REVIEW article
The state of music therapy studies in the past 20 years: a bibliometric analysis.

- 1 School of Kinesiology, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai, China
- 2 Department of Sport Rehabilitation, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai, China
- 3 Department of Sport Rehabilitation Medicine, Shanghai Shangti Orthopedic Hospital, Shanghai, China
Purpose: Music therapy is increasingly being used to address physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs of individuals. However, publications on the global trends of music therapy using bibliometric analysis are rare. The study aimed to use the CiteSpace software to provide global scientific research about music therapy from 2000 to 2019.
Methods: Publications between 2000 and 2019 related to music therapy were searched from the Web of Science (WoS) database. The CiteSpace V software was used to perform co-citation analysis about authors, and visualize the collaborations between countries or regions into a network map. Linear regression was applied to analyze the overall publication trend.
Results: In this study, a total of 1,004 studies met the inclusion criteria. These works were written by 2,531 authors from 1,219 institutions. The results revealed that music therapy publications had significant growth over time because the linear regression results revealed that the percentages had a notable increase from 2000 to 2019 ( t = 14.621, P < 0.001). The United States had the largest number of published studies (362 publications), along with the following outputs: citations on WoS (5,752), citations per study (15.89), and a high H-index value (37). The three keywords “efficacy,” “health,” and “older adults,” emphasized the research trends in terms of the strongest citation bursts.
Conclusions: The overall trend in music therapy is positive. The findings provide useful information for music therapy researchers to identify new directions related to collaborators, popular issues, and research frontiers. The development prospects of music therapy could be expected, and future scholars could pay attention to the clinical significance of music therapy to improve the quality of life of people.

Introduction
Music therapy is defined as the evidence-based use of music interventions to achieve the goals of clients with the help of music therapists who have completed a music therapy program ( Association, 2018 ). In the United States, music therapists must complete 1,200 h of clinical training and pass the certification exam by the Certification Board for Music Therapists ( Devlin et al., 2019 ). Music therapists use evidence-based music interventions to address the mental, physical, or emotional needs of an individual ( Gooding and Langston, 2019 ). Also, music therapy is used as a solo standard treatment, as well as co-treatment with other disciplines, to address the needs in cognition, language, social integration, and psychological health and family support of an individual ( Bronson et al., 2018 ). Additionally, music therapy has been used to improve various diseases in different research areas, such as rehabilitation, public health, clinical care, and psychology ( Devlin et al., 2019 ). With neurorehabilitation, music therapy has been applied to increase motor activities in people with Parkinson's disease and other movement disorders ( Bernatzky et al., 2004 ; Devlin et al., 2019 ). However, limited reviews about music therapy have utilized universal data and conducted massive retrospective studies using bibliometric techniques. Thus, this study demonstrates music therapy with a broad view and an in-depth analysis of the knowledge structure using bibliometric analysis of articles and publications.
Bibliometrics turns the major quantitative analytical tool that is used in conducting in-depth analyses of publications ( Durieux and Gevenois, 2010 ; Gonzalez-Serrano et al., 2020 ). There are three types of bibliometric indices: (a) the quantity index is used to determine the number of relevant publications, (b) the quality index is employed to explore the characteristics of a scientific topic in terms of citations, and (c) the structural index is used to show the relationships among publications ( Durieux and Gevenois, 2010 ; Gonzalez-Serrano et al., 2020 ). In this study, the three types of bibliometric indices will be applied to conduct an in-depth analysis of publications in this frontier.
While research about music therapy is extensively available worldwide, relatively limited studies use bibliometric methods to analyze the global research about this topic. The aim of this study is to use the CiteSpace software to perform a bibliometric analysis of music therapy research from 2000 to 2019. CiteSpace V is visual analytic software, which is often utilized to perform bibliometric analyses ( Falagas et al., 2008 ; Ellegaard and Wallin, 2015 ). It is also a tool applied to detect trends in global scientific research. In this study, the global music therapy research includes publication outputs, distribution and collaborations between authors/countries or regions/institutions, intense issues, hot articles, common keywords, productive authors, and connections among such authors in the field. This study also provides helpful information for researchers in their endeavor to identify gaps in the existing literature.
Materials and Methods
Search strategy.
The data used in this study were obtained from WoS, the most trusted international citation database in the world. This database, which is run by Thomson & Reuters Corporation ( Falagas et al., 2008 ; Durieux and Gevenois, 2010 ; Chen C. et al., 2012 ; Ellegaard and Wallin, 2015 ; Miao et al., 2017 ; Gonzalez-Serrano et al., 2020 ), provides high-quality journals and detailed information about publications worldwide. In this study, publications were searched from the WoS Core Collection database, which included eight indices ( Gonzalez-Serrano et al., 2020 ). This study searched the publications from two indices, namely, the Science Citation Index Expanded and the Social Sciences Citation Index. As the most updated publications about music therapy were published in the 21st century, publications from 2000 to 2019 were chosen for this study. We performed data acquisition on July 26, 2020 using the following search terms: title = (“music therapy”) and time span = 2000–2019.
Inclusion Criteria
Figure 1 presents the inclusion criteria. The title field was music therapy (TI = music therapy), and only reviews and articles were chosen as document types in the advanced search. Other document types, such as letters, editorial materials, and book reviews, were excluded. Furthermore, there were no species limitations set. This advanced search process returned 718 articles. In the end, a total of 1,004 publications were obtained and were analyzed to obtain comprehensive perspectives on the data.
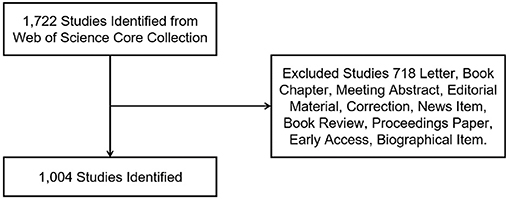
Figure 1 . Flow chart of music therapy articles and reviews inclusion.
Data Extraction
Author Lin-Man Weng extracted the publications and applied the EndNote software and Microsoft Excel 2016 to conduct analysis on the downloaded publications from the WoS database. Additionally, we extracted and recorded some information of the publications, such as citation frequency, institutions, authors' countries or regions, and journals as bibliometric indicators. The H-index is utilized as a measurement of the citation frequency of the studies for academic journals or researchers ( Wang et al., 2019 ).
Analysis Methods
The objective of bibliometrics can be described as the performance of studies that contributes to advancing the knowledge domain through inferences and explanations of relevant analyses ( Castanha and Grácio, 2014 ; Merigó et al., 2019 ; Mulet-Forteza et al., 2021 ). CiteSpace V is a bibliometric software that generates information for better visualization of data. In this study, the CiteSpace V software was used to visualize six science maps about music therapy research from 2000 to 2019: the network of author co-citation, collaboration network among countries and regions, relationship of institutions interested in the field, network map of co-citation journals, network map of co-cited references, and the map (timeline view) of references with co-citation on top music therapy research. As noted, a co-citation is produced when two publications receive a citation from the same third study ( Small, 1973 ; Merigó et al., 2019 ).
In addition, a science map typically features a set of points and lines to present collaborations among publications ( Chen, 2006 ). A point is used to represent a country or region, author, institution, journal, reference, or keyword, whereas a line represents connections among them ( Zheng and Wang, 2019 ), with stronger connections indicated by wider lines. Furthermore, the science map includes nodes, which represent the citation frequencies of certain themes. A burst node in the form of a red circle in the center indicates the number of co-occurrence or citation that increases over time. A purple node represents centrality, which indicates the significant knowledge presented by the data ( Chen, 2006 ; Chen H. et al., 2012 ; Zheng and Wang, 2019 ). The science map represents the keywords and references with citation bursts. Occurrence bursts represent the frequency of a theme ( Chen, 2006 ), whereas citation bursts represent the frequency of the reference. The citation bursts of keywords and references explore the trends and indicate whether the relevant authors have gained considerable attention in the field ( Chen, 2006 ). Through this kind of map, scholars can better understand emerging trends and grasp the hot topics by burst detection analysis ( Liang et al., 2017 ; Miao et al., 2017 ).
Publication Outputs and Time Trends
A total of 1,004 articles and reviews related to music therapy research met the criteria. The details of annual publications are presented in Figure 2 . As can be seen, there were <30 annual publications between 2000 and 2006. The number of publications increased steadily between 2007 and 2015. It was 2015, which marked the first time over 80 articles or reviews were published. The significant increase in publications between 2018 and 2019 indicated that a growing number of researchers became interested in this field. Linear regression can be used to analyze the trends in publication outputs. In this study, the linear regression results revealed that the percentages had a notable increase from 2000 to 2019 ( t = 14.621, P < 0.001). Moreover, the P < 0.05, indicating statistical significance. Overall, the publication outputs increased from 2000 to 2019.
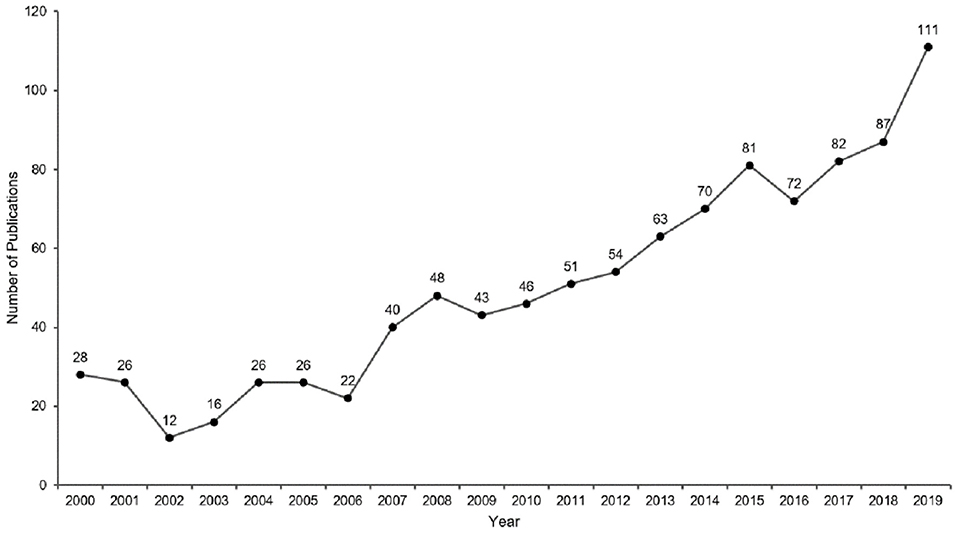
Figure 2 . Annual publication outputs of music therapy from 2000 to 2019.
Distribution by Country or Region and Institution
The 1,004 articles and reviews collected were published in 49 countries and regions. Table 1 presents the top 10 countries or regions. Figure 3 shows an intuitive comparison of the citations on WoS, citations per study, Hirsch index (H-index), and major essential science indicator (ESI) studies of the top five countries or regions. The H-index is a kind of index that is applied in measuring the wide impact of the scientific achievements of authors. The United States had the largest number of published studies (362 publications), along with the following outputs: citations on WoS (5,752), citations per study (15.89), and a high H-index value (37). Norway has the largest number of citations per study (27.18 citations). Figure 4 presents the collaboration networks among countries or regions. The collaboration network map contained 32 nodes and 38 links. The largest node can be found in the United States, which meant that the United States had the largest number of publications in the field. Meanwhile, the deepest purple circle was located in Austria, which meant that Austria is the country with the most number of collaborations with other countries or regions in this research field. A total of 1,219 institutions contributed various music therapy-related publications. Figure 5 presents the collaborations among institutions. As can be seen, the University of Melbourne is the most productive institution in terms of the number of publications (45), followed by the University of Minnesota (43), and the University of Bergen (39). The top 10 institutions featured in Table 2 contributed 28.884% of the total articles and reviews published. Among these, Aalborg University had the largest centrality (0.13). The top 10 productive institutions with details are shown in Table 2 .
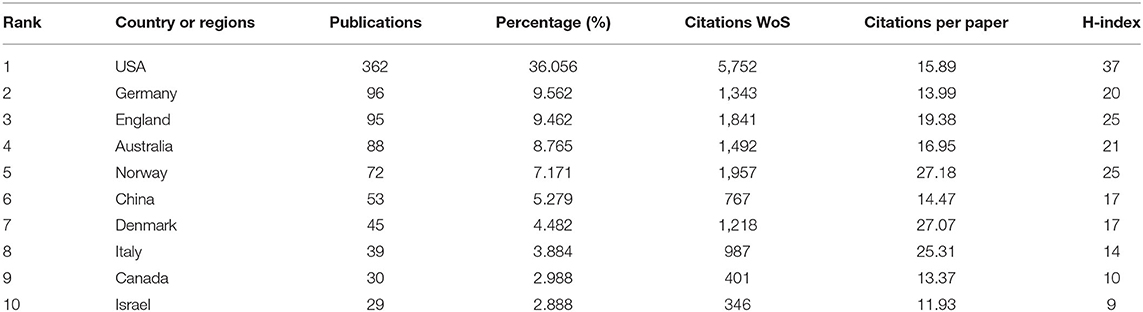
Table 1 . Top 10 countries or regions of origin of study in the music therapy research field.
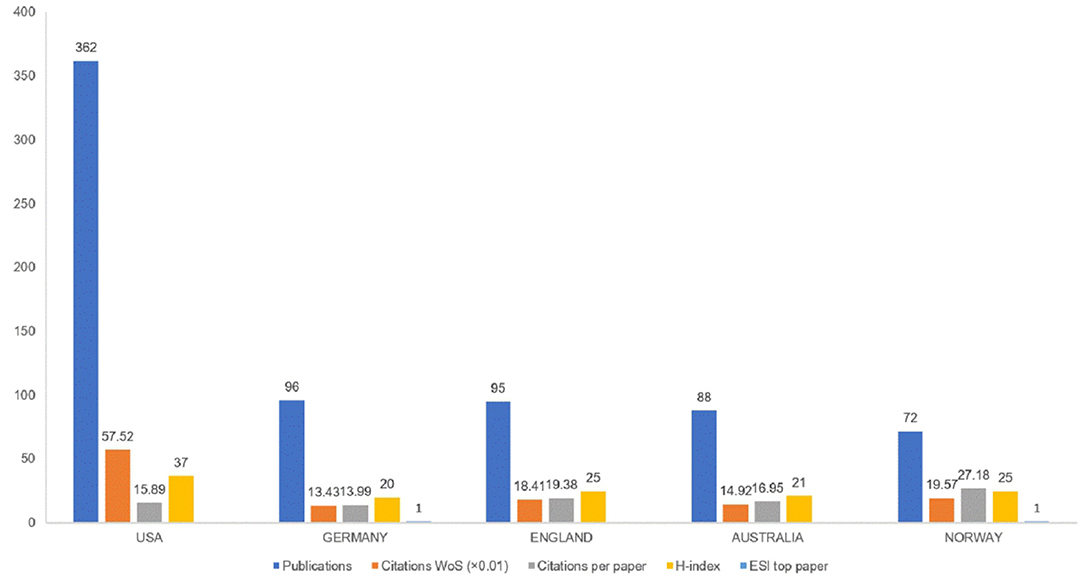
Figure 3 . Publications, citations on WoS (×0.01), citations per study, H-index, and ESL top study among top five countries or regions.
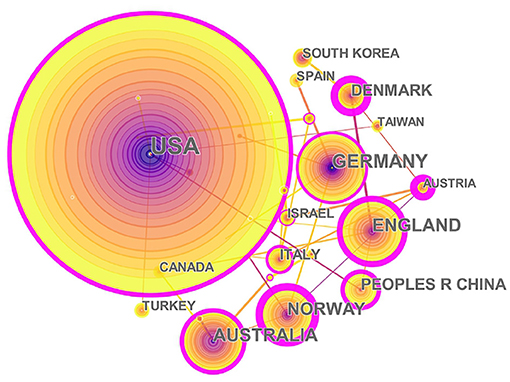
Figure 4 . The collaborations of countries or regions interested in the field. In this map, the node represents a country, and the link represents the cooperation relationship between two countries. A larger node represents more publications in the country. A thicker purple circle represents greater influence in this field.
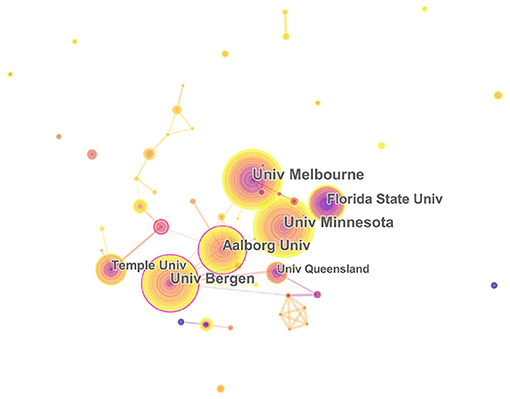
Figure 5 . The relationship of institutions interested in the field. University of Melbourne, Florida State University, University of Minnesota, Aalborg University, Temple University, University of Queensland, and University of Bergen. In this map, the node represents an institution, and the link represents the cooperation relationship between two institutions. A larger node represents more publications in the institution. A thicker purple circle represents greater influence in this field.
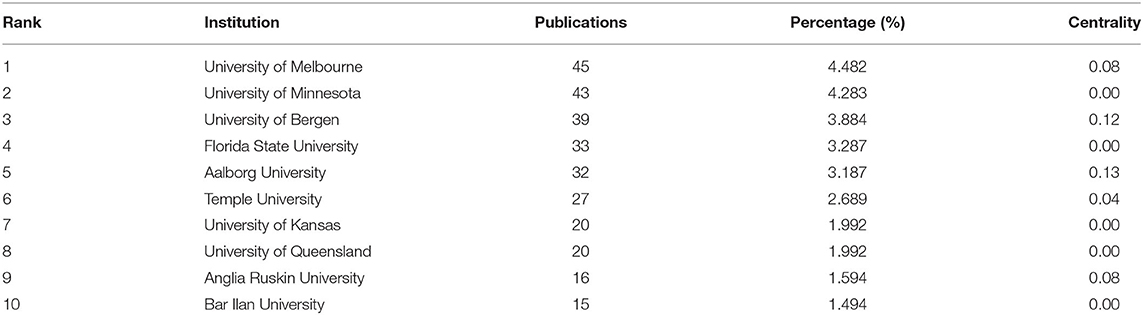
Table 2 . Top 10 institutions that contributed to publications in the music therapy field.
Distribution by Journals
Table 3 presents the top 10 journals that published articles or reviews in the music therapy field. The publications are mostly published in these journal fields, such as Therapy, Medical, Psychology, Neuroscience, Health and Clinical Care. The impact factors (IF) of these journals ranged between 0.913 and 7.89 (average IF: 2.568). Four journals had an impact factor >2, of which Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews had the highest IF, 2019 = 7.89. In addition, the Journal of Music Therapy (IF: 2019 = 1.206) published 177 articles or reviews (17.629%) about music therapy in the past two decades, followed by the Nordic Journal of Music Therapy (121 publications, 12.052%, IF: 2019 = 0.913), and Arts in Psychotherapy (104 publications, 10.359%, IF: 2019 = 1.322). Furthermore, the map of the co-citation journal contained 393 nodes and 759 links ( Figure 6 ). The high co-citation count identifies the journals with the greatest academic influence and key positions in the field. The Journal of Music Therapy had the maximum co-citation counts (658), followed by Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (281), and Arts in Psychotherapy (279). Therefore, according to the analysis of the publications and co-citation counts, the Journal of Music Therapy and Arts in Psychotherapy occupied key positions in this research field.
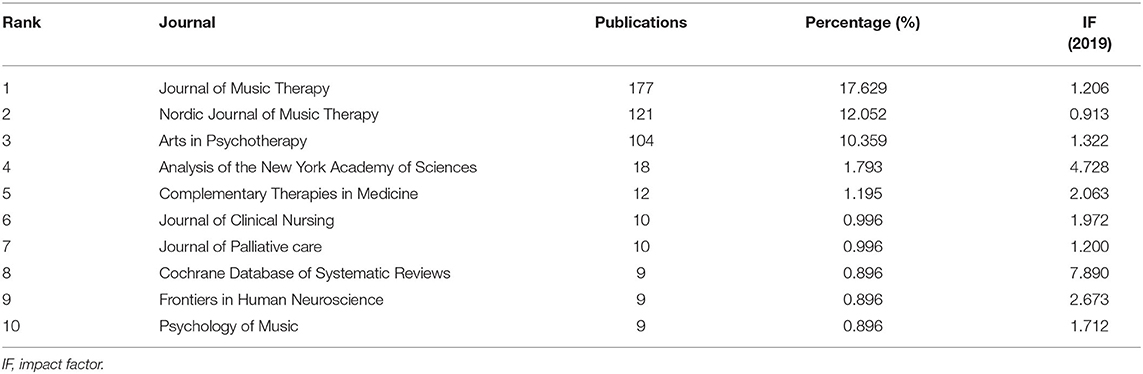
Table 3 . Top 10 journals that published articles in the music therapy field.
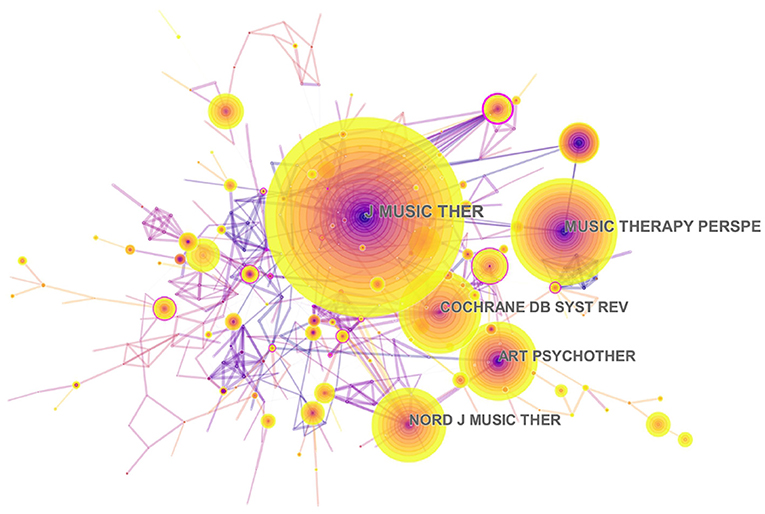
Figure 6 . Network map of co-citation journals engaged in music therapy from 2000 to 2019. Journal of Music Therapy, Arts in Psychotherapy, Nordic Journal of Music Therapy, Music Therapy Perspectives, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. In this map, the node represents a journal, and the link represents the co-citation frequency between two journals. A larger node represents more publications in the journal. A thicker purple circle represents greater influence in this field.
Distribution by Authors
A total of 2,531 authors contributed to the research outputs related to music therapy. Author Silverman MJ published most of the studies (46) in terms of number of publications, followed by Gold C (41), Magee WL (19), O'Callaghan C (15), and Raglio A (15). According to co-citation counts, Bruscia KE (171 citations) was the most co-cited author, followed by Gold C (147 citations), Wigram T (121 citations), and Bradt J (117 citations), as presented in Table 4 . In Figure 7 , these nodes highlight the co-citation networks of the authors. The large-sized node represented author Bruscia KE, indicating that this author owned the most co-citations. Furthermore, the linear regression results revealed a remarkable increase in the percentages of multiple articles of authors ( t = 13.089, P < 0.001). These also indicated that cooperation among authors had increased remarkably, which can be considered an important development in music therapy research.
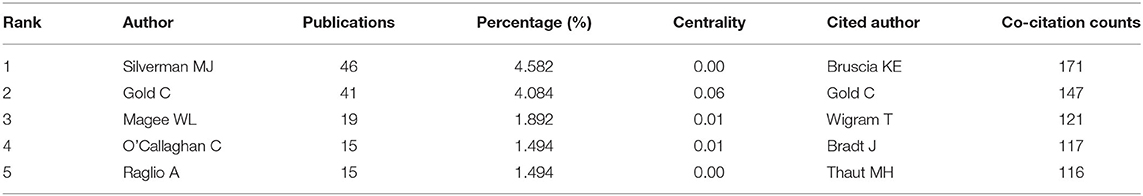
Table 4 . Top five authors of publications and top five authors of co-citation counts.
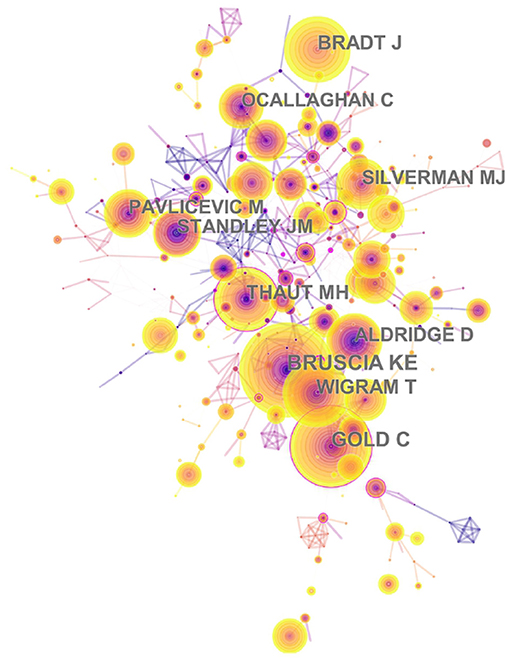
Figure 7 . The network of author co-citaion. In this map, the node represents an author, and the link represents the co-citation frequency between two authors. A larger node represents more publications of the author. A thicker purple circle represents greater influence in this field.
Analysis of Keywords
The results of keywords analysis indicated research hotspots and help scholars identify future research topics. Table 5 highlights 20 keywords with the most frequencies, such as “music therapy,” “anxiety,” “intervention,” “children,” and “depression.” The keyword “autism” has the highest centrality (0.42). Figure 8 shows the top 17 keywords with the strongest citation bursts. By the end of 2019, keyword bursts were led by “hospice,” which had the strongest burst (3.5071), followed by “efficacy” (3.1161), “health” (6.2109), and “older adult” (4.476).
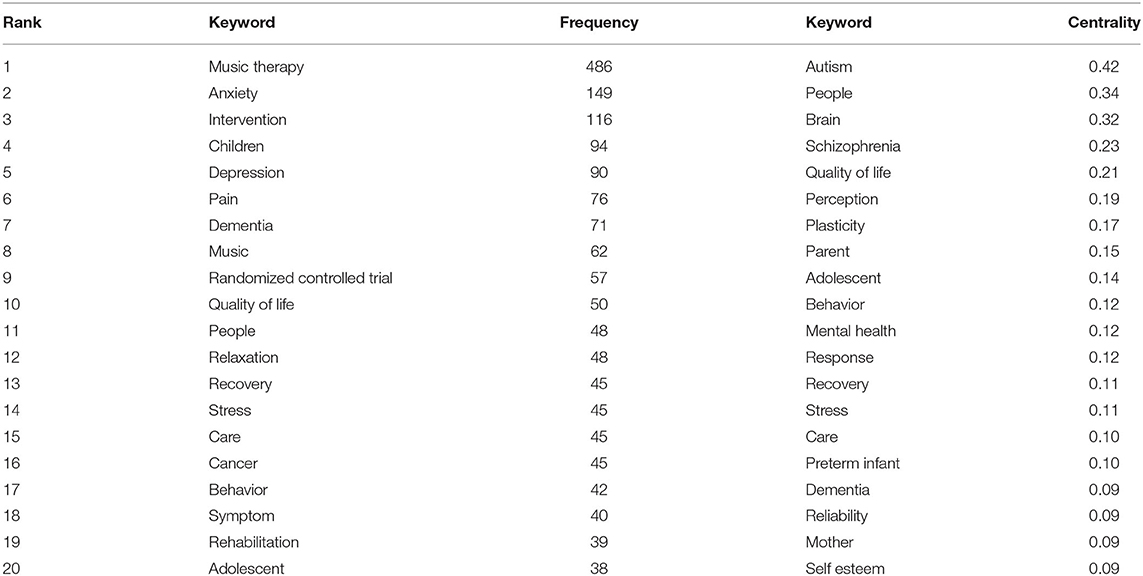
Table 5 . Top 20 keywords with the most frequency and centrality in music therapy study.
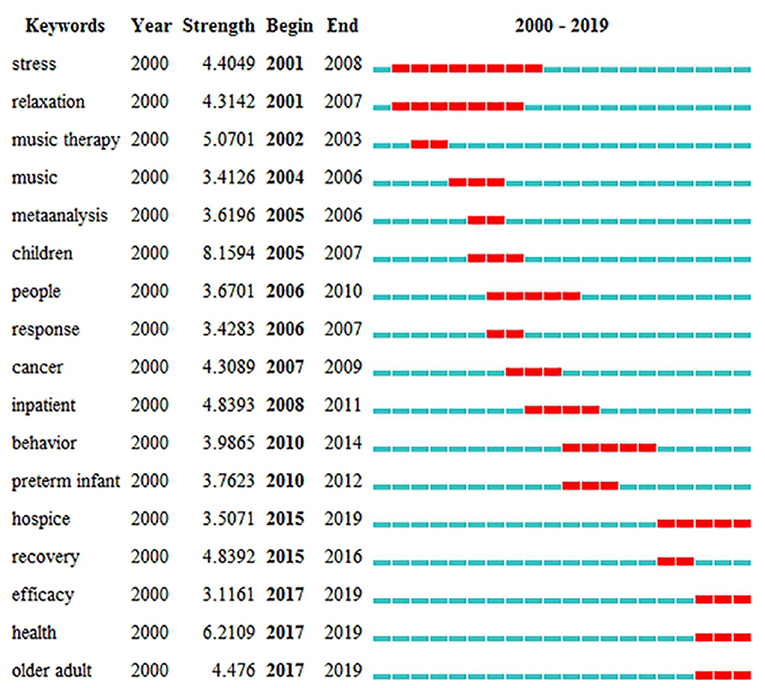
Figure 8 . The strongest citation bursts of the top 17 keywords. The red measures indicate frequent citation of keywords, and the green measures indicate infrequent citation of keywords.
Analysis of Co-cited References
The analysis of co-cited references is a significant indicator in the bibliometric method ( Chen, 2006 ). The top five co-cited references and their main findings are listed in Table 6 . These are regarded as fundamental studies for the music therapy knowledge base. In terms of co-citation counts, “individual music therapy for depression: randomized controlled trial” was the key reference because it had the most co-citation counts. This study concludes that music therapy mixed with standard care is an effective way to treat working-age people with depression. The authors also explained that music therapy is a valuable enhancement to established treatment practices ( Erkkilä et al., 2011 ). Meanwhile, the strongest citation burst of reference is regarded as the main knowledge of the trend ( Fitzpatrick, 2005 ). Figure 9 highlights the top 71 strongest citation bursts of references from 2000 to 2019. As can be seen, by the end of 2019, the reference burst was led by author Stige B, and the strongest burst was 4.3462.
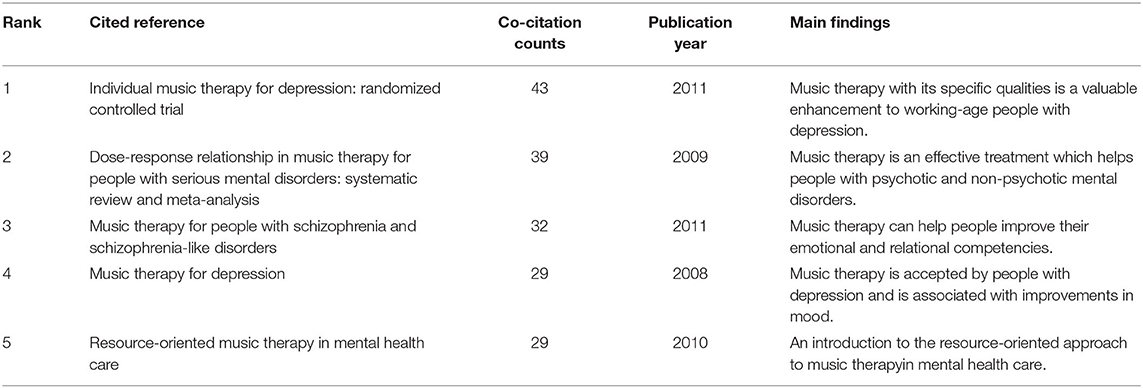
Table 6 . Top five co-cited references with co-citation counts in the study of music therapy from 2000 to 2019.
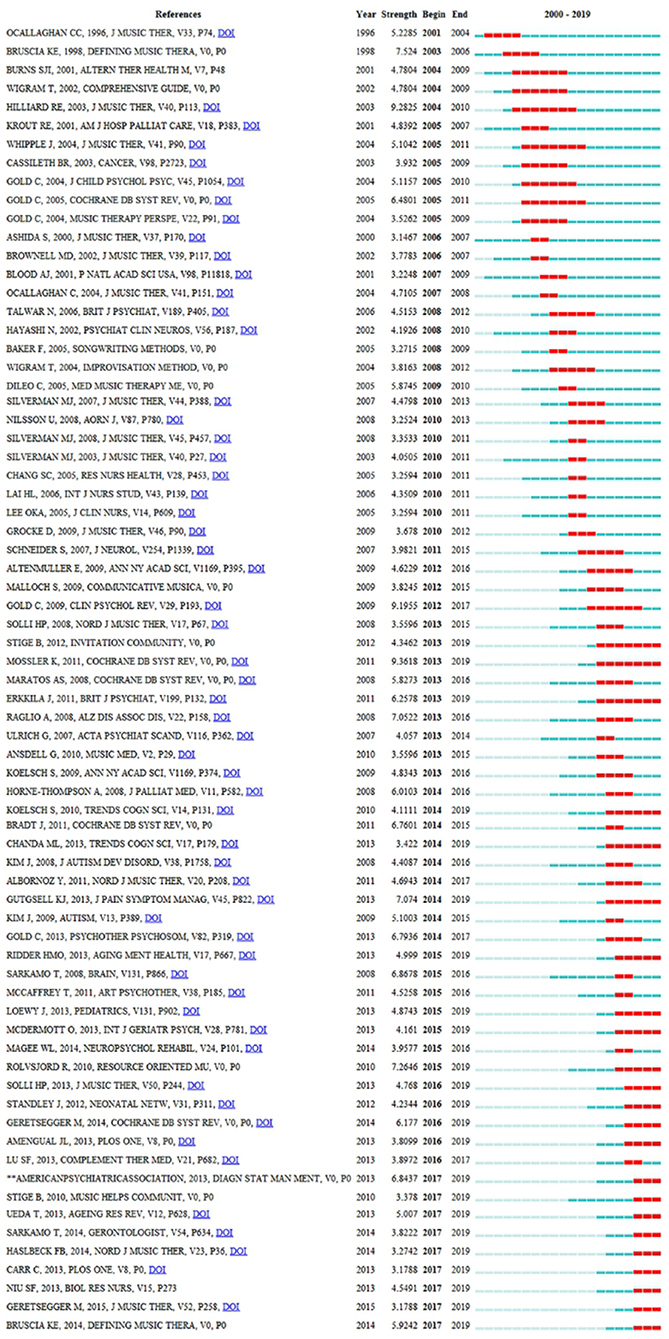
Figure 9 . The strongest citation bursts among the top 71 references. The red measures indicate frequent citation of studies, and the green measures indicate infrequent citation of studies.
Figure 10A presents the co-cited reference map containing 577 nodes and 1,331 links. The figure explains the empirical relevance of a considerable number of articles and reviews. Figure 10B presents the co-citation map (timeline view) of reference from publications on top music therapy research. The timeline view of clusters shows the research progress of music therapy in a particular period of time and the thematic concentration of each cluster. “Psychosis” was labeled as the largest cluster (#0), followed by “improvisational music therapy” (#1) and “paranesthesia anxiety” (#2). These clusters have also remained hot topics in recent years. Furthermore, the result of the modularity Q score was 0.8258. That this value exceeded 0.5 indicated that the definitions of the subdomain and characters of clusters were distinct. In addition, the mean silhouette was 0.5802, which also exceeded 0.5. The high homogeneity of individual clusters indicated high concentration in different research areas.
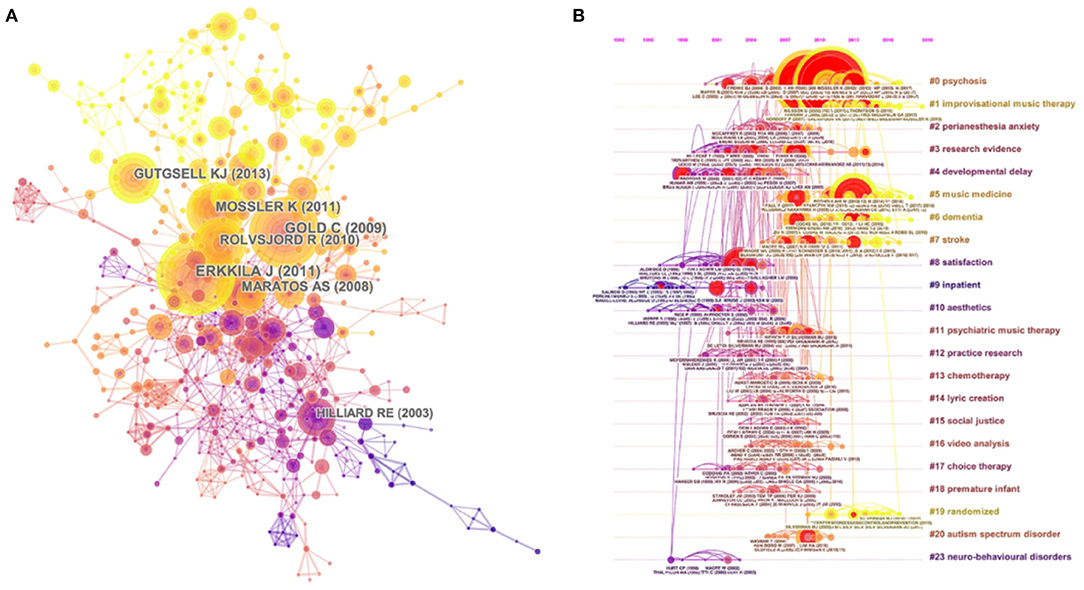
Figure 10. (A) The network map of co-cited references and (B) the map (timeline view) of references with co-citation on top music therapy research. In these maps, the node represents a study, and the link represents the co-citation frequency between two studies. A larger node represents more publications of the author. A thicker purple circle represents greater influence in this field. (A) The nodes in the same color belong to the same cluster. (B) The nodes on the same line belong to the same cluster.
Global Trends in Music Therapy Research
This study conducted a bibliometric analysis of music therapy research from the past two decades. The results, which reveal that music therapy studies have been conducted throughout the world, among others, can provide further research suggestions to scholars. In terms of the general analysis of the publications, the features of published articles and reviews, prolific countries or regions, and productive institutions are summarized below.
I. The distribution of publication year has been increasing in the past two decades. The annual publication outputs of music therapy from 2000 to 2019 were divided into three stages: beginning, second, and third. In the beginning stage, there were <30 annual publications from 2000 to 2006. The second stage was between 2007 and 2014. The number of publications increased steadily. It was 2007, which marked the first time 40 articles or reviews were published. The third stage was between 2015 and 2019. The year 2015 was the key turning point because it was the first time 80 articles or reviews were published. The number of publications showed a downward trend in 2016 (72), but it was still higher than the average number of the previous years. Overall, music therapy-related research has received increasing attention among scholars from 2000 to 2020.
II. The articles and reviews covered about 49 countries or regions, and the prolific countries or regions were mainly located in the North American and European continents. According to citations on WoS, citations per study, and the H-index, music therapy publications from developed countries, such as United States and Norway, have greater influence than those from other countries. In addition, China, as a model of a developing country, had published 53 studies and ranked top six among productive countries.
III. In terms of the collaboration map of institutions, the most productive universities engaged in music therapy were located in the United States, namely, University of Minnesota (43 publications), Florida State University (33 publications), Temple University (27 publications), and University of Kansas (20 publications). It indicated that institutions in the US have significant impacts in this area.
IV. According to author co-citation counts, scholars can focus on the publications of such authors as Bruscia KE, Gold C, and Wigram T. These three authors come from the United States, Norway, and Denmark, and it also reflected that these three countries are leading the research trend. Author Bruscia KE has the largest co-citation counts and is based at Temple University. He published many music therapy studies about assessment and clinical evaluation in music therapy, music therapy theories, and therapist experiences. These publications laid a foundation and facilitate the development of music therapy. In addition, in Figure 11 , the multi-authored articles between 2000 and 2003 comprised 47.56% of the sample, whereas the publications of multi-authored articles increased significantly from 2016 to 2019 (85.51%). These indicated that cooperation is an effective factor in improving the quality of publications.
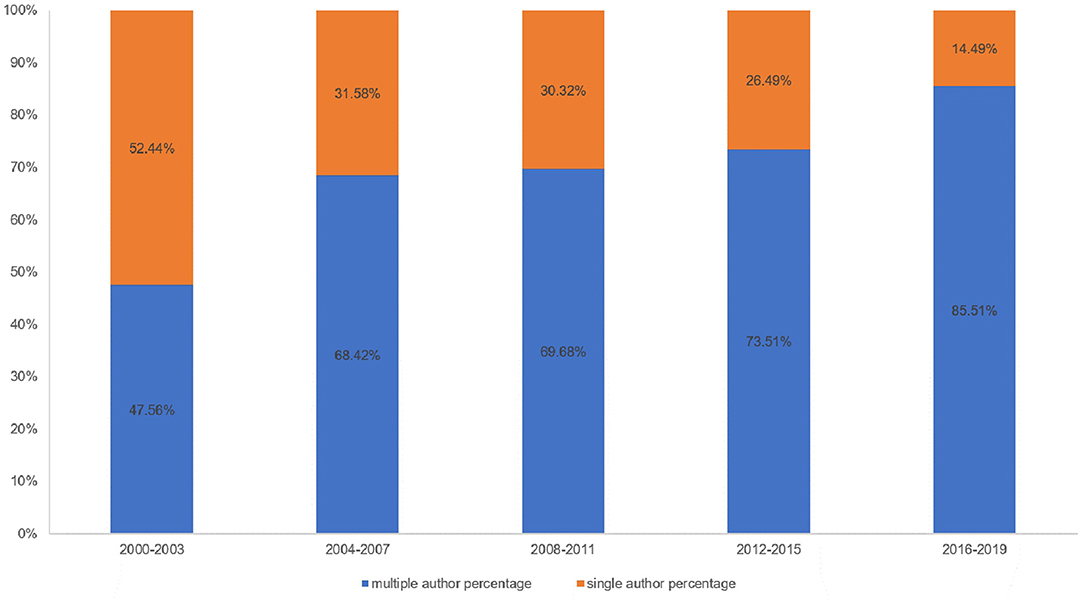
Figure 11 . The percentage of single- vs. multiple-authored articles. Blue bars mean multiple-author percentage; orange bars mean single-author percentage.
Research Focus on the Research Frontier and Hot Topics
According to the science map analysis, hot music therapy topics among publications are discussed.
I. The cluster “#1 improvisational music therapy” (IMT) is the current research frontier in the music therapy research field. In general, music therapy has a long research tradition within autism spectrum disorders (ASD), and there have been more rigorous studies about it in recent years. IMT for children with autism is described as a child-centered method. Improvisational music-making may enhance social interaction and expression of emotions among children with autism, such as responding to communication acts ( Geretsegger et al., 2012 , 2015 ). In addition, IMT is an evidence-based treatment approach that may be helpful for people who abuse drugs or have cancer. A study applied improving as a primary music therapeutic practice, and the result indicated that IMT will be effective in treating depression accompanied by drug abuse among adults ( Albornoz, 2011 ). By applying the interpretative phenomenological analysis and psychological perspectives, a study explained the significant role of music therapy as an innovative psychological intervention in cancer care settings ( Pothoulaki et al., 2012 ). IMT may serve as an effective additional method for treating psychiatric disorders in the short and medium term, but it may need more studies to identify the long-term effects in clinical practice.
II. Based on the analysis of co-citation counts, the top three references all applied music therapy to improve the quality of life of clients. They highlight the fact that music therapy is an effective method that can cover a range of clinical skills, thus helping people with psychological disorders, chronic illnesses, and pain management issues. Furthermore, music therapy mixed with standard care can help individuals with schizophrenia improve their global state, mental state (including negative and general symptoms), social functioning, and quality of life ( Gold et al., 2009 ; Erkkilä et al., 2011 ; Geretsegger et al., 2017 ).
III. By understanding the keywords with the strongest citation bursts, the research frontier can be predicted. Three keywords, “efficacy,” “health,” and “older adults,” emphasized the research trends in terms of the strongest citation bursts.
a. Efficacy: This refers to measuring the effectiveness of music therapy in terms of clinical skills. Studies have found that a wide variety of psychological disorders can be effectively treated with music. In the study of Fukui, patients with Alzheimer's disease listened to music and verbally communicated with their music therapist. The results showed that problematic behaviors of the patients with Alzheimer's disease decreased ( Fukui et al., 2012 ). The aim of the study of Erkkila was to determine the efficacy of music therapy when added to standard care. The result of this study also indicated that music therapy had specific qualities for non-verbal expression and communication when patients cannot verbally describe their inner experiences ( Erkkilä et al., 2011 ). Additionally, as summarized by Ueda, music therapy reduced anxiety and depression in patients with dementia. However, his study cannot clarify what kinds of music therapy or patients have effectiveness. Thus, future studies should investigate music therapy with good methodology and evaluation methods ( Ueda et al., 2013 ).
b. Health: Music therapy is a methodical intervention in clinical practice because it uses music experiences and relationships to promote health for adults and children ( Bruscia, 1998 ). Also, music therapy is an effective means of achieving the optimal health and well-being of individuals and communities, because it can be individualized or done as a group activity. The stimulation from music therapy can lead to conversations, recollection of memories, and expression. The study of Gold indicated that solo music therapy in routine practice is an effective addition to usual care for mental health care patients with low motivation ( Gold et al., 2013 ). Porter summarized that music therapy contributes to improvement for both kids and teenagers with mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, and increases self-esteem in the short term ( Porter et al., 2017 ).
c. Older adults: This refers to the use of music therapy as a treatment to maintain and slow down the symptoms observed in older adults ( Mammarella et al., 2007 ; Deason et al., 2012 ). In terms of keywords with the strongest citation bursts, the most popular subjects of music therapy-related articles and reviews focused on children from 2005 to 2007. However, various researchers concentrated on older adults from 2017 to 2019. Music therapy was the treatment of choice for older adults with depression, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disorders ( Brotons and Koger, 2000 ; Bernatzky et al., 2004 ; Johnson et al., 2011 ; Deason et al., 2012 ; McDermott et al., 2013 ; Sakamoto et al., 2013 ; Benoit et al., 2014 ; Pohl et al., 2020 ). In the study of Zhao, music therapy had positive effects on the reduction of depressive symptoms for older adults when added to standard therapies. These standard therapies could be standard care, standard drug treatment, standard rehabilitation, and health education ( Zhao et al., 2016 ). The study of Shimizu demonstrated that multitask movement music therapy was an effective intervention to enhance neural activation in older adults with mild cognitive impairment ( Shimizu et al., 2018 ). However, the findings of the study of Li explained that short-term music therapy intervention cannot improve the cognitive function of older adults. He also recommended that future researchers can apply a quality methodology with a long-term research design for the care needs of older adults ( Li et al., 2015 ).
Strengths and Limitations
To the best of our knowledge, this study was the first one to analyze large-scale data of music therapy publications from the past two decades through CiteSpace V. CiteSpace could detect more comprehensive results than simply reviewing articles and studies. In addition, the bibliometric method helped us to identify the emerging trend and collaboration among authors, institutions, and countries or regions.
This study is not without limitations. First, only articles and reviews published in the WoS Science Citation Index Expanded and Social Sciences Citation Index were analyzed. Future reviews could consider other databases, such as PubMed and Scopus. The document type labeled by publishers is not always accurate. For example, some publications labeled by WoS were not actually reviews ( Harzing, 2013 ; Yeung, 2021 ). Second, the limitation may induce bias in frequency of reference. For example, some potential articles were published recently, and these studies could be not cited with frequent times. Also, in terms of obliteration by incorporation, some common knowledge or opinions become accepted that their contributors or authors are no longer cited ( Merton, 1965 ; Yeung, 2021 ). Third, this review applied the quantitative analysis approach, and only limited qualitative analysis was performed in this study. In addition, we applied the CitesSpace software to conduct this bibliometric study, but the CiteSpace software did not allow us to complicate information under both full counting and fractional counting systems. Thus, future scholars can analyze the development of music therapy in some specific journals using both quantitative and qualitative indicators.
Conclusions
This bibliometric study provides information regarding emerging trends in music therapy publications from 2000 to 2019. First, this study presents several theoretical implications related to publications that may assist future researchers to advance their research field. The results reveal that annual publications in music therapy research have significantly increased in the last two decades, and the overall trend in publications increased from 28 publications in 2000 to 111 publications in 2019. This analysis also furthers the comprehensive understanding of the global research structure in the field. Also, we have stated a high level of collaboration between different countries or regions and authors in the music therapy research. This collaboration has extremely expanded the knowledge of music therapy. Thus, future music therapy professionals can benefit from the most specialized research.
Second, this research represents several practical implications. IMT is the current research frontier in the field. IMT usually serves as an effective music therapy method for the health of people in clinical practice. Identifying the emerging trends in this field will help researchers prepare their studies on recent research issues ( Mulet-Forteza et al., 2021 ). Likewise, it also indicates future studies to address these issues and update the existing literature. In terms of the strongest citation bursts, the three keywords, “efficacy,” “health,” and “older adults,” highlight the fact that music therapy is an effective invention, and it can benefit the health of people. The development prospects of music therapy could be expected, and future scholars could pay attention to the clinical significance of music therapy to the health of people.
Finally, multiple researchers have indicated several health benefits of music therapy, and the music therapy mechanism perspective is necessary for future research to advance the field. Also, music therapy can benefit a wide range of individuals, such as those with autism spectrum, traumatic brain injury, or some physical disorders. Future researchers can develop music therapy standards to measure clinical practice.
Author Contributions
KL and LW: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, resources, writing—review, and editing. LW: software and data curation. KL: validation and writing—original draft preparation. XW: visualization, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This study was supported by the Fok Ying-Tong Education Foundation of China (161092), the scientific and technological research program of the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (19080503100), and the Shanghai Key Lab of Human Performance (Shanghai University of Sport) (11DZ2261100).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
WoS, Web of Science; ESI, essential science indicators; IF, impact factor; IMT, improvisational music therapy; ASD, autism spectrum disorder.
Albornoz, Y. (2011). The effects of group improvisational music therapy on depression in adolescents and adults with substance abuse: a randomized controlled trial. Nord. J. Music Ther. 20, 208–224. doi: 10.1080/08098131.2010.522717
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Association, A. M. T. (2018). History of Music Therapy . Available online at: https://www.musictherapy.org/about/history/ (accessed November 10, 2020).
Google Scholar
Benoit, C. E., Dalla Bella, S., Farrugia, N., Obrig, H., Mainka, S., and Kotz, S. A. (2014). Musically cued gait-training improves both perceptual and motor timing in Parkinson's disease. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 8:494. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00494
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bernatzky, G., Bernatzky, P., Hesse, H. P., Staffen, W., and Ladurner, G. (2004). Stimulating music increases motor coordination in patients afflicted with Morbus Parkinson. Neurosci. Lett. 361, 4–8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.022
Bronson, H., Vaudreuil, R., and Bradt, J. (2018). Music therapy treatment of active duty military: an overview of intensive outpatient and longitudinal care programs. Music Ther. Perspect. 36, 195–206. doi: 10.1093/mtp/miy006
Brotons, M., and Koger, S. M. (2000). The impact of music therapy on language functioning in dementia. J. Music Ther. 37, 183–195. doi: 10.1093/jmt/37.3.183
Bruscia, K. (1998). Defining Music Therapy 2nd Edition . Gilsum: Barcelona publications.
Castanha, R. C. G., and Grácio, M. C. C. (2014). Bibliometrics contribution to the metatheoretical and domain analysis studies. Knowl. Organiz. 41, 171–174. doi: 10.5771/0943-7444-2014-2-171
Chen, C. (2006). CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inform. Sci. Technol. 57, 359–377. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317
Chen, C., Hu, Z., Liu, S., and Tseng, H. (2012). Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 12, 593–608. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507
Chen, H., Zhao, G., and Xu, N. (2012). “The analysis of research hotspots and fronts of knowledge visualization based on CiteSpace II,” in International Conference on Hybrid Learning , Vol. 7411, eds S. K. S. Cheung, J. Fong, L. F. Kwok, K. Li, and R. Kwan (Berlin; Heidelberg: Springer), 57–68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-32018-_6
Deason, R., Simmons-Stern, N., Frustace, B., Ally, B., and Budson, A. (2012). Music as a memory enhancer: Differences between healthy older adults and patients with Alzheimer's disease. Psychomusicol. Music Mind Brain 22:175. doi: 10.1037/a0031118
Devlin, K., Alshaikh, J. T., and Pantelyat, A. (2019). Music therapy and music-based interventions for movement disorders. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 19:83. doi: 10.1007/s11910-019-1005-0
Durieux, V., and Gevenois, P. A. (2010). Bibliometric indicators: quality measurements of scientific publication. Radiology 255, 342–351. doi: 10.1148/radiol.09090626
Ellegaard, O., and Wallin, J. A. (2015). The bibliometric analysis of scholarly production: How great is the impact? Scientometrics 105, 1809–1831. doi: 10.1007/s11192-015-1645-z
Erkkilä, J., Punkanen, M., Fachner, J., Ala-Ruona, E., Pöntiö, I., Tervaniemi, M., et al. (2011). Individual music therapy for depression: randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Psychiatry 199, 132–139. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.110.085431
Falagas, M. E., Pitsouni, E. I., Malietzis, G. A., and Pappas, G. (2008). Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: strengths and weaknesses. Faseb J. 22, 338–342. doi: 10.1096/FJ.07-9492LSF
Fitzpatrick, R. B. (2005). Essential Science IndicatorsSM. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 24, 67–78. doi: 10.1300/J115v24n04_05
Fukui, H., Arai, A., and Toyoshima, K. (2012). Efficacy of music therapy in treatment for the patients with Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2012, 531646–531646. doi: 10.1155/2012/531646
Geretsegger, M., Holck, U., Carpente, J. A., Elefant, C., Kim, J., and Gold, C. (2015). Common characteristics of improvisational approaches in music therapy for children with autism spectrum disorder: developing treatment guidelines. J. Music Ther. 52, 258–281. doi: 10.1093/jmt/thv005
Geretsegger, M., Holck, U., and Gold, C. (2012). Randomised controlled trial of improvisational music therapy's effectiveness for children with autism spectrum disorders (TIME-A): study protocol. BMC Pediatr. 12:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-2
Geretsegger, M., Mossler, K. A., Bieleninik, L., Chen, X. J., Heldal, T. O., and Gold, C. (2017). Music therapy for people with schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 5:CD004025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004025.pub4
Gold, C., Mössler, K., Grocke, D., Heldal, T. O., Tjemsland, L., Aarre, T., et al. (2013). Individual music therapy for mental health care clients with low therapy motivation: multicentre randomised controlled trial. Psychother. Psychosom. 82, 319–331. doi: 10.1159/000348452
Gold, C., Solli, H. P., Krüger, V., and Lie, S. A. (2009). Dose-response relationship in music therapy for people with serious mental disorders: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 29, 193–207. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2009.01.001
Gonzalez-Serrano, M. H., Jones, P., and Llanos-Contrera, O. (2020). An overview of sport entrepreneurship field: a bibliometric analysis of the articles published in the Web of Science. Sport Soc. 23, 296–314. doi: 10.1080/17430437.2019.1607307
Gooding, L. F., and Langston, D. G. (2019). Music therapy with military populations: a scoping review. J. Music Ther. 56, 315–347. doi: 10.1093/jmt/thz010
Harzing, A.-W. (2013). Document categories in the ISI web of knowledge: misunderstanding the social sciences? Scientometrics 94, 23–34. doi: 10.1007/s11192-012-0738-1
Johnson, J. K., Chang, C. C., Brambati, S. M., Migliaccio, R., Gorno-Tempini, M. L., Miller, B. L., et al. (2011). Music recognition in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and Alzheimer disease. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 24, 74–84. doi: 10.1097/WNN.0b013e31821de326
Li, H. C., Wang, H. H., Chou, F. H., and Chen, K. M. (2015). The effect of music therapy on cognitive functioning among older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 16, 71–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2014.10.004
Liang, Y. D., Li, Y., Zhao, J., Wang, X. Y., Zhu, H. Z., and Chen, X. H. (2017). Study of acupuncture for low back pain in recent 20 years: a bibliometric analysis via CiteSpace. J. Pain Res. 10, 951–964. doi: 10.2147/jpr.S132808
Mammarella, N., Fairfield, B., and Cornoldi, C. (2007). Does music enhance cognitive performance in healthy older adults? The Vivaldi effect. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 19, 394–399. doi: 10.1007/bf03324720
McDermott, O., Crellin, N., Ridder, H. M., and Orrell, M. (2013). Music therapy in dementia: a narrative synthesis systematic review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 28, 781–794. doi: 10.1002/gps.3895
Merigó, J. M., Mulet-Forteza, C., Valencia, C., and Lew, A. A. (2019). Twenty years of tourism Geographies: a bibliometric overview. Tour. Geograph. 21, 881–910. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2019.1666913
Merton, R. K. (1965). On the Shoulders of Giants: A Shandean Postscript . New York, NY: Free Press.
Miao, Y., Xu, S. Y., Chen, L. S., Liang, G. Y., Pu, Y. P., and Yin, L. H. (2017). Trends of long noncoding RNA research from 2007 to 2016: a bibliometric analysis. Oncotarget 8, 83114–83127. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20851
Mulet-Forteza, C., Lunn, E., Merigó, J. M., and Horrach, P. (2021). Research progress in tourism, leisure and hospitality in Europe (1969–2018). Int. J. Contemp. Hospit. Manage. 33, 48–74. doi: 10.1108/IJCHM-06-2020-0521
Pohl, P., Wressle, E., Lundin, F., Enthoven, P., and Dizdar, N. (2020). Group-based music intervention in Parkinson's disease - findings from a mixed-methods study. Clin. Rehabil. 34, 533–544. doi: 10.1177/0269215520907669
Porter, S., McConnell, T., McLaughlin, K., Lynn, F., Cardwell, C., Braiden, H. J., et al. (2017). Music therapy for children and adolescents with behavioural and emotional problems: a randomised controlled trial. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 58, 586–594. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12656
Pothoulaki, M., MacDonald, R., and Flowers, P. (2012). An interpretative phenomenological analysis of an improvisational music therapy program for cancer patients. J. Music Ther. 49, 45–67. doi: 10.1093/jmt/49.1.45
Sakamoto, M., Ando, H., and Tsutou, A. (2013). Comparing the effects of different individualized music interventions for elderly individuals with severe dementia. Int. Psychogeriatr. 25, 775–784. doi: 10.1017/s1041610212002256
Shimizu, N., Umemura, T., Matsunaga, M., and Hirai, T. (2018). Effects of movement music therapy with a percussion instrument on physical and frontal lobe function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. Aging Ment. Health 22, 1614–1626. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2017.1379048
Small, H. (1973). Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. J. Am. Soc. Inform. Sci. 24, 265–269. doi: 10.1002/asi.4630240406
Ueda, T., Suzukamo, Y., Sato, M., and Izumi, S. (2013). Effects of music therapy on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 12, 628–641. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2013.02.003
Wang, X. Q., Peng, M. S., Weng, L. M., Zheng, Y. L., Zhang, Z. J., and Chen, P. J. (2019). Bibliometric study of the comorbidity of pain and depression research. Neural. Plast 2019:1657498. doi: 10.1155/2019/1657498
Yeung, A. W. K. (2021). Is the influence of freud declining in psychology and psychiatry? A bibliometric analysis. Front. Psychol. 12:631516. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.631516
Zhao, K., Bai, Z. G., Bo, A., and Chi, I. (2016). A systematic review and meta-analysis of music therapy for the older adults with depression. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 31, 1188–1198. doi: 10.1002/gps.4494
Zheng, K., and Wang, X. (2019). Publications on the association between cognitive function and pain from 2000 to 2018: a bibliometric analysis using citespace. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 8940–8951. doi: 10.12659/msm.917742
Keywords: music therapy, aged, bibliometrics, health, web of science
Citation: Li K, Weng L and Wang X (2021) The State of Music Therapy Studies in the Past 20 Years: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Psychol. 12:697726. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.697726
Received: 20 April 2021; Accepted: 12 May 2021; Published: 10 June 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Li, Weng and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xueqiang Wang, wangxueqiang@sus.edu.cn
† These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Effects of music therapy on depression: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Roles Conceptualization, Writing – original draft
Affiliation Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
Roles Methodology, Software
Affiliation Anhui Provincial Center for Women and Child Health, Hefei, Anhui, China
Roles Writing – review & editing
Affiliations Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China, National Drug Clinical Trial Institution, The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
Roles Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
- Qishou Tang,
- Zhaohui Huang,
- Huan Zhou,

- Published: November 18, 2020
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
We aimed to determine and compare the effects of music therapy and music medicine on depression, and explore the potential factors associated with the effect.
PubMed (MEDLINE), Ovid-Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Clinical Evidence were searched to identify studies evaluating the effectiveness of music-based intervention on depression from inception to May 2020. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) were estimated with random-effect model and fixed-effect model.
A total of 55 RCTs were included in our meta-analysis. Music therapy exhibited a significant reduction in depressive symptom (SMD = −0.66; 95% CI = -0.86 to -0.46; P <0.001) compared with the control group; while, music medicine exhibited a stronger effect in reducing depressive symptom (SMD = −1.33; 95% CI = -1.96 to -0.70; P <0.001). Among the specific music therapy methods, recreative music therapy (SMD = -1.41; 95% CI = -2.63 to -0.20; P <0.001), guided imagery and music (SMD = -1.08; 95% CI = -1.72 to -0.43; P <0.001), music-assisted relaxation (SMD = -0.81; 95% CI = -1.24 to -0.38; P <0.001), music and imagery (SMD = -0.38; 95% CI = -0.81 to 0.06; P = 0.312), improvisational music therapy (SMD = -0.27; 95% CI = -0.49 to -0.05; P = 0.001), music and discuss (SMD = -0.26; 95% CI = -1.12 to 0.60; P = 0.225) exhibited a different effect respectively. Music therapy and music medicine both exhibited a stronger effects of short and medium length compared with long intervention periods.
Conclusions
A different effect of music therapy and music medicine on depression was observed in our present meta-analysis, and the effect might be affected by the therapy process.
Citation: Tang Q, Huang Z, Zhou H, Ye P (2020) Effects of music therapy on depression: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 15(11): e0240862. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862
Editor: Sukru Torun, Anadolu University, TURKEY
Received: June 10, 2020; Accepted: October 4, 2020; Published: November 18, 2020
Copyright: © 2020 Tang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding: The Key Project of University Humanities and Social Science Research in Anhui Province (SK2017A0191) was granted by Education Department of Anhui Province; the Research Project of Anhui Province Social Science Innovation Development (2018XF155) was granted by Anhui Provincial Federation of Social Sciences; the Ministry of Education Humanities and Social Sciences Research Youth fund Project (17YJC840033) was granted by Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China. These funders had a role in study design, text editing, interpretation of results, decision to publish and preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
Depression was reported to be a common mental disorders and affected more than 300 million people worldwide, and long-lasting depression with moderate or severe intensity may result in serious health problems [ 1 ]. Depression has become the leading causes of disability worldwide according to the recent World Health Organization (WHO) report. Even worse, depression was closely associated with suicide and became the second leading cause of death, and nearly 800 000 die of depression every year worldwide [ 1 , 2 ]. Although it is known that treatments for depression, more than 3/4 of people in low and middle-income income countries receive no treatment due to a lack of medical resources and the social stigma of mental disorders [ 3 ]. Considering the continuously increased disease burden of depression, a convenient effective therapeutic measures was needed at community level.
Music-based interventions is an important nonpharmacological intervention used in the treatment of psychiatric and behavioral disorders, and the obvious curative effect on depression has been observed. Prior meta-analyses have reported an obvious effect of music therapy on improving depression [ 4 , 5 ]. Today, it is widely accepted that the music-based interventions are divided into two major categories, namely music therapy and music medicine. According to the American Music Therapy Association (AMTA), “music therapy is the clinical and evidence-based use of music interventions to accomplish individualized goals within a therapeutic relationship by a credentialed professional who has completed an approved music therapy program” [ 6 ]. Therefore, music therapy is an established health profession in which music is used within a therapeutic relationship to address physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs of individuals, and includes the triad of music, clients and qualified music therapists. While, music medicine is defined as mainly listening to prerecorded music provided by medical personnel or rarely listening to live music. In other words, music medicine aims to use music like medicines. It is often managed by a medical professional other than a music therapist, and it doesn’t need a therapeutic relationship with the patients. Therefore, the essential difference between music therapy and music medicine is about whether a therapeutic relationship is developed between a trained music therapist and the client [ 7 – 9 ]. In the context of the clear distinction between these two major categories, it is clear that to evaluate the effects of music therapy and other music-based intervention studies on depression can be misleading. While, the distinction was not always clear in most of prior papers, and no meta-analysis comparing the effects of music therapy and music medicine was conducted. Just a few studies made a comparison of music-based interventions on psychological outcomes between music therapy and music medicine. We aimed to (1) compare the effect between music therapy and music medicine on depression; (2) compare the effect between different specific methods used in music therapy; (3) compare the effect of music-based interventions on depression among different population [ 7 , 8 ].
Materials and methods
Search strategy and selection criteria.
PubMed (MEDLINE), Ovid-Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Clinical Evidence were searched to identify studies assessing the effectiveness of music therapy on depression from inception to May 2020. The combination of “depress*” and “music*” was used to search potential papers from these databases. Besides searching for electronic databases, we also searched potential papers from the reference lists of included papers, relevant reviews, and previous meta-analyses. The criteria for selecting the papers were as follows:(1) randomised or quasi-randomised controlled trials; (2) music therapy at a hospital or community, whereas the control group not receiving any type of music therapy; (3) depression rating scale was used. The exclusive criteria were as follows: (1) non-human studies; (2) studies with a very small sample size (n<20); (3) studies not providing usable data (including sample size, mean, standard deviation, etc.); (4) reviews, letters, protocols, etc. Two authors independently (YPJ, HZH) searched and screened the relevant papers. EndNote X7 software was utilized to delete the duplicates. The titles and abstracts of all searched papers were checked for eligibility. The relevant papers were selected, and then the full-text papers were subsequently assessed by the same two authors. In the last, a panel meeting was convened for resolving the disagreements about the inclusion of the papers.
Data extraction
We developed a data abstraction form to extract the useful data: (1) the characteristics of papers (authors, publish year, country); (2) the characteristics of participators (sample size, mean age, sex ratio, pre-treatment diagnosis, study period); (3) study design (random allocation, allocation concealment, masking, selection process of participators, loss to follow-up); (4) music therapy process (music therapy method, music therapy period, music therapy frequency, minutes per session, and the treatment measures in the control group); (5) outcome measures (depression score). Two authors independently (TQS, ZH) abstracted the data, and disagreements were resolved by discussing with the third author (YPJ).
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two authors independently (TQS, ZH) assessed the risk of bias of included studies using Cochrane Collaboration’s risk of bias assessment tool, and disagreements were resolved by discussing with the third author (YPJ) [ 10 ].
Music therapy and music medicine
Music Therapy is defined as the clinical and evidence-based use of music interventions to accomplish individualized goals within a therapeutic relationship by a credentialed professional who has completed an approved music therapy program. Music medicine is defined as mainly listening to prerecorded music provided by medical personnel or rarely listening to live music. In other words, music medicine aims to use music like medicines.
Music therapy mainly divided into active music therapy and receptive music therapy. Active music therapy, including improvisational, re-creative, and compositional, is defined as playing musical instruments, singing, improvisation, and lyrics of adaptation. Receptive music therapy, including music-assisted relaxation, music and imagery, guided imagery and music, lyrics analysis, and so on, is defined as music listening, lyrics analysis, and drawing with musing. In other words, in active methods participants are making music, and in receptive music therapy participants are receiving music [ 6 , 7 , 9 , 11 – 13 ].
Evaluation of depression
Depression was evaluated by the common psychological scales, including Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), Children’s Depression Inventory (CDI), Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D), Cornell Scale (CS), Depression Mood Self-Report Inventory for Adolescence (DMSRIA), Geriatric Depression Scale-15 (GDS-15); Geriatric Depression Scale-30 (GDS-30), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD/HAMD), Montgomery-sberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS), Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS), Short Version of Profile of Mood States (SV-POMS).
Statistical analysis
The pooled effect were estimated by using the standardized mean differences (SMDs) and its 95% confidence interval (95% CI) due to the different depression rate scales were used in the included papers. Heterogeneity between studies was assessed by I-square ( I 2 ) and Q-statistic (P<0.10), and a high I 2 (>50%) was recognized as heterogeneity and a random-effect model was used [ 14 – 16 ]. We performed subgroup analyses and meta-regression analyses to study the potential heterogeneity between studies. The subgroup variables included music intervention categories (music therapy and music medicine), music therapy methods (active music therapy, receptive music therapy), specific receptive music therapy methods (music-assisted relaxation, music and imagery, and guided imagery and music (Bonny Method), specific active music therapy methods (recreative music therapy and improvisational music therapy), music therapy mode (group therapy, individual therapy), music therapy period (weeks) (2–4, 5–12, ≥13), music therapy frequency (once weekly, twice weekly, ≥3 times weekly), total music therapy sessions (1–4, 5–8, 9–12, 13–16, >16), time per session (minutes) (15–40, 41–60, >60), inpatient settings (secure [locked] unit at a mental health facility versus outpatient settings), sample size (20–50, ≥50 and <100, ≥100), female predominance(>80%) (no, yes), mean age (years) (<50, 50–65, >65), country having music therapy profession (no, yes), pre-treatment diagnosis (mental health, depression, severe mental disease/psychiatric disorder). We also performed sensitivity analyses to test the robustness of the results by re-estimating the pooled effects using fixed effect model, using trim and fill analysis, excluding the paper without information on music therapy, excluding the papers with more high biases, excluding the papers with small sample size (20< n<30), excluding the papers using an infrequently used scale, excluding the studies focused on the people with a severe mental disease. We investigated the publication biases by a funnel plot as well as Egger’s linear regression test [ 17 ]. The analyses were performed using Stata, version 11.0. All P-values were two-sided. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Characteristics of the eligible studies
Fig 1 depicts the study profile, and a total of 55 RCTs were included in our meta-analysis [ 18 – 72 ]. Of the 55 studies, 10 studies from America, 22 studies from Europe, 22 studies from Asia, and 1 study from Australia. The mean age of the participators ranged from 12 to 86; the sample size ranged from 20 to 242. A total of 16 different scales were used to evaluate the depression level of the participators. A total of 25 studies were conducted in impatient setting and 28 studies were in outpatients setting; 32 used a certified music therapist, 15 not used a certified music therapist (for example researcher, nurse), and 10 not reported relevent information. A total of 16 different depression rating scales were used in the included studies, and HADS, GDS, and BDI were the most frequently used scales ( Table 1 ).
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
PRISMA diagram showing the different steps of systematic review, starting from literature search to study selection and exclusion. At each step, the reasons for exclusion are indicated. Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052562.g001.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.g001
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.t001
Of the 55 studies, only 2 studies had high risks of selection bias, and almost all of the included studies had high risks of performance bias ( Fig 2 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.g002
The overall effects of music therapy
Of the included 55 studies, 39 studies evaluated the music therapy, 17 evaluated the music medicine. Using a random-effects model, music therapy was associated with a significant reduction in depressive symptoms with a moderate-sized mean effect (SMD = −0.66; 95% CI = -0.86 to -0.46; P <0.001), with a high heterogeneity across studies ( I 2 = 83%, P <0.001); while, music medicine exhibited a stronger effect in reducing depressive symptom (SMD = −1.33; 95% CI = -1.96 to -0.70; P <0.001) ( Fig 3 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.g003
Twenty studies evaluated the active music therapy using a random-effects model, and a moderate-sized mean effect (SMD = −0.57; 95% CI = -0.90 to -0.25; P <0.001) was observed with a high heterogeneity across studies ( I 2 = 86.3%, P <0.001). Fourteen studies evaluated the receptive music therapy using a random-effects model, and a moderate-sized mean effect (SMD = −0.73; 95% CI = -1.01 to -0.44; P <0.001) was observed with a high heterogeneity across studies ( I 2 = 76.3%, P <0.001). Five studies evaluated the combined effect of active and receptive music therapy using a random-effects model, and a moderate-sized mean effect (SMD = −0.88; 95% CI = -1.32 to -0.44; P <0.001) was observed with a high heterogeneity across studies ( I 2 = 70.5%, P <0.001) ( Fig 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.g004
Among specific music therapy methods, recreative music therapy (SMD = -1.41; 95% CI = -2.63 to -0.20; P <0.001), guided imagery and music (SMD = -1.08; 95% CI = -1.72 to -0.43; P <0.001), music-assisted relaxation (SMD = -0.81; 95% CI = -1.24 to -0.38; P <0.001), music and imagery (SMD = -0.38; 95% CI = -0.81 to 0.06; P = 0.312), improvisational music therapy (SMD = -0.27; 95% CI = -0.49 to -0.05; P = 0.001), and music and discuss (SMD = -0.26; 95% CI = -1.12 to 0.60; P = 0.225) exhibited a different effect respectively ( Fig 5 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.g005
Sub-group analyses and meta-regression analyses
We performed sub-group analyses and meta-regression analyses to study the homogeneity. We found that music therapy yielded a superior effect on reducing depression in the studies with a small sample size (20–50), with a mean age of 50–65 years old, with medium intervention frequency (<3 times weekly), with more minutes per session (>60 minutes). We also found that music therapy exhibited a superior effect on reducing depression among people with severe mental disease /psychiatric disorder and depression compared with mental health people. While, whether the country have the music therapy profession, whether the study used group therapy or individual therapy, whether the study was in the outpatients setting or the inpatient setting, and whether the study used a certified music therapist all did not exhibit a remarkable different effect ( Table 2 ). Table 2 also presents the subgroup analysis of music medicine on reducing depression.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.t002
In the subgroup analysis by total session, music therapy and music medicine both exhibited a stronger effects of short (1–4 sessions) and medium length (5–12 sessions) compared with long intervention periods (>13sessions) ( Fig 6 ). Meta-regression demonstrated that total music intervention session was significantly associated with the homogeneity between studies ( P = 0.004) ( Table 3 ).
A, evaluating the effect of music therapy; B, evaluating the effect of music medicine.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.g006
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.t003
Sensitivity analyses
We performed sensitivity analyses and found that re-estimating the pooled effects using fixed effect model, using trim and fill analysis, excluding the paper without information regarding music therapy, excluding the papers with more high biases, excluding the papers with small sample size (20< n<30), excluding the studies focused on the people with a severe mental disease, and excluding the papers using an infrequently used scale yielded the similar results, which indicated that the primary results was robust ( Table 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.t004
Evaluation of publication bias
We assessed publication bias using Egger’s linear regression test and funnel plot, and the results are presented in Fig 7 . For the main result, the observed asymmetry indicated that either the absence of papers with negative results or publication bias.
A, evaluating the publication bias of music therapy; B, evaluating the publication bias of music medicine; BDI = Beck Depression Inventory; CDI = Children’s Depression Inventory; CDSS = depression scale for schizophrenia; CES-D = Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression; CS = Cornell Scale; DMSRIA = Depression Mood Self-Report Inventory for Adolescence; EPDS = Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale; GDS-15 = Geriatric Depression Scale-15; GDS-30 = Geriatric Depression Scale-30; HADS = Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; HRSD (HAMD) = Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression; MADRS = Montgomery-sberg Depression Rating Scale; PROMIS = Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System; SDS = Self-Rating Depression Scale; State-Trait Depression Questionnaire = ST/DEP; SV-POMS = short version of Profile of Mood Stat.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.g007
Our present meta-analysis exhibited a different effect of music therapy and music medicine on reducing depression. Different music therapy methods also exhibited a different effect, and the recreative music therapy and guided imagery and music yielded a superior effect on reducing depression compared with other music therapy methods. Furthermore, music therapy and music medicine both exhibited a stronger effects of short and medium length compared with long intervention periods. The strength of this meta-analysis was the stable and high-quality result. Firstly, the sensitivity analyses performed in this meta-analysis yielded similar results, which indicated that the primary results were robust. Secondly, considering the insufficient statistical power of small sample size, we excluded studies with a very small sample size (n<20).
Some prior reviews have evaluated the effects of music therapy for reducing depression. These reviews found a significant effectiveness of music therapy on reducing depression among older adults with depressive symptoms, people with dementia, puerpera, and people with cancers [ 4 , 5 , 73 – 76 ]. However, these reviews did not differentiate music therapy from music medicine. Another paper reviewed the effectiveness of music interventions in treating depression. The authors included 26 studies and found a signifiant reduction in depression in the music intervention group compared with the control group. The authors made a clear distinction on the definition of music therapy and music medicine; however, they did not include all relevant data from the most recent trials and did not conduct a meta-analysis [ 77 ]. A recent meta-analysis compared the effects of music therapy and music medicine for reducing depression in people with cancer with seven RCTs; the authors found a moderately strong, positive impact of music intervention on depression, but found no difference between music therapy and music medicine [ 78 ]. However, our present meta-analysis exhibited a different effect of music therapy and music medicine on reducing depression, and the music medicine yielded a superior effect on reducing depression compared with music therapy. The different effect of music therapy and music medicine might be explained by the different participators, and nine studies used music therapy to reduce the depression among people with severe mental disease /psychiatric disorder, while no study used music medicine. Furthermore, the studies evaluating music therapy used more clinical diagnostic scale for depressive symptoms.
A meta-analysis by Li et al. [ 74 ] suggested that medium-term music therapy (6–12 weeks) was significantly associated with improved depression in people with dementia, but not short-term music therapy (3 or 4 weeks). On the contrary, our present meta-analysis found a stronger effect of short-term (1–4 weeks) and medium-term (5–12 weeks) music therapy on reducing depression compared with long-term (≥13 weeks) music therapy. Consistent with the prior meta-analysis by Li et al., no significant effect on depression was observed for the follow-up of one or three months after music therapy was completed in our present meta-analysis. Only five studies analyzed the therapeutic effect for the follow-up periods after music therapy intervention therapy was completed, and the rather limited sample size may have resulted in this insignificant difference. Therefore, whether the therapeutic effect was maintained in reducing depression when music therapy was discontinued should be explored in further studies. In our present meta-analysis, meta-regression results demonstrated that no variables (including period, frequency, method, populations, and so on) were significantly associated with the effect of music therapy. Because meta-regression does not provide sufficient statistical power to detect small associations, the non-significant results do not completely exclude the potential effects of the analyzed variables. Therefore, meta-regression results should be interpreted with caution.
Our meta-analysis has limitations. First, the included studies rarely used masked methodology due to the nature of music therapy, therefore the performance bias and the detection bias was common in music intervention study. Second, a total of 13 different scales were used to evaluate the depression level of the participators, which may account for the high heterogeneity among the trials. Third, more than half of those included studies had small sample sizes (<50), therefore the result should be explicated with caution.
Our present meta-analysis of 55 RCTs revealed a different effect of music therapy and music medicine, and different music therapy methods also exhibited a different effect. The results of subgroup analyses revealed that the characters of music therapy were associated with the therapeutic effect, for example specific music therapy methods, short and medium-term therapy, and therapy with more time per session may yield stronger therapeutic effect. Therefore, our present meta-analysis could provide suggestion for clinicians and policymakers to design therapeutic schedule of appropriate lengths to reduce depression.
Supporting information
S1 checklist. prisma checklist..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.s001
S1 Dataset.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240862.s002
- 1. World Health Organization. Depression. 2017. Retrieved from http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/ .
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
- 6. American Music Therapy Association (2020). Definition and Quotes about Music Therapy. Available online at: https://www.musictherapy.org/about/quotes/ (Accessed Sep 13, 2020).
- 9. Wigram Tony. Inge Nyggard Pedersen&Lars Ole Bonde, A Compmhensire Guide to Music Therapy. London and Philadelphia: Jessica Kingsley Publishers. 2002:143. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0387-7604(02)00058-x pmid:12142064
- 10. Higgins J, Altman D, Sterne J. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In I. J. Higgins, R. Churchill, J. Chandler &M. Cumpston (Eds.), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). Cochrane 2017.
- 11. Wheeler BL. Music Therapy Handbook. New York, New York, USA: Guilford Publications, 2015.
- 12. Bruscia KE. Defining Music Therapy. 3rd Edition. University Park, Illinois, USA: Barcelona Publishers, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-06-507582 pmid:24574460
- 13. Wigram Tony. Inge Nyggard Pedersen&Lars Ole Bonde, A Compmhensire Guide to Music Therapy. London and Philadelphia: Jessica Kingsley Publishen. 2002: 143. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0387-7604(02)00058-x pmid:12142064
- 52. Radulovic R. The using of music therapy in treatment of depressive disorders. Summary of Master Thesis. Belgrade: Faculty of Medicine University of Belgrade, 1996.
80 Music Therapy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best music therapy topic ideas & essay examples, 📌 good research topics about music therapy, 🔍 interesting topics to write about music therapy, ❓ music therapy research questions.
- Music Therapy as a Social Work Intervention One of such interventions is music therapy which is aimed at helping people in a sensitive way accurately adjusting the possibilities this therapy may offer to the requirements of a particular client of a group […]
- Music Therapy for Schizophrenic Patients’ Quality of Life Consequently, the purpose of the project will be to review the existing literature and prepare a document with recommendations regarding MT in the discussed population, including psychiatric nurses’ acceptable role in delivering such interventions.
- Art and Music Therapy Coverage by Health Insurance However, I do believe that creative sessions should be available for all patients, and I am going to prove to you that music and art are highly beneficial for human health.
- Music Therapy in Healthcare Therefore, the article suggests that music can be used for relaxation, as well as managing the health issues that may arise due to the lack of relaxation.
- Music Therapy for Children With Learning Disabilities This review includes the evidence supporting music therapy as an effective strategy for promoting auditory, communication, and socio-emotional progression in children with ASD.
- Music Therapy as a Related Service for Students With Disabilities From a neuroscientific perspective, how would music intervention improve classroom behaviors and academic outcomes of students with ADHD as a way to inform policy-makers of the importance of music therapy as a related service?
- Music Therapy: The Impact on Older Adults There is therefore the need to focus more energy to aid more understating on the role of music therapy on older residents.”The recent qualitative review of literature in the area of music and music therapy […]
- Music Therapy: Alternative to Traditional Pain Medicine The sources underline that therapists should pay attention to the subjects of music and their impact on the health of clients.
- The Role of Music Therapy as Alternative Treatment Music therapy is the use of music interventions to achieve individualized goals of healing the body, mind, and spirit. Thereafter, several developments occurred in the field of music therapy, and the ringleaders founded the American […]
- Music Therapy Effectiveness In addition to this, research has shown that stroke patients become more involved in therapy sessions once music is incorporated in the treatment program; this is the motivational aspect of music.
- Sound as an Element of Music Therapy This is one of the reasons why in the Abrams study the participants explained that they preferred the sound of rain, ocean waves and the soft strumming of a guitar as compared to the work […]
- Music Therapy Throughout the Soloist Globally, classical music in its sense has always been known to adjoin the listener to some transcendent understanding of the world order, the feeling of integrity with the Universe and enormous delight rising up from […]
- Music Therapy: Where Words Cease In spite of the fact that, as a rule, one indulges into art to find the shelter from the reality, the author of the book called The Soloist explores quite a different issue of the […]
- Active Music Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease
- Effectiveness of Music Therapy for Survivors of Abuse
- Music Therapy Effectiveness of Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
- The Link Between Ancestral Hormones and Music Therapy
- Analysis of the Effectiveness of Art and Music Therapy
- Music Therapy Usefulness for Cancer Patients
- Music Therapy Impact on Students With Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- How Music Therapy Can Be Used to Reduce Pre-Operative Anxiety
- Healing Chronic Pain With Music Therapy
- Music Therapy Effect on the Wellness and Mood of Adolescents
- Comparing Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Music Therapy
- Constructing Optimal Experience for the Hospitalized Newborn Through Neuro-Based Music Therapy
- Music Therapy: Considerations for the Clinical Environment
- “Dementia and the Power of Music Therapy” by Steve Matthews Analysis
- Music Therapy for Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Discussing Music Therapy Reducing Stress Health and Social Care
- Does Music Therapy Help Children With Special Needs?
- Music Therapy for Delinquency Involved Juveniles Through Tripartite Collaboration
- Heidelberg Neuro-Music Therapy Enhances Task-Negative Activity in Tinnitus Patients
- Music Therapy for Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
- How Does Music Therapy Promote Positive Mental Health?
- Music Therapy and Its Positive Effects on the Brain
- The Relationships Between Learning and Music Therapy
- Music Therapy for Sexually Abused Children
- Managing Sickle Cell Pain With Music Therapy
- Music Therapy: How Does Music Impact Our Emotions
- Dealing With Depression With the Help of Music Therapy
- Effectiveness of Music Therapy and Drug Therapy for Children With Autism
- Music Therapy and Its Effect on the Levels of Anxiety
- The Link Between Music Therapy and Personality Theory Psychology
- How Music Therapy Improves Depression Among Older Adults
- Music Therapy: The Best Way to Help Children With Mental Illness
- Interventions of Music Therapy for Stress Reduction
- The Real Science Behind the Theory of Music Therapy
- Music Therapy Should Not Be Considered a Therapy
- Neurologic Music Therapy Training for Mobility and Stability Rehabilitation
- Nursing Theory for Music Therapy Quality Improvement Program
- The Help of Music Therapy in Pain Management
- Relationship Between Hypertension and Music Therapy
- Yoga and Music Therapy as Effective Methods of Stress Management
- What Is Music Therapy Used For?
- What Are Some Examples of Music Therapy?
- What Kind of Music Is Used in Music Therapy?
- What Are the Side Effects of Music Therapy?
- What Mental Illnesses Does Music Therapy Help?
- Can Music Therapy Help With Anxiety?
- What Type of Music Therapy Helps Depression?
- Does Music Therapy Actually Work?
- Do Psychiatrists Use Music Therapy?
- Do Doctors Recommend Music Therapy?
- How Long Does Music Therapy Last?
- Why Is Music Therapy Not Used?
- What Is a Typical Music Therapy Session Like?
- What Are the Two Main Benefits of Music Therapy?
- How Can Music Therapy Be Done at Home?
- What Does Music Therapy Do to the Brain?
- Is Music Therapy Good for Stress?
- Can Music Therapy Help With Trauma?
- What Ages Benefit From Music Therapy?
- What Is the First Step of Music Therapy?
- Does Music Therapy Include Talking?
- What Instruments Are Used for Music Therapy?
- What Is the Difference Between Sound Therapy and Music Therapy?
- Can You Do Music Therapy Without a Degree?
- Why Is Music Therapy Better Than Medicine?
- Nursing Home Questions
- Mozart Essay Ideas
- Nursing Theory Questions
- Psychotherapy Paper Topics
- Music Topics
- Stress Titles
- Yoga Questions
- Therapy Paper Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 80 Music Therapy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/music-therapy-essay-topics/
"80 Music Therapy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/music-therapy-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '80 Music Therapy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "80 Music Therapy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/music-therapy-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "80 Music Therapy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/music-therapy-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "80 Music Therapy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/music-therapy-essay-topics/.
- Accessibility Options:
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Search
- Skip to footer
- Office of Disability Services
- Request Assistance
- 305-284-2374
- High Contrast
- School of Architecture
- College of Arts and Sciences
- Miami Herbert Business School
- School of Communication
- School of Education and Human Development
- College of Engineering
- School of Law
- Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science
- Miller School of Medicine
Frost School of Music
- School of Nursing and Health Studies
- The Graduate School
- Division of Continuing and International Education
- People Search
- Class Search
- IT Help and Support
- Privacy Statement
- Student Life

- Search Site
- FROST Admissions
- FROST Events
- Alumni Achievements
- Ress Project
- Clinical Training
- Undergraduate
- Bachelor of Music
- Master with Undergraduate Equivalency
- Master of Music
- Non-Credit Certificate
- Faculty Research
- Student Research

Student Research Projects
- Music Therapy Research
Research activity is critical to the advancement of the music therapy profession as it enhances the understanding of music as unique human behavior and provides best practice guidelines for clinicians.
Masters Theses and Clinical Projects
Alison Belinsky (clinical project), Development of a Musical Executive Function Training protocol for adults with schizophrenia
John Britton (clinical project), The Development of a M usic-mindfulness Intervention for Patients with Cancer
Ruthanne Cain (clinical project), The Role of Musical Triggers in Substance Use Disorder
Carolyn Dachinger (thesis), Impulsivity and Performance on a Music-based C ognitive R ehabilitation P rotocol in Persons with Alcohol Dependence
Angela Davis (thesis), The Effect of Film S core on Emotion and Self-talk
Jenny Denk (thesis), An Exploratory Study Examining the Impact of a Music Therapy Support Group on Perceived Stress, Anxiety, and Depression in Long-term Caregivers
Esther Hood (clinical project), Developing the Music Assessment of Pediatric Voice (MA-PV)
Anqi Jiang (thesis), The Effect of Rhythmic Auditory Stimulation (RAS) on Gait in Young Children with Cerebral Palsy
Amy Kalas (thesis), Joint Attention Responses to Simple versus C omplex Music of Children with Autism Spectrum D isorder
Stephanie Kawzenuk (thesis), Music Therapy Undergraduate Education and S tudent Clinical Training Learning
Erin Keenan (thesis), The Immediate Effects of Rhythm on the Timing of U pper Extremity Movements in Patients with Parkinson ’ s Disease
Emily Lambert (thesis), Rhythmic Motor Tempo in Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Katherine Lantigua (clinical project), Development of a Music Attention Control Training (MACT) program to improve selective attention in toddlers with developmental delay
Allison Lockhart (thesis), The Effect of Rhythmic Proprioceptive Input on Attention in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): An Exploratory Study
Jessica MacLean (thesis), An Exploratory Study to Examine a Drumming-to-Speech Intervention for Prosody Perception in Preschoolers with Cochlear Implants
Brianna McCulloch (thesis), The Effect of Music on Alternating Attention in a M atch/mismatch Task in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Alecia Meila (thesis), Exploring the Use of Music Interventions on Emotion Competence in Individuals with Special Needs: A Systematic Review
Brea Murakami (thesis), Music as a Mnemonic Device for Verbal Recall in Healthy Older Adults
Andy Panavides (thesis), The Role of Personality and M ood in Music-use in a High C ognitive Task
Allison Pindale (thesis), The Effect of Musical Mnemonics and Music Training on Word Recall
Evan Privoznik (thesis), Perception of Music-Emotion in Veterans with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Marlén Rodrigeuz-Wolfe (thesis), The Effect of Preferred Music Listening on Pain Tolerance in a C old-pressor Task
Hilary Yip (thesis), A Rhythmic Cueing in Martial Arts Protocol For the Motor Skills of Children with Autism: An Exploratory Pilot Study
Doctoral Dissertations
Carolyn Dachinger, The Effect of a Music-movement Intervention on Arousal and C ognitive Flexibility in O lder Adults with and without Mild N eurocognitive Disorder
Eunju Jeong, Music Therapy Assessment of Attention for Traumatic Brain Injury
Linda Lathroum, The Relationship between Pitch Processing and Phonological A wareness in Five- to Six-year-old Children
Hayoung Lim, Developmental Speech and Language Training through Music for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders
Julie Stordahl, The Influence of Music on Depression, Affect, and B enefit finding Among Women at the Completion of Treatment for Breast Cancer

- Messinger Music Executive Building 5501 San Amaro Drive Coral Gables , FL 33146
- 305-284-2241 305-284-2241
- Academic Calendar
- Alumni & Friends
- Medical Center
- Hurricane Sports
- UM Campus Map
- Frost Campus Map
- Parking & Transportation
- social-facebook
- social-twitter
- social-youtube
- social-instagram
Copyright: 2024 University of Miami. All Rights Reserved. Emergency Information Privacy Statement & Legal Notices
Individuals with disabilities who experience any technology-based barriers accessing the University’s websites or services can visit the Office of Workplace Equity and Inclusion .
Hayes School of Music Graduate Studies
- Music Therapy Theses
Reising, M. M. (2022). Music therapy for patients who are mechanically ventilated: A phenomenological study.
Smith, W. L. (2022). What about black music? Exploring a gap in music therapy training .
Santiago, K. (2022). The music in me: The impact of music therapy on identity development in college students. A phenomenological inquiry.
McAfee, A. L. (2021). Promoting self-determination in music therapy with individuals with I/DD who communicate extraverbally: Reflections and implications for practice.
Kiefer, E. K. (2021). Heartbeat recordings in music therapy: A sequential-explanatory mixed methods study.
Cooke, C. J. (2020). Maximizing referrals and acceptance of medical music therapy: A sequential-explanatory mixed methods study.
Beebe, K. J. (2020). Perceptions of self-determination in music therapy for individuals diagnosed with intellectual disabilities: A survey of music therapists.
Tart, M. F. (2019). Music therapy for infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome in the NICU: A qualitative content analysis .
Solberg, S. (2019). Neurologic music therapy to improve speaking voice in individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
Berry, A. (2019). A collaborative coalition: Action research response to a music therapy group for gender and sexual minority college students.
Esposito, K. (2019). Creating new music therapy programs in medical settings: A phenomenological inquiry.
Mercier, A. E. (2019). The use of creative arts in music therapy supervision: A sequential-explanatory mixed methods study.
Bodry, K. L. (2018). Clinical applications of feminist theory in music therapy: A phenomenological study.
Waller-Wicks, C. (2018). Music therapy and expressive arts to promote self-awareness and self-care in direct care staff: A phenomenological inquiry .
Donley, J. M. (2017). Understanding how Western-trained music therapists incorporate Chinese culture in their practice In China: An ethnographic study .
Lingafelt, H. H. (2017). Psychological factors in the use of music therapy with individuals experiencing pain: A survey of current practice.
Neel, K. M. (2017). Self-care for students: A pilot study on self-care education on the pre-internship music therapy students.
Barmore, E. A. (2017). The Bonny Method of Guided Imagery and Music (GIM) and eating disorders: Learning from therapist, trainer, and client experiences.
King, K. W. (2016). The practice of teaching therapeutic songwriting: A survey of educators and internship supervisors.
Grimmer, M. S. (2016). Cross-cultural music therapy: Reflections of music therapists working internationally .
Dorris, A. D. (2015). Music therapy when death is imminent: A phenomenological inquiry .
Renshaw, S. (2015). The use of rap music in music therapy treatment with adolescents and young adults: A survey.
Stith, C. C. (2015). The effects of musical tempo and dynamic range on heart rate variability in healthy adults.
Honig, T. J. (2014). Wilderness imagery in the Bonny Method of Guided Imagery and Music: A phenomenological inquiry .
Tate, C. E. (2014). Breaking the silence: A qualitative study on the use of Guided Imagery and Music, expressive arts, and a body-centered perspective to address women's issues .
Barwick, C. A. (2014). Describing the subtle factors that influence moments of interactive responses during music therapy sessions for people with late-stage Alzheimer’s disease and other related major neurocognitive disorders: A multiple case study.
Johnson, A. E. (2014). Benefits and challenges of therapeutic songwriting with deaf adolescent girls: A qualitative feasibility study .
Rosenblum, S. O. (2014). Group music therapy versus individual verbal therapy for mandated college students.
Wilson, S. H. (2014). Music therapy support groups for family caregivers of individuals residing in long- term care facilities: A survey of music therapists and interviews with current family caregivers.
Chwalek, C. M. (2013). The use of dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) in music therapy: A survey of current practice.
Rayburn, A. D. (2013). A phenomenological inquiry into systemic music therapy to accompany the grief journey of a boy with high functioning autism.
Deans, C. M. (2012). The use of dreamwork with the Bonny Method of Guided Imagery and Music: A survey of current practice .
Roberts, S. M. (2012). Current use of augmentative and alternative communication in music therapy: A survey and case study .
Dempsey, D. (2011). Grief rock band: The use of music therapy interventions to decrease depressive symptoms and facilitate expression of grief in bereaved adolescents.
Biron, R. N. (2010). Supporting pregnancy and childbirth using techniques from music therapy, counseling, and doula training .
Cloud, J. P. (2010). The use of music therapy and motivational interviewing with college student drinkers to invite “change talk.”
Hoyle, J. L. P. (2010). The role of music therapy in the bereavement process of adults with intellectual disabilities.
Leonard, K. R. (2010). A search for wholeness: Songs of healing for adolescents with emotional and behavioral disorders.
Brown, L. R. (2009). The effect of music therapy social skills interventions on children with behavioral and emotional disabilities or autism .
Schwantes, M. B. (2007). Music therapy with Mexican migrant farm workers in rural NC: A pilot study .
The Edvocate
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- Write For Us
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Assistive Technology
- Best PreK-12 Schools in America
- Child Development
- Classroom Management
- Early Childhood
- EdTech & Innovation
- Education Leadership
- First Year Teachers
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
- Parental Involvement
- Policy & Reform
- Best Colleges and Universities
- Best College and University Programs
- HBCU’s
- Higher Education EdTech
- Higher Education
- International Education
- The Awards Process
- Finalists and Winners of The 2023 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Award Seals
- GPA Calculator for College
- GPA Calculator for High School
- Cumulative GPA Calculator
- Grade Calculator
- Weighted Grade Calculator
- Final Grade Calculator
- The Tech Edvocate
- AI Powered Personal Tutor
$13 Million Gift to Cleveland Clinic from Howley Foundation Expands ASPIRE Program
Okaloosa school district to launch esports program across all high schools, white house initiative celebrates 10th anniversary with diverse 2024 hbcu cohort, college students are already regretting their student loans, fafsa rollout was ‘a stunning failure,’ college aid expert says. here’s how next year will compare, igniting the torch of progress’: stark state college opens new welding and joining lab, ‘a lovely legacy’: falk college remembers professor emerita sarah ‘sally’ short, fort leonard wood hosts combined college graduation event, huntington president announces plans for 2025 retirement, new scholarship available to nc residents with thursday deadline.
Good Research Topics about Music Therapy

- Active Music Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease
- Effectiveness of Music Therapy for Survivors of Abuse
- Music Therapy Effectiveness for Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
- The Link between Ancestral Hormones and Music Therapy
- Analysis of the Effectiveness of Art and Music Therapy
- Music Therapy Usefulness for Cancer Patients
- Music Therapy Impact on Students with Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- Healing Chronic Pain with Music Therapy
- Music Therapy Effect on the Wellness and Mood of Adolescents
- Comparing Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Music Therapy
- Constructing Optimal Experience for the Hospitalized Newborn Through Neuro-Based Music Therapy
- Music Therapy: Considerations for the Clinical Environment
- Music Therapy for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Discussing Music Therapy: Reducing Stress, Health, and Social Care
- Music Therapy for Delinquency Involved Juveniles through Tripartite Collaboration
- Heidelberg Neuro Music Therapy Enhances Task-Negative Activity in Tinnitus Patients
- Music Therapy for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Interesting Topics to Write about Music Therapy
- How Does Music Therapy Promote Positive Mental Health?
- The Relationships between Learning and Music Therapy
- Music Therapy for Sexually Abused Children
- Managing Sickle Cell Pain with Music Therapy
- Music Therapy: How Does Music Impact Our Emotions?
- Dealing with Depression with the Help of Music Therapy
- Effectiveness of Music Therapy and Drug Therapy for Children with Autism
- The Link between Music Therapy and Personality Theory Psychology
- How Music Therapy Improves Depression Among Older Adults
- Music Therapy: The Best Way to Help Children with Mental Illness
- Interventions of Music Therapy for Stress Reduction
- Neurologic Music Therapy Training for Mobility and Stability Rehabilitation
- Nursing Theory for Music Therapy Quality Improvement Program
- The Help of Music Therapy in Pain Management
- Relationship between Hypertension and Music Therapy
- Yoga and Music Therapy as Effective Methods of Stress Management
17 Ways to Support Students Whose Behavior ...
Research topics about ebola.
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author, employee motivation essay topic ideas & examples, essay topics for ethical dilemmas, writing prompts about childhood, simple & easy homer essay topics, criticism essay topics, collaboration essay topics.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Healthc Eng
- v.2022; 2022

This article has been retracted.
Analysis of the effectiveness of music therapy on mental health of college students.
Art College of Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610021, China
Associated Data
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Music therapy is a relatively mature marginal subject at present, and it is also a relatively common treatment method. This kind of treatment can better help college students get rid of bad psychology and guide their psychology to develop in a healthy direction. Mental health is one of the important indicators to measure the comprehensiveness of human quality and plays an important role in the sustainable development of human beings. Music therapy plays a very important role in college students' mental health education. As a marginal subject, music therapy combines music, medicine, and psychology, which is beneficial to alleviate students' bad emotions and psychological problems, and helps college students form a sound personality. Using music therapy can let college students vent their emotions in a suitable environment and atmosphere and then guide them correctly. This paper introduces the effectiveness of music therapy in college students' mental health education and then puts forward important measures to promote the implementation of music therapy in college students' mental health education.
1. Introduction
In the stage of higher education, college students' psychology and physiology are not yet mature, but they have high sensitivity and perception, high sensitivity to the changes of the objective world, and poor psychological quality, and are easy to go to extremes [ 1 ]. In terms of the current college students' mental health, there are a variety of problems, which have a negative impact on learning and physical and mental development [ 2 ]. Therefore, the reality also requires colleges and universities to carry out appropriate mental health education to help college students establish good psychological quality. From the current development, college students' mental health has become a very concerned problem. In the teaching process of colleges and universities, we need to choose teaching methods that are more close to students' real life to promote the development of college students' mental health [ 3 ]. From the relevant investigation and analysis, college students are interested in learning music, which provides an effective basis for college students to use music to treat psychological problems [ 4 ]. Music therapy can let college students vent their emotions in the appropriate environment and atmosphere and then guide them correctly to get out of the haze and welcome the sunshine [ 5 ]. The soothing effect of music can enable college students to maintain stable emotions and actively detect their own psychological changes, so as to achieve the effect of self-regulation and self-healing [ 6 ]. It can be seen that music therapy has good feasibility in the intervention of college students' psychological problems, which can promote the improvement of college students' self-cognitive ability and interpersonal skills and make them maintain a good psychological state.
Music has the function of arousing personal personality. Colleges and universities can use music to treat and solve the psychological obstacles of college students, which requires colleges to pay attention to college students' psychological counseling, cultivate students' healthy emotions, and promote the healthy development of college students' psychology [ 7 ]. When the emotion of college students is vented to a certain extent, the mood gradually changes to a positive direction. At this time, the teacher will play some music full of positive energy, so as to stimulate the positive emotion of the treated and help them get rid of their psychological problems [ 8 ]. Music therapy uses music as a carrier to help college students improve their psychological environment and promote emotional communication. At the same time, music is a common medium; using music can carry out a variety of activities, which can not only play the therapeutic role of music, but also create a good growth environment for college students [ 9 ]. This paper introduces the effectiveness of music therapy in college students' mental health education and then puts forward some important methods to promote the implementation of music therapy in college students' mental health education.
This paper is divided into four sections. Section 1 expounds the relationship between music therapy and college students' mental health. The relevant background is described. Section 2 expounds the influence of music therapy on college students' mental health. Section 3 expounds the application of music therapy in college students' mental health. The related research is summarized. Finally, the full text is summarized.
2. Effectiveness of Music Therapy on Mental Health of College Students
With the improvement of living standards and the acceleration of social rhythm, today's college students are facing the dual pressure of employment and study. At the same time, colleges and universities have begun to implement all kinds of education reform. Due to the immature judgment of the relationship between the two sexes, some college students have unpleasant communication experience with the opposite sex. As time goes by, it is easy to cause long-term depression and depression in their heart and even lead to suicide due to excessive inferiority. The purpose of psychological education is to guide college students to establish correct emotional values. It is worth noting that because the college students are in the regional mature stage of physical and mental development and gradually enter the society, they may have doubts about many social problems or phenomena, or even show psychological barriers, which are a manifestation of mental loss. The stage of college students is an important period for one's growth. Through years of knowledge preparation, one is about to enter the society. A sincere, enthusiastic, confident, and charming person is easier to base himself on society and integrate into social life. Music itself can help college students cultivate their temperament, constantly improve their personality, and bring people a happy mood. In the development of mental health education, music therapy is introduced. Under the alternation of rhythm and melody, people's emotional experience is mobilized and psychological barriers and problems are relieved. Therefore, the application of music therapy in college students' mental health education plays a positive role in strengthening students' emotional experience. In the role of school education, music therapy is suitable for the educational situation of the school. It plays an important role in preventing and treating students' physical and mental diseases, adjusting bad emotions, cultivating students' healthy emotions and cooperative spirit, and promoting students' self-expression, development, and innovation.
With the promotion of socialist spiritual civilization construction, it is an important task for colleges and universities to strengthen the spiritual civilization construction of college students and help them build healthy psychology. Music can help people express their feelings and, at the same time, correct people in interpersonal communication in a variety of bad state and establish a positive way of communication. In music therapy, other forms, such as role play and music performance, can create specific situations for students. While students enjoy the fun, they also know how to use music to express their emotions and emotions and get a successful experience. This kind of experience is the key to promote students' correct self-evaluation and self-concept, so the application of music therapy is an important way to solve students' psychological problems. In treatment, college students are allowed to not only listen to cheerful and inspirational music but also listen to some sad and slow music [ 10 ], so as to induce students to release their deep feelings, release their negative emotions, and then listen to some positive, full of positive energy, and inspirational music, guide them to break the psychological problems, re-face themselves, get a new life in spirit, and move towards a new life journey. From the specific form of music therapy, the main part is body participation. Take the common chorus as an example; if there is a discordant tone, it will reduce the overall chorus effect, so the cooperation of all participants is extremely important. No matter in training or performance, students pay attention to how to control their own individual reactions and strive to cooperate with and respect other members.
For music, it is not good music if it keeps going up or down. Use the following formula to evaluate the overall outline of a piece of music:
For music, it is not good to keep the pitch rising or falling. Use the following formula to evaluate the overall outline of a piece of music:
The original audio file is not conducive to research, so the audio file is converted into frequency spectrum, that is, the time domain is converted into frequency domain, and the frequency spectrum of the audio file is obtained. The process of realizing this function is shown in Figure 1 .

Audio file feature extraction process.
At present, college students are in their youth, with broad hobbies, being willing to make friends and good mental outlook. They hope to constantly know the world, broaden their horizons, increase their knowledge, make interesting friends, seek recognition from others, and gain sincere friendship. It is easy for the cooperative spirit in music activities to migrate to real life, which helps most students who are pessimistic and self-enclosed to open their hearts, promote their ability to communicate and understand with others, and build a good relationship with others while knowing themselves correctly. In the daily treatment process, the counselor will not just play positive energy songs, but first play a series of sad, lyrical, and soothing songs in a guiding way to guide students to fully release their inner feelings and help them express the most fundamental, depressed, and contradictory emotions in their hearts. In the stage of higher education, it is an important period for college students to shape their personality, and music can play a positive role in cultivating human sentiment and promote the realization of emotional training [ 11 ]. From the content of music art, it is the synthesis of hearing art, expression art, and emotion art. With the development of economy, society, and times, people's life rhythm is becoming faster and faster, while college students have already felt various pressures in school, such as studying, interacting with others, and employment, which make them upset and seriously affect the healthy development of college students' psychology.
3. The Application of Music Therapy in College Students' Mental Health
College students' mental health problems need to be solved, and music therapy is a relatively simple form of treatment. Many students have a wrong understanding of music therapy or do not understand the situation. Colleges and universities should pay attention to the propaganda of music therapy, guide college students to correctly understand their psychological problems, and timely relieve and treat the problems that may or have occurred. The new music therapy mode is based on the theoretical essence of different psychotherapy schools. According to the different needs of college students, it chooses adaptive music therapy technology to help college students release bad emotions, purify the mind and improve interpersonal relationships in a good experience, and create a campus cultural atmosphere of knot, friendship, and mutual help. As an important implementer of music therapy, music therapists have a very important impact on the future development of college students. Music therapists in colleges and universities need to improve their own music therapy propaganda ability, promotion ability, teaching ability, and scientific research ability. Based on the actual situation of music therapists at home and abroad, combined with the characteristics of college students' mental health education, music teachers are encouraged to participate in music therapy training and obtain technical qualification certificate.
Music therapy is a comprehensive subject, which involves music, medicine, psychology, and other aspects of professional knowledge, so the requirements of music therapy for practitioners are relatively high. In order to carry out music therapy activities or courses, colleges and universities need to build a team of high-quality music therapists. According to the basic and complex characteristics of music, the overall characteristics of music are identified, including musical form structure, style, and emotional connotation. The specific structure is shown in Figure 2 .

Composition of music form.
Today's society is full of impetuousness, and college students are prone to breed bad emotions due to various negative influences in their study and life. We help them to prevent bad emotions in time, digest negative emotions, and even help their relatives and friends solve psychological problems by popularizing music therapy. Receptive music therapy is to use the unique rhythm, harmony, and other factors in music to awaken the positive inner strength of college students, so as to adjust and improve their emotional and social adaptability and finally get cured. On the choice of listening music tracks, music therapists tailor-made and choose different tracks according to different objects and psychological problems. College music therapists need not only rich music knowledge but also professional knowledge in psychology, medicine, and pedagogy. Due to the limitation of university environment, music therapists need to truly love students and enhance their affinity.
Emotion plays an important and undeniable role in the formation of personality and cognition. At the same time, music can influence our emotions in some way. Therefore, we can use music therapy to stabilize students' emotions, make their values, world outlook, and outlook on life development in a positive direction, and help students better face setbacks in life and meet new challenges with enthusiasm. The interactive relationship of students' social development is shown in Figure 3 .

Interactive relationship of students' social development.
Music therapy is mainly divided into group therapy and individual therapy, and colleges and universities should prepare for music therapy rooms from these two aspects. Using environmental construction, building a harmonious and friendly state between music therapists and students, using audition and games to carry out effective music therapy activities, and promoting the healthy development of college students' psychology, music teachers in colleges and universities have very strong musical ability. Music teachers should not only have basic knowledge of music major but also have knowledge of pedagogy and psychology and improve their comprehensive quality with the help of psychological counselor training. Colleges and universities need to pay attention to the propaganda work of music therapy, carry out university lectures and public elective courses, and use various channels such as publicity columns and campus networks to guide college students to correctly understand music therapy, feel the benefits of music therapy, and mobilize students' enthusiasm for participating in music therapy. In the process of music therapy, we need to choose music-related activities, such as music creation, impromptu singing, and music games, but most people just think that music therapy is listening to music and relaxing. Music therapy itself is a kind of therapeutic activity, so there are certain requirements for the environment in order to achieve therapeutic effect. First of all, we need a relatively basic environment, which is quiet and comfortable and can make students in a relaxed and warm environment. In such a therapeutic environment, it is easier for students to open their hearts and tell their inner emotional world.
4. Conclusions
With the development of society, college students face a more complex environment during their growth, which has an important impact on their mental health. Therefore, it is necessary for colleges and universities to actively carry out mental health education activities for college students through effective teaching strategies, so as to guide students to keep a good mood, actively cope with difficulties and frustrations, establish a correct outlook on life and values, and realize self-worth in life. In the process of mental health education for college students, music therapy plays an irreplaceable role. Music therapy can effectively interfere with college students' mental health, promote their physical and mental health, improve their psychological quality, guide them to form healthy personality, and cultivate their sentiment. Music therapy, as a new psychological treatment method, has its unique advantages, and its rich treatment methods can effectively meet the diversified needs of college students for mental health. The music therapy is extended to the field of mental health education for college students, which effectively expands the channels of mental health education for college students and further promotes the innovation and development of mental health education in colleges and universities [ 12 ].
Data Availability
Conflicts of interest.
The authors declare that they have are no conflicts of interest in this study.
The Transformative Power of Music in Mental Well-Being
- August 01, 2023
- Healthy living for mental well-being, Patients and Families, Treatment
Music has always held a special place in our lives, forming an integral part of human culture for centuries. Whether we passively listen to our favorite songs or actively engage in music-making by singing or playing instruments, music can have a profound influence on our socio-emotional development and overall well-being.

Recent research suggests that music engagement not only shapes our personal and cultural identities but also plays a role in mood regulation. 1 A 2022 review and meta-analysis of music therapy found an overall beneficial effect on stress-related outcomes. Moreover, music can be used to help in addressing serious mental health and substance use disorders. 2 In addition to its healing potential, music can magnify the message of diversity and inclusion by introducing people to new cultures and amplifying the voice of marginalized communities, thereby enhancing our understanding and appreciation for diverse communities.
Healing Trauma and Building Resilience
Many historically excluded groups, such as racial/ethnic and sexual minorities and people with disabilities, face systemic injustices and traumatic experiences that can deeply impact their mental health. Research supports the idea that discrimination, a type of trauma, increases risk for mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. 3
Music therapy has shown promise in providing a safe and supportive environment for healing trauma and building resilience while decreasing anxiety levels and improving the functioning of depressed individuals. 4 Music therapy is an evidence-based therapeutic intervention using music to accomplish health and education goals, such as improving mental wellness, reducing stress and alleviating pain. Music therapy is offered in settings such as schools and hospitals. 1 Research supports that engaging in music-making activities, such as drumming circles, songwriting, or group singing, can facilitate emotional release, promote self-reflection, and create a sense of community. 5
Empowerment, Advocacy and Social Change
Music has a rich history of being used as a tool for social advocacy and change. Artists from marginalized communities often use music to shed light on social issues (.pdf) , challenge injustices, and inspire collective action. By addressing topics such as racial inequality, gender discrimination, and LGBTQ+ rights, music becomes a powerful medium for advocating for social justice and promoting inclusivity. Through music, individuals can express their unique experiences, struggles, and triumphs, forging connections with others who share similar backgrounds. Research has shown that exposure to diverse musical genres and artists can broaden perspectives, challenge stereotypes, and foster empathy among listeners especially when dancing together. 7
Genres such as hip-hop, reggae, jazz, blues, rhythm & blues and folk have historically served as platforms for marginalized voices, enabling them to reclaim their narratives and challenge societal norms. The impact of socially conscious music has been observed in movements such as civil rights, feminism, and LGBTQ+ rights, where songs have played a pivotal role in mobilizing communities and effecting change. Music artists who engage in activism can reach new supporters and help their fans feel more connected to issues and motivated to participate. 6

Fostering Social Connection and Support
Music can also serve as a catalyst for social connection and support, breaking down barriers and bridging divides. Emerging evidence indicates that music has the potential to enhance prosocial behavior, promote social connectedness, and develop emotional competence. 2 Communities can leverage music’s innate ability to connect people and foster a sense of belonging through music programs, choirs, and music education initiatives. These activities can create inclusive spaces where people from diverse backgrounds can come together, collaborate, and build relationships based on shared musical interests. These experiences promote social cohesion, combat loneliness, and provide a support network that can positively impact overall well-being.
Musicians and Normalizing Mental Health
Considering the healing effects of music, it may seem paradoxical that musicians may be at a higher risk of mental health disorders. 8 A recent survey of 1,500 independent musicians found that 73% have symptoms of mental illness. This could be due in part to the physical and psychological challenges of the profession. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics in Germany found that musically active people have, on average, a higher genetic risk for depression and bipolar disorder.
Commendably, many artists such as Adele, Alanis Morrisette, Ariana Grande, Billie Eilish, Kendrick Lamar, Kid Cudi and Demi Lovato have spoken out about their mental health battles, from postpartum depression to suicidal ideation. Having high-profile artists and celebrities share their lived experiences has opened the conversation about the importance of mental wellness. This can help battle the stigma associated with seeking treatment and support.
Dr. Regina James (APA’s Chief of the Division of Diversity and Health Equity and Deputy Medical Director) notes “Share your story…share your song and let's help each other normalize the conversation around mental wellness through the influence of music. My go-to artist for relaxation is jazz saxophonist, “Grover Washington Jr” …what’s yours?” Submit to [email protected] to get featured!
More on Music Therapy
- Music Therapy Fact Sheets from the American Music Therapy Association
- Music Therapy Resources for Parents and Caregivers from Music Therapy Works
By Fátima Reynolds DJ and Music Producer Senior Program Manager, Division of Diversity and Health Equity American Psychiatric Association
- Gustavson, D.E., et al. Mental health and music engagement: review, framework, and guidelines for future studies. Transl Psychiatry 11, 370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01483-8
- Golden, T. L., et al. (2021). The use of music in the treatment and management of serious mental illness: A global scoping review of the literature. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.649840
- Schouler-Ocak, M., et al. (2021). Racism and mental health and the role of Mental Health Professionals. European Psychiatry, 64(1). https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.2216
- Aalbers, S., et al. (2017). Music therapy for Depression. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2017(11). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd004517.pub3
- Dingle, G. A., et al. (2021). How do music activities affect health and well-being? A scoping review of studies examining Psychosocial Mechanisms. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.713818
- Americans for the Arts. (n.d.). A Working Guide to the Landscape of Arts for Change. Animating Democracy. http://animatingdemocracy.org/sites/default/files/Potts%20Trend%20Paper.pdf
- Stupacher, J., Mikkelsen, J., Vuust, P. (2021). Higher empathy is associated with stronger social bonding when moving together with music. Psychology of Music, 50(5), 1511–1526. https://doi.org/10.1177/03057356211050681
- Wesseldijk, L.W., Ullén, F. & Mosing, M.A. The effects of playing music on mental health outcomes. Sci Rep 9, 12606 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49099-9
Medical leadership for mind, brain and body.
Mobile menu.
- Psychiatrists
- Residents & Medical Students
- Patients and Families
- Advocacy & APAPAC
- Diversity & Health Equity
- Research & Registry
- Meetings & Events
- Search Directories & Databases
- International
- Medical Students
- What is Psychiatry?
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Addiction and Substance Use Disorders
- Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
- Alcohol Use Disorder
- Anxiety Disorders
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Bipolar Disorders
- Climate Change and Mental Health Connections
- Coping After Disaster
- Disruptive, Impulse-Control and Conduct Disorders
- Dissociative Disorders
- Domestic Violence
- Eating Disorders
- E-Cigarettes and Vaping
- Gambling Disorder
- Gender Dysphoria
- Helping a Loved One Cope with Mental Illness
- Hoarding Disorder
- Integrated Behavioral Healthcare
- Intellectual Disability
- Internet Gaming
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- Opioid Use Disorder
- Perinatal Depression (formerly Postpartum)
- Personality Disorders
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prolonged Grief Disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
- Sleep Disorders
- Somatic Symptom Disorder
- Specific Learning Disorders
- Stigma, Prejudice and Discrimination Against People with Mental Illness
- Suicide Prevention
- Technology Addictions: Social Media, Online Gaming, and More
- Warning Signs of Mental Illness
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
- What is Mental Illness?
- What is Psychotherapy?
- What is Telepsychiatry?
- La Salud Mental
- Childhood Disorders: Medication Guides for Parents
- Lifestyle to Support Mental Health
- Member Benefits
- Honorary Fellowship (FAPA & DFAPA)
- Awards & Leadership Opportunities
- Get Involved
- Directories, Contact Info & FAQs
- District Branches
- APA's Vision, Mission, Values, and Goals
- Meet Our Organization
- Read APA Organization Documents and Policies
- Work At APA
- About APA's Headquarters
- Policy Finder
- News Releases
- Messages from the APA President
- Reporting on Mental Health Conditions
- Goldwater Rule
- Annual Meeting Press Registration + Guidelines
- APA Public Opinion Polls
- Reporter Toolkit: Recommendations on Covering the AAPI Community
- Comunicados de prensa en español
- APA Annual Meeting
- APA Communities
- APA Foundation
- APA JobCentral
- APA Learning Center
- APA Publishing
- Center for Workplace Mental Health
- Melvin Sabshin, M.D. Library & Archives
- Psychiatric News
- Psychiatry Online
- Annual Meeting
- APA On Demand
- At the APA Educational Series
- Books and Journals
- Certification and Licensure
- Diversity and Health Equity Education Resources
- Meeting Submission and Guidelines
- Mental Health Innovation Zone
- The Mental Health Services Conference
- The Virtual Immersive
- Virtual Paid Courses
- Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Covid-19 / Coronavirus
- Digital Mental Health
- Helping Patients Access Care
- Media and Communications
- Mental Health Apps
- Mental Health Parity
- Practice Management
- Professional Interests
- Quality Improvement
- Risk Management
- Social Media
- Sunshine Act
- Telepsychiatry
- The Clozapine Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program
- Transition to Practice and Early Career Resources
- Well-being and Burnout
- Mental Health and Faith Community Partnership
- Mental Health Equity Looking Beyond Series
- Minority and Underrepresented (M/UR) Caucuses
- Moore Equity in Mental Health Initiative
- News and Updates
- Striving for Excellence Series
- AMNet: Addiction Medicine Practice Based Research Network
- PsychPRO: APA's Mental Health Registry
- Research Colloquium for Junior Psychiatrist Investigators
- Perinatal Mental Health Toolkit
- Psychiatric Bed Crisis Report
- Advocacy Action Center
- Congressional Advocacy Network
- Election Resource Center
- Federal Affairs
- State Affairs
- Implementing 9-8-8
- Advocacy Update Webinars
- 2025 Annual Meeting
- The 2024 Mental Health Services Conference
- Addressing Structural Racism Town Hall Series
- APA Meetings App
- Governance Meetings
- Mental Health Equity Fireside Chat Series
- Moore Equity in Mental Health 5K
- Policy & Practice Insights Series
- September Component Meetings
- Social Determinants of Mental Health Town Hall Series
- Amicus Briefs
- Assembly Directory
- Component Directory
- Conference Publications
- Library and Archive
- Member Directory
- Member Obituaries
- Practice Guidelines
- Resource Documents
- International Trainees
- International Humanitarian Opportunities
- Global Mental Health
- International Medical Graduates Resources
- Residents' Journal
- Featured Publications
- APA/APAF Fellowships
- External Fellowships and Awards
- Helping Residents Cope with a Patient Suicide
- Vacant Resident Positions
- Leadership Positions
- SET for Success
- Apply for Psychiatric Residency
- Choosing a Career in Psychiatry
- Building a Career in Psychiatry
- Medical Student Programs
- Resident-Fellow Census
- Transitioning to Residency During COVID-19
- What Is a Substance Use Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Addiction and Substance Use Disorders
- What Are Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease?
- Expert Q&A: Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
- What are Anxiety Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Anxiety Disorders
- What is ADHD?
- Expert Q&A: ADHD
- What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Autism Spectrum Disorder
- What Are Bipolar Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Bipolar Disorder
- How Extreme Weather Events Affect Mental Health
- Who Is Affected by Climate Change?
- What Is Depression?
- Expert Q&A: Depression
- What are Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorders
- What Are Dissociative Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Dissociative Disorders
- What are Eating Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Eating Disorders
- What is Gambling Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Gambling Disorder
- What is Gender Dysphoria?
- Expert Q&A: Gender Dysphoria
- What is Hoarding Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Hoarding Disorder
- What is Intellectual Disability?
- Expert Q&A: Intellectual Disability
- What Is Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- What is Perinatal Depression (formerly Postpartum)?
- Expert Q&A: Perinatal Depression
- What are Personality Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Personality Disorders
- What is Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
- Expert Q&A: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- What is Schizophrenia?
- Expert Q&A: Schizophrenia
- What are Sleep Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Sleep Disorders
- What is Somatic Symptom Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Somatic Symptom Disorder
- What Are Specific Learning Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Specific Learning Disorders
- What is Technology Addiction?
- Expert Q&A: Technology Addiction
- Cigarrillos electrónicos y vapeo
- Trastorno del espectro autista
- Trastorno por consumo de alcohol
- Trastorno por consumo de opioides
- Trastorno de estrés postraumático (TEPT)
- Adicción a la tecnología: redes sociales, juegos en línea, y más
- ¿Qué es la psiquiatría?
- Conexiones entre el cambio climático y la salud mental
- Más temas de salud mental
- General Members
- Early Career Psychiatrists
- Residents and Fellows
- International Resident-Fellows
- Semi-Retired and Retired
- View Your Profile
- Resident-Fellow Members
- Fellow of the APA
- Distinguished Fellow of the APA
- International Fellow of the APA
- International Distinguished Fellow of the APA
- 2024 Class of Honorary Fellows
- 2025 APA National Elections
- Councils, Committees and Components
- Resident-Fellow Leadership Opportunities
- Advocacy and APAPAC
- APA Insider Sessions
- APA Specialty Interest Caucuses, Listservs & Communities
- Leadership, Equity and Diversity Institute
- Mentorship Program for APA/APAF Fellows
- Research Colloquium
- Contact Your Membership Specialist
- Contact Your District Branch
- Membership FAQs
- Semi-Retired and Retired FAQs
- Lump Sum Dues
- District Branch Resources
- District Branch Dues for General Members
- District Branch Dues for Residents and Fellows
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Topics
120 Music Research Paper Topics
How to choose a topic for music research paper:.

Music Theory Research Paper Topics:
- The influence of harmonic progression on emotional response in music
- Analyzing the use of chromaticism in the compositions of Johann Sebastian Bach
- The role of rhythm and meter in creating musical tension and release
- Examining the development of tonality in Western classical music
- Exploring the impact of cultural and historical context on musical form and structure
- Investigating the use of polyphony in Renaissance choral music
- Analyzing the compositional techniques of minimalist music
- The relationship between melody and harmony in popular music
- Examining the influence of jazz improvisation on contemporary music
- The role of counterpoint in the compositions of Ludwig van Beethoven
- Investigating the use of microtonality in experimental music
- Analyzing the impact of technology on music composition and production
- The influence of musical modes on the development of different musical genres
- Exploring the use of musical symbolism in film scoring
- Investigating the role of music theory in the analysis and interpretation of non-Western music
Music Industry Research Paper Topics:
- The impact of streaming services on music consumption patterns
- The role of social media in promoting and marketing music
- The effects of piracy on the music industry
- The influence of technology on music production and distribution
- The relationship between music and mental health
- The evolution of music genres and their impact on the industry
- The economics of live music events and festivals
- The role of record labels in shaping the music industry
- The impact of globalization on the music industry
- The representation and portrayal of gender in the music industry
- The effects of music streaming platforms on artist revenue
- The role of music education in fostering talent and creativity
- The influence of music videos on audience perception and engagement
- The impact of music streaming on physical album sales
- The role of music in advertising and brand marketing
Music Therapy Research Paper Topics:
- The effectiveness of music therapy in reducing anxiety in cancer patients
- The impact of music therapy on improving cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease
- Exploring the use of music therapy in managing chronic pain
- The role of music therapy in promoting emotional well-being in children with autism spectrum disorder
- Music therapy as a complementary treatment for depression: A systematic review
- The effects of music therapy on stress reduction in pregnant women
- Examining the benefits of music therapy in improving communication skills in individuals with developmental disabilities
- The use of music therapy in enhancing motor skills rehabilitation after stroke
- Music therapy interventions for improving sleep quality in patients with insomnia
- Exploring the impact of music therapy on reducing symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- The role of music therapy in improving social interaction and engagement in individuals with schizophrenia
- Music therapy as a non-pharmacological intervention for managing symptoms of dementia
- The effects of music therapy on pain perception and opioid use in hospitalized patients
- Exploring the use of music therapy in promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety during surgical procedures
- The impact of music therapy on improving quality of life in individuals with Parkinson’s disease
Music Psychology Research Paper Topics:
- The effects of music on mood and emotions
- The role of music in enhancing cognitive abilities
- The impact of music therapy on mental health disorders
- The relationship between music and memory recall
- The influence of music on stress reduction and relaxation
- The psychological effects of different genres of music
- The role of music in promoting social bonding and cohesion
- The effects of music on creativity and problem-solving abilities
- The psychological benefits of playing a musical instrument
- The impact of music on motivation and productivity
- The psychological effects of music on physical exercise performance
- The role of music in enhancing learning and academic performance
- The influence of music on sleep quality and patterns
- The psychological effects of music on individuals with autism spectrum disorder
- The relationship between music and personality traits
Music Education Research Paper Topics:
- The impact of music education on cognitive development in children
- The effectiveness of incorporating technology in music education
- The role of music education in promoting social and emotional development
- The benefits of music education for students with special needs
- The influence of music education on academic achievement
- The importance of music education in fostering creativity and innovation
- The relationship between music education and language development
- The impact of music education on self-esteem and self-confidence
- The role of music education in promoting cultural diversity and inclusivity
- The effects of music education on students’ overall well-being and mental health
- The significance of music education in developing critical thinking skills
- The role of music education in enhancing students’ teamwork and collaboration abilities
- The impact of music education on students’ motivation and engagement in school
- The effectiveness of different teaching methods in music education
- The relationship between music education and career opportunities in the music industry
Music History Research Paper Topics:
- The influence of African music on the development of jazz in the United States
- The role of women composers in classical music during the 18th century
- The impact of the Beatles on the evolution of popular music in the 1960s
- The cultural significance of hip-hop music in urban communities
- The development of opera in Italy during the Renaissance
- The influence of folk music on the protest movements of the 1960s
- The role of music in religious rituals and ceremonies throughout history
- The evolution of electronic music and its impact on contemporary music production
- The contribution of Latin American musicians to the development of salsa music
- The influence of classical music on film scores in the 20th century
- The role of music in the Civil Rights Movement in the United States
- The development of reggae music in Jamaica and its global impact
- The influence of Mozart’s compositions on the classical music era
- The role of music in the French Revolution and its impact on society
- The evolution of punk rock music and its influence on alternative music genres
Music Sociology Research Paper Topics:
- The impact of music streaming platforms on the music industry
- The role of music in shaping cultural identity
- Gender representation in popular music: A sociological analysis
- The influence of social media on music consumption patterns
- Music festivals as spaces for social interaction and community building
- The relationship between music and political activism
- The effects of globalization on local music scenes
- The role of music in constructing and challenging social norms
- The impact of technology on music production and distribution
- Music and social movements: A comparative study
- The role of music in promoting social change and social justice
- The influence of socioeconomic factors on music taste and preferences
- The role of music in constructing and reinforcing gender stereotypes
- The impact of music education on social and cognitive development
- The relationship between music and mental health: A sociological perspective
Classical Music Research Paper Topics:
- The influence of Ludwig van Beethoven on the development of classical music
- The role of women composers in classical music history
- The impact of Johann Sebastian Bach’s compositions on future generations
- The evolution of opera in the classical period
- The significance of Mozart’s symphonies in the classical era
- The influence of nationalism on classical music during the Romantic period
- The portrayal of emotions in classical music compositions
- The use of musical forms and structures in the works of Franz Joseph Haydn
- The impact of the Industrial Revolution on the production and dissemination of classical music
- The relationship between classical music and dance in the Baroque era
- The role of patronage in the development of classical music
- The influence of folk music on classical composers
- The representation of nature in classical music compositions
- The impact of technological advancements on classical music performance and recording
- The exploration of polyphony in the works of Johann Sebastian Bach

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research
Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account

Things I’ve Learned as a Music Therapist
Personla perspective: in a hospital setting, music is profound, powerful, and healing.
Posted August 14, 2024 | Reviewed by Gary Drevitch
- Music therapy in a hospital setting can be very powerful, profound, and healing.
- Music, for those who are suffering, can bring some humanity into their healing process.
- When there is nothing left, we still have music.
One of the great things about my job as a music therapist working in a hospital is that I learn something on an almost daily basis. And I learn all of these things from the people I share music with, people who are working through unbelievable challenges, both physically and mentally. Here are some of the things that I’ve learned that have truly affected me:
Music Creates Connection
So many times, I walk into a hospital room and the visitors are sitting in various spots, or in corners, and seemingly distracted. Sometimes, distracted in their own thoughts and reflections, sometimes on their phones. And I know that a lot of that has to do with coping with the situation. But, almost like hitting a switch, when music is introduced, they come together. They connect. They connect with the patient. They connect with each other. And they connect with the music.
She’s in her 90s and recently moved to hospice care. Her eyes were closed, and she was mainly non-responsive, but seemed comfortable. Her family was there: her adult daughter, her grandson and a friend. Everyone seemed to be in their own little world, as if waiting for… I said, "hello" and offered some music, for comfort. “Sure,” her daughter said. I took out my guitar and played a little. Then I transitioned into an easy version of "Somewhere Over the Rainbow." And then… all three moved to the bed. And then… they took her hands... and they all joined in singing. And in beautiful harmony! The patient suddenly opened her eyes and looked lovingly into her grandson’s gaze as he sang to her. An incredible smile overtook her face… and his too, through his tears. It was such a profound and beautiful moment that I don’t think they will ever forget. (And neither will I.) All because of…music .
Music Is the Universal Language
In the hospital, there are many languages. And sometimes that can be a barrier in the healing process. But I am lucky. I have music. Yes, music is the universal language. Especially when you are alone, sick, afraid, and unsure.
“He speaks no English so we can’t really talk with him. And he’s had no visitors,” the nurse told me when she asked me to visit with him. He’d already been isolated in the hospital for some time receiving cancer treatment. I walked into his dark room, and it was so quiet I could hear the IV drip. He looked at me and I showed him the guitar and gestured to a chair as if to ask, “May I sit?” He tentatively shook his head “yes." He was in bed with the covers pulled up and looked weak. I just started playing something soothing, offering some music for comfort. He was looking straight up but seemed to be listening. After a few moments, though, I noticed his feet slowly moving. I kept the rhythm solid. And then, some movement in his head. I followed him with the music, adding a little more structure. Gradually, his eyes opened fully and slowly his body seemed to… activate. He transformed—and the music followed. More rhythm. More movement. And soon, it felt as though we were… grooving? He looked at me with a big smile. And the movement in his body seemed to give him some energy. I eventually worked my way to ‘One Love’ without even thinking about it and starting singing. He pointed at me, laughed, and said “Ahhh…” Of course he knew Bob Marley! He took it in. He felt the music. He could not stop smiling. No words were spoken for the time I was there. There was no need. We had music . Then as I was about to walk out—three words… “Come back again.”
Music Brings Hope Where Hope Seems Hard to Find
Music can help in many ways, including reducing anxiety and pain, helping with coping with treatment, or as a prompt for emotional outlet. But the best thing that music can provide when someone is hurting is hope.
“What's that song about?” I asked the group, at an in-patient behavioral health facility where I was running a music therapy session, after listening to "Don’t Stop" (Fleetwood Mac). There was silence. Many looking down with flat, tired faces. No eye contact between anyone. But then, a quiet voice from a young woman sitting to the side, “Maybe that things will be different tomorrow? Maybe better? Maybe it won’t be the same as it was before?” Then, with tears in her eyes she looked up and said, “The song is about hope.” I played the song again and one of the older women, who was sitting on the other side, got up, walked over, and took her hand… and they started dancing. Soon the flat, tired faces showed some smiles. Soon… more got up to dance. One of the nurses joined in. Suddenly there was laughter , connection, and some sense of joy in a mostly joyless place. And… a feeling of hope filled the room. Music for reflection. Music for empowerment. Music to create hope for a better tomorrow.
When There Is Nothing Left, We Still Have Music
The most profound work for me in the hospital is with patients at the end of life; providing music and comfort for them, and their families, as they are about to "transition." There is sadness and reflection, but there is also a sense of resolve, contentedness, and even joy in its own way. One of the most powerful moments for me happened a few years ago when someone said to me, after I provided music for their mother during her final moments, “You realize, that is the last music she will ever hear.” I will never forget the feeling that came over me when he said it. But also powerful are the connections that are created between the person leaving and the person saying goodbye.
When I walked into the quiet room, his adult daughter was sitting next to the bed holding his hand. She didn't hear me enter, so I gently said, "Hello." She looked up and gave a slight smile through pensive eyes. He was mainly non-responsive at this point, but seemingly comfortable—and very near the end. I offered some music, for comfort (thinking for both of them.) She again gave a slight smile and returned her gaze back to him. I started slowly on the guitar with a little 'soundscape' and eventually merged into a 'lullaby' version of ‘Can't Help Falling in Love’. As I started to sing, she snapped her head around and looked right at me with wide eyes, startling me enough to stop. A few tears glistened on her face. After a pause she said, "That song... He used to sing me to sleep to that song when I was a little girl." I caught my breath… and then I said, "Should I continue?" A nod "yes." She was still holding my eye contact but seemed a little unsure. So I asked, "Would you like to sing along?" Her voice was sweet, soft, and comforting. After a verse, I backed out vocally and became her accompanist as she looked at him and sang as she held his hand. It was now her turn to sing him to sleep.
The healing power of music.
(*The stories presented in this post are based on accounts or experiences and are not actual accounts or experiences.)

Raymond Leone MMT, MT-BC, is a board-certified music therapist based in Northern Virginia and writes extensively on music therapy and music and wellness.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

IMAGES
COMMENTS
In the present meta-analysis, we examine the overall effect of music therapy on stress reduction, accounting for differences in physiological and psychological stress-related outcomes, and we aim to gain more insight into study, sample, outcome and intervention characteristics that might moderate the effects of music therapy on stress reduction.
Conclusions A different effect of music therapy and music medicine on depression was observed in our present meta-analysis, and the effect might be affected by the therapy process.
The objective of this review was to summarize evidence for the effectiveness of music therapy (MT) and to assess the quality of systematic reviews (SRs) based on randomized controlled trials (RCTs).An SR of SRs based on RCTs.Studies were eligible if they ...
Abstract and Figures Music therapy is increasingly being used as an intervention for stress reduction in both medical and mental healthcare settings.
Journal of Music Therapy is a forum for authoritative articles of current music therapy research and theory, including book reviews and guest editorials. Journal of Music Therapy authors have the option to publish their paper under the Oxford Open initiative, whereby, for a charge, their paper will be made freely available online immediately ...
Results showed that singing improved verbal fluency and alleviated psychiatric symptoms and caregiver distress compared to lyric reading. Specifically, music therapy was more effective for cognitive measures in mild cases of AD but more effective for emotional and social measures in moderate to severe cases.
While research about music therapy is extensively available worldwide, relatively limited studies use bibliometric methods to analyze the global research about this topic. The aim of this study is to use the CiteSpace software to perform a bibliometric analysis of music therapy research from 2000 to 2019.
Abstract Music therapy is an evidence-based profession. Music therapy research aims to provide information about outcomes that support music therapy practice including contributing to theoretical perspectives that can explain why changes occur during treatment. Music therapy research has been conducted in a range of health, education, and community contexts throughout the world. Initially many ...
Music therapy and music medicine both exhibited a stronger effects of short and medium length compared with long intervention periods. Conclusions A different effect of music therapy and music medicine on depression was observed in our present meta-analysis, and the effect might be affected by the therapy process.
tween physiological signals and music, which can lead to improvements in music therapy. for mental health care and musicogenic epilepsy reduction (our long term goal). Keywords: psychological ...
It is also effective therapy for pain, reducing blood pressure, medicine for the heart, stroke, alzheimer, autism, speeds post-stroke recovery, chronic headaches & migraine remedy. Music boosts ...
Music interventions have been shown to be a potential alternative for depression therapy but the number of up-to-date research literature is quite limited. We present a review of original research trials which utilize music or music therapy as intervention to treat participants with depressive symptoms.
Looking for a good essay, research or speech topic on Music Therapy? Check our list of 80 interesting Music Therapy title ideas to write about!
Abstract Previous literature in music therapy suggests a need for greater clarity and insight concerning correlations between music and spirituality for the modern clinician. The purpose of this article is to provide a clear explanation of these correlations and some possible implications for the practice of music therapy. My method is one of 'reflective synthesis' - combining ...
Student Research Projects. Research activity is critical to the advancement of the music therapy profession as it enhances the understanding of music as unique human behavior and provides best practice guidelines for clinicians. The following list includes some of the outstanding student research projects that have been completed by music ...
The American Music Therapy Association produces two scholarly journals where research in music therapy is published and shared: The Journal of Music Therapyis published by AMTA as a forum for authoritative articles of current music therapy research and theory.
Improving Quality and Access: Music Therapy Research 2025 MTR2025 Launches at the AMTA Annual Conference - Originally published in Music Therapy Matters, December 2014. Improving Quality and Access: Music Therapy Research 2025, or simply "MTR2025," is an AMTA initiative, which is part of the Strategic Priority on Research.
Abstract Music is motivational, accessible and engaging for individuals with learning disabilities. Several systematic reviews have addressed the effects of music activity on people with learning disabilities; however, none has specifically reviewed the use of musical activity with people with profound and multiple learning disabilities.
Solberg, S. (2019). Neurologic music therapy to improve speaking voice in individuals with Parkinson's disease. Berry, A. (2019). A collaborative coalition: Action research response to a music therapy group for gender and sexual minority college students. Esposito, K. (2019).
Discussing Music Therapy: Reducing Stress, Health, and Social Care. Music Therapy for Delinquency Involved Juveniles through Tripartite Collaboration. Heidelberg Neuro Music Therapy Enhances Task-Negative Activity in Tinnitus Patients. Music Therapy for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Interesting Topics to Write about Music Therapy.
This paper introduces the effectiveness of music therapy in college students' mental health education and then puts forward some important methods to promote the implementation of music therapy in college students' mental health education. This paper is divided into four sections.
Recent research suggests that music engagement not only shapes our personal and cultural identities but also plays a role in mood regulation. 1 A 2022 review and meta-analysis of music therapy found an overall beneficial effect on stress-related outcomes. Moreover, music can be used to help in addressing serious mental health and substance use disorders. 2 In addition to its healing potential ...
Music research papers provide an opportunity for students to explore various aspects of music, including its history, theory, cultural significance, and impact on society. Choosing an appropriate topic for your music research paper is crucial as it sets the foundation for your study.
One of the great things about my job as a music therapist working in a hospital is that I learn something on an almost daily basis. And I learn all of these things from the people I share music ...