

A Level History Coursework AQA – A Guide
- Post author By admin
- Post date January 8, 2024
- No Comments on A Level History Coursework AQA – A Guide
This guide shows you how to plan, research and write A Level History Coursework for AQA using ideas, resources, examples and structure. This coursework is weighted in the following format. Assessment Objective One (AO1) 10% (20 marks), Assessment Objective Two (AO2) 5% (10 marks) and Assessment Objective Three (AO3) 5% (10 marks). For AQA coursework this gives a total of 20% (40 marks) divided as shown above across all three of the A Level History Assessment Objectives.
A Level History Coursework AQA – Ideas, Examples and Resources
Choosing an Issue and Question – You are required to identify an issue or topic that you wish to study and develop a question from this. This gives a broad scope for potential questions. There are however two specific requirements of the question.
- The question must not duplicate any of the content that you are studying for examination assessment in components 1 and 2.
- The question must place the issue or topic in the context of approximately 100 years of history.
Question Ideas, Example and Selection
There are two potential ways to ensure that you cover the 100 year requirement for this coursework. You could identify an issue and related question which traces development over approximately 100 years. Alternatively, you could focus on a narrower issue but place it in the context of a 100 year period. Lets look at a couple of examples below to make this clear.
- Q1. Q. ‘Despite a period of unprecedented economic and social change, British women remained marginalised and downtrodden’. During the period 1760-1867, assess the validity of this view. – This is the perfect example of a broad issue and question from which you could analyse development over the time period.
- Q2. In the context of the period 1905 to 2003, to what extent was the Cuban missile crisis the biggest turning point in the relationship between Russia and the USA? – This question highlights a more specific issue (the Cuban missile crisis) and places it in context of the relationship between the two countries over the c100 year period.
There are some key points to consider when selecting a question for your coursework.
- Question formulation – Students are advised to use the type of question formulations seen in AQA examinations and shown in the examples above.
- Historiographical debate – There needs to be a scholarly debate around the question or issue. This means differing views on the question from different historians. This makes it easier to select appropriate works to analyse and compare.
- Primary sources – Is there a range of primary sources and primary material available to support the coursework? These primary resources need to be accessible to the student.
Coursework Resources
- Library – school, local, college, university – you should be able to borrow appropriate works.
- Teacher – your teacher should be able to provide you with copies of appropriate resources to use.
- JSTOR – www.jstor.org – contains a large collection of journal articles from historical publications covering numerous topics. These will often engage in the historical debate by replying to opposing views.
- Purchase Books – many second-hand books are available to purchase at very cheap prices through Amazon or similar sites.
A Level History Coursework AQA – Structure and Planning
First section – introduction to the question (c. 350 words).
Introduction to the overall topic. You need to put the question into context by providing relevant information regarding what was happening at the time. You then need to define any key terms in the question. For the British women example question above you would need to define ‘remained marginalised and downtrodden’ .
This we could do by defining;
- remained as showing continuity rather than change
- marginalised as a group treated as insignificant and peripheral.
- downtrodden as a group oppressed or treated badly by those in power.
You would then need to set-out valid criteria by which the question can be judged in order to provide an accurate answer. These criteria will go on to become your factors as you can see in the plan below.
For the British women example question, we could potentially use the following criteria to judge whether they remained marginalised and downtrodden. Did women’s lives change for the better, during the period, in the following different areas?
- Socially and Culturally
- Legally and Politically
- Education and Work
Second Section – Historians Viewpoints (c. 800 words – 400 each)
In this section we look at the viewpoints of two different academic historians. In order to achieve the highest marks, Level 5 (9-10 Marks) we need to do the following:
- Show a very good understanding of the differing historical interpretations raised in the question.
- Convincingly evaluate the interpretations with reference to time, context and/or limitations placed on the historians.
Using the example Cold War question shown above, you could analyse the views of a US historian writing after the Cold War has ended, with a Soviet historian writing during the period. This would enable you to contrast the content of both works and evaluate the interpretations given. This would also show how the time period affected the works, how limitations affected the works, how purpose affected the works, amongst many other issues that help to explain the authors differing viewpoints.
Third Section – Factor 1 and Source 1 (c. 650 words Factor 1 and 350 words Source 1)
In this section you cover the first factor that you have identified from your criteria in the introduction, as well as one of your primary sources that matches with this theme. So for the British women example question this section would concentrate on the Socially and Culturally factor that we are using as criteria to answer the question. Crucially you have to cover the time period and show your understanding of change and continuity as illustrated by the mark scheme detailed below.
- Level 5 (17-20) marks – Very good understanding of change and continuity within the context of approximately 100 years.
You then add to this section your evaluation of your first primary source that matches with this theme. So for the British women example question you would have a primary source that related to the Socially and Culturally factor being covered here.
Fourth Section – Factor 2 and Source 2 (c. 650 words Factor 2 and 350 words Source 2 )
In this section you cover the second factor that you have identified from your criteria in the introduction, as well as one of your primary sources that matches with this theme. So for the British women example question this section would concentrate on the Legally and Politically factor that we are using as criteria to answer the question. Crucially you have to cover the time period and show your understanding of change and continuity as illustrated by the mark scheme detailed below.
You then add to this section your evaluation of your first primary source that matches with this theme. So for the British women example question you would have a primary source that related to the Legally and Politically factor being covered here.
Fifth Section – Factor 3 and Source 3 (c. 650 words Factor 3 and 350 words Source 3 )
In this section you cover the second factor that you have identified from your criteria in the introduction, as well as one of your primary sources that matches with this theme. So for the British women example question this section would concentrate on the Education and Work factor that we are using as criteria to answer the question. Crucially you have to cover the time period and show your understanding of change and continuity as illustrated by the mark scheme detailed below.
You then add to this section your evaluation of your first primary source that matches with this theme. So for the British women example question you would have a primary source that related to the Education and Work factor being covered here.
Sixth Section – Overall Conclusion (c. 350 words)
In the final section you need to produce an overall conclusion that fully answers the coursework question. So for the British women question you would be answering ‘did they remain marginalised and downtrodden during this period?’. This will take into account everything you have considered throughout the piece of work including your criteria, the viewpoints of the academic historians, the primary sources and the factors that you have covered from your criteria. In reaching a final judgement and conclusion, you need to take into account the entire period considering continuity and change across it, as you should have done throughout the rest of the coursework.
A Level History Coursework AQA – Primary Source Analysis

Looking at the primary source mark scheme table from the AQA website can help you to understand the requirements. Firstly, you must ensure that three sources are used and that there are a minimum of two different types (can be two different types of written source). To achieve the highest marks you must then ensure that a range of relevant and well supported comments are made on the value of the sources. Finally, you must provide a balanced and convincing judgement on the merits of each source in relation to our question.
Assessing Your Primary Sources
- Provenance – The five W’s of Who, Why, What, When, Where; can help you to identify the provenance of a primary source and assess its value or limitations.
- Tone and Emphasis – How does the tone and emphasis impact the value of the source. Is it impartial, critical, formal, aggressive, empathetic, mocking, candid etc?
- Content – What is the actual content of the source saying? How true is this in terms of your contextual knowledge? Is there value in the inaccuracies of the content?
- Value/Limitations and Judgement – The above three points ( Provenance, Tone and Emphasis and Content ) can be used to assess how much we can learn from the source, by weighing up value and limitations, as well as giving judgement on the merit of the source.
How To Improve Further at A Level History
Pass A Level History – is our sister site, which shows you step by step, how to most effectively answer any A Level History extract, source or essay question. Please click the following link to visit the site and get access to your free preview lesson. www.passalevelhistory.co.uk
Previous and Next Blog Posts
Previous – A Level History Coursework Edexcel Guide – passhistoryexams.co.uk/a-level-history-coursework-edexcel/
Next – A Level History Extract Questions – How To Answer – passhistoryexams.co.uk/a-level-history-extract-questions/
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

A-Level History: A Complete Guide
Dr Rahil Sachak-Patwa
Starting your A-Level journey and thinking if History is the choice for you? You're in good company. A-Level History is a captivating subject, giving you a deep look into the past and its impact on today. Why choose History, you might ask? It's not just about dates and events; it’s about understanding the why and how behind major global happenances. Can it open doors for your future? Absolutely. In our guide, we'll explore everything from the difficulty level to the best resources, ensuring you have all the information to make an informed decision.
Is History a good A-Level to do?
Choosing A-Level History is a decision that many students ponder over. Its value isn't just academic; it equips you with skills highly regarded by universities and employers alike. According to a survey by the Russell Group universities , History is listed among the 'facilitating subjects' recommended for entry into a wide range of university courses. But what makes it such a commendable choice?
- Critical Thinking : History teaches you to analyse sources and arguments, fostering a critical approach to information.
- Communication Skills : You'll learn to articulate complex ideas clearly, both in writing and orally.
- Research Abilities : Tackling historical questions requires effective research, a skill that's invaluable in any career.
- Understanding of Contemporary Issues : By studying the past, you gain insights into current global issues, making you more informed about the world around you.
Here is what an expert A-Level History tutor has to say:
"Many of my students who've taken A-Level History have exceled in careers like law, education, journalism, and public policy. Their deep understanding of history enhanced their critical thinking, and helped their professional contributions by enabling them to solve complex issues with insight from past events."
Experts in education and career development often highlight the versatility of History A-Level. It opens doors to careers in law, journalism, politics, and education, to name a few. The analytical and evaluative skills gained are what set History students apart in the competitive job market.
📈Boost your grades with our revision platform, used by 100,000+ students! 📝Access thousands of practice questions, study notes, and past papers for every subject. 📚 View IB Resources 📚 View A-Level Resources 📚 View GCSE Resources 📚 View IGCSE Resources
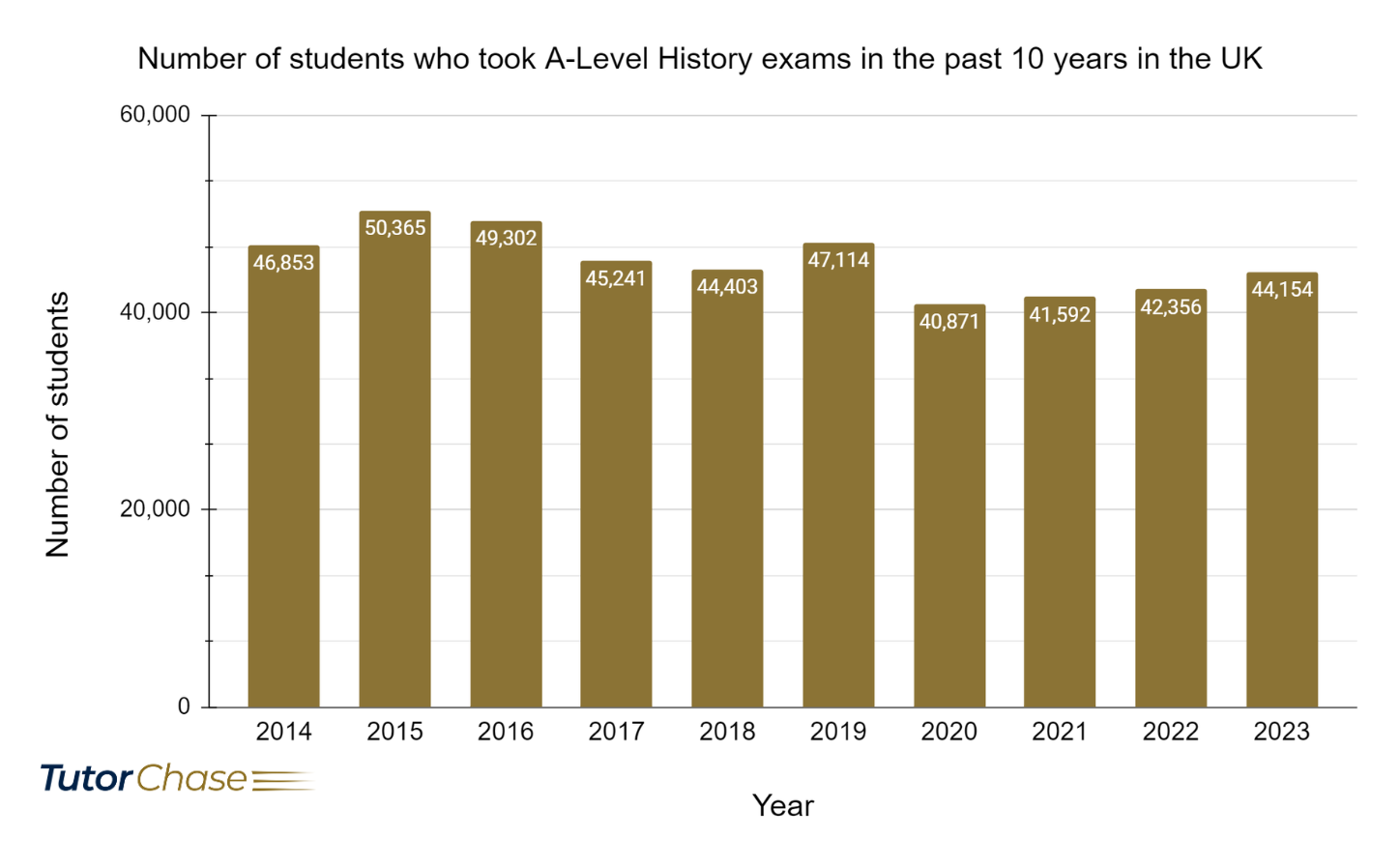
Graph showing number of students who took A-Level History exams in the past 10 years in the UK
Is it hard to pass A-level History?
A-level History is perceived by many as a challenging subject due to its in-depth analysis and extensive content and is ranked as the 7th hardest A-Level subject . However, the notion of difficulty is subjective and can vary based on a student's interests and strengths. The pass rate for A-level History has been relatively stable, indicating that with the right preparation and study habits, passing is certainly achievable. Key points to consider include:
- Pass Rates : Data from Ofqual shows a consistent pass rate for A-level History, with recent years reporting pass rates of 98.7% in 2023, 99.2% in 2022, and 99.6% in 2021. These statistics suggest that while achieving top grades may be challenging, passing the subject is within reach for the majority of students.
- Achieving High Grades : Obtaining an A* in A-level History is challenging and requires extensive subject knowledge, sophisticated argumentation, and a coherent writing style. The proportion of students achieving an A* has varied, with a decrease observed from 16% in 2021 to 5.5% in 2023.
- Content Volume : A-level History is considered one of the most content-intensive A-level subjects. This means that students should be prepared for a significant amount of reading, research, and memorisation.
- Exam Structure and Skills : Success in A-level History exams requires not only knowledge of historical facts but also the ability to critically analyse sources, construct coherent arguments, and write clearly under timed conditions.
Table showing A-level History grades distribution
While A-level History presents certain challenges, careful preparation, consistent effort, and effective study strategies can greatly increase the likelihood of not only passing but excelling in this subject.
Get help with A-Level History
The world's leading online A-Level History tutors trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
4.93 /5 based on 486 reviews
What topics are in History A-level?
A-Level History covers a broad and diverse range of topics, offering students the opportunity to explore various periods and events in depth. The subject matter spans across centuries and continents, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the world's history. Key areas of study typically include:
- Modern History : Focusing on the 19th and 20th centuries, topics often cover significant global events, revolutions, and the development of modern nations.
- British History : An essential component, with studies ranging from mediaeval times to the present day, reflecting on the social, political, and economic evolution of Britain.
- European and World History : Encompassing a wide array of subjects such as the rise and fall of empires, the World Wars, and the Cold War era.
- Thematic Studies : These might explore specific themes like migration, trade, religion, or science and technology across different periods and locations.
The AQA exam board, for example, offers topics such as the British Empire c1857–1967, the making of a Superpower: USA, 1865–1975, and the quest for political stability: Germany, 1871–1991. The OCR board provides over 50 topics including British period studies and non-British history, encouraging critical thinking and reflection.
CIE A-Level History Syllabus
The CIE A-Level History syllabus offers an extensive study of key historical events and figures, fostering critical analysis and evaluation skills. It prepares students to understand and interpret complex narratives, crucial for navigating today’s information-rich world.
Table showing CIE A-Level History syllabus
Note : AS Level topics rotate between papers 1 and 2 year-on-year. The prescribed topic for Paper 1 in any given year is not used for Paper 2.
AQA A-Level History Syllabus
The AQA A-Level History syllabus delves into diverse historical themes and periods, enhancing students' ability to critically evaluate sources and arguments. It sharpens analytical skills, preparing them to tackle complex issues and understand their historical context in today’s world.
Table showing AQA A-Level History syllabus
Further instructions are provided by AQA for the A-Level History exam:
Prohibited Combinations
Students must study a British history option for either Component 1 or Component 2. If a British history option is chosen for Component 1, it must be combined with a non-British option for Component 2. If a British history option is chosen for Component 2, it must be combined with a non-British option for Component 1. Any British option may be combined with any non-British option, other than the following:
- 1C The Tudors may not be combined with 2C The Reformation in Europe
- 1D Stuart Britain and the Crisis of Monarchy may not be combined with 2F The Sun King: Louis XIV, France and Europe
This is because there is a strong conceptual emphasis which runs across both breadth and depth options which would result in a narrowing of the student’s experience.
The following are designated British history options:
Component 1
- 1C The Tudors: England, 1485–1603
- 1D Stuart Britain and the Crisis of Monarchy, 1603–1702
- 1F Industrialisation and the People: Britain, c1783–1885
- 1G Challenge and Transformation: Britain, c1851–1964
- 1J The British Empire, c1857–1967
Component 2
- 2A Royal Authority and the Angevin Kings, 1154–1216
- 2B The Wars of the Roses, 1450–1499
- 2D Religious Conflict and the Church in England, c1529–c1570
- 2E The English Revolution, 1625–1660
- 2M Wars and Welfare: Britain in Transition, 1906–1957
- 2S The Making of Modern Britain, 1951–2007
Edexcel A-Level History Syllabus
The Edexcel A-Level History syllabus emphasizes detailed studies of specific eras, cultivating students' abilities to analyse and debate historical evidence and perspectives. This prepares them for informed critical thinking and engagement with current and historical debates.
Table showing Edexcel A-Level History syllabus
Note : Students take one option each from the following:
- 2A.1 to 2H.2
This sums up to be a total of 3 for 3 papers. It is discussed in depth in the exam structure section.
OCR A-Level History Syllabus
The OCR A-Level History syllabus enhances critical thinking through deep analysis of historical events and interpretations, equipping students with the skills to evaluate evidence and construct coherent arguments, vital for academic and professional success.
Table showing OCR A-Level History syllabus
Each exam board has its own set of modules and topics, allowing schools to choose those most relevant or interesting to their students. This flexibility means that students can engage with a variety of historical perspectives and methodologies, preparing them for further education or careers where analytical and evaluative skills are essential.
What is the A-Level History exam structure?
The A-Level History exam structure is designed to assess students' understanding, analytical skills, and ability to engage with historical evidence and debates. While the specific format of key questions can vary between exam boards, the general structure across AQA, OCR, and Edexcel includes:
- Written Examinations : These form the core of the assessment and are typically divided into several papers, focusing on different periods or themes.
- Breadth Study : Examines a broad period of history, assessing understanding of long-term changes and continuities.
- Depth Study : Focuses on a shorter, more detailed timeframe, requiring in-depth knowledge and analysis.
- Historical Investigation : A component that involves coursework or a written project on a chosen topic, contributing to the final grade for some exam boards.
Key features include:
- Essay Questions : Require students to construct coherent arguments, supported by historical evidence.
- Source Analysis : Students analyse primary and secondary sources to interpret perspectives and biases.
- Comparative Questions : Involve comparing different historical periods, events, or figures.
The exams are typically held at the end of the two-year A-Level course. The exact duration and number of questions can differ, but exams usually last between 1.5 to 3 hours. The coursework element, where applicable, allows students to explore a historical topic of their choice in depth, demonstrating research skills and critical analysis.
CIE A-Level History Exam Structure
The CIE A-Level History exam structure includes detailed essays, source analysis, and thematic studies, designed to test students' knowledge, analytical abilities, and understanding of historical context and perspectives, ensuring a comprehensive assessment of their grasp of the subject.
Table showing CIE A-Level History exam structure
AQA A-Level History Exam Structure
The AQA A-Level History exam structure features a mix of source-based questions and essay writing, assessing students' ability to critically evaluate evidence and present coherent arguments. It includes breadth and depth studies, ensuring a well-rounded evaluation of students' historical understanding and analytical skills.
Table showing AQA A-Level History exam structure
Note : Through the topics studied in Components 1, 2 and 3 (Historical investigation), A-level students must cover a chronological range of at least 200 years.
Edexcel A-Level History Exam Structure
The Edexcel A-Level History exam consists of thematic studies and breadth with source evaluations, focusing on depth studies and historical interpretations. This structure assesses students’ comprehension, analytical skills, and ability to engage critically with historical themes and evidence, fostering a detailed understanding of specific periods.
Table showing Edexcel A-Level History exam structure
OCR A-Level History Exam Structure
The OCR A-Level History exam structure combines thematic studies, source evaluations, and period studies to assess students' analytical skills, understanding of historical context, and ability to construct well-supported arguments. It's designed to test a comprehensive range of historical knowledge and critical thinking abilities.
Table showing OCR A-Level History exam structure
*Learners who are retaking a qualification can choose either to retake the non exam assessment unit or to carry forward their mark for that unit. See Section 4d of OCR A-Level History specification for more details.
*Also includes synoptic assessment.
This structured approach ensures that students not only memorise historical facts but also develop the ability to critically evaluate information and present reasoned arguments, skills that are valuable in many fields beyond history.
Choosing the Right Exam Board
Selecting the appropriate exam board for A-Level History is crucial as it can influence the topics studied, the exam format, and the assessment criteria. In the UK, the main exam boards offering A-Level History are CIE , AQA , Edexcel and OCR . Each has its own focus and approach to history, making the choice significant for teachers and students alike. Key considerations include:
- CIE : Known for its international perspective, CIE attracts the most applicants globally, offering a wide range of historical themes with a global outlook.
- AQA : With 20,964 candidates in the UK in 2023, AQA is popular for its comprehensive coverage of British and modern European history.
- Edexcel : Attracting 13,272 applicants in the UK in 2023, Edexcel is favoured for its structured approach and detailed study options, including coursework.
- OCR : With 10,388 candidates in the UK in 2023, OCR offers unique topics that often include British history, making it a choice for those interested in a deep dive into the history of the UK.
When choosing an exam board, consider:
- Content and Topics : Which periods or themes are you most interested in?
- Assessment Method : Do you prefer coursework or solely exam-based assessment?
- Resources and Support : Which exam board offers the best resources and support for your learning style?
Deciding on an exam board is a decision that should be based on your interests, strengths, and future aspirations. Discussing with teachers and researching each board's specifications can help make an informed choice that aligns with your academic goals.
How do you get an A* in A-Level History?
Achieving an A* in A-Level History requires a combination of depth of knowledge, analytical skills, and effective revision and examination strategies. Given the rigorous nature of the subject, students need to go beyond the basic requirements to stand out. Key strategies include:
- Comprehensive Understanding : Master the breadth and depth of your chosen topics, ensuring you have a thorough grasp of the key events, figures, and trends.
- Critical Analysis : Develop the ability to critically evaluate historical sources and arguments. This involves recognising bias, analysing different interpretations, and forming your own reasoned conclusions.
- Essay Writing Skills : Practise structuring coherent and persuasive essays that are well-supported with evidence. High marks are awarded for clear, analytical writing that directly addresses the question.
- Effective Revision : Utilise a variety of revision techniques, including study notes, mind maps, and flashcards to reinforce your memory and understanding of complex topics.
- Tutoring : Consider engaging with an A-Level tutor who can provide personalised feedback, help refine your exam technique, and deepen your understanding of challenging material.
- Utilisation of Past Papers : Regularly practise with past exam papers and questions to familiarise yourself with the exam format and improve your time management skills.
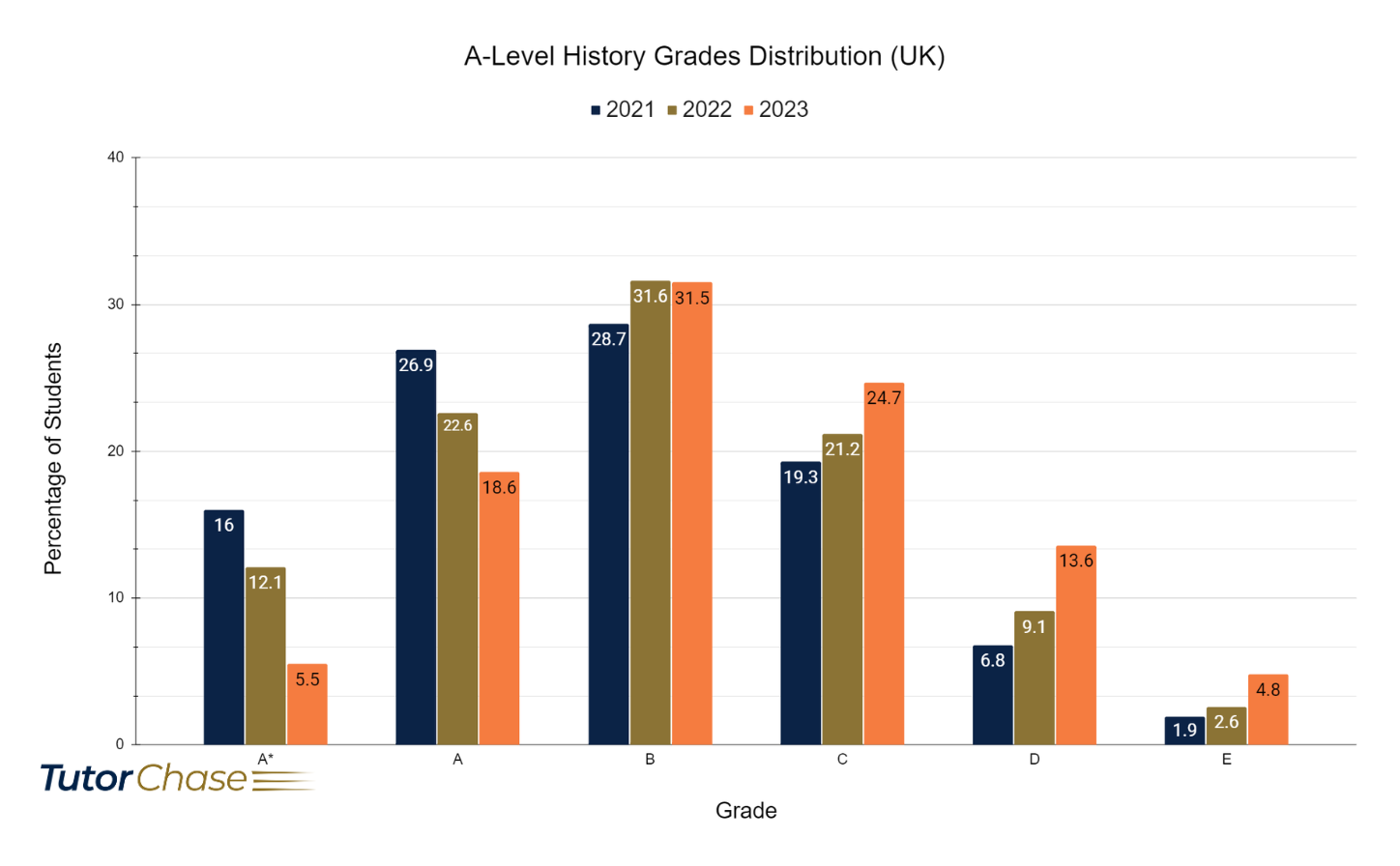
Graph showing grades distribution of A-Level History in UK 2021-2023
Consistent effort and utilisation of available resources is very important. This can include school-provided materials, online resources, and study groups, alongside tutoring. Balancing broad factual knowledge with sharp analytical acumen and refined exam strategies is key to achieving the top grade in A-Level History.
Have a look at our comprehensive set of A-Level History Study Notes developed by expert A-Level teachers and examiners!
How do you write A-Level History essays?
Writing an A-Level History essay involves several key steps to ensure it is well-structured, insightful, and evidently supported:
1. Understand the Question : Identify key terms and what the question is asking you to do (e.g., analyse, compare, review, evaluate).
2. Plan Your Answer : Organise your thoughts and structure your essay into a clear introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point or argument.
3. Use Evidence : Support your arguments with relevant historical evidence, including primary and secondary sources. Be sure to analyse the evidence, not just describe it.
4. Critical Analysis : Evaluate the significance of the evidence and different historians' interpretations. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of these viewpoints.
5. Conclusion : Summarise your main points and clearly state your conclusion, ensuring it directly answers the specific question above.
6. Proofread : Check for clarity, coherence, and any grammatical or spelling errors.
Focus on presenting a coherent argument supported by evidence, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and your ability to critically engage with historical material.
What are the best A-Levels to take with History?
Selecting A levels that complement History can enhance your understanding, offer interdisciplinary skills, and broaden your future academic and career options. The best A levels to take with History are those that develop critical thinking, analytical skills, and written communication. Complementary A levels include:
- A-Level English Literature : Enhances your ability to analyse texts and understand historical contexts, improving essay-writing skills.
- A-Level Politics : Offers insights into governmental systems and political theories, relevant to historical study.
- A-Level Geography : Provides knowledge of how historical events have shaped landscapes and human societies.
- A-Level Modern Foreign Languages : Improves understanding of other cultures, which can be beneficial for studying international history.
- A-Level Economics : Gives an understanding of economic principles and historical economic trends.
Experts recommend choosing subjects that not only complement History but also match your interests and career aspirations. Universities often value the combination of History with subjects that demonstrate strong literacy skills and the ability to critically analyse information. This combination can prepare students for a range of degrees and career paths in law, journalism, education, and beyond.
Best A-Level History Resources
Identifying top-quality resources is essential for excelling in A-Level History. The right materials can deepen your understanding of complex historical events and themes, enhancing your ability to analyse and evaluate sources critically. Here are some of the best resources for A-Level History students, tailored to various exam boards:
- Official Textbooks: Textbooks from official exam board sources provide the best study material required to ace the exam. Such can be found at the CIE resources page .
- Tutoring : Personalised support can help clarify complex topics and refine exam techniques.
- Study Notes : Customised study notes, particularly from services like TutorChase , and A-Level History Q&A Revision Notes are invaluable for revision.
- Online Resources : Platforms such as BBC Bitesize , History Learning Site , and the Khan Academy offer a wealth of free content, including articles, video lessons, and quizzes.
- Past Papers and Mark Schemes : Engaging with past exam papers and understanding mark schemes are crucial for exam success, providing insights into the types of questions asked and how to structure high-scoring answers.
Combining these resources with dedicated study can significantly enhance your performance in A-Level History, providing a solid foundation for both exams and coursework.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
A-Level History students often face several challenges throughout their course, but with effective strategies and practice, these obstacles can be overcome.
- Vast Amount of Content : The comprehensive syllabus can seem daunting. To manage this, create a structured revision timetable that breaks down the content into manageable segments, ensuring all topics are covered systematically.
- Analysing Sources : Interpreting a variety of sources is essential but can be complex. Improve this skill by practising with a wide range of source materials and seeking feedback on your analyses to understand different perspectives and biases.
- Essay Writing : The ability to write cohesive, argument-driven essays under exam conditions is critical. Enhance this skill by practising essay planning under timed conditions, focusing on structuring your arguments clearly and supporting them with relevant evidence.
- Retention of Information : Remembering key dates, figures, and events is challenging. Employ active recall techniques such as flashcards, mind maps, and quiz-based revision apps to aid memory retention and make revising more interactive and engaging.
Employing these strategies can significantly alleviate the common hurdles faced by A-Level History students, leading to a more comprehensive understanding and better performance in exams.
Past Papers and Practise Questions
Utilising past papers and practise questions is a proven method for improving exam performance in A-Level History. These resources are invaluable for understanding the exam format, the types of test questions asked, and for honing your time management skills during the exam. Benefits include:
- Familiarity with Exam Format : Regular practise with past papers helps students become accustomed to the structure and timing of the actual exam.
- Identification of Weak Areas : Engaging with a wide range of questions allows students to identify areas where they need further study or understanding.
- Application of Knowledge : Practise questions provide an opportunity to apply knowledge in an exam context, reinforcing learning and improving recall under pressure.
- Improvement of Essay Writing Skills : Writing timed essays in response to past paper questions can significantly enhance the ability to construct coherent and persuasive arguments quickly.
Experts recommend beginning to work with past papers and practise questions well before the exam period. This should be integrated into your revision plan, with time set aside for reviewing answers and understanding mark schemes. Resources are available through exam board websites, educational platforms, and tutoring services, offering a wealth of questions for practise across all topics covered in the A-Level History syllabus.
Opportunities with A-Level History
A-Level History opens a wide array of opportunities, laying a strong foundation for further education and a variety of career paths. This qualification not only deepens understanding of historical events and processes but also hones analytical, research, and writing skills that are highly valued in many fields.
Pie chart showing gender distribution across A-Level History
Majors in Higher Education:
- History and Related Disciplines : Direct progression to degrees in history, politics, archaeology, and international relations.
- Law : Equips students with critical thinking and analytical skills necessary for legal studies.
- Journalism and Media : Develops skills in research, analysis, and communication, essential for careers in writing, reporting, and broadcasting.
Career Paths:
- Historian : Engaging with archives, museums, and educational institutions to research, interpret, and present history.
- Lawyer or Barrister : Utilising analytical skills and an understanding of historical contexts in legal practice.
- Journalist or Writer : Crafting compelling narratives based on thorough research and analysis.
- Education : Teaching history or social sciences at various levels, from secondary education to university professorship.
- Public Sector and Policy Making : Analysing historical data to inform policy decisions and government strategies.
Skills Development:
- Critical Analysis : The ability to evaluate sources and arguments critically.
- Research Skills : Proficiency in conducting thorough and effective research.
- Communication : Articulating complex ideas clearly and persuasively in both written and oral form.
- Problem-Solving : Approaching challenges with a strategic and analytical mindset.
Pursuing A-Level History not only paves the way for academic pursuits in a range of humanities and social science subjects but also equips students with a versatile skill set applicable in numerous professional sectors, including education, law, public administration, and the media. This breadth of opportunities highlights the value of history in fostering a well-rounded and adaptable skill set.
Conclusion on A-Level History
A-Level History stands out as a rigorous and enriching subject that offers students a profound understanding of the past and its impact on the present and future. Through the study of a wide range of periods and themes, students develop a comprehensive skill set, including critical analysis, research, and communication, which are highly valued in both higher education and the workplace. It is a subject that challenges students to think critically about the past, understand its complexities, and apply these insights to the challenges of the modern world.
Can I study A-Level History without a GCSE in History?
Yes, you can study A-Level History without having a GCSE in the subject . Many schools and colleges understand that students may develop an interest in history later on or may not have had the opportunity to study it at GCSE level. However, it's important to demonstrate strong reading and writing skills, as these are crucial for success in A-Level History. It would be beneficial to discuss your interest and academic background with your teachers, as they can provide guidance and support to help bridge any knowledge gaps.
How many hours should I study for A-Level History weekly?
For A-Level History, aiming for around 4-5 hours of independent study per week , in addition to your class time, is a good guideline. This allows you to thoroughly cover the syllabus content, develop your essay-writing skills, and engage with primary and secondary sources. Remember, quality over quantity is key; focused, uninterrupted study sessions are more effective than longer, less productive ones. Tailor your study time to suit your learning pace and adjust as needed, especially before exams or when working on coursework.
Are there any recommended documentaries for A-Level History students?
Certainly! Documentaries can offer engaging insights into historical events, figures, and periods, complementing your A-Level History studies. Here are a few recommendations:
- "The World at War" - An in-depth series on World War II.
- "The Civil War" by Ken Burns - A comprehensive look at the American Civil War.
- "The Vietnam War" also by Ken Burns - Explores the Vietnam War from multiple perspectives.
- "The Ascent of Civilisations" - Examines the history of civilisations around the globe.
- "Russia's History Revealed" - Delves into the complex history of Russia.
These documentaries can provide a broader historical context for the specific topics you're studying, making historical events more relatable and easier to understand.

Can A-Level History be combined with Science A-Levels?
Absolutely, A-Level History can be effectively combined with Science A-Levels . This combination offers a well-rounded education, enhancing both your analytical and empirical skills. History develops critical thinking, argumentation, and essay-writing abilities, which complement the logical, problem-solving skills fostered by Science subjects. This interdisciplinary approach can open up diverse pathways for higher education and careers, ranging from law and journalism to science and engineering. It demonstrates to universities and employers that you have a broad skill set and are adaptable to various challenges.
What is AO2 in history A-level?
In A-Level History, AO2 refers to the assessment objective focused on "Analysis and Evaluation." This objective assesses your ability to analyse historical events, periods, and concepts critically. It involves evaluating different interpretations of history, including contrasting opinions and historiographies, and making informed judgments. Excelling in AO2 requires you to not only present facts but also to engage with them critically, discussing their significance, the reliability of sources, and the perspectives of historians. This skill is vital for constructing well-argued essays and achieving high marks.
What are the most popular history topics?
The most popular history topics at A-Level often include those that cover significant events, periods, and movements that have shaped the modern world. These typically involve:
- The World Wars : Examining the causes, major battles, and consequences of World Wars I and II.
- The Cold War : Exploring the geopolitical tension between the Eastern and Western blocs.
- The Tudors : Delving into the reigns and impacts of Tudor monarchs on England.
- The Civil Rights Movement in the USA : Studying the struggle for racial equality in the 20th century.
- The French Revolution : Understanding the causes, key events, and outcomes of the revolution.
These topics are popular due to their profound impact on contemporary society and politics, offering students a deep insight into the complexities of historical change and continuity.
What are easy history topics?
While "easy" can be subjective, depending on individual interests and strengths, some history topics are considered more accessible due to their straightforward narrative and abundance of resources. These might include:
- The Industrial Revolution : Focused on technological advancements and their societal impacts, with clear cause-and-effect relationships.
- The Elizabethan Era : Centred around Queen Elizabeth I's reign, this period is well-documented, making it easier to study.
- The American Revolution : Offers a clear storyline of the struggle for independence from Britain, with defined events and figures.
- Ancient Civilisations : Such as Ancient Egypt or Rome, where the focus is often on culture, society, and innovations, which can be more straightforward to understand.
- The Suffragette Movement : A specific social change movement with a wealth of sources and a clear narrative of progress and impact.
These topics often have extensive resources available, including textbooks, documentaries, and online materials, making them more accessible for students.
How many paragraphs are in a level history?
An A-Level History essay typically consists of an introduction, several body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The number of body paragraphs depends on the essay's length and complexity but usually ranges from three to six . Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea or argument, supported by evidence and analysis. This structure ensures a clear and logical progression of ideas, helping to articulate a coherent response to the essay question. The key is to ensure each paragraph contributes effectively to your overall argument.
Need help from an expert?
The world’s top online tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
Study and Practice for Free
Trusted by 100,000+ Students Worldwide
Achieve Top Grades in your Exams with our Free Resources.
Practice Questions, Study Notes, and Past Exam Papers for all Subjects!
Need Expert Help?
If you’re looking for assistance with your A-Levels, get in touch with the TutorChase team and we’ll be able to provide you with an expert A-Level History tutor . We’ll be there every step of the way!

Professional tutor and Cambridge University researcher

Written by: Dr Rahil Sachak-Patwa
Rahil spent ten years working as private tutor, teaching students for GCSEs, A-Levels, and university admissions. During his PhD he published papers on modelling infectious disease epidemics and was a tutor to undergraduate and masters students for mathematics courses.
Related Posts

Top 10 Hardest A-Levels

Top A-Level Revision Websites

A-Levels: A Complete Guide

Hire a tutor
Please fill out the form and we'll find a tutor for you
- Select your country
- Afghanistan
- Åland Islands
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bouvet Island
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Brunei Darussalam
- Burkina Faso
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Congo, The Democratic Republic of the
- Cook Islands
- Cote D'Ivoire
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Guinea-Bissau
- Heard Island and Mcdonald Islands
- Holy See (Vatican City State)
- Iran, Islamic Republic Of
- Isle of Man
- Korea, Democratic People'S Republic of
- Korea, Republic of
- Lao People'S Democratic Republic
- Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- Liechtenstein
- Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- Moldova, Republic of
- Netherlands
- Netherlands Antilles
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territory, Occupied
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Russian Federation
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Serbia and Montenegro
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Taiwan, Province of China
- Tanzania, United Republic of
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Virgin Islands, British
- Virgin Islands, U.S.
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara

Alternatively contact us via WhatsApp, Phone Call, or Email

How to Write A-Level History Coursework
History coursework is an academic paper which requires students’ critical thinking and evaluation on any historical events or on a series of events. This is done by including and mentioning different resources, perspectives, and interpretation of the happenings. A-level history coursework is all about writing essays. Regardless of your knowledge, if you are unable to produce a good essay you won’t be awarded good marks by your examiner.
To write a coursework, you need to have reliable resources from where you can collect information. You must also possess analytical thinking skills which help to determine the causes and effects of an event. You may also consider coursework sample to have a better understanding of the work which you are required to ask.
Taking a history course in A-levels seems to be very easy until you are asked to write a coursework. From here things become difficult for majority students as they don’t have any clear guidance to come up with a good essay. If you are also facing this difficulty, then don’t worry because you’re at the right place. This post will provide complete guidance on how to write A-level history coursework . Let’s find out more about it.
How to write a good coursework introduction?
History coursework usually depends on the thesis statement which is written in the introduction. Come up with a strong thesis statement. It is because the thesis statement describes the writer’s area of interest and the context which you are going to cover.
The introduction should be catchy and must sound appealing to the readers. While writing the introduction focus more on writing about the historical events which you have chosen to evaluate. Refer it with some pieces of evidence or facts. You can also show support by including relevant historical policies and statistics.
To make a great start, mind map a sheet with questions as it might help in building a better understanding of the subject. By doing so, it will be easy to formulate an impressive introduction. You can take help from your teacher, friend, or tutor in this regard. Moreover, look at different A-level coursework examples available at the school library.
Things to Include in Your History Coursework Body:
In the body paragraph of the history coursework, including all the arguments which support the introductory statements. For this purpose, you must have a list of outlined facts in chronological order. First, explain your quotes. Try to explain them in your own words rather than copying exact words and then shows how they support your point of view. Do include other historian’s interpretation in the same paragraph before finalizing your view.
Create a table which tabulates the data and by using statistics support your analysis with the relevant historical shreds of evidence as well as support the original interpretation. Also, highlights the limitations of the interpretation by giving a rough idea of the things which you haven’t included.
Then introduce the next interpretation and observe how similar and different it is with the previous one. Later, by following the same format conclude your essay.
How to Write a Compelling Conclusion:
The conclusion of your coursework should focus on two sources which are the most credible and detailed along with the reasons which show that your answer is according to the question. While writing the conclusion, restate your thesis statement and summarize the entire idea of the paper in just two to three lines. Also, justifies the shreds of evidence which are provided throughout the essay.
Some Easy to Understand Tips on Structuring a History Coursework:
The structure of history coursework is not much different from other academic papers. All you need is a precise introduction, main body paragraphs, and a conclusion which summarizes the entire essay.
Mentioned below are few easy A-level history tips to write a fine quality of coursework:
- Stick to the required word limit. If the required word count is of 2000 words so, avoid exceeding it unlike most students do. Writing more than the required word limit often leads to the repetition of ideas and sentences. Moreover, writing more put you in danger of the penalty of writing too much.
- Do structure your work like other academic essays. As it is not much different from other academic paper so, do write an introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Provide evidence to ensure that you refer to facts frequently. Also, give citation of quotes which you have taken from different sources.
- Make sure that you fully concentrate on your coursework question. Make it clear while introducing the subject along with the interpretation’s view. The side which you think is most credible support it with various historical pieces of evidence and examples. This will help you in forming a basis on which your judgment would be made.
- Remember in school, you were provided with an essay structure and how you can handle the sources. Here too, this will be very helpful as it will assist you to come up with not just a good structure but also a good flow of the essay. However, if you are not provided with a structure then simply familiarize yourself with each interpretation of the question as it might prove to be useful. Beginning your essay with a clear understanding which supports your arguments will help you in developing a good introduction.
Final Words:
Although, it is very stressful to come up with a competitive and coherent piece of work, especially when you lack research skills and don’t have a good grasp of grammar. However, all these things can be overcome if you know how to correct them. Producing a quality history coursework is not easy but it is not that much difficult. Follow the above-mentioned guide and try to create a better paper which not just impresses your teacher but also awards you with good grades.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

courseworkhelpuk.co.uk is an online writing service providing academic assistance to students in United Kingdom. The services are primarily for reference and assistance purposes to make educational journey easier.
- Testimonials
- Terms & Condition
Contact Info
- [email protected]
- +44 20 3332 0848
Genius High
A Level History NEA: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students
What is the a level history nea, choosing your topic, structure and word count, research & sources, writing and analysis, proofreading and editing, nea checklist.

- UCAS Guide Home >
- A-Level History
Revision Tips to Achieve A* in A Level History
Ever wondered about A-Level History success? Check this out: According to the Joint Council for Qualifications (JCQ) , in 2022, 87.8% aced it, but in 2019, only 81% made the grade.
Table of Contents
Understanding the A-Level History Exam
Mastering the A-Level History exam begins with a clear comprehension of its structure and components. Let’s break it down:
Exam Structure:
The A-Level History exam typically comprises multiple components. Understand the weight each section carries to prioritise your focus.
Assessment Components:
- Source Analysis : This section assesses your ability to critically evaluate historical sources. Practice interpreting documents , maps , and visuals .
- Essay Writing: Essays demand in-depth historical knowledge, effective analysis, and a structured argument. Grasp the nuances of crafting compelling essays.
Key Focus Areas for Higher Grades:
- Depth over Breadth : It’s not about covering every era; it’s about mastering select topics thoroughly.
- Critical Thinking: Emphasise critical analysis of historical events, ideologies, and interpretations.
- Historiography: Incorporate differing historical perspectives and theories into your responses.
Creating a Strategic Study Plan
Crafting a focused study plan is the key to conquering your A-Level History exam. Here’s your roadmap:
Importance of Time Management:
- Prioritise Topics : Identify high-priority areas based on exam weighting and personal strengths.
- Allocate Study Time : Dedicate specific time slots to each topic, ensuring balanced coverage.
Personalised Study Schedule:
- Daily Goals: Set achievable daily goals to maintain steady progress.
- Variety in Study Sessions: Mix source analysis, essay writing, and note review for a well-rounded approach.
Balancing Content Coverage and Depth:
- Thematic Approach: Group related topics to enhance understanding and retention.
- Regular Review: Schedule periodic reviews to reinforce learned content.
Utilising Resources Wisely
To excel in A-Level History, harnessing the right resources is paramount. Here’s how to do it effectively:
Leveraging Textbooks, Databases, and Articles:
- Textbooks: Choose authoritative texts that align with your syllabus for comprehensive coverage.
- Online Databases: Utilise reputable databases like JSTOR or Google Scholar for in-depth research.
- Scholarly Articles: Incorporate recent scholarly articles to stay updated on historical perspectives.
Incorporating Primary and Secondary Sources:
- Primary Sources: Dive into firsthand accounts, documents, and artefacts for authentic insights.
- Secondary Sources: Reference scholarly works that analyse and interpret historical events for depth.
Making the Most of Study Guides and Examiner’s Reports:
- Study Guides: Supplement your notes with study guides tailored to your exam board for focused revision.
- Examiner’s Reports: Learn from past exams’ feedback to understand common pitfalls and refine your approach.
By strategically navigating these resources, you equip yourself with a well-rounded understanding of historical events.
Perfecting Exam Technique
Unlocking the secrets to flawless A-Level History exam performance involves mastering strategic techniques. Here’s your guide:
Understanding Mark Schemes and Assessment Criteria:
- Detailed Review: Study past mark schemes to grasp how examiners evaluate responses.
- Assessment Criteria: Align your writing with specific criteria, ensuring targeted and precise answers.
Time Management During the Exam:
- Practise Time Trials: Simulate exam conditions to refine your pacing and allocate time wisely.
- Prioritise Questions: Tackle questions based on marks allocated; focus on high-value questions first.
Practising with Past Papers and Mock Exams:
- Realistic Simulations: Mimic exam conditions with past papers to enhance familiarity.
- Learn from Mistakes: Analyse errors in mock exams to fine-tune your approach and improve.
Embracing Continuous Improvement
Achieving A* excellence in A-Level History is an ongoing journey. Here’s how to ensure continuous improvement:
Regular Self-Assessment and Reflection:
- Review Progress: Regularly assess your understanding and identify areas for improvement.
- Reflect on Strategies: Evaluate the effectiveness of your study techniques and adjust as needed.
Setting Realistic Goals for Improvement:
- Identify Weaknesses: Pinpoint specific weaknesses and set realistic goals to address them.
- Measurable Objectives: Establish clear , measurable objectives for steady progress.
Adjusting Study Strategies Based on Performance Feedback:
Feedback Analysis: Analyse feedback from teachers and exams to refine your study strategies.
Adaptation : Be flexible; adjust your approach based on what works and what needs improvement.
Mastering A-Level History demands more than knowledge—it requires strategy . By understanding the exam, crafting a precise study plan , utilising resources wisely, perfecting exam techniques, and embracing continuous improvement, you’re primed for A* success.
Stay committed, adapt, and triumph. Need personalised guidance? Connect with a top-notch A Levels History tutor at Study Mind. Contact us today!
How can I balance covering all historical periods without feeling overwhelmed?
Prioritise depth over breadth. Focus on key themes and events within each period, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding. This targeted approach ensures a deeper grasp of the material without overwhelming yourself with excessive details.
What’s the best strategy for managing time during the A-Level History exam?
Practise time trials with past papers to refine your pacing. Prioritise questions based on allocated marks, ensuring you allocate time wisely. This strategic approach maximises your efficiency and enhances overall exam performance.
Are study guides really beneficial, or can I rely solely on textbooks?
Study guides are invaluable supplements. While textbooks offer comprehensive content, study guides provide condensed, exam-focused insights. Combining both resources enhances your understanding, offering a well-rounded preparation for the A-Level History exam.
How can I stay updated on recent historical perspectives and interpretations?
Incorporate scholarly articles from reputable databases like JSTOR and Google Scholar. These sources offer insights into evolving historical perspectives, keeping your knowledge base current and demonstrating a nuanced understanding in your responses.
Is memorisation the key to success in the A-Level History exam?
Memorisation is crucial but not enough. Emphasise understanding, critical analysis, and the ability to apply knowledge to different contexts. A balanced approach ensures you not only recall facts but also demonstrate a higher-order understanding in your exam responses.
How do I overcome stress and anxiety during the A-Level History exam?
Implement stress-management techniques, such as deep breathing and mindfulness, to stay calm. Prioritise self-care in the days leading up to the exam, ensuring adequate rest and relaxation. Remember, a clear mind enhances your ability to recall and articulate historical knowledge effectively.
Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment, cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Let's get acquainted ? What is your name?
Nice to meet you, {{name}} what is your preferred e-mail address, nice to meet you, {{name}} what is your preferred phone number, what is your preferred phone number, just to check, what are you interested in, when should we call you.
It would be great to have a 15m chat to discuss a personalised plan and answer any questions
What time works best for you? (UK Time)
Pick a time-slot that works best for you ?
How many hours of 1-1 tutoring are you looking for?
My whatsapp number is..., for our safeguarding policy, please confirm....
Please provide the mobile number of a guardian/parent
Which online course are you interested in?
What is your query, you can apply for a bursary by clicking this link, sure, what is your query, thank you for your response. we will aim to get back to you within 12-24 hours., lock in a 2 hour 1-1 tutoring lesson now.
If you're ready and keen to get started click the button below to book your first 2 hour 1-1 tutoring lesson with us. Connect with a tutor from a university of your choice in minutes. (Use FAST5 to get 5% Off!)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This guide shows you how to plan, research and write A Level History coursework for Edexcel using ideas, resources, examples and structure. This coursework is weighted towards Assessment Objective Three (AO3) 15% and Assessment Objective One (AO1) 5%.
This guide shows you how to plan, research and write your A Level History coursework for AQA using ideas resources, examples and structure.
In this video I give some guidance on how to get started with A Level History Coursework.Here is my video discussing coursework structure, writing and mark s...
A video giving an overview of the Edexcel A Level History coursework, which makes up 20% of the overall A Level grade.Introduction to video (including a joke...
Explore our A-Level History guide for strategies, vital topics, and key resources to excel in your A-Levels and master historical analysis.
Mentioned below are few easy A-level history tips to write a fine quality of coursework: Stick to the required word limit. If the required word count is of 2000 words so, avoid exceeding it unlike most students do.
What is the A Level history coursework? In the Pearson Edexcel A Level History coursework, students are required to investigate a historical problem, question or issue to form a critical view based on relevant reading on the topic. As part of their research, they are specifically required to analyse, explain and evaluate the interpretations of ...
Are you a student preparing for your A Level History NEA (Non-Examined Assessment)? This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the NEA process, addressing key aspects including structure, word count, and essential tips for success.
This guide has been written by Dr Leif Jerram, a Senior Lecturer in History at the University of Manchester. This guide gives excellent insight into skills and techniques that you could use to plan and write their coursework; as well as indicating the kinds of skills that will be developed if you go on to study History at University.
Unlock A* in A-Level History with strategic tips on exam prep, time management, and resource utilisation. Your path to success starts here.