

Easy Guide to Questions in Simple Past with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
English language proficiency entails a clear understanding of the various tenses, one of which is the Past Simple tense. This tense, as the name implies, is employed when discussing actions completed in the past. Among its most intriguing aspects are the ways to form questions. This article aims to explore and simplify the intricacies of forming questions in Past Simple tense.
Pn this page:
Understanding the Past Simple
The Past Simple tense , also referred to as the Simple Past, is used to express completed actions that took place at a specific time in the past. These actions can range from recent activities (e.g., “I ate breakfast an hour ago”) to historical events (e.g., “The Romans invaded Britain in AD 43”).
How To Form Past Tense Questions
Creating interrogative sentences or questions in the Past Simple involves a certain degree of finesse and understanding. The typical structure of such questions is as follows:
‘Did’ + subject + base form of the verb + …?
For example:
- Did you finish your homework last night?
- Did she pass her driving test?
- Did we forget to turn off the lights before we left?
- Did they enjoy the picnic yesterday?
- Did it rain while you were at the beach?
- Did John and Lisa arrive on time for the dinner?
- Did you see the latest episode of that show?
- Did the meeting end early?
- Did you buy groceries on your way home?
- Did they win the football match yesterday?
- Note that ‘did’ is used for all subjects – I, you, we, they, he, she, it. Also, no matter what the subject is, the verb stays in its base form.
How To Form Negative Past Tense Questions
Negative questions in the Past Simple follow a slightly different formula:
‘Didn’t’ + subject + base form of the verb + …?
- Didn’t you have lunch already?
- Didn’t they see the movie last week?
- Didn’t she pass her driving test?
- Didn’t we have a meeting scheduled for today?
- Didn’t it rain during the concert?
- Didn’t John and Lisa attend the party?
- Didn’t you visit the museum when you were in Paris?
- Didn’t the dog bark when the postman arrived?
- Didn’t you like the new restaurant we tried?
- Didn’t they live in Chicago last year?
These questions are often used to express surprise or disbelief or to seek confirmation of what we believe to be true.
WH Questions in Simple Past Tense
When forming questions with wh- words (who, what, where, when, why, how) in Past Simple, the structure changes slightly:
Wh- word + ‘did’ + subject + base form of the verb + …?
- What did you do last weekend?
- Where did they go on their vacation?
- When did she finish her project?
- Why didn’t you come to the party last night?
- Who did you meet at the conference?
- How did John fix the computer so quickly?
- Which book did you choose for the book club?
- Why didn’t they take the train to work yesterday?
- What did you eat for dinner last night?
- When did they move to their new house?
For questions involving the subject of the action, ‘did’ is typically omitted: Who broke the window?Who made the cake?In these cases, the ‘who’ takes the place of the subject.
Yes or No Questions in Past Simple
The above type of question is also known as ‘Yes or No’ question because the answer to such a question is often ‘yes’ or ‘no’. For example:
- Did you watch the football match yesterday? Yes, I did.
- Did she take her medicine this morning? No, she didn’t.
- Did they go to the concert last night? Yes, they did.
- Did we have any homework for English class? No, we didn’t.
- Did it rain during your picnic? Yes, it did.
- Did you like the new Italian restaurant downtown? Yes, I did.
- Did the dog eat all its food? No, it didn’t.
- Did you remember to lock the car? Yes, I did.
- Did the parcel arrive on time? No, it didn’t.
- Did they pass their driving tests? Yes, they did.
The Past Simple tense is a fundamental part of English grammar, and understanding its rules is vital for forming accurate and meaningful sentences. Creating questions in the Past Simple may seem daunting at first, but with knowledge and practice, it becomes second nature. It’s crucial to remember the basic structure, the role of ‘did’ as an auxiliary verb, and how wh- words can affect the sentence structure.
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

What did you do last night? The Simple Past Tense in English
- Post author: Language Garage
- Post published: April 30, 2024
- Post category: English / Grammar / Verbs
Image by rohatcom68 from Pixabay
English has a few different ways to talk about things that happened in the past. In this post, we’re going to look at the most common tense that’s used, the simple past ( went , did , lived , worked , etc.):
- We heard a great DJ last night.
- I woke up very early this morning.
- She did n’t work yesterday.
- Did you see Bill last week?

Forming the Simple Past Tense
Most English verbs form their past tense regularly, just by adding – ed . But a lot of the most common verbs are irregular. We won’t cover all of the details here, but if you’re interested, there are sections at the end of this post that give you a lot of details around spelling, pronunciation, and irregular forms. For now, just keep in mind a few quick points:
- Regular verbs add – ed : talk > talked ; smile > smiled ; upload > uploaded
- The – ed ending can be pronounced /t/ as in talked , /d/ as in smiled , or /id/ as in uploaded . There are predictable rules below explaining this, which we cover below.
- There are some minor spelling changes to keep in mind, for example: just add – d to verbs that end in a vowel ( bake > baked ), change – y to – i if – y followed a consonant ( study > studied ) but not if – y follows a vowel ( stay > stayed ). If the verb ends in a single consonant in a stressed syllable, double it ( stop > stopped ; refer > referred ), but don’t double it if the syllable is unstressed ( travel > traveled ), at least not in American English.
- Irregular verbs usually involve vowel changes ( take > took ; eat > ate ), and there are several typical patterns, but irregulars must be memorized. We divide them into categories and cover each one below.
Uses of the Simple Past Tense
The simple past tense is used to express a state or action that happened in the past. Often, but not always, you’ll see a past time adverbial used along with the simple past tense, for example yesterday , last week , last year , in 2001 , and so on. The time adverbials are all underlined in these examples:
- I worked out and went for a run yesterday .
- The DJ was amazing last night .
- They had dinner and saw a movie last week .
- Bob and John got a new apartment last month .
- The family moved to Chicago in 2001 .
- From 2004 to 2016 I lived in Los Angeles
- Barack Obama was president of the US in 2011 .
- My family had two dogs when I was a child .
- Before coming to Venice , we visited Rome.
Of course, it isn’t necessary for a sentence with the simple past tense to include a time adverbial. In these cases, it’s understood from context or common knowledge that the action happened in the past.
- Jill met David at a party.
- We bought our car at this dealership.
- I heard a really cool new DJ.
- Mary went to college in a small town in Vermont.
- Vikings were the first Europeans who came to North America.
There are other past tenses that are used in English, so it’s important to contrast the simple past tense with those other tenses in order to better understand when and how to use the simple past.
Complete each sentence with the simple past tense of the verb in parentheses.
- We _____ for hours about the film after seeing it. (talk)
- I ____ home all night. (be)
- She _____ for that company for over ten years. (work)
- Sam and Linda _____ their house about five years ago. (buy)
- We _____ dinner late last night. (eat)
- Peter last _____ his family about three months ago. (see)
- She _____ her resume. (upload)
- They _____ history together in college. (study)
- I _____ dinner for some friends. (make)
- Yuming _____ Chinese as a child. (speak)
Answers: 1. talked; 2. was; 3. worked; 4. bought; 5. ate; 6. saw; 7. uploaded; 8. studied; 9. made; 10. spoke
Contrast 1: The Simple Past and the Present Perfect
Notice something very important about time adverbials like yesterday , last week , last year , and in 2001 . They are all closed , meaning that they are finished and over . ( Yesterday is over; it’s today now. Last week is over, it’s this week now, 2001 is over, and so on.) This is important because English only uses the simple past in cases when the time frame is over/complete/finished. If the time frame is open or unfinished, especially if there’s an effect on the present or the possibility of continued action, the present perfect ( have done , have eaten , have worked ) is used instead. Compare:
- I worked five days last week. Today is Wednesday, so I have worked three days this week. (I’ll probably work two more days.)
- Bill saw four movies last month. Bill has only seen one movie this month. (Maybe he’ll see more, maybe he won’t.)
- Sandra ate three meals yesterday. It’s 2pm, so she’s only eaten two meals so far today. (She’ll probably eat dinner, too.)
- I saw my family five or six times last year. I haven’t seen this yet this year. (Hopefully I will.)
The adverb yet means “up until now” or “so far,” so it refers to an open/unfinished time frame. For this reason, you always use the present perfect (and not the simple past) with yet . Yet is usually used in questions or negatives. In affirmative statements or answers, use already .
- Have you eaten yet? Yes, I’ve (already) eaten, so I’m not hungry.
- Have the students all finished their term papers yet? No, they haven’t all finished their terms papers yet.
- Has Sam met your brother yet? Yes, Sam has (already) met my brother.
Notice though that if you introduce a completed or finished time frame in the answer to a question in the present perfect, you must use the simple past.
- Have you eaten yet? Yes, I have. I ate earlier today. I’m not hungry.
- Have the students all finished their term papers yet? Yes, they have. They all finished their papers last week.
- Has Sam met your brother yet? Yes, he has. They met at a party last month.
The adverb ever usually refers to open/unfinished time frames, something along the lines of “at any time during your life.” When it has this meaning, you always use the present perfect instead of the simple past. You’ll sometimes hear ever paired with before .
- Have you ever visited Thailand?
- Has John ever seen your new apartment?
- Have you ever been seriously ill before?
- Have you ever eaten Georgian food before?
Ever is only used in questions. In negative statements, use not ever or never . In affirmative statements, you don’t need to use any adverb, but you may hear before .
- Have you ever visited Thailand? No, I’ve never visited Thailand. Yes, I have visited Thailand.
- Has John ever seen your new apartment? No, he hasn’t ever seen my new apartment.
- Have you ever been seriously ill? Yes, I’ve been seriously ill before.
- Have you ever eaten Georgian food before? Yes, I’ve eaten Georgian food before. It’s delicious.
There is one situation where it’s correct to use the simple past with ever (or not ever / never ), and it makes perfect sense if you keep in mind that the simple past is used with closed or finished time frames. Imagine a situation where you expected your friend to call her brother at some point last week. There was no specific time other than “at any point last week.” In this case, you could ask:
- Did you ever call your brother (last week)? No, I never called him. / No, I didn’t ever call him. Yes, I called him last Wednesday evening.
This has the same meaning of ever that we saw earlier, at any time , but now ever is in a closed time frame, last week . Compare:
- Have you ever eaten sushi? (in your entire life) Yes, I’ve eaten sushi before. No, I’ve never eaten sushi.
- Did you ever eat sushi at that new Japanese restaurant you wanted to go to last month? Yes, I ate sushi there last month like I said I would. No, I never ate sushi there (last month). Maybe I’ll go this month.
Choose the simple past or the present perfect.
- I (haven’t eaten/didn’t eat) yet today.
- When (have you met/did you meet) your husband?
- It’s only Tuesday, but it feels like I (have worked/worked) for the entire week.
- We (have gone/went) to Tokyo three years ago.
- (Have you ever gone/Did you ever go) to South America?
- Yes, we (have gone/went) to Brazil and Argentina about ten years ago.
- Do you remember that book you were meaning to buy? (Have you ever bought/Did you ever buy) it?
- I (have read/read) that book when I was in college. It’s fantastic.
- So far, I (have only read/only read) about half of it, but I like it a lot.
- How many times (have you seen/did you see) that film?
Answers: 1. haven’t eaten; 2. did you meet; 3. have worked; 4. went; 5. Have you ever gone; 6. went; 7. Did you ever buy; 8. read; 9. have only read; 10. Both are possible. Probably “have you seen” is the better answer, assuming that it’s a film that the listener really likes and may see again. But “did you see” is also possible if you’re talking about a finished time, for example when the listener was a child.
Contrast 2: The Simple Past and the Past Progressive
Most often, the simple past refers to a “point” action in the past. For example, imagine that you have a timeline with a line in the middle representing now . The right is the future, and the left is the past. You would represent most actions expressed in the simple past as a simple point, represented with the red X.
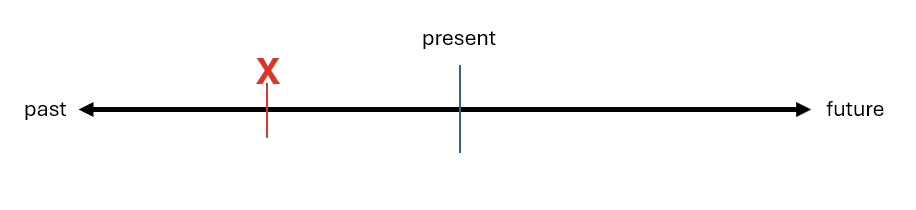
Each of the actions or states in these examples could be represented as that red X:
- I ate breakfast early today.
- She left work late last night.
- I met my wife in 2006.
- He wrote his first book in 1948.
The point doesn’t have to literally last a moment, it can last for quite a long time, as long as that amount or span of time is thought of a completed and finished point.
- I worked from 10am until 7pm yesterday. (Here, the point lasts nine hours.)
- They lived in San Francisco from 1995 until 2017. (This point lasts 22 years!)
- Dinosaurs ruled the Earth for millions of years. (This is a much longer point!)
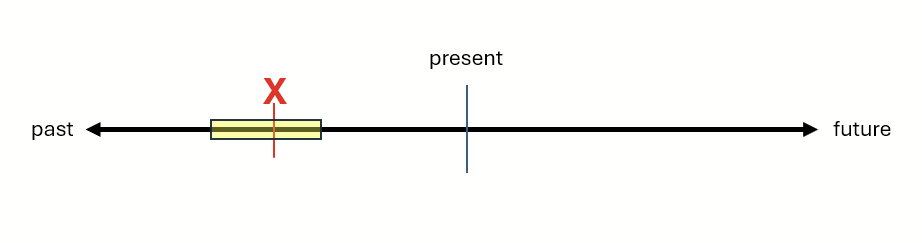
If there’s a background action happening when that point occurs, a bit like scenery on a stage behind where the action takes place, English uses the past continuous (or past progressive): was/were doing , going , sleeping , etc.. Take a look at these examples:
- We were eating dinner when the phone rang.
- We were eating dinner when someone knocked at the door.
- We were eating dinner when the game started.
In each of these examples, there are point actions: the phone rang , someone knocked at the door , and the game started . And there’s one background action happening in all three cases: we were eating dinner . If we think of this as a timeline, we would have a simple past point, and then a longer-lasting past progressive. The red X is again the simple past, and the yellow, longer-lasting event is the past progressive, representing the time when we were eating dinner in those three examples.
Complete the sentences with the simple past or past progressive of the verb in parentheses.
- I (work) at a restaurant when they (offer) me this new job.
- I (get) a phone call when we (ate) dinner.
- When no one (look) the child (eat) all the cookies.
- Bill (run) into an old friend while he (wait) in line at the supermarket.
- Meagan’s parents (sleep) when she (get) home last night.
- It (rain) when I (wake) up this morning.
Answers: I worked at a restaurant when they offered me this new job. 2. I got a phone call when we were eating dinner. 3. When no one was looking the child ate all the cookies. 4. Bill ran into an old friend while he was waiting in line at the supermarket. 5. Meagan’s parents were sleeping when she got home last night. 6. It was raining when I woke up this morning.
Contrast 3: The Simple Past and the Past Perfect
If there are two actions or states that happened in the past, and it’s important to stress that one happened BEFORE the other, use the past perfect ( had done , had eaten , had worked ) to express the first, earlier action.
- Bill had visited Paris in 2013 before he visited Madrid in 2015.
- Mary had graduated from college before she started grad school.
- We had just started to eat when the phone rang.
The past perfect is very often completely optional. It’s perfectly fine to say:
- Bill visited Paris in 2013 before he visited Madrid in 2015.
- Mary graduated from college before she started grad school.
- We started to eat, and the phone rang.
Use the past perfect only when you need to, in order to stress or emphasize that one action (had) happened before another one happened.
Did in the Simple Past Tense
In the simple present tense, do (or does ) is used in negatives and questions, or in short answers and short forms.
- Does she speak French? –Yes, she does . –No, she doesn’t .
- She doesn’t speak French.
- She speaks French better than he does .
In the past, simply use did instead of do or does .
- Did she live in Paris? –Yes, she did . –No, she didn’t .
- She didn’t live in Paris.
- She lived in Paris for longer than he did .
Make sure you use the basic form of the verb after did . In other words, don’t say “Did she lived in Paris?” or “She didn’t lived in Paris.”
Regular Verbs in the Past Tense
There are only a few things to keep in mind about regular verbs in the past tense. First, there are three different pronunciations for the – ed ending, but they’re completely predictable based on the ending of the verb.
| | | |
And there are also a few spelling rules to remember when adding – ed .
- To most verbs, just add – ed. walk > walked, add > added, look > looked
- If the verb ends in -e , just add -d. bake > baked, smoke > smoked, love > loved
- If the verb ends in consonant + y , change the y to i and then add -ed . try > tried, dry > dried, study > studied
- If the verb ends in vowel + y , just add -ed . stay > stayed, enjoy > enjoyed, obey > obeyed
- If the verb is one syllable and ends in a consonant, double the consonant and add -ed. stop > stopped, bat > batted, sip > sipped
- If the verb has more than one syllable and ends in a consonant, only double the consonant if the stress is on the last syllable. refer > referred, prefer > preferred, entrap > entrapped
- If the verb has more than one syllable and ends in a consonant, don’t double the consonant if the last syllable is not stressed, at least not in American English. cancel > canceled, travel > traveled, label > labeled
Irregular Verbs in the Past Tense
A lot of very common verbs in English have irregular (or “strong”) simple past forms. These usually involve a vowel change, but there are a few other types of changes – including none at all – that you should know about. In this section we’ll divide irregular verbs into categories based on how they change in the past tense. These changes are grouped by pronunciation, not spelling. In just a few cases, the spelling is irregular.
A. Completely Different Words
be > was, were go > went
B. No Change
beat > beat bet > bet burst > burst cast > cast ( broadcast , forecast ) cost > cost cut > cut fit > fit hit > hit hurt > hurt let > let put > put quit > quit set > set shed > shed shut > shut split > split spread > spread
C. Vowel + Consonant Change or Other Changes
bend > bent build > built burn > burnt can > could creep > crept deal > dealt dream > dreamt (or dreamed ) feel > felt flee > fled hold > held keep > kept kneel > knelt have > had hear > heard lean > leant (or leaned ) leave > left lend > lent lose > lost make > made mean > meant say > said see > saw send > sent sleep > slept spend > spent sweep > swept weep > wept
D. /eh/ as in f e ll
bleed > bled breed > bred fall > fell feed > fed lead > led meet > met read > read
E. /ō/ as in br o ke
arise > arose awake > awoke break > broke choose > chose drive > drove freeze > froze ride > rode rise > rose sell > sold shine > shone speak > spoke steal > stole tell > told wake > woke write > wrote
F. /a/ as in beg a n
begin > began drink > drank ring > rang run > ran shrink > shrank sing > sang sink > sank sit > sat spit > spat spring > sprang stink > stank swim > swam
G. /ā/ as in bec a me
become> became come > came eat > ate forbid > forbade forgive > forgave give > gave lay > laid lie > lay (as in to recline , lie as in to tell an untruth is regular lied .) make > made pay > paid
H. – ought or – aught
bring > brought buy > bought catch > caught fight > fought seek > sought teach > taught think > thought
I. /i/ as in d i d
bite > bit do > did hide > hid light > lit slide > slid
J. /oo/ as in t oo k
shake > shook stand > stood take > took understand > understood
K. /ew/ as in bl ew
blow > blew draw > drew fly > flew grow > grew know > knew throw > threw
L. /uh/ as in h u ng
cling > clung dig > dug hang > hung spin > spun stick > stuck sting > stung strike > struck swing > swung win > won
M. /ore/ as in wore
bear > bore swear > swore tear > tore wear > wore
N. /ou/ as in f ou nd
bind > bound find > found grind > ground wind > sound
O. /o/ as in g o t
forget > forgot get > got lose > lost shoot > shot

Learn English with the Language Garage!
If you’re interested in ESL/EFL lessons, please check out o ur English courses . We have private lessons, lessons for you and a friend or colleague, or small groups. Or see our other posts on English grammar, vocabulary, and more.
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window
You Might Also Like

Would you like some tea? Sí or si, tú or tu?

The Preposition de in Brazilian Portuguese

How to Say “And” in Japanese
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Which is the right response for the question "Did you do your homework?"
I am trying to refresh my grammar and I want to remember what was the right past tense for this question
Did you do your homework? Yes I did it Yes I have done it Yes I had done it
Which is correct and when should I use others ?
3 Answers 3
“Yes, I did it” is the right answer to “Did you do your homework?”. But it would be more likely for the question to be “Have you done your homework?”, to which the answer is “Yes, I have done it” (or in speech, nearly always “Yes, I’ve done it”).
The difference is that “Did you do your homework?” is asking about the past —— did you, at some time in the past, do your homework? “Have you done your homework?” is asking about the present situation — are you, right now, in a state of having done your homework?
- I think "Did you do your homework?" would be idiomatic in American English, but I'll leave it to the Americans to suggest what the natural reply would be. – Kate Bunting Commented Sep 9, 2020 at 7:52
Yes I did it
Yes I have done it
are correct and good responses to the question. It would be normal to reflect the form of the question, so if asked "Did you do your homework?" you would normally say "Yes, I did it." If asked "Have you done your homework?" (which means the same thing) you would answer "Yes, I have done it."
"Yes I had done it" is pluperfect tense and incorrect here.
Did you do your homework?
Have you done your homework?
Yes I have.
You must log in to answer this question.
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- Is it safe to carry Butane canisters bought at sea level up to 5500m?
- How should Form 990: Part IV Question 3 be answered?
- Documents hardware engineers should write and prepare
- How do you establish a relationship on a library such that a breaking change in the library forces an update on all dependencies?
- Optimal Algorithm to Append and Access Tree Data
- When does bundling wire with zips become a problem?
- Why do decimal reciprocals pair to 9?
- What to do if sample size obtained is much larger than indicated in the power analysis?
- Problem with enumeration in Texlive 2023
- Is there a law against biohacking your pet?
- Is there an efficient way to extract a slice of a 3d array?
- Are "lie low" and "keep a low profile" interchangeable?
- Finding a Linear Algebra reading topic
- What does "off" mean in "for the winter when they're off in their southern migration breeding areas"?
- Derivation in Robert Solow's "A Contribution to the Theory of Economic Growth"
- Why would an incumbent politician or party need to be re-elected to fulfill a campaign promise?
- Keeping the actual bottom bracket/crankset while increasing the chainring size
- Polynomials with rational roots
- Can You Build a Propeller or Airfoil for a Higgs Field?
- LED lights tripping the breaker when installed on the wrong direction?
- Are epochs the same as data duplication?
- What if something goes wrong during the seven minutes of terror?
- Does a Way of the Astral Self Monk HAVE to do force damage with Arms of the Astral Self from 10' away, or can it be bludgeoning?
- Tipped Wages: What is a Tip
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Grammar: When to Use Do, Does, and Did

- 3-minute read
- 12th August 2022
Verbs are essential to creating complete sentences, as they help us express physical actions ( She jumped in the puddle) , mental actions ( He thought about puppies) , and states of being ( I am hungry) .
There are several types of verbs that can each be written in different tenses, so they can be tricky to work with, especially if English isn’t your first language . We’ve put together a guide to help you use one of the most common verbs, do , in your writing . Read on below to learn more!
Action Verbs
As the name suggests, action verbs are used to express actions completed by the subject of a sentence. The base verb do is conjugated according to the tense:
1. Present Tense
In the present tense, do takes the form do or does, depending on the subject:
| Subject: | Verb: |
| I/you/we/they | Do |
| He/she/it | Does |
Consider the following examples:
We do our homework every night.
She does her homework every night.
2. Past Tense
In the simple past tense , the base verb do takes the form did with all subjects:
| Subject: | Verb: |
| I/you/we/they | Did |
| He/she/it | Did |
We did our homework last night.
She did her homework last night.
Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary , or helping verbs, are used with another base verb to create negative sentences, questions, or add emphasis. Here’s how do should be used as an auxiliary verb:
1. Negative Sentences
Following the same subject–verb pairings introduced above, we combine the auxiliaries do , does , and did with the adverb not to create negative sentences:
We do not do our homework every night.
She did not do her homework last night.
Note that we can combine the auxiliary and the adverb to create the contractions don’t , doesn’t , and didn’t . You simply remove the space between the two words and replace the letter o in not with an apostrophe (’).
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Contractions are more common in conversations and informal writing and typically shouldn’t be used in formal writing (e.g., academic or business).
2. Questions
To create questions, the auxiliary is combined with the infinitive of another verb in this way: auxiliary verb + subject + infinitive verb .
● Simple present questions:
Do they sell children’s books?
Does he speak English?
Note that the third person verb speaks isn’t spelled with the s when paired with the auxiliary to form a question.
● Simple past questions:
Did you buy anything at the bookstore?
Did he learn how to speak English?
Note that did indicates the past tense, so the main verbs don’t also take the past tense (i.e., bought and learned ).
3. Emphasis
In positive sentences, we can also combine the auxiliaries do , does , and did with the main verb to emphasize that something is true:
We do sell children’s books.
He did learn to speak English.
Try saying these sentences aloud and adding emphasis to the auxiliary terms with your tone. It adds a dramatic effect!
Proofreading and Editing Services
Hopefully, this guide will help you feel more confident when using different forms of the verb do in your writing. If you’re still learning or want to be sure your work is error-free, our editors are ready to help. You can upload a free trial document today to learn more!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
" Did you were at home ? " or "Were you at home ?" [closed]
I don't know when I should use " Did you were... " and when I should use " Were you... ". For example, Why do we say:
" Were you at home last night? "
" Did you were at home last night? "
- simple-past
- A more challenging question—because it doesn't involve running afoul of grammatical rules governing how to indicate that something happened in the past without over-identifying it as past—might be "Why isn't 'Did you be at home?' a standard alternative way of inquiring about whether someone was at home at a particular time in the past?" – Sven Yargs Commented Dec 20, 2015 at 19:36
You would never use "Did you were" in proper English, because "did" is the past tense of "do," a verb. Example: "I did my homework last night." Also, you could correctly ask, "Did you stay home last night?" instead of "Were you home last night?" Both are acceptable usage.
- I agree with Mark. I've never heard "Did you were" used in informal/idiomatic English, either. I would call that a grammatical error. – Duncan C Commented Dec 20, 2015 at 20:43
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged past-tense simple-past or ask your own question .
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- VerificationTest leaks message?
- John 1:1, "the Word was with God, and the Word was God." Vs2, He was in the beginning with God. Does this not prove Jesus existed before Genesis 1:1?
- Why would an incumbent politician or party need to be re-elected to fulfill a campaign promise?
- Optimal Algorithm to Append and Access Tree Data
- Very old fantasy adventure movie where the princess is captured by evil, for evil, and turned evil
- Who is affected by Obscured areas?
- Can You Build a Propeller or Airfoil for a Higgs Field?
- Definition of the electric field
- Move line matching string to top of the file
- Venus’ LIP period starts today, can we save the Venusians?
- How can I prove both series are equal?
- What is the meaning of the biblical term "divine nature", and what does it tell us about the biblical use of the title "God"?
- Font showing in Pages but not in Font book (or other apps)
- Could a gas giant still be low on the horizon from the equator of a tidally locked moon?
- Choosing a relative large density subsequence from a low density sequence
- Why is the identity of the actor voicing Spider-Man kept secret even in the commentary?
- Is my encryption format secure?
- Derivation in Robert Solow's "A Contribution to the Theory of Economic Growth"
- How to read data from Philips P2000C over its serial port to a modern computer?
- False Color Objects by Size
- Is math a bad discipline for teaching jobs or is it just me?
- Did the United States have consent from Texas to cede a piece of land that was part of Texas?
- Finding a Linear Algebra reading topic
- Will all orbits emitting gravitational waves inevitably coalesce?
Learn American English Online
UPDATED DAILY








COMMENTS
For example: Did you finish your homework last night? Did she pass her driving test? Did we forget to turn off the lights before we left? Did they enjoy the picnic yesterday? Did it rain while you were at the beach? Did John and Lisa arrive on time for the dinner? Did you see the latest episode of that show? Did the meeting end early?
Using the simple past ("did you do your homework") in situations that actually call for the present perfect ("have you done your homework", because the enquirer wishes to know if the person's homework is now done) is especially common in American English.
The simple past tense is used to express a state or action that happened in the past. Often, but not always, you'll see a past time adverbial used along with the simple past tense, for example yesterday, last week, last year, in 2001, and so on. The time adverbials are all underlined in these examples:
Good vs. Well Noun Clause Do Vs. Does Grammar - First Conditional Family Vocabulary Uncountable Nouns Adverbial Clauses Adverbs, Infinitives, Definite Article Verb Patterns / Ing Other quiz:
1 "Yes, I did it" is the right answer to "Did you do your homework?". But it would be more likely for the question to be "Have you done your homework?", to which the answer is "Yes, I have done it" (or in speech, nearly always "Yes, I've done it").
Here's how do should be used as an auxiliary verb: 1. Negative Sentences. Following the same subject-verb pairings introduced above, we combine the auxiliaries do, does, and did with the adverb not to create negative sentences: We do not do our homework every night. She did not do her homework last night.
2 You would never use "Did you were" in proper English, because "did" is the past tense of "do," a verb. Example: "I did my homework last night." Also, you could correctly ask, "Did you stay home last night?" instead of "Were you home last night?" Both are acceptable usage. Share Improve this answer answered Dec 20, 2015 at 19:04 Mark Hubbard
Do (present tense) and Did (past tense)as Helping Verbsto Make Negative Sentences. The verb "do" is a helping verb. We add it to the simple form of a verb to make questions and negatives in the present tense and the past tense. I don't work on the weekend. (present tense negative).
E.g.: I had finished my homework by 8 o'clock last night. Both sentences are syntactically incorrect, i.e. the word order is not respected. You have two options: 1) to use a comma for emphasis: At 8 o'clock last night, I was doing my homework; 2) to put the whole adverbial phrase after the object: I was doing my homework at 8 o'clocklast night.
A : __________ you doing your homework at six o'clock last night? B: Yes,I ___. A. Was / weren't B. Were / wasn't C. Was / were D. Were / was Select your answer: Next Quiz > Random Topics: Comparative Adjective Despite, In Spite Of, Although, Even Though, However Irregular Verb Wish clause Grammar - direct/indirect objects Adverbs of Frequency & Simple Present Tense Wish + Verb 2 Passive ...
A. a gerund. B. an infinitive phrase. C. a prepositional phrase. D. an adverb. How to use : Read the question carefully, then select one of the answers button. About grammarquiz.net. GrammarQuiz.Net - Improve your knowledge of English grammar, the best way to kill your free time. What did you (do) ______ last night?
Simple past tense (past simple tense) is a verb tense that describes completed actions or past habits before now. It is also used to talk about a series of events in the past. "Did" is the helping verb of simple past tense. For affirmative (positive) sentences we use past simple form of a verb.
Past simple - questions We can use past simple questions to ask about the past. Did you have fun with your friends yesterday? Where did she go for her last holiday? What did they watch on TV last night?
The Verb to do: do, does and did The words do, does and did often cause confusion in the English language. They are all forms of the verb to do. The verb to do can be used as an action verb and also as an auxiliary verb. Write better and faster Ginger helps you write confidently.
Reported Questions 1 Make reported questions. Use 'she asked me' at the beginning of each answer. It's the same day, so you don't need to change the time expressions.
Past simple - negatives and questions. We use 'did' or 'didn't' in past simple negatives and questions. A1 - Elementary English grammar and exercises.
I ___do my homework last night. A. not could. B. didn´t can. C. couldn´t. D. can´t. Select your answer: Next Quiz >. Random Topics: Conditional Sentence Type 1 Too / Very / So Interrogative Pronoun Transitional Words Third Conditional Will and Will not Describing Words Present Continuos Tense Wish, Unless, If sentence.
Jan 21, 2014. #2. "What were you doing at (a specific time)?" is certainly much more common. The simple past would be appropriate in some contexts. For example: A: So, at 5:30, I ate dinner. At 6:00, I did the dishes. At 6:30, I watched the news on television.
Is 'Did you do your homework last night' an interrogative? - Answers Subjects > Arts & Entertainment > English Language Arts Yes, it is asking a question.
The aim of this lesson is to introduce students to the simple past.
I don't have the ability to do homework as I am a computer program designed to provide information and assistance. How can I help you with your homework? Resources Leaderboard All Tags Unanswered