- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
- Remember language
- Português (do Brasil)

SyntaxError: invalid assignment left-hand side
The JavaScript exception "invalid assignment left-hand side" occurs when there was an unexpected assignment somewhere. It may be triggered when a single = sign was used instead of == or === .
SyntaxError or ReferenceError , depending on the syntax.
What went wrong?
There was an unexpected assignment somewhere. This might be due to a mismatch of an assignment operator and an equality operator , for example. While a single = sign assigns a value to a variable, the == or === operators compare a value.
Typical invalid assignments
In the if statement, you want to use an equality operator ( === ), and for the string concatenation, the plus ( + ) operator is needed.
Assignments producing ReferenceErrors
Invalid assignments don't always produce syntax errors. Sometimes the syntax is almost correct, but at runtime, the left hand side expression evaluates to a value instead of a reference , so the assignment is still invalid. Such errors occur later in execution, when the statement is actually executed.
Function calls, new calls, super() , and this are all values instead of references. If you want to use them on the left hand side, the assignment target needs to be a property of their produced values instead.
Note: In Firefox and Safari, the first example produces a ReferenceError in non-strict mode, and a SyntaxError in strict mode . Chrome throws a runtime ReferenceError for both strict and non-strict modes.
Using optional chaining as assignment target
Optional chaining is not a valid target of assignment.
Instead, you have to first guard the nullish case.
- Assignment operators
- Equality operators
- JS Tutorial
- JS Exercise
- JS Interview Questions
- JS Operator
- JS Projects
- JS Examples
- JS Free JS Course
- JS A to Z Guide
- JS Formatter
JavaScript TypeError – Invalid assignment to const “X”
This JavaScript exception invalid assignment to const occurs if a user tries to change a constant value. Const declarations in JavaScript can not be re-assigned or re-declared.
Error Type:
Cause of Error: A const value in JavaScript is changed by the program which can not be altered during normal execution.
Example 1: In this example, the value of the variable(‘GFG’) is changed, So the error has occurred.
Output(in console):
Example 2: In this example, the value of the object(‘GFG_Obj’) is changed, So the error has occurred.
Similar Reads
- Web Technologies
- JavaScript-Errors
Please Login to comment...
Improve your coding skills with practice.

What kind of Experience do you want to share?
TypeError: Assignment to Constant Variable in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024 Reading time · 3 min

# TypeError: Assignment to Constant Variable in JavaScript
The "Assignment to constant variable" error occurs when trying to reassign or redeclare a variable declared using the const keyword.
When a variable is declared using const , it cannot be reassigned or redeclared.
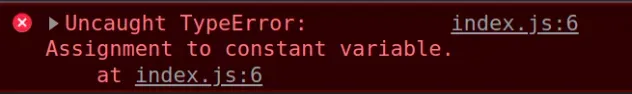
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
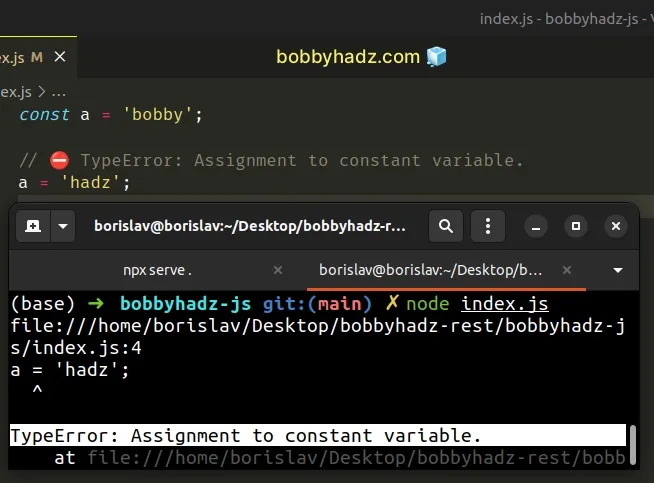
# Declare the variable using let instead of const
To solve the "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error, declare the variable using the let keyword instead of using const .
Variables declared using the let keyword can be reassigned.
We used the let keyword to declare the variable in the example.
Variables declared using let can be reassigned, as opposed to variables declared using const .
You can also use the var keyword in a similar way. However, using var in newer projects is discouraged.
# Pick a different name for the variable
Alternatively, you can declare a new variable using the const keyword and use a different name.
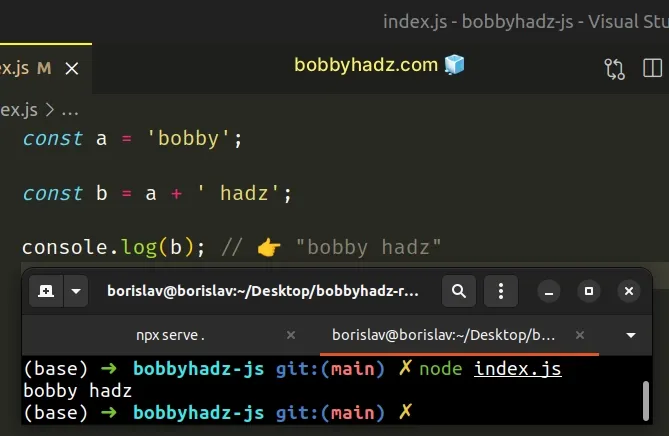
We declared a variable with a different name to resolve the issue.
The two variables no longer clash, so the "assignment to constant" variable error is no longer raised.
# Declaring a const variable with the same name in a different scope
You can also declare a const variable with the same name in a different scope, e.g. in a function or an if block.
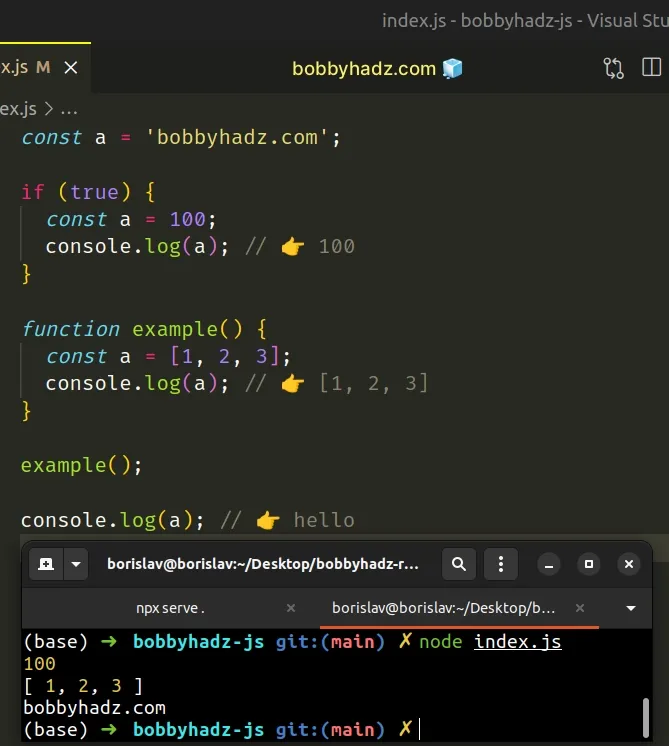
The if statement and the function have different scopes, so we can declare a variable with the same name in all 3 scopes.
However, this prevents us from accessing the variable from the outer scope.
# The const keyword doesn't make objects immutable
Note that the const keyword prevents us from reassigning or redeclaring a variable, but it doesn't make objects or arrays immutable.
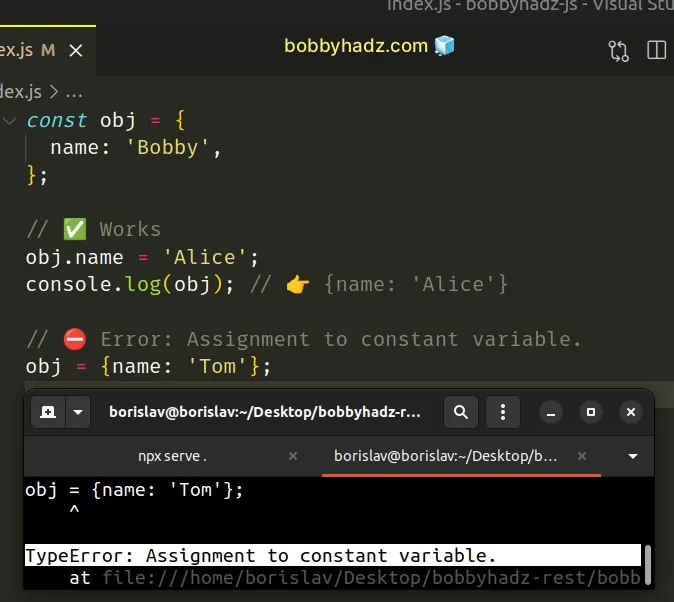
We declared an obj variable using the const keyword. The variable stores an object.
Notice that we are able to directly change the value of the name property even though the variable was declared using const .
The behavior is the same when working with arrays.
Even though we declared the arr variable using the const keyword, we are able to directly change the values of the array elements.
The const keyword prevents us from reassigning the variable, but it doesn't make objects and arrays immutable.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- SyntaxError: Unterminated string constant in JavaScript
- TypeError (intermediate value)(...) is not a function in JS

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The problem is that the assignment operator, =, is a low-precedence operator, so it's being interpreted in a way you don't expect. If you put that last expression in parentheses, it …
The JavaScript exception "invalid assignment left-hand side" occurs when there was an unexpected assignment somewhere. It may be triggered when a single = sign was …
The Logical AND assignment operator is used between two values. If the first value is true, the second value is assigned.
In JavaScript, a SyntaxError : Invalid Assignment Left-Hand Side occurs when the interpreter encounters an invalid expression or structure on the left side of an assignment …
The "Assignment to constant variable" error occurs when trying to reassign or redeclare a variable declared using the `const` keyword.
The ?= operator, also known as the safe assignment operator, simplifies conditional assignments. It only assigns a value if the variable on the left-hand side is already …