract]
59. DiMatteo MR, Morton SC, Lepper HS, et al. Cesarean childbirth and psychosocial outcomes: a meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 1996 Jul;15(4):303-14. [Abstract]
60. Greene R, Gardeit F, Turner MJ. Long-term implications of cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997 Jan;176(1 Pt 1):254-5. [Abstract]
61. Coughlan C, Kearney R, Turner MJ. What are the implications for the next delivery in primigravidae who have an elective caesarean section for breech presentation? BJOG. 2002 Jun;109(6):624-6. [Abstract]
62. Hemminki E, Merilainen J. Long-term effects of cesarean sections: ectopic pregnancies and placental problems. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996 May;174(5):1569-74. [Abstract]
63. Gilliam M, Rosenberg D, Davis F. The likelihood of placenta previa with greater number of cesarean deliveries and higher parity. Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Jun;99(6):976-80. [Abstract]
64. Morrison JJ, Rennie JM, Milton PJ. Neonatal respiratory morbidity and mode of delivery at term: influence of timing of elective caesarean section. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1995 Feb;102(2):101-6. [Abstract]
65. Annibale DJ, Hulsey TC, Wagner CL, et al. Comparative neonatal morbidity of abdominal and vaginal deliveries after uncomplicated pregnancies. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1995 Aug;149(8):862-7. [Abstract]
66. Hook B, Kiwi R, Amini SB, et al. Neonatal morbidity after elective repeat cesarean section and trial of labor. Pediatrics. 1997 Sep;100(3 Pt 1):348-53. [Abstract]
67. Stock SJ, Thomson AJ, Papworth S, et al. Antenatal corticosteroids to reduce neonatal morbidity and mortality: Green-top Guideline No. 74. BJOG. 2022 Jul;129(8):e35-60. [Abstract] [Full Text]
68. American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Committee opinion no. 713: antenatal corticosteroid therapy for fetal maturation. Aug 2017 (reaffirmed 2024) [internet publication]. [Full Text]
69. Nassar N, Roberts CL, Cameron CA, et al. Outcomes of external cephalic version and breech presentation at term: an audit of deliveries at a Sydney tertiary obstetric hospital, 1997-2004. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2006;85(10):1231-8. [Abstract]
70. Nwosu EC, Walkinshaw S, Chia P, et al. Undiagnosed breech. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1993 Jun;100(6):531-5. [Abstract]
71. Flamm BL, Ruffini RM. Undetected breech presentation: impact on external version and cesarean rates. Am J Perinatol. 1998 May;15(5):287-9. [Abstract]
72. Cockburn J, Foong C, Cockburn P. Undiagnosed breech. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994 Jul;101(7):648-9. [Abstract]
73. Leung WC, Pun TC, Wong WM. Undiagnosed breech revisited. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999 Jul;106(7):638-41. [Abstract]
74. Wilcox C, Nassar N, Roberts C. Effectiveness of nifedipine tocolysis to facilitate external cephalic version: a systematic review. BJOG. 2011 Mar;118(4):423-8. [Abstract]
75. Qureshi H, Massey E, Kirwan D, et al. BCSH guideline for the use of anti-D immunoglobulin for the prevention of haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Transfus Med. 2014 Feb;24(1):8-20. [Abstract] [Full Text]
76. Hutton EK, Hofmeyr GJ, Dowswell T. External cephalic version for breech presentation before term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 29;(7):CD000084. [Abstract] [Full Text]
77. Coyle ME, Smith CA, Peat B. Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD003928. [Abstract] [Full Text]
78. Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R. Cephalic version by postural management for breech presentation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;(10):CD000051. [Abstract] [Full Text]
79. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Caesarean birth. Jan 2024 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
80. Hannah ME, Whyte H, Hannah WJ, et al. Maternal outcomes at 2 years after planned cesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: the International Randomized Term Breech Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Sep;191(3):917-27. [Abstract]
81. Eide MG, Oyen N, Skjaerven R, et al. Breech delivery and Intelligence: a population-based study of 8,738 breech infants. Obstet Gynecol. 2005 Jan;105(1):4-11. [Abstract]
82. Whyte H, Hannah ME, Saigal S, et al. Outcomes of children at 2 years after planned cesarean birth versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: the International Randomized Term Breech Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Sep;191(3):864-71. [Abstract]
83. Brown S, Lumley J. Maternal health after childbirth: results of an Australian population based survey. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998 Feb;105(2):156-61. [Abstract]
Sign in to access our clinical decision support tools
- Getting Results.
- Newsletters
WEATHER ALERT
4 advisories in effect for Flagler, Coastal, Inland and Volusia, Coastal, Inland Regions
Billions of personal records stolen in florida data breach. were you a victim, gang claims to have stolen personal data of up to 2.9 billion people.
Robert Breuer , Editor
Anthony Talcott , Digital Journalist
ORLANDO, Fla. – “I found out that I have been a victim of the National Public Data Breach.”
That is not the kind of quote we usually expert to hear from a cybersecurity expert, but that is exactly what Chief Product Officer Rob Allen at ThreatLocker , a cybersecurity firm based in Orlando, told News 6 on Thursday.
That conversation was in reference to reports that billions of personal records were stolen from National Public Data (NPD), a background-check company headquartered in Coral Springs.
According to a class-action lawsuit filed in South Florida on Aug. 1, NPD was believed to have been hacked in April, with potentially billions of individual records being stolen by a criminal gang using the handle “USDoD.”
In that lawsuit — filed by Christopher Hofmann of California — Hofmann says he received an alert from his identity-theft protection service back in July. He was told that his personal information and social security numbers (SSN) had been found on the Dark Web as a result of the NPD breach.
[EXCLUSIVE: Become a News 6 Insider (it’s FREE) | PINIT! Share your photos ]
The lawsuit shows that USDoD claimed to have taken the personal information of up to 2.9 billion people, and the gang offered the database online at a price of $3.5 million back in April.
But according to the tech news site BleepingComputer , others have already released different copies of the stolen data. One hacker by the name of “Fenice” has leaked the most complete version of the data for free on an online forum, the website reports.
“It is important to note that a person will have multiple records, one for each address they are known to have lived,” BleepingComputer wrote. “This also means that this data breach did not impact 3 billion people as has been erroneously reported in many articles that did not properly research the data.”
Meanwhile, Allen received an email from “ Have I Been Pwned.com ,” confirming that he was one of at least 133 million individuals involved in the breach.
“Generally speaking, it’s not people’s fault. It’s not your fault. Your information has got out there,” Allen said. “But it’s out there, so act accordingly. Be vigilant, be careful. Don’t trust somebody when they ring you or email you or text you with whatever it happens to be. Always verify.”
The scope of the breach has not been confirmed, but on Tuesday, NPD published a breach disclosure to its website, acknowledging that the personal records — including names, email addresses, phone numbers, SSNs and mailing addresses — may have been accessed.
The class-action law firm Schubert, Jonckheer & Kolbe LLP announced earlier this week that the stolen information reportedly includes over 277 gigabytes of data spanning back at least three decades.
“Because individuals did not affirmatively provide their private information to NPD, individuals may not even know that they have been affected,” the law firm wrote. “To date, NPD has not confirmed the breach or what information may have been stolen.”
Additionally, the law firm warns that anyone whose private information was impacted by the breach could be at risk of identity theft, financial fraud or other privacy violations.
To check whether your email address has been impacted by a data breach, click here .
The full class-action lawsuit has been attached to this story and can be read below.
Hofmann v Jerico Pictures (Complaint) by Anthony Talcott on Scribd
Get today’s headlines in minutes with Your Florida Daily :
Copyright 2024 by WKMG ClickOrlando - All rights reserved.
About the Authors
Anthony talcott.
Anthony, a graduate of the University of Florida, joined ClickOrlando.com in April 2022.
RELATED STORIES
News 6 rides with daytona beach police amid search for drug traffickers, ‘i am not going to testify:’ susan lorincz, accused in shooting death of florida neighbor, won’t take stand, ‘professional burglars:’ suspects in $1.7m theft ring came to us illegally, florida sheriff says.
Recommended Videos

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Learn more about the types, causes, and risks of breech presentation, along with how breech babies are typically delivered. By Elizabeth Stein, CNM and Laura Riley, M.D.
Breech Births. In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby's buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
Frank breech. When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head.
At full term, around 3%-4% of births are breech. The different types of breech presentations include: Complete: The fetus's knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first. Frank: The fetus's legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first. Footling: The fetus's foot is showing first.
Breech presentation refers to the baby presenting for delivery with the buttocks or feet first rather than head. Associated with increased morbidity and mortality for the mother in terms of emergency cesarean section and placenta previa; and for the baby in terms of preterm birth, small fetal size, congenital anomalies, and perinatal mortality.
Breech presentation is a type of malpresentation and occurs when the fetal head lies over the uterine fundus and fetal buttocks or feet present over the maternal pelvis (instead of cephalic/head presentation). The incidence in the United Kingdom of breech presentation is 3-4% of all fetuses. 1.
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the ...
Browse Getty Images' premium collection of high-quality, authentic Breech Presentation stock photos, royalty-free images, and pictures. Breech Presentation stock photos are available in a variety of sizes and formats to fit your needs.
This pamphlet explains what a breech presentation is, the different types of breech presentation, discusses ECV and provides balanced information related to birth mode options along with visual representations of statistics comparing the perinatal mortality rate between cephalic vaginal birth, VBB and C/S. This pamphlet was also developed in ...
Overview. Breech presentation is defined as a fetus in a longitudinal lie with the buttocks or feet closest to the cervix. This occurs in 3-4% of all deliveries. The percentage of breech deliveries decreases with advancing gestational age from 22-25% of births prior to 28 weeks' gestation to 7-15% of births at 32 weeks' gestation to 3-4% of ...
A study noted that 11.7% of infants born breech had at least one congenital anomaly. In comparison, only 5.1% of babies born with vertex presentation had any congenital anomaly . This occurred regardless of the term of pregnancy. The study established that breech presentation at birth may indicate congenital anomalies.
A frank breech is the most common breech presentation, especially when a baby is born at full term. Of the 3% to 4% of term breech births, babies are in the frank breech position 50% to 70% of the ...
What Causes Breech Presentation? - Only about 15% of breech presentations have an identifiable etiology.5 - Established risks for breech presentation are: Previous breech presentation pregnancy,5,6,7,8 Late or lack of antenatal care,8,9 Prematurity (<37 weeks gestation),6,7,8 Comparatively lower birth weight,8,9 and Congenital anomalies.8,9,10
Doula and birth photographer Jennifer Wakefield caught this amazing photos series of twins being born; one born breech and the other transverse! On her blog, My Doula Heart, Jennifer explained that this mom had her vaginal breech birth in the hospital. "That's a phrase one rarely hears," she wrote. 5/16. My Doula Heart.
Breech presentation ; descent of breech. (Faraboeuf and Varnier.) The course of labor in breech presentations consists, first, in the descentof the breech and its passage through the pelvis. The posterior hip, 220 PREGNANCY AND LABOR. usually the right, comes first into the pelvic cavity, the body of the chil.
Browse 38 authentic breech birth stock photos, ... fetal breech presentation - breech birth stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images. Fetal breech presentation. Breech birth, Before childbirth, it sometimes happens that the fetus is in a position with its buttocks towards the cervix. This is the breech...
Browse 31 breech presentation photos and images available, or search for breech birth to find more great photos and pictures. fetal breech presentation - breech presentation stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images.
FOOTLING BREECH: One or both legs are raised at the hip so that the foot is the presenting part. CLINICAL FEATURES Breech presentation is usually identified on clinical examination.
Complete breech presentation is the next most favorable position, but these babies sometimes shift and become footling breeches during labour. Footling and kneeling breeches have a higher risk of cord prolapse and head entrapment. [28] Parity - Parity refers to the number of times a woman has given birth before. If a woman has given birth ...
Breech Presentation. Breech presentation occurs in 3-4% of all deliveries. The occurrence of breech presentation decreases with advancing gestational age. Breech presentation occurs in 25% of births that occur before 28 weeks?gestation, in 7% of births that occur at 32 weeks, and 1-3% of births that occur at term.
X-ray of normal human foetus in breech presentation in womb. of 1. Browse Getty Images' premium collection of high-quality, authentic Breech Presentation stock photos, royalty-free images, and pictures. Breech Presentation stock photos are available in a variety of sizes and formats to fit your needs.
Key Highlights. Breech presentation refers to the baby presenting for delivery with the buttocks or feet first rather than head. Associated with increased morbidity and mortality for the mother in terms of emergency cesarean section and placenta previa; and for the baby in terms of preterm birth, small fetal size, congenital anomalies, and ...
Share your photos] The lawsuit shows that USDoD claimed to have taken the personal information of up to 2.9 billion people, and the gang offered the database online at a price of $3.5 million back ...