

How to write an essay: Body
- What's in this guide
- Introduction
- Essay structure
- Additional resources
Body paragraphs
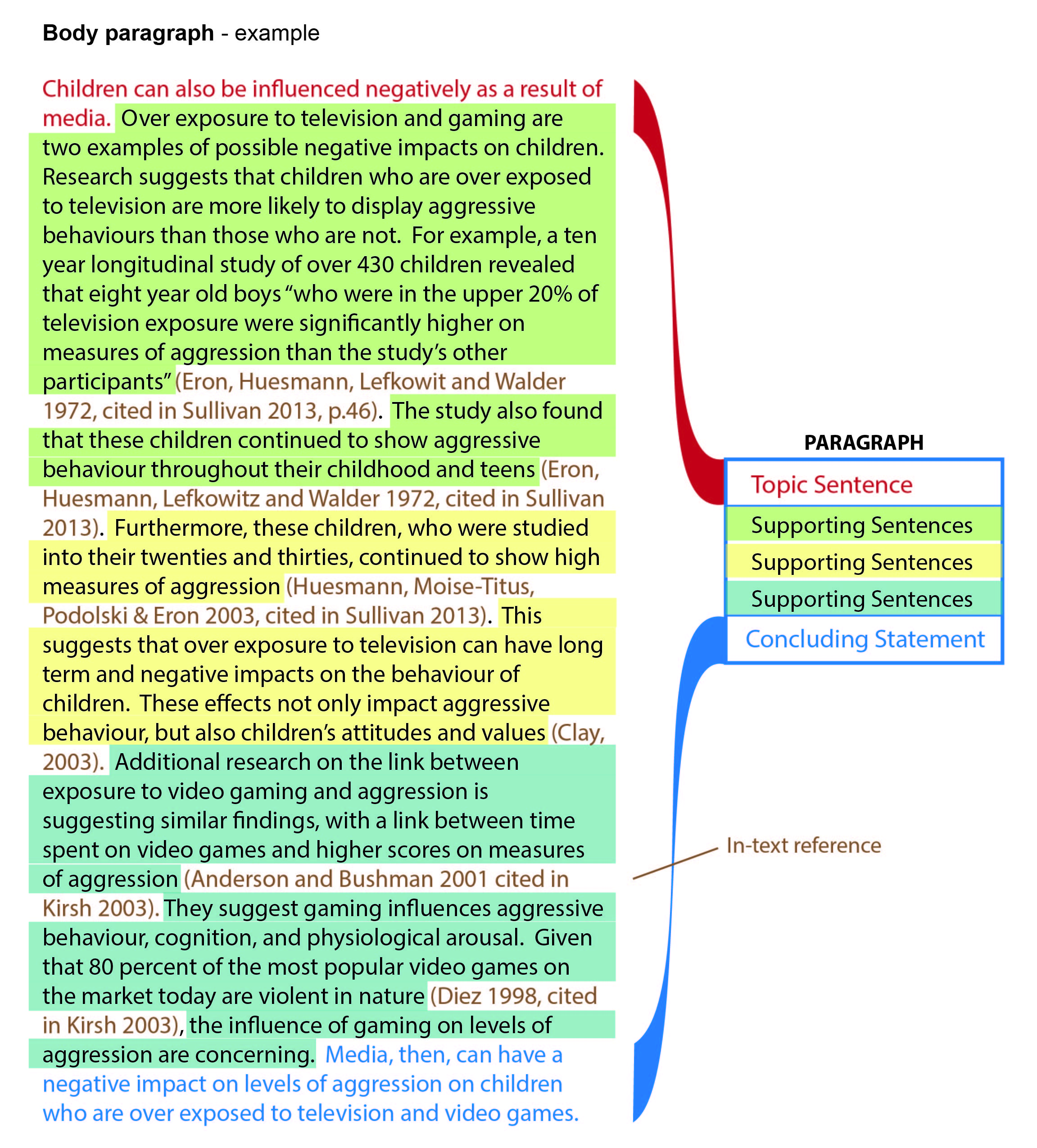
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly.
Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence . This lets the reader know what the paragraph is going to be about and the main point it will make. It gives the paragraph’s point straight away. Next – and largest – is the supporting sentences . These expand on the central idea, explaining it in more detail, exploring what it means, and of course giving the evidence and argument that back it up. This is where you use your research to support your argument. Then there is a concluding sentence . This restates the idea in the topic sentence, to remind the reader of your main point. It also shows how that point helps answer the question.
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay

TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution.
Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis.
- picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph
Essay writing: Main body
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- Analysing questions
- Planning & drafting
- Revising & editing
- Proofreading
- Essay writing videos
Jump to content on this page:
“An appropriate use of paragraphs is an essential part of writing coherent and well-structured essays.” Don Shiach, How to write essays
The main body of your essay is where you deliver your argument . Its building blocks are well structured, academic paragraphs. Each paragraph is in itself an individual argument and when put together they should form a clear narrative that leads the reader to the inevitability of your conclusion.
The importance of the paragraph
A good academic paragraph is a special thing. It makes a clear point, backed up by good quality academic evidence, with a clear explanation of how the evidence supports the point and why the point is relevant to your overall argument which supports your position . When these paragraphs are put together with appropriate links, there is a logical flow that takes the reader naturally to your essay's conclusion.
As a general rule there should be one clear key point per paragraph , otherwise your reader could become overwhelmed with evidence that supports different points and makes your argument harder to follow. If you follow the basic structure below, you will be able to build effective paragraphs and so make the main body of your essay deliver on what you say it will do in your introduction.

Paragraph structure

- A topic sentence – what is the overall point that the paragraph is making?
- Evidence that supports your point – this is usually your cited material.
- Explanation of why the point is important and how it helps with your overall argument.
- A link (if necessary) to the next paragraph (or to the previous one if coming at the beginning of the paragraph) or back to the essay question.
This is a good order to use when you are new to writing academic essays - but as you get more accomplished you can adapt it as necessary. The important thing is to make sure all of these elements are present within the paragraph.
The sections below explain more about each of these elements.

The topic sentence (Point)
This should appear early in the paragraph and is often, but not always, the first sentence. It should clearly state the main point that you are making in the paragraph. When you are planning essays, writing down a list of your topic sentences is an excellent way to check that your argument flows well from one point to the next.

This is the evidence that backs up your topic sentence. Why do you believe what you have written in your topic sentence? The evidence is usually paraphrased or quoted material from your reading . Depending on the nature of the assignment, it could also include:
- Your own data (in a research project for example).
- Personal experiences from practice (especially for Social Care, Health Sciences and Education).
- Personal experiences from learning (in a reflective essay for example).
Any evidence from external sources should, of course, be referenced.

Explanation (analysis)
This is the part of your paragraph where you explain to your reader why the evidence supports the point and why that point is relevant to your overall argument. It is where you answer the question 'So what?'. Tell the reader how the information in the paragraph helps you answer the question and how it leads to your conclusion. Your analysis should attempt to persuade the reader that your conclusion is the correct one.
These are the parts of your paragraphs that will get you the higher marks in any marking scheme.

Links are optional but it will help your argument flow if you include them. They are sentences that help the reader understand how the parts of your argument are connected . Most commonly they come at the end of the paragraph but they can be equally effective at the beginning of the next one. Sometimes a link is split between the end of one paragraph and the beginning of the next (see the example paragraph below).
Paragraph structure video
Length of a paragraph
Academic paragraphs are usually between 200 and 300 words long (they vary more than this but it is a useful guide). The important thing is that they should be long enough to contain all the above material. Only move onto a new paragraph if you are making a new point.
Many students make their paragraphs too short (because they are not including enough or any analysis) or too long (they are made up of several different points).
Example of an academic paragraph
Using storytelling in educational settings can enable educators to connect with their students because of inborn tendencies for humans to listen to stories. Written languages have only existed for between 6,000 and 7,000 years (Daniels & Bright, 1995) before then, and continually ever since in many cultures, important lessons for life were passed on using the oral tradition of storytelling. These varied from simple informative tales, to help us learn how to find food or avoid danger, to more magical and miraculous stories designed to help us see how we can resolve conflict and find our place in society (Zipes, 2012). Oral storytelling traditions are still fundamental to native American culture and Rebecca Bishop, a native American public relations officer (quoted in Sorensen, 2012) believes that the physical act of storytelling is a special thing; children will automatically stop what they are doing and listen when a story is told. Professional communicators report that this continues to adulthood (Simmons, 2006; Stevenson, 2008). This means that storytelling can be a powerful tool for connecting with students of all ages in a way that a list of bullet points in a PowerPoint presentation cannot. The emotional connection and innate, almost hardwired, need to listen when someone tells a story means that educators can teach memorable lessons in a uniquely engaging manner that is common to all cultures.
The cross-cultural element of storytelling can be seen when reading or listening to wisdom tales from around the world...
Key: Topic sentence Evidence (includes some analysis) Analysis Link (crosses into next paragraph)
- << Previous: Introductions
- Next: Conclusions >>
- Last Updated: Jul 4, 2024 10:15 AM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/essays
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem


IMAGES
VIDEO