Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates

How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on September 5, 2024.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2024, September 05). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
Research Proposal Template
Used 7,990 times
4.2 Rating ( 26 reviews)
Reviewed by Olga Asheychik
e-Sign with PandaDoc
Prepared by: [Researcher.FirstName] [Researcher.LastName]

Prepared for: [Supervisor.FirstName]
[Supervisor.LastName]
This should be clear and concise, leaving the reader with no doubt regarding your field of study. A good title structure can often be “Short Title: Longer Explanation of Your Field.” Your academic institution may have a preferred format for the title, or even a title page. Find out before you submit your proposal. If there is no preferred format, keep it simple and clear, and use a “serif” font that is easily legible.
(Main title: What I am trying to find out by taking on this project)
(Academic Institution)
(Subject Area)
[Supervisor.FirstName]
[Supervisor.LastName] (if you already have one)
[Researcher.FirstName]
[Researcher.LastName]
(Student ID/Number)
2. Abstract
100-200 words. This summarizes the central theme of your research. Use concise, clipped language that is academic without being over-wordy and verbose. The abstract needs to be entirely your own words, as every abstract should be completely different, unique in its approach to your topic. Like the rest of the document, apart from block quotations, it should be double-spaced and laid out clearly.
3. Contents
Depending on the length of your research proposal, you may wish to include a contents page for the proposal itself (not for your main research project: suggested contents for this are included in your Proposed Chapter Outline, section 9) , as follows (add page numbers/subsections when you know them, depending on your research) . As you introduce sub-sections into your different sections, number them accordingly e.g. subsections of the literature review could be numbered 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, etc.
Abstract………………………………………pn
Contents……………………………………..pn
Introduction………………………………..pn
Problem Statement……………………pn
Objectives…………………………………..pn
Literature Review……………………….pn
Notion of Original Research……..pn
Key Assertions / Objectives……..pn
Research Methods…………………….pn
Sample Audience……………………….pn
Research Questions…………………..pn
Research Design………………………..pn
Analysis………………………………………pn
Proposed Chapter Outline…………pn
Research Limitations…………………pn
Proposed Timescale………………….pn
Funding (Optional)……………………..pn
References/ Bibliography………….pn
4. Introduction
200-400 words. Unlike the abstract, this is not a summary of everything you are about to say — you can afford to grab your readers’ attention right out of the gate. Deliver a surprise beginning, perhaps a quote from someone who inspires you on this topic, and show your knowledge of the research area (include, if you like, your previous research experience in this field; in fact, it may serve you well to be personal in this section) and why it is relevant to today’s world.
Try to provide facts and references here in order to give relevance to your study and why it is being conducted. This will help to explain the motivation behind your research and how important it is for academia, the industry or public sector it is being conducted in.
5. Problem Statement
Keep this short and informative. This section is meant to provide the reader with a summarized description of the problems you seek to address through your research proposal. Showcase the questions you seek to answer through your research and how it will help benefit those who read it. A problem statement should include the context of the problem, a particular audience you are targeting, and a timeline for the study. This will ensure that your research is well-focused and relevant to the current time and people.
The application of (topic, aka the main title of the subject you are researching) for (a particular group of people) in (timeline, this should either be current year or upcoming years but research can be done on past years as well) .
6. Objectives
This follows up on the problem statement section. It elaborates further on the problem statement by dividing it into a set of 3 to 5 descriptive assertions or intentions that relate to the problem. Objectives establish the scope and depth of your project and also help set up the idea for the research design (as seen later in the research proposal template) . The objectives can also indicate a section that shows how your research will contribute to already existing research and knowledge.
To study the applications of blockchain in the gaming industry and how it can help be a new source of revenue.
To study how blockchain gaming can influence people who don’t gamble to actively invest time in gaming.
To determine whether blockchain gaming can be a viable job opportunity in the future.
7. Literature review
Length can vary immensely, but probably 300-1500 words or more, depending on the nature of your research. This is one of the most important sections of your research proposal. It demonstrates that you know your field, who the key research players are in it, what has been said in the past and what is being said at the moment. You will want to mention — and where appropriate, quote from — key works in your area.
This is the section that requires the most preliminary research, so be sure you spend ample time in an academic library and use search engines for relevant academic papers before presenting. You do not need to discuss every work in your area, but you need to present a competent outline, and (especially if this is a proposal for doctoral research) you need to be sure that no one else has already done the same project. A good way of presenting a literature review coherently is in the form of a narrative, which can either be chronological or thematic.
There has been a (small/considerable/state value here) amount of previous academic research in this field.
(For a chronological narrative) I will outline how the understanding of (subject) has developed over (the last number of) years.
(Insert chronological narrative, remembering to introduce key players, dates, and academic works, and end with the state of the field as it is today.)
(For a thematic narrative) I will outline the major themes that are of relevance in this field, and go through them each in turn:
• (use a bulleted list to outline what themes/topics you are planning on covering)
After your bulleted list, you can use the themes from your list as subtitles to split up your literature review. Put them in bold. You could also add them as subsections in your contents page.
Under each subtitle, describe the state of the field of research in this area, including the most important researchers and works in this area.
8. Notion of original research
Length varies here as well, but similar in length to the literature review is likely a good place to start. This is where you sell your research proposal to the reader. You need to explain, clearly and simply, how your research will complement the field you have just described in your literature review — what you will add, how it fills an existing gap, why the academic world would benefit from your research, etc.
9. Key Assertions/Objectives
One sentence for each question/assertion. This is really part of the “notion of original research” section. A good way of making your research aim clear is to state a clear research question, and back it up with 2-4 specific assertions or objectives.
My central research question is as follows:
(insert research question here, in bold)
In the light of this, I will make the following observations/assertions: (insert observations/assertions here, in bulleted list.)
10. Research methods
Approx. 50-1000 words, depending on the nature of your research. This is where you explain how and where you plan to carry out your research. This will vary hugely depending on your subject. Will you be researching in libraries and archives? Which ones hold the books and documents you will need? Will you need to travel? If so, where? Will your research involve extensive field work? How and where? State whether you will plan to use different methods of data collection, and if so what they will be.
Do you need to be in a laboratory? Will you be emphasizing qualitative or quantitative collection of data, or both equally? Do you have the necessary skills and qualifications to undertake your research (for instance, foreign languages, statistical analysis, laboratory training, etc) ? If not, what are your plans to acquire these skills? (Note: many postgraduate institutions offer considerable support in the acquisition of new skills necessary to perform research, but this will require discussion at the proposal stage.)
11. Sample Audience
This section aims to provide the reader of the proposal with a description of who the sample audience is. You can add a brief description of your ideal sample audience and why such a person is relevant or necessary to the research. You can also mention what measures can be taken to gain their consent for the research in order to get a more enthusiastic and unbiased response. Lastly, you should mention where you propose to find this sample audience and any barriers that may occur in finding or engaging them.
12. Research Questions
13. research design.
This section will give the reader a description of what the research stimuli will look like. It gives a background of the different variations you may employ to better help test your hypothesis. It should also showcase the different factors that may vary a person's response to the research problem while you are researching the topic. This is important in a research proposal, because as with method, different factors help show what could affect you by confirming or denying your hypothesis. Keep your design descriptive and show how you will rule out or control factors that may come up.
14. Analysis
Approx. 50-300 words. Once you have collected your data, include details about what you plan to do with it. Again, depending on the nature of your research, this section could be anywhere from one or two sentences to several paragraphs.
If your research is in a survey format, then include the questions to the survey along with the method of collecting the survey. You can also include a few examples of how you plan to present the data, such as in a pie chart format or as a bar graph.
15. Proposed chapter outline
Probably less than 200 words, unless you have a very detailed plan already in mind. Note: this is like the preliminary contents page, but it does not need to be very specific, and can suggest sections rather than chapters at this stage. The academics reading your proposal will be impressed to know that you have some idea how you may wish to present your work, and that you have some way in mind of translating your research to paper.
(title of your first chapter) (explanation of your first chapter contents: one sentence)
(first subsection of your first chapter)
(second subsection of your first chapter)
(title of your second chapter) (explanation of your second chapter contents: one sentence)
(first subsection of your second chapter)
(second subsection of your second chapter)
(smaller section)
(another small section)
(title of your third chapter) (explanation of your third chapter contents: one sentence)
16. Research limitations
Approx 50-300 words. This section states everything you won’t be able to do in your research. It is surprisingly important, as it shows that you can recognise the limited scale of your work. Every project needs distinct limiting factors and clear boundaries in order to be manageable.
Naturally, the scope of this project is limited. This section describes specific limitations. (add limitations here) .
17. Proposed Timetable
Approx 50-300 words. This section is optional, but may be helpful to show your potential supervisors that you are being realistic and recognize that your project has set parameters within which to conduct the study. It also will help you to know the scale of your work in the preliminary stages of planning, and help you to maintain realistic expectations of yourself.
I predict that this research project will take (number) months/years. I propose a rough timeline, as follows:
(Here, include a list of tasks that will need completing as part of your research project, and how long you predict each will take in terms of weeks or months. End with a final count of months. If you have a predicted start date, you can begin with this and work towards a proposed end date.)
You can also use a project schedule table in order to plan out the project for yourself as well as give a better understanding as to the breakup of the project timeline. An example of this is:
Week | 1 | 2 | 3 | Project End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Date | Jan 1 – Jan 7 | Jan 8 – Jan 14 | Jan 15 – Jan 21 | |
Phase 1 | Planning | | | |
Phase 2 | | Research | | |
Phase 3 | | | Analysis | |
18. Funding
For example, your money allocation table can look like this:
|
|
|---|---|
Items required for research | X amount of dollars |
Permissions | X amount of dollars |
To pay survey respondents | X amount of dollars |
Add in additional details | X amount of dollars |
Add in additional details | X amount of dollars |
|
|
19. References/Bibliography
The reference list should always begin on a new page. Depending on your subject, there will probably be a specific format and referencing pattern for written work (Chicago, Harvard, MLA, Social Sciences) . Before you start writing, make sure you know what the convention for your subject area is, learn it and stick to it. There are a wide variety of different referencing conventions so it is important to make sure you find the correct one and stay consistent.
This will make doing your research proposal (and future research) a lot easier. Depending on your subject, your referencing may involve in-text citations or footnotes. Either way, your proposal will need a full reference list or bibliography at the end, including all of the secondary works you have mentioned in your literature review and primary sources (if applicable) .
You do not, however, need to include work that you have read in preparation but not used or mentioned in your work. Make sure this is correctly formatted — plenty of style guides for each referencing style are available online. Also, remember to lay out your reference list in alphabetical order by the authors’ surnames.
[Researcher.FirstName] [Researcher.LastName]
Care to rate this template?
Your rating will help others.
Thanks for your rate!
Useful resources
- Featured Templates
- Sales Proposals
- NDA Agreements
- Operating Agreements
- Service Agreements
- Sales Documents
- Marketing Proposals
- Rental and Lease Agreements
- Quote Templates
- Business Proposals
- Agreement Templates
- Purchase Agreements
- Contract Templates
How to write a research proposal?
To make a comprehensive research proposal, make sure you answer all the questions your review committee might have, such as who is your sample audience, what kind of questions you plan to ask them, why you are conducting this research, what you think will come out of it, etc. Leave no room for assumptions. Alternatively, you can also use this template to best understand which nitty-gritty details to cover.

Proposal Templates > Research Proposal Template
Research Proposal Template
Ready to start on a research proposal, but don’t know where to begin? Why not start with our polished research proposal template that helps you get your research thoughts on paper and gives you a solid structure to present your research.


Free Research Proposal Examples
Free Download
Research Proposal Checklist
The simplest way to ensure that your research proposal ticks the necessary academic boxes and gets your study approved .
Rating: 4.9 out of 5 Downloads: 5000 +

Step-By-Step Instructions
Tried & Tested Format
Plain-Language Terminology
Pro Tips, Tricks And Resources
download your copy
100% Free to use. Instant access.
I agree to receive the checklist and other useful resources.
Download Now (Instant Access)

Learn The Basics
This video covers the big-picture process of how to craft a convincing research proposal.
Additional Resources
If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis, you’ll also want to check these out…
1-On-1 Private Coaching
Research Bootcamps
The Grad Coach YouTube Channel
The Grad Coach Podcast
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Active funding opportunity
Nsf 24-576: gen-4 engineering research centers, program solicitation, document information, document history.
- Posted: May 20, 2024
- Replaces: NSF 22-580
Program Solicitation NSF 24-576
|
Letter of Intent Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
September 03, 2024
Preliminary Proposal Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
September 30, 2024
Full Proposal Deadline(s) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
By Invitation Only
Important Information And Revision Notes
This solicitation encourages proposals addressing a broad spectrum of engineering topics, including but not limited to advanced manufacturing, advanced wireless, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, microelectronics and semiconductors, net-zero technologies, quantum engineering, and systems engineering for healthcare.
This solicitation is updated to clarify the definition of underrepresented students in STEM and to welcome proposal submissions that broaden geographic and demographic participation. More details are provided in Section IV. ELIGIBILITY INFORMATION .
Cost Sharing: Cost sharing is required. The formula for required cost sharing is described in the full text of this solicitation.
Any proposal submitted in response to this solicitation should be submitted in accordance with the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) that is in effect for the relevant due date to which the proposal is being submitted. The NSF PAPPG is regularly revised and it is the responsibility of the proposer to ensure that the proposal meets the requirements specified in this solicitation and the applicable version of the PAPPG. Submitting a proposal prior to a specified deadline does not negate this requirement.
Summary Of Program Requirements
General information.
Program Title:
Gen-4 Engineering Research Centers (ERC) Convergent Research and Innovation through Inclusive Partnerships and Workforce Development
Founded in 1984, the Engineering Research Centers (ERC) program brings technology-based industry and universities together in an effort to strengthen the competitive position of American industry in the global marketplace. These partnerships are expected to establish cross-disciplinary centers focused on advancing fundamental engineering knowledge and engineered systems technology while exposing students to the integrative aspects of engineered systems and industrial practice. The goal of the ERC program has traditionally been to integrate engineering research and education with technological innovation to transform and improve national prosperity, health, and security. Building upon this tradition, NSF is interested in supporting ERCs to develop and advance engineered systems, which if successful, will have a high Societal Impact. The ERC program supports convergent research (CR) that will lead to strong societal impact. Each ERC has interacting foundational components that go beyond the research project, including engineering workforce development (EWD) at all participant stages, where all participants gain mutual benefit, and value creation within an innovation ecosystem (IE) that will outlast the lifetime of the ERC. These foundational elements are integrated throughout ERC activities and in alignment with the Center's vision and targeted societal impact. The overall impact of the ERC program is expected within the Engineering Community, the Scientific Enterprise, and Society.
Cognizant Program Officer(s):
Please note that the following information is current at the time of publishing. See program website for any updates to the points of contact.
Sandra Cruz-Pol, telephone: (703) 292-2928, email: [email protected]
Dana L. Denick, telephone: (703) 292-8866, email: [email protected]
Randy Duran, telephone: (703) 292-5326, email: [email protected]
Nadia A. El-Masry, telephone: (703) 292-4975, email: [email protected]
Paul Torrens, telephone: (703) 292-2473, email: [email protected]
Lan Wang, telephone: (703) 292-5098, email: [email protected]
- 47.041 --- Engineering
Award Information
Anticipated Type of Award: Cooperative Agreement
Up to 4 depending on the quality of the proposals and the availability of funds. ERCs are generally funded for ten years, with an initial award for the first five years and second award based on performance and review of a renewal proposal. This solicitation seeks to make awards for the first five years for new ERCs.
See Section III of this solicitation for additional information about the allowable maximum annual budget for years one through five.
NSF expects to make the ERC awards in the summer of 2026. The budget distribution among the lead and core partners should be appropriate for the scope of work and activities planned for each foundational component.
Note that ERCs will not be granted no-cost extensions (NCE).
Co-funding:
NSF is currently in negotiations with other government agencies to form partnerships in support of ERC awards. These partnerships have the potential to expand the total number of awards. This is contingent upon realization of these partnerships, and budgets provided to these organizations by Congress for FY 2026 and 2027.
Eligibility Information
Who May Submit Proposals:
Proposals may only be submitted by the following:
Only U.S. Institutions of Higher Education (IHEs), also referred to in this solicitation as universities and academic institutions, accredited in, and having a campus located in the US, that grant engineering degrees at the undergraduate, masters, and doctoral engineering level may submit proposals as the lead university. The Lead university submits the proposal, and the award is made to the lead university. Support is provided to core partner universities and any affiliated faculty from other partner institutions through subawards. NSF welcomes proposal submissions that broaden geographic and demographic participation. Proposals from STEM-minority-serving institutions (STEM-MSI*), non-R1 schools, emerging research institutions, and IHEs in EPSCoR-eligible jurisdictions, as lead or core partners, as well as IHEs that primarily serve populations of students with disabilities or women in engineering interested in STEM, are encouraged.
Invited full proposals must meet all the following organizational requirements or they will be returned without review:
- The Lead must be an Institution of Higher Education per the Carnegie Foundational Attribute: https://carnegieclassifications.acenet.edu/
- A proposed ERC must be multi-institutional, with a lead university and additional domestic university core partners. There is no maximum number of partner institutions.
- To qualify as a core partner institution, there must be financial support for a minimum of three faculty participating in the ERC along with financial support for a minimum of three students (Postdoctoral scholars may not be included as students).
- The lead or at least one of the core partner universities must be a STEM-MSI* university.
- Commitments from lead and core partner universities for cost sharing must be in place.
*For this solicitation STEM-MSI is defined by the Department of Education as institutions of higher education enrolling populations with significant percentages of undergraduate minority students, or that serve certain populations of minority students under various programs created by Congress.
Eligibility may be determined by reference to the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) of the US Department of Education National Center for Education Statistics ( https://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/ ).
Who May Serve as PI:
The Lead PI must be a faculty member at the Lead university. Non-Lead PIs are the co-PIs listed on the Cover Sheet after the Lead PI and may be from institutions other than the lead university. In order to provide more flexibility for the Center's management, the Lead PI and the ERC Director are not required to be the same person, however, both must be affiliated with the lead institution.
Limit on Number of Proposals per Organization:
If an institution has two active ERC awards, it does not qualify to submit an ERC preliminary proposal as a lead institution. There are no other restrictions or limits on the number of preliminary proposals submitted by a Lead institution. Full Proposals may be submitted only by invitation and only by the lead institution designated in the preliminary proposal.
Limit on Number of Proposals per PI or co-PI:
There are no restrictions or limits.
Proposal Preparation and Submission Instructions
A. proposal preparation instructions.
Letters of Intent: Submission of Letters of Intent is required. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Preliminary Proposals: Submission of Preliminary Proposals is required. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Full Proposals:
- Full Proposals submitted via Research.gov: NSF Proposal and Award Policies and Procedures Guide (PAPPG) guidelines apply. The complete text of the PAPPG is available electronically on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg .
- Full Proposals submitted via Grants.gov: NSF Grants.gov Application Guide: A Guide for the Preparation and Submission of NSF Applications via Grants.gov guidelines apply (Note: The NSF Grants.gov Application Guide is available on the Grants.gov website and on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=grantsgovguide ).
B. Budgetary Information
Cost Sharing Requirements:
Cost Sharing is required. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Indirect Cost (F&A) Limitations:
Not Applicable
Other Budgetary Limitations:
Other budgetary limitations apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
C. Due Dates
Letter of Intent Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization's local time):
Preliminary Proposal Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization's local time):
Proposal Review Information Criteria
Merit Review Criteria:
National Science Board approved criteria. Additional merit review criteria apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Award Administration Information
Award Conditions:
Additional award conditions apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Reporting Requirements:
Additional reporting requirements apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
I. Introduction
The National Science Foundation (NSF) created the Engineering Research Centers (ERC) program in 1984 to bring technology-based industry and universities together in an effort to strengthen the competitive position of American industry in the global marketplace. These partnerships established cross-disciplinary centers focused on advancing fundamental engineering knowledge and engineered systems technology while exposing students to the integrative aspects of engineered systems and industrial practice. As a result, ERCs have produced a wide range of new fundamental knowledge, engineered systems and other technologies aimed at spawning whole new fields or industries or radically transforming the product lines, processes, and practices of current industries. At the same time, they have produced a new generation of engineering graduates who are highly innovative, diverse, globally engaged, and effective as technology leaders in academia and industry.
NSF has continually refined the goals and purposes of the ERC program to meet shifting needs. The NSF-requested 2017 study from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) "A New Vision for Center-Based Engineering Research" ( https://www.nap.edu/catalog/24767/a-new-vision-for-center-based-engineering-research ) recommends that NSF places a greater emphasis on forming research centers focused on convergent research and education approaches that address challenges with significant societal impact. Complex societal problems require a convergent approach for the deep integration of knowledge, tools, and ways of thinking across disciplinary boundaries. A detailed explanation of the convergence concept can be found in a 2014 National Academies report, "Convergence: Facilitating Transdisciplinary Integration of Life Sciences, Physical Sciences, Engineering and Beyond" ( https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18722/convergence-facilitating-transdisciplinary-integration-of-life-sciences-physical-sciences-engineering ).
This current iteration of the ERC program reflects the recommendations from the NASEM study as well as other sources. The program continues to focus on advancing an engineered system through inclusive cross-disciplinary and cross-sector partnerships, while placing greater emphasis on research with high- risk/high-payoff ideas that lead to societal impact through convergent approaches, engaging broader stakeholder communities, and using team science concepts for their team formation.
II. Program Description
A. ERC Program Model
The ERC program is grounded by the four foundational components of the ERC: Convergent Research (CR), Engineering Workforce Development (EWD), Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI), and the Innovation Ecosystem (IE) (Figure 1). These foundational components are connected by an integrated, holistic ERC vision and strategic plan. The whole of the ERC has added value and synergies that require a center or institute-like approach as opposed to individual projects.
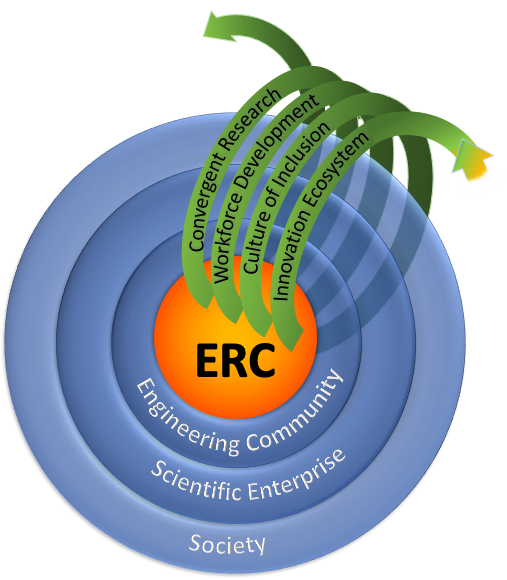
Convergent Research (CR): High-risk/high-payoff research ideas and discoveries that push the frontiers of engineering knowledge; ERC convergent research is a highly collaborative and interdisciplinary approach that leads to positive impacts on society. Convergence involves the integration of various fields in engineering and science, including all branches of science, in a coordinated and interdependent manner. This approach fosters strong collaborations that are essential for successful inquiry.
Engineering Workforce Development (EWD): In addition to training opportunities for ERC participants, the Center engages in human resource capacity development aligned with the targeted engineered system. ERC EWD strengthens a robust spectrum of engineering education pathways and technical workforce opportunities. EWD occurs at all levels of the Center and provides opportunities for engagement by all ERC members including students, faculty, and external partners as appropriate. The ERC EWD program is driven by the future education, workforce development, and labor market needs relevant to the proposed Center.
Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI): In addition to fomenting a diverse team, the culture of the ERC and teams within the ERC demonstrate an environment of inclusion in which all members feel valued and welcomed, creatively contribute, and gain mutual benefit from participating. Because of the ERC's attention to diversity and culture of inclusion, participation from members of groups traditionally underrepresented in engineering as well as diverse scientific and other perspectives is required. The ERC DCI program ensures diversity at all levels of the Center and employs an intentional and evidence-based approach to developing a culture of inclusion.
Innovation Ecosystem (IE): Trusted partners that work together to create and enhance the capacity for innovation and new ways for delivering value with positive societal impact. ERC innovation ecosystems (IE) include effective translational efforts from ideation to implementation, workforce development that creates the workforce needed for the enterprise, and deliberate efforts to attract funding and resources. ERCs articulate plans for strategic engagement of stakeholder communities while including the legal, ethical, civic, and societal acceptance frameworks needed to protect the participants.
The ERC foundational elements are carried out in concert through ERC activities and in alignment with the Center's vision and targeted societal impact. The overall impact of the ERC program is expected within the Engineering Community , the Scientific Enterprise , and Society , shown in Figure 1 (above). These may be thought of as nested regions of increasing influence, where the largest scale of impact is on society itself. Potential outcomes of ERCs are organized within each of the four ERC foundational components.
Engineering Community: ERCs not only create fundamental knowledge and technology, but also impact the engineering community, preparing students and researchers by highlighting new engineering approaches and best practices for engineering workforce development, diversity and inclusion, and academic-industrial partnerships.
Scientific Enterprise: ERCs should be exemplars of how cohesive, high-performing teams engage in convergent research and innovative approaches to create major impact that informs and inspires the scientific community, engineering and beyond.
Society: ERCs enable society to have a better quality of life, and be more resilient, productive, and safe. Each ERC is expected to have a transformational positive impact on significant societal challenges and opportunities. This is the level where the introduction of value creation and technology innovation requires an understanding of socio-technical interactions and how they might impact society at large. In response, new strategies, concepts, ideas and/or re- organizations may be needed to shore-up, extend, or strengthen society. The desired outcome is the ERC's ability to assist society in its drive to advance the national health, prosperity, welfare, and to secure the national defense.
The goal of the ERC program has traditionally been to integrate engineering research and education with technological innovation to transform and improve national prosperity, health, and security. Building upon this tradition, NSF is interested in supporting ERCs to develop and advance engineered systems, which if successful, will have a high Societal Impact .
ERCs create inclusive cultures not only to integrate scientific discovery with technological innovation through convergent engineered systems research and education, but also to include the participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in engineering. ERCs build partnerships with industry, practitioners, and other key stakeholders to strengthen the innovative capacity of the United States in a global context. In addition to building capacity for research, innovation, and a diverse workforce, ERCs are expected to produce significant outcomes within the 10-year timeframe of NSF support and beyond.
ERCs should realize a vision of advancing an engineered system driven by clearly articulated societal impact and should have strong synergies or value-added rationale that justifies a center or institute-like approach. As part of creating sustainable positive impacts on society and communities, ERCs should focus on positive outcomes that can be seen within engineering communities and build and empower human resource capacity for their targeted engineering challenges. Beyond this, ERCs should contribute to the scientific enterprise by advancing research, science, engineering fundamentals, and research communities. This should be demonstrated with benchmarks against the state-of-the-art. ERCs should build knowledge, prepare students and researchers that respect and flourish in an environment with diverse perspectives, impact how engineering research is conducted and provide value for society. The ERC program encourages proposals addressing a broad spectrum of engineering topics, including but not limited to advanced manufacturing, advanced wireless, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, microelectronics and semiconductors, net zero technologies, quantum engineering, and systems engineering for healthcare.
C. Key Elements of an ERC
Vision: The ERC vision guides discovery and technology to uniquely transform US prosperity, health, and/or security in 10 years. The vision describes the compelling new idea, explains how it relates to national needs, and makes the connection to engineering.
Strategic Plan: The ERC strategic plan connects and leverages research, engineering workforce development, diversity and culture of inclusion, and innovation ecosystem to address the chosen societal challenge. The overall plan should employ three strategic approaches:
Convergence : "Convergence is an approach to problem solving that cuts across disciplinary boundaries. It integrates knowledge, tools, and ways of thinking across disciplinary boundaries in STEM fields to form a comprehensive synthetic framework for tackling scientific and societal challenges that exist at the interfaces of multiple fields." ( https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18722/convergence-facilitating-transdisciplinary-integration-of-life-sciences-physical-sciences-engineering ). This is also stated in another report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) from the Committee on a Vision for the Future of Center-based Multidisciplinary Engineering Research, which defined convergent engineering as a deeply collaborative, team-based engineering approach for defining and solving important and complex societal problems ( https://www.nap.edu/catalog/24767/a-new-vision-for-center-based-engineering-research ). Hence, convergent research blends scientific disciplines in a coordinated, reciprocal way and fosters the robust collaboration needed for successful inquiry and has the strong potential to lead to transformative solutions and new fields of study. The research thrusts, testbeds, team formation, and other major aspects of the research plan should support a convergent approach.
Stakeholder Engagement : The intentional and early-stage engagement of all parties who may contribute to the ERC or may be impacted by the ERC along its capacity-building and value creation responsibilities. Stakeholders can include, but are not limited to, relevant researchers across partner institutions with complementary research and education expertise; undergraduate and graduate students, postdoctoral researchers; industry leaders who can guide the innovation effort; partners for innovation, education, workforce development, and diversity and culture of inclusion of all participants; and beneficiaries of the ERC outcomes (e.g., community members, users, customers, patients, and watchdog organizations).
Team Formation : The process by which all necessary disciplines, skills, perspectives, and capabilities are brought together. Successful teams are interdependent, multidisciplinary, and diverse and can work and communicate effectively even when geographically dispersed. Team formation includes evidence-based strategies and team science training to overcome barriers to effective, collaborative teaming, including the integration of members with different areas of expertise, different vocabularies and core values and ways of approaching problems, different understanding of the problems to be addressed, different values, and different working styles. This is especially needed during the early stages of the Center.
Organization and Management Structure:
Effective Leadership: ERC leaders have intellectual vision, demonstrable leadership, successful entrepreneurial experience, a track record of delivering results, and the ability to communicate clearly and effectively with diverse audiences such as team members, sponsors, partners, host institutions, stakeholders, press and media, and the public. Below are some example practices desired for effective ERC leadership and management teams:
- Empowers all team members to contribute;
- Builds consensus around goals and problem definition;
- Facilitates communication to ensure a common understanding among all stakeholders; and resolves conflicts and builds trust.
It is rare that a single individual will have all of these attributes; thus, a strong leader will need to assemble an executive team that covers this broad spectrum of skills. The Center Director should understand their strengths and limitations, should be effective in assembling an executive leadership team that fills in the gaps of their limitations, and should be supported by an effective Council of Deans (See Section II.C. for details of the formation of the Council of Deans).The Director does not need to be a faculty member.
Organization and Management: An effective management structure begins with a clear understanding of the goals of the ERC and how the structure (including the ERC four foundational components) will support those goals. The structure should have the flexibility to adapt as the needs of the ERC change, as key people transition into or out of the ERC, or change roles, and to handle other changes as the ERC matures.
It is critical to have one person or team that has clear responsibility for each foundational component of the ERC. However, each ERC participant and each of the core participants should also understand the importance of each foundational component and be engaged in their role in carrying it out. Core partner institutions must meet the eligibility requirements of at least 3 faculty and 3 students participating in the ERC; postdoctoral scholars may not be included as students. Proposing teams will determine the funding source(s) of student support and nature of participation, whether graduate or undergraduate. Typically, ERC’s have many more fully/partly funded graduate and undergraduate students engaged in the ERC, in addition to faculty or postdocs.
ERC program experience has shown that an important role in the ERC structure is that of an administrative director, as described below. This remains a mandatory piece of the management structure.
Administrative Director: An experienced staff member at the lead university who is responsible for operational management, financial management, data collection, publicity, and reporting, etc. for the ERC. Post-award NSF training is available for this position given the ERC reporting complexities.
Lead Institution: The lead institution effectively guides the multiple elements of the ERC. The ERC headquarters are located at the lead institution, and the lead institution is the NSF recipient and is ultimately responsible for the financial and reporting obligations of the ERC award.
Core Partners: To qualify as a core partner university, there must be a minimum of three faculty participating in the ERC along with a minimum of three students; postdoctoral scholars may not be included as students. Core partners are included in the Cost Sharing requirements and in the Council of Deans (See Section II.C. for details of the formation of the Council of Deans.)
Other potential partners may include universities contributing affiliated faculty, federal laboratories, private-sector or non-profit organizations, educational partners, and/or foreign collaborators' universities or institutions. While not considered core partners, the involvement of such partners can be valuable.
Industrial/Practitioner Member: An organization that satisfies all requirements for membership according to the Center's membership agreement which may include financial support (cash or in-kind).
ERCs should engage industrial/practitioner members from sectors such as the Federal Government, State government, local government, quasi-government research, industry, industry association, policy organization, regulatory agency, medical facility, private foundation, nonprofit, venture capitalists, community organizations, professional/trade union, and other stakeholders as appropriate for the center's mission.
Affiliated Faculty Member: The ERC may include affiliated faculty members, which are faculty members who are contributing to the ERC from institutions other than the lead or core partner universities and are included in the budget.
Institutional Commitment: The lead and all core partner institutions must augment support for the ERC through cost-sharing and other allowed means and sustain the ERC once NSF's support ceases. Lead, core, and other partner academic institutions must commit to:
- Joining in partnership to support the ERC's vision, strategic plans, and activities in CR, EWD, DCI, IE and their integration across the institutions.
- Assuring cross-university industrial membership and intellectual property (IP) policies that recognize shared rights for joint work.
- Adopting institutional policies to reward faculty, particularly those in the promotion and tenure process, for participating in convergent research and innovation, technological advance, mentoring, university and pre-college education activity, and delivering on the ERC's plans for workforce development and creating an inclusive and diverse culture. NSF strongly encourages the full spectrum of diverse talent that society has to offer.
- Official recognition for university students engaged in mentoring of other university students and in pre-college outreach. This recognition is crucial to acknowledge their efforts and motivate them to continue their valuable work
Community Feedback: Broad-based stakeholder feedback to the ERCs is one of the important mechanisms used by the ERC to provide continual monitoring of the Center's health.
Advisory Boards: Advisory boards are formed to reinforce and support the proper functioning of the ERC's foundational components which are CR, EWD, DCI, and IE, as described above. Careful consideration must be given to defining each advisory board's functional role and selecting quality board members capable of overseeing that role. An example of a generic ERC feedback loop structure is illustrated in Figure 2. As part of the NSF Management/Oversight, the NSF Program Director and the NSF Site Visit Team (SVT) typically interact with the ERC and give feedback to the ERC once a year at a minimum. The advisory boards provide feedback at least twice a year; usually more often on an as needed basis. It may occasionally be necessary to form additional special committees to support special needs of the Center's vision. The staffing of these committees may be either internal or external. The Council of Deans and Student Leadership Council, as defined below, are mandatory advisory groups; however, the ERC is expected to propose appropriate advisory groups beyond these two.
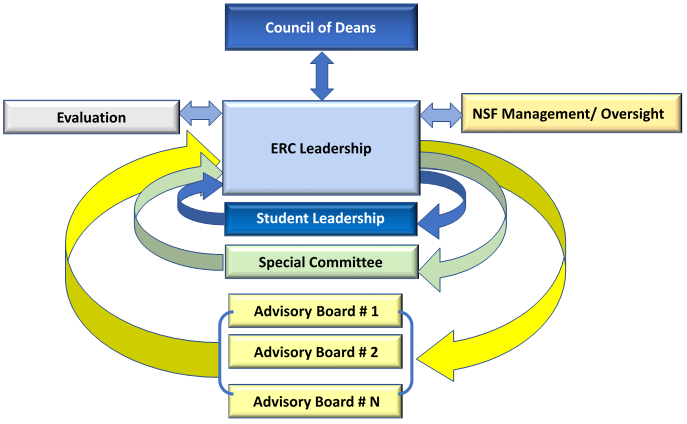
Student Leadership Council (SLC): Undergraduate and graduate students from all partner universities responsible for coordinating their various activities in support of the ERC. A student president and a student co-president lead the SLC. The SLC will prepare a written Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis and present the SWOT findings during the annual visit of the NSF Site Visit Team (SVT).
Council of Deans: Led by the Dean of Engineering from the Lead university, this Council includes the Deans from the lead and each core partner institution. They meet collectively to provide administrative support of the ERC and to help facilitate multiple ERC elements across the lead and core partner universities. The Dean may not designate an alternate unless a PI, Co-PI, Director, or any senior personnel is also a Dean at the Institution. The two roles cannot be performed by the same person.
III. Award Information
Estimated program budget, number of awards, and average award size/duration are subject to the availability of funds. The maximum annual budget allowed is shown in the table below.
|
|
1 | $3,500,000 |
2 | $4,500,000 |
3 | $6,000,000 |
4 | $6,000,000 |
5 | $6,000,000 |
Year 1 budget will be committed upon award, and subsequent year budgets are subject to satisfactory annual review of accomplishments and availability of funds. After a gradual ramp up, years three through five are projected to level off at $6,000,000 in each of those years. Pending performance and outcome of a renewal review in the fourth year, support for years six to eight will continue at $6,000,000 per year until the eighth year. Support for years nine and ten will be phased down, with $4,000,000 in year 9 and $2,600,000 in year 10. No-cost extensions (NCEs) will not be granted.
IV. Eligibility Information
Proposals may only be submitted by the following: Only U.S. Institutions of Higher Education (IHEs), also referred to in this solicitation as universities and academic institutions, accredited in, and having a campus located in the US, that grant engineering degrees at the undergraduate, masters, and doctoral engineering level may submit proposals as the lead university. The Lead university submits the proposal, and the award is made to the lead university. Support is provided to core partner universities and any affiliated faculty from other partner institutions through subawards. NSF welcomes proposal submissions that broaden geographic and demographic participation. Proposals from STEM-minority-serving institutions (STEM-MSI*), non-R1 schools, emerging research institutions, and IHEs in EPSCoR-eligible jurisdictions, as lead or core partners, as well as IHEs that primarily serve populations of students with disabilities or women in engineering interested in STEM, are encouraged. Invited full proposals must meet all the following organizational requirements or they will be returned without review: The Lead must be an Institution of Higher Education per the Carnegie Foundational Attribute: https://carnegieclassifications.acenet.edu/ A proposed ERC must be multi-institutional, with a lead university and additional domestic university core partners. There is no maximum number of partner institutions. To qualify as a core partner institution, there must be financial support for a minimum of three faculty participating in the ERC along with financial support for a minimum of three students (Postdoctoral scholars may not be included as students). The lead or at least one of the core partner universities must be a STEM-MSI* university. Commitments from lead and core partner universities for cost sharing must be in place. *For this solicitation STEM-MSI is defined by the Department of Education as institutions of higher education enrolling populations with significant percentages of undergraduate minority students, or that serve certain populations of minority students under various programs created by Congress. Eligibility may be determined by reference to the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) of the US Department of Education National Center for Education Statistics (https://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/).
V. Proposal Preparation And Submission Instructions
Letters of Intent (required) :
1. LETTER OF INTENT
A Letter of Intent (LOI) is required to facilitate the NSF review process. The LOI must be submitted via Research.gov no later than the LOI deadline date. Please note the following conditions:
- LOIs must be submitted through Research.gov (not Grants.gov). A Minimum of one PI and up to four co-PIs are allowed.
- A list of all anticipated Core Partner Universities is required.
- The lead university cannot change after submission of the Letter of Intent.
Title: The title should begin with "NSF Engineering Research Center for ( insert the rest of the title and the Center's acronym )". The title should reflect the engineered system of the proposed ERC.
Lead PI and/or Center Director: The Lead PI's information is automatically included when the LOI is created. If the Lead PI and the Center Director are different individuals, please include the Center Director's name, university, department, phone number, and e-mail address at the beginning of the Synopsis section.
Anticipated ERC Non-Lead PIs (co-PIs): Identify up to four co-PIs. For the LOI, the participating team (Senior/Key Personnel) will be limited to the lead PI and up to four co-PIs who may come from any or all the domestic core partner universities.
Anticipated Core Partner Universities: The Lead university (not PI) is binding throughout the process. Other partners may change. The anticipated core partner universities should be included in the Manage Participating Organizations section of the LOI.
Synopsis (not to exceed one page): Upload brief statements of the vision and goals of the ERC, its potential for societal impact, and an integrated plan for the Center. Include an overview of the research program, such as research thrust titles, goals, and fundamental gaps or barriers in knowledge/technology that it meets. Although the EWD, DCI, and the IE are also critical foundational components of an ERC, they do not need to be described in detail in the LOI.
Other Comments (an additional max 2,500 characters including any blank spaces): Continue Synopsis as needed in this section.
Keywords: In order of decreasing emphasis, list up to ten keywords that represent the scientific interdisciplinary content in the proposal.
Letter of Intent Preparation Instructions :
When submitting a Letter of Intent through Research.gov in response to this Program Solicitation please note the conditions outlined below:
Submission by an Authorized Organizational Representative (AOR) is not required when submitting Letters of Intent.
A Minimum of 0 and Maximum of 4 Other Senior Project Personnel are permitted
A Minimum of 0 and Maximum of 6 Other Participating Organizations are permitted
- Keywords is required when submitting Letters of Intent
- Submission of multiple Letters of Intent is permitted
Preliminary Proposals (required) : Preliminary proposals are required and must be submitted via Research.gov, even if full proposals will be submitted via Grants.gov.
2. PRELIMINARY PROPOSAL
Submission of a Preliminary Proposal is required to be eligible for an invitation to submit a Full Proposal.
Preliminary Proposal Preparation Instructions:
Preliminary proposals must explicitly address the following questions in the project description:
- What are the compelling new ideas and what is the potential for high societal impact?
- What is the ERC engineered system? Is it high-risk but high payoff? Is the 3-plane chart well-conceived and justified?
- Why is an ERC necessary to tackle the idea?
- What is the proposed management structure for the ERC? How will the ERC's organization and management structure integrate and implement the four foundational components (CR, EWD, DCI, and IE) and foster the desired team formation?
- What are the proposed strategies for engaging and developing the appropriate stakeholder community?
- Does the proposed ERC create an inclusive environment where all the ERC participants learn to work in a team towards a common goal?
Preliminary Proposal Set-Up: Select "Prepare New Preliminary Proposal" in Research.gov. Search for and select this solicitation title in Step One of the Preliminary Proposal wizard. The information in Step 2 is pre-populated by the system. In Step 3 select "Single proposal (with or without subawards). Separately submitted collaborative preliminary proposals will be returned without review.
Title: The title should begin with "NSF Engineering Research Center for ( insert the rest of the title and the Center's acronym )". The rest of the title and acronym can change from the LOI to the submitted preliminary proposal as long as it is in the same topic area. The title should reflect the system focus of the proposed ERC.
The required components of the preliminary proposal are given below. Page limitations given here will be strictly enforced. Proposers should review the most current PAPPG for specific information and format for the required sections. No other sections are required or may be included in the preliminary proposal.
Cover Sheet: Select the proposed start date and proposed duration.
Project Summary (1 page): The Project Summary must have three separate section headers entitled "Overview", "Intellectual Merit", and "Broader Impacts"; each heading must be on its own line with no other text on that line. Within the Overview section, include a separate sub-section entitled "Proposed Vision". The summary should be informative to those working in the same or related fields and understandable to a scientifically or technically literate reader.
Project Description: Maximum 10 pages, total, containing the following sections, not necessarily in this order. All figures and tables must be included within the 10-page limit.
The proposing team (Participant Table) should be submitted as a supplementary document.
The Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts of the ERC must be addressed and described throughout the narrative as an integral part of the Project Description. Between Sections IV and V, include a separate header for Broader Impacts, as specified below. In addition, Results from Prior Support is not a required section for the preliminary proposal.
Outline for the Preliminary Proposal Project Description (up to 10 pages)
II. Strategic Plan
III. Organization and Management Structure
IV. Convergent Research
BROADER IMPACTS ( Please note: The Project Description must include a separate section header labeled Broader Impacts and the heading must be on its own line with no other text on that line. )
V. Engineering Workforce Development
VI. Diversity and Culture of Inclusion
VII. Innovation Ecosystem
I. Vision: The proposed vision for the ERC must be explained, with a discussion of the convergent engineering research theme and the anticipated societal impact. Explain the proposed transformative engineered system and the potential for impact on society, the engineering community and the greater scientific community.
II. Strategic Plan: The plan must define the engineered system and describe how the features of the ERC will be integrated to achieve the vision, in particular the cohesive plan for involving participants at all levels in the four foundational components:
- Convergent Research (CR)
- Engineering Workforce Development (EWD)
- Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI)
- Innovation Ecosystem (IE)
III. Organization and Management Structure: Describe the proposed management, including the functions of key personnel and the role of any advisory committee (including the required Student Leadership Council and the Council of Deans), executive committee, program committee, or their equivalent. Note that there is no recommendation for how ERCs should be managed. This solicitation provides for flexibility on organization structure and management and is part of the review criteria – as such the proposal should clearly justify the proposed structure.
IV. Convergent Research (CR): The role of convergence and team formation in the proposed research must be described. Research activities must address any gaps and barriers to achieve the proposed vision. Research must advance fundamental knowledge and support the development of technology that is proven through proof-of-concept testbeds as part of a well-defined engineered system. Integration of research activities must be graphically depicted on a clearly legible version of the ERC Program's 3-Plane Strategic Planning Chart ( http://erc-assoc.org/content/three-plane-diagram ) that is tailored to the proposed ERC. The chart should be at least half a page, but a full page is recommended for legibility, as this chart is used at several stages of the NSF review process. This section should clearly state what new knowledge is expected that would advance the state of the art in key research areas.
V. Engineering Workforce Development (EWD): A proposed evidence-based program for human capacity development for the future engineering and technical workforce must be described. The program goals and expected outcomes must be described. Proposed activities should logically lead to targeted outcomes and support diverse pathways and experiences for participants. Existing programs and partnerships may be leveraged to support the ERC EWD program and provide opportunities to engage with potential participants.
VI. Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI): Preliminary ideas to create and nurture a culture of inclusion to foster the engagement of all ERC participants. This section should include evidence-based and intentional programming approach.
VII. Innovation Ecosystem (IE): An innovation ecosystem development effort must be proposed. However, DO NOT list potential or committed industrial or other supporters.
In addition, the preliminary proposal must also include these documents and information.
References Cited (required): See PAPPG for format guidelines.
Senior/Key Personnel Documents: The Lead PI, Center Director (if different from the Lead PI) and up to four co-PIs) must be designated as Senior/Key Personnel and must provide the following documents in accordance with the guidance contained in PAPPG Chapter II.D.2.h.
- Biographical Sketches
- Collaborators & Other Affiliations (COA)Information
Supplementary Documents:
A letter of commitment from the Dean of Engineering of the lead institution must be submitted which describes the support for and commitment to the ERC (including space for the ERC headquarters) should it be funded. While the Lead PI does not need to be from the School of Engineering, this letter must be from the Dean of Engineering to demonstrate the Engineering Dean's support for the proposed impact of the ERC on the engineering community.
The Dean should NOT include any financial commitments. Instead, the Dean should make a statement as to how the proposed ERC will align with the strategic directions of the college or the university. Proposals submitted without a letter of commitment from the Dean of Engineering will be returned without review. No letters of collaboration are allowed.
Participant Table (one page maximum): Provide a participant table that includes all committed ERC personnel: (1) Name of the Lead PI (and ERC Director, if different from the Lead PI) and Non-Lead PIs, (2) Institution(s), (3) Department(s), and (4) Most Relevant Field(s) of Expertise. In addition, please list all committed senior/key personnel. Do not identify members of advisory boards. The team table should include only those personnel who would receive NSF funds. This table is used by NSF in the merit review process to manage reviewer selection.
Single Copy Documents:
Collaborators & Other Affiliations Information: Information regarding collaborators and other affiliations (COA) must be separately provided for all members of the ERC Leadership Team and key faculty who are not designated as Senior/Key Personnel. Proposers must follow the guidance contained in PAPPG Chapter II.D.2.h. and include the COA information in the Additional Single Copy Documents section of the preliminary proposal. The accuracy of this section is very important to the integrity of the ERC review process. Please be accurate, up to date, and complete with the entries, including professional email addresses.
Institutional Affiliations: Beyond the affiliations captured on the COA form for individual ERC participants, the ERC Lead University must report any institutional affiliations arising from partnerships including any government agencies, international partners, industry partners or other non-academic institutional partners. The institutional affiliation information must be entered into the ERC Preliminary Proposal Institutional Conflict template (See bullet #2 on http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 ) and uploaded into the Additional Single Copy Documents section.
DO NOT SUBMIT other documents, including letters of commitment or collaboration from the domestic partner universities, prospective industrial members, or other future partners. The only allowed item is the required letter of commitment from the Dean of Engineering at the Lead Institution.
RELIMINARY PROPOSAL REQUIREMENTS
(Note: This is NOT a total list of the ERC preliminary proposal requirements. Refer to the ERC Solicitation and the PAPPG for complete requirements).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Full Proposal Preparation Instructions : Proposers may opt to submit proposals in response to this Program Solicitation via Research.gov or Grants.gov.
- Full Proposals submitted via Research.gov: Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation should be prepared and submitted in accordance with the general guidelines contained in the NSF Proposal and Award Policies and Procedures Guide (PAPPG). The complete text of the PAPPG is available electronically on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg . Paper copies of the PAPPG may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from [email protected] . The Prepare New Proposal setup will prompt you for the program solicitation number.
- Full proposals submitted via Grants.gov: Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation via Grants.gov should be prepared and submitted in accordance with the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide: A Guide for the Preparation and Submission of NSF Applications via Grants.gov . The complete text of the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide is available on the Grants.gov website and on the NSF website at: ( https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=grantsgovguide ). To obtain copies of the Application Guide and Application Forms Package, click on the Apply tab on the Grants.gov site, then click on the Apply Step 1: Download a Grant Application Package and Application Instructions link and enter the funding opportunity number, (the program solicitation number without the NSF prefix) and press the Download Package button. Paper copies of the Grants.gov Application Guide also may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from [email protected] .
See PAPPG Chapter II.D.2 for guidance on the required sections of a full research proposal submitted to NSF. Please note that the proposal preparation instructions provided in this program solicitation may deviate from the PAPPG instructions.
3. FULL PROPOSAL
Full Proposal Preparation Instructions :
As a multi-university ERC, the proposal must be submitted as a single integrated proposal by the Lead university, with proposed subawards to the other partner institutions. Separately submitted collaborative proposals from each partner will not be accepted.
Select "Prepare New Full Proposal" in Research.gov. Search for and select this solicitation title in Step One of the Full Proposal wizard. Select "Center" as the proposal type. In the proposal details section, select "Single proposal (with or without subawards)." Separately submitted collaborative proposals will be returned without review.
Title: Research.gov will pre-pend the title with "Center." The remainder of the title should begin with "NSF Engineering Research Center for ( insert the rest of the title and the Center's acronym )". The title should reflect the engineering system of the proposed ERC.
Cover Sheet: For planning purposes, September 1, 2026 should be shown as the requested start date. The award duration should be 60 months.
Project Summary (1 page): The Project Summary must have three separate section headers entitled "Overview", "Intellectual Merit", and "Broader Impacts"; each heading must be on its own line with no other text on that line. Within the Overview section, include a separate sub-section entitled "Proposed Vision".
The summary should be informative to those working in the same or related fields and understandable to a scientifically or technically literate reader. Full proposals that do not contain the Project Summary as described above will be returned without review.
Project Description: Maximum 26 pages, total, containing the following sections, not necessarily in this order. Figures and tables must be included within the 26-page limit.
Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts: The intellectual merit and broader impacts of the ERC must be addressed and described throughout the narrative as an integral part of the Project Description. Between Sections IV and V, include a separate header for Broader Impacts, as specified below.
Outline for the Full Proposal Project Description (up to 26 pages)
BROADER IMPACTS ( Please note: The Project Description must include a separate section header labeled Broader Impacts and the heading must be on its own line with no other text on that line .)
VIII. Evaluation Plan
IX. Financial Support and Functional Allocation of Resources
X. Results from Prior NSF Support
The proposed vision for the ERC must be explained, with a discussion of the convergent engineering research theme and the anticipated societal impact. Explain the proposed transformative engineered system and the potential for impact on society, the engineering community and the greater scientific community.
Rationale: Make the case for why the proposed ERC is appropriate and why a convergent approach is needed for the targeted societal impact. Articulate why this vision cannot be realized with a series of individual investigators awards, the additional value of the proposed ERC compared with the sum of its parts.
The plan must clearly define the engineered system and describe how the features of the ERC will be integrated to achieve the vision, in particular the cohesive plan for involving participants at all levels in the four foundational components:
The Strategic Plan should include the high-level goals within each of these foundational components that will be described in more detail in later sections and the interrelationships among those goals, as well as the strategic role of partner institutions in integrating the foundation components and achieving these goals. The plan should also include the high-level expected progress of the ERC efforts across the 10-years of support in these four fundamental components, including ERC growth. The plan should further include discussions on the overarching convergent approach, the engagement of the stakeholder community, and the plans for convergent team formation. The ERC Strategic Plan should provide a roadmap with major milestones and describe how the ERC will know when it has been successful in meeting its goals. Finally, the ERC Strategic Plan should also articulate the logical reasoning that connects the proposed activities to the identified goals as well as the connections between the goals and the desired impacts expressed in the ERC Vision. The overall strategy must have the flexibility and the agility to evolve over time. An ERC needs to continually refine its vision based on a reliable feedback mechanism to focus on core advances, prune less compelling ERC elements, and refine as necessary the level of detail of its strategic plan over time.
Leadership Team: To properly address the four foundational components of the ERC, among the ERC Leadership Team, there must be identified individuals with: (a) deep expertise in the fundamental science/engineering areas envisioned by the ERC; (b) strategic leadership in innovation including intellectual property; (c) expertise in engineering workforce development and (d) experience in diversity and inclusion. Provide a chart summarizing the composition and expertise of the leadership team. Justify how each of the disciplines in this spectrum is needed for the convergent approach.
Management Plan: Proposals must include a management plan that describes the administration of the Center, including the functions of the leadership team, key personnel, and the role of any advisory committees, including the required Student Leadership Council and the Council of Deans, executive committee(s), and/or program committees or their equivalent. While the details of the structure are left to the proposers, the management structure should be designed to facilitate and integrate the ERC's critical and foundational components (CR, EWD, DCI, and IE). In addition, the proposed management plan should address the roles, authorities, and accountability for the leadership team that will ensure no bottlenecks in decision making.
Specifically, the successful proposal will delineate:
- The overall management and reporting structure of the ERC.
- Which personnel or groups will be responsible for CR, EWD, DCI, and IE. Please explain the relevant experience and expertise of these individuals and how they fit their assigned roles.
- These individuals should be included in the leadership team.
- An organizational chart, including advisory boards and the reporting/feedback loops involved.
The accompanying narrative for the organization chart should define the functional roles and responsibilities of each leadership position, and how these positions support the integrated strategic plan described earlier. It should also define the functional purpose of any additional advisory bodies that are deemed necessary to support the four foundational components, accomplish the proposed ERC vision, and achieve the desired long-term societal impact. Note that the functional roles of the two mandated ERC Advisory Bodies, the Council of Deans and the Student Leadership Council, are defined earlier in the section on Community Feedback. Since the quality of team member interaction is critical to team effectiveness, describe the managerial processes overlaying the organization chart that will be used to integrate the team. Please provide sufficient detail to allow critical evaluation.
Institutional Configuration: Describe the institutional configuration given the proposed vision for the ERC. Discuss the value added by each core partner university in meeting the goals of the four foundational components. Discuss the value added by any partnerships as described in the Key Elements of an ERC – Partners section.
IV. Convergent Research (CR)
ERCs are expected to have center-scale convergent engineering research that will support the ERC's overall potential for societal impact. The research program is the core of the ERC from which all ERC activities evolve.
Research Strategy: Clearly describe the proposed engineered system (a combination of components and elements that work together to perform a useful function) for the ERC. This section must include detailed research strategies, such as the 3-plane diagram (described below), research thrusts, and testbeds. A 10-year roadmap must illustrate the critical path, milestones, contributions from research projects, interdependence of research activities, short- and long-term deliverables, and overarching objectives in knowledge, technology, and proof of principle testbeds included in the ERC's vision. Impacts of the proposed research and technology outcomes on society, stakeholders, and the scientific and engineering communities must be included. Discuss how the research strategy will support the proposed societal impact of the ERC, including any potential negative consequences that would arise from the development of new technologies. Include risk mitigation strategies if appropriate. This section should also include strategies for building and maintaining teams appropriate for the proposed convergent approach and the process for starting, managing, and potentially ending research projects throughout the lifetime of the ERC. This section should clearly state what fundamental knowledge is expected within each thrust to advance the state of the art, including engineering as a whole discipline.
ERC 3-Plane Strategic Planning Chart: Identify and characterize interdependent research thrusts and activities at fundamental knowledge, enabling technology, and systems-level testbed(s) scales. Integration of research activities must be graphically depicted on a clearly legible version of the ERC Program's 3-Plane Strategic Planning Chart ( https://erc-assoc.org/content/strategic-planning-research-3-plane-chart ) that is tailored to the proposed ERC. The chart should be at least half a page, but a full page is recommended for legibility, as this chart is used at several stages of the NSF review process.
Research Thrusts: Each thrust description should start with a table that lists the thrust leader and other faculty/research participants by name, department, and institution. International partners, if any, who may be involved in the early stages of the thrust efforts must also be listed. Discuss the goals and objectives of the thrust vis-à-vis the goals of the ERC and the convergent research strategic plan and how these thrusts will support each other. Provide information on fundamental knowledge and technology deliverables. Identify the gaps and barriers the thrust will address in the context of the ERC's strategic plan. Discuss the convergent cross-disciplinary mix of expertise needed to achieve the goals of the thrust, as well as how the proposed team fulfills that need. Describe how future team building will support the convergent approach. Benchmark the research proposed for the thrust with respect to the state-of-the-art. Discuss the role of the thrust's research relative to the ERC's 3- Plane Strategic Planning Chart.
Project-level descriptions of specific research activities for each thrust must describe the proposed research and link it to the thrust goals. Describe a few exemplar projects in depth to allow judgment of the quality of the effort proposed, rather than superficially describing all projects. For these projects, provide examples of fundamental barriers the research will address, the need for a convergent approach, and project-level methods to address the barriers.
Demonstrate that the desired results constitute breakthroughs and are attainable in ten years. Discuss how projects support and integrate with other thrusts, enabling technologies, and systems-level testbeds in an overall convergent research approach.
Testbeds: Enabling- and systems-level testbeds must include a description of proposed proof-of-concept demonstration(s) in each testbed and personnel needed to construct and implement each proposed testbed. The research program budget should support technical staff to work with students and faculty to build these testbeds.
Note: NSF funds may not be used to support clinical trials. If the research involves vertebrate animals or includes human subjects, PAPPG requirements must be followed for the full proposal.
V. Engineering Workforce Development (EWD)
The ERC EWD program is driven by the future education, workforce development, and labor market needs relevant to the proposed Center. A proposed evidence-based program for building human capacity for the future engineering and technical workforce must be described. The proposed program should provide strategic goals for the ERC as well as targeted and specific outcomes related to workforce development and education.
Workforce Development occurs at all levels of the Center and provides opportunities for all ERC members including students, faculty, and external partners as appropriate. Proposed activities should logically lead to targeted outcomes and support diverse pathways and experiences for participants. Engineering workforce activities should contribute to a diverse, globally competitive, and team-oriented engineering workforce that has experience in convergent research, technology advancement, industrial practice, and innovation. Rather than a comprehensive set of training opportunities (general public, faculty, professional, vocational, graduate students, undergraduate students, and K-12), EWD programs should include a strategic selection of targeted activities that logically connect to each other and that will enable the long-term vision of the Center ERCs should leverage team and institutional expertise and resources to maximize impact with targeted activities.
At least 6 non-ERC students must enroll in a Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) program budgeted at a minimum of $80K per year from the ERC base budget, as well as at least 6 participants must be engaged in a Research Experiences for Teachers (RET) program budgeted at a minimum of $60K per year from the ERC base budget. Awarded ERCs are encouraged to submit proposals to the annual Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) Site and Research Experiences for Teachers (RET) Site competitions to expand the Center's workforce development impact. Partnerships with inner city, rural, or other high needs schools are especially encouraged, as is participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in STEM. Suitable metrics to assess progress towards meeting the ERC's goals should be described, and feedback loops should be in place for continuous program improvement.
Describe how the leadership team will effectively support workforce development and educational programming and their growth. This section should also clearly describe how the proposed workforce development program will interact with existing educational or training systems at all partner institutions. Include a description of plans for engaging with partners, recruiting participants, and anticipated participant experiences. Educational partnerships may be leveraged to support the program and provide opportunities to engage with potential participants. All Engineering Workforce Development program participants, whether internal or external to the ERC, should have opportunities that are unique and would otherwise not be possible without the ERC.
VI. Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI)
Describe the vision and plans for nurturing a culture that ensures participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in STEM. A culture of inclusion has many important aspects that are essential for deep collaboration, including the participation of members from diverse scientific backgrounds and training which is necessary for true convergent research and innovation. A culture of inclusion must also foster participation of a diversity of partner institutions, including industry and practitioners, that will bring different perspectives to bear on the goals of the ERC. At least one core partner institution that enrolls and graduates a high percentage of underrepresented students in engineering and STEM fields must be included.
Describe preliminary ideas to create and nurture a culture that fosters the engagement of all ERC participants, including those from a diverse range of scientific backgrounds. This section should include evidence-based and intentional programming to support the inclusion of all talent that integrates and strengthen convergent research efforts across all institutions. Suitable metrics to assess the ERC's goals should be described, and feedback loops should be in place for independent assessment and continuous improvement in all dimensions of ERC operation.
In this section, describe how the leadership team will effectively create an inclusive culture for the ERC in which all members feel valued and welcomed, creatively contribute, and gain mutual benefit from participating. Include a description of plans for recruiting, mentoring, and retaining undergraduates, graduate students, and members of the research and leadership team from full spectrum of diverse talent in engineering. Describe the role of all partners, including plans to connect with ERC’s research and innovation goals in meaningful way, benefiting the students and faculty in the Center.
The ERC program is committed to including the participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in STEM.
VII. Innovation Ecosystem (IE)
At its core, the innovation ecosystem is a network formed among trusted partners working together towards the common goal of creating and enhancing the capacity for innovation within the ecosystem.
In this section, discuss how the ERC will foster the creation of societal value from innovations (e.g., inventions, goods, services, businesses) that benefit society in a sustainable fashion (i.e., value creation). Identify the innovation ecosystem stakeholders relevant to realizing the proposed vision and societal impact.
Describe the strategy to form relationships with stakeholders to garner support for the Center's vision. Specifically, include the ERC's plans for developing and fostering industrial/practitioner memberships and involvement; technology transfer to member and non-member firms; if included, the role of university and state and local government as facilitators of entrepreneurship, civics, economic/workforce development and innovation; or regulatory agencies as influencers of the ERC innovation , end users or customers as beneficiaries of the ERC innovation, and plans for supporting translational research when appropriate.
To maximize positive social impact, any anticipated potential negative consequences caused by the introduction of the ERC technology should be addressed. In these cases, make sure to include stakeholder(s) that will work to mitigate the negative impacts, such as through consideration of regulation and ethics.
Provide a description of how the proposed member firms (e.g., innovation partners, facilitators, influencers, and beneficiaries) align to the proposed ERC's technology area. That is, as the ERC's research program evolves, note at which points in time in the ERC development over its 10-year lifespan different types of stakeholders engage with the ERC to enable success and create societal value. Some stakeholders may be engaged for the entire 10 years, and others may be involved with focused research activities at critical points in time (e.g., testbed development).
Discuss the integration of all stakeholders into the governance and operations of the ERC. Include a letter of collaboration ( please make sure to use the template provided in the PAPPG ) from each stakeholder that identifies their commitment to work with the ERC as described in the project description. The letters should be uploaded in the Supplementary Documents section.
Legal Frameworks: The different stakeholder groups/organizations/partners operate under very different legal frameworks that can make seamless collaboration difficult. Consequently, the ERC must work within the university structure to create an environment where the frameworks can be modified so that the different entities can come together for productive interaction. In advance of anyone joining the ERC, it is important to put in place legal agreements that protect the interests of the stakeholder entities and the university partners. Therefore, at a minimum, all ERCs require two legal frameworks to handle (1) intellectual property and (2) industry/practitioner membership agreements. The specifics of the ERC vision and the nature of the stakeholder community will determine whether additional legal frameworks are necessary.
- Intellectual Property: Describe the overall Intellectual Property (IP) strategy consistent with planned value creation in the ERC, and the corresponding management of the ERC IP across the lead and partner institutions and the approaches that will enable licensing of ERC's IP and/or adopting of other ERC outcomes. This plan must discuss management of possible conflicts-of-interest of any ERC researchers and the ERC's technology transfer endeavors. If an award is made, the IP policy must be prepared and submitted within 90 days of the award.
- Industry/Practitioner Membership Agreement: Discuss the terms of the draft membership agreement including the proposed fee structure and benefits. Describe the type(s) of support to be received. A letter of commitment (one page maximum for each) from each firm/practitioner organization committed to joining the ERC as a member and providing (cash and/or in-kind) support in the event that an award is made must be uploaded in Supplementary Documents.
Based on the goals and desired outcomes of the ERC strategic plan, a proposed evaluation plan is required that includes all four foundational components as well as a risk analysis . The purpose of ERC evaluation is to provide feedback on progress towards meeting Center goals. The evaluation plan should include formative aspects that allow the Center to make evidence-based decisions about changes in its activities and summative aspects to provide evidence of impact across all elements of the ERC. This section should include the evaluation questions, as well as, a description of the type of evaluation design and methods that will be used to address each question. This section should specify the mechanisms and timeline for how the results and recommendations from evaluation and assessment will be fed back into ERC goals, objectives, and milestones to ensure continual progress and attainment of goals, targets, and impacts during the project period. It should also identify the person(s) who will lead the ERC evaluation and briefly describe their academic training and professional experience that qualifies them to serve as an evaluator. Evaluator(s) may be internal or external to ERC institutions but should be positioned to carry out the evaluation plan as objectively as possible.
Awardees may be required to participate in program-level evaluation activities by which NSF can assess implementation processes and progress toward program level outcomes. NSF, an NSF contractor, or a grantee on behalf of NSF, may periodically conduct program evaluations or special projects that necessitate access to project level staff and data. This activity may occur at any time during the award period and could occur after NSF support has ended. ERC participation includes responding to inquiries, interview and other methods of common data collection and/or aggregation across ERCs. In addition, PIs and ERC evaluators may be asked to assist in developing program evaluation activities that will mutually benefit the agency and ERC participants.
Discuss the plans for financial and in-kind support from all sources, except cost sharing. Include plans for allocation of those resources to fulfill the goals of the ERC. Include a functional budget table, showing only the estimated proportional distribution of effort across the ERC in its first 5 years without showing the support levels from any sources. The table must not show the sources of support, since the reviewers cannot have access to the level of academic support. A template of the table can be found on bullet #3: http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 .
This section of the proposal must also include a pie chart showing the allocation of resources and committed levels of support for the first five years from industrial or practitioner member firms and any additional non-member commitments from state and/or local governments for cash and/or in-kind support. A template of the table for Pie Chart Showing Allocation of Resources and Committed Levels of Support can be found on bullet #4: http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 .
Provide a pie chart showing the planned distribution of the requested NSF funds for year one between the lead, each domestic partner university, and each university contributing affiliated faculty.
If the Director and Lead PI (if different) identified on the proposal have received prior NSF support, including any award with an end date in the past five years or current funding including any no-cost extensions, the intellectual merit and broader impacts accomplished under that award should be discussed. In cases where the Director and Lead PI have received more than one award (excluding amendments to existing awards), they should only report on the award that is most closely related to the proposal (for each, if the Director and Lead PI are different people) . See PAPPG II.D.2.iii for the required format of this section. Recommended length – no more than one page.
In addition, the proposal must also include these documents and information.
References Cited: See PAPPG for format guidelines.
Budgetary Information: Travel Funds for ERC Leadership Team's Participation in Biennial Meetings: Members of the ERC Leadership Team are required to participate in the ERC Biennial Meeting (typically held in odd years) and the cross- ERC Leadership Team retreats (which are typically held annually). The purpose of biennial meeting is to share successes and failures across the ERCs, receive updates on the ERC Program, and provide input for future ERC Program improvements. The purpose of the retreats is to focus on issues and best practices specific to the different leadership team groups. The biennial meetings are held in the Washington DC area for 2.5 days. Retreats are held in various locations for 1-2 days. Travel funds must be included in each annual budget to support participation in alternating biennial and leadership retreats for each person identified.
Note: The budget justification section should only identify items that are not cost shared. A justification and explanation of cost shared items needs to be appended to the cost sharing tables that are submitted in the single-copy documents section of the proposal.
Cost sharing is mandatory and is specific to the ERC solicitation . The percentage of cost share is determined using the Cost Sharing Formula in the Budgetary Information section of this solicitation. Lead and core partner institutions are responsible for cost share on their entire portion of NSF funds, including sub-awards from their institutions to affiliate partners or other payees. Please see the Budgetary Information section of this solicitation for additional information.
Facilities, Equipment and Other Resources . In this section, please include ONLY facilities, equipment, and personnel that are directly relevant and unique to the proposed ERC. Briefly discuss such laboratories, facilities, cyberinfrastructure, personnel, and equipment, particularly those shared by the ERC team members. Distinguish existing facilities and equipment from any that will be acquired by the ERC (see PAPPG Chapter II.C.2.i). Space must be identified on the campus of the lead academic institution for the ERC headquarters. Describe the headquarters, including the size, functionality, and features. Discuss how the cyberinfrastructure, facilities, and equipment of the ERC will be used to form and sustain a collaborative ERC team with shared resources and information.
Letters of commitment should be included in the supplementary documents for facilities, equipment, etc. that are being provided by institutions or collaborators which are not from the lead institution or the core partners.
Senior/Key Personnel Documents
In accordance with the guidance in the PAPPG, the following information must be provided for all individuals designated as Senior/Key Personnel. This includes the Lead PI, Center Director if different from the Lead PI, co-PIs, all members of the ERC Leadership Team and key faculty.
- Biographical Sketch
- Current and Pending (Other) Support
- Collaborators & Other Affiliations Information
- Synergistic Activities
Supplementary Documents . In addition to the requirements contained in the PAPPG, the following items must be provided as supplementary documents.
Table of Academic/Other Participants and Industrial/Practitioner Members: The table should be created using the table format available on the ERC Association website on bullet #5 at: http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 . Download and use the Word file named " ERC Participants Table Template for Inclusion in Full Proposal. " Provide all the required information in each section of the table.
Letters of Commitment : These letters should express commitment, but should not praise or advocate for the project, and must follow the format for letters of collaboration given in the PAPPG. Submit the following required letters as indicated:
- Lead university: Senior university administrators (Dean of Engineering plus one other higher-level university official) for the lead university attesting to the institutional commitment to the goals of the ERC and a commitment to headquarters space in both letters. The letters should not mention cost sharing, as that information cannot be revealed to reviewers. The letters should indicate the institutional commitment to all major aspects of the ERC, including each of the four foundational components, and assure the development of a cross-ERC IP policy within 90 days, if an award is made.
- Each Core Partner University: A senior administrator (Dean or equivalent) attests to the partner's institutional commitment to the goals of the ERC.
- If applicable, officials from any participating federal laboratories indicating their involvement in the ERC and their commitment to provide support for their staff participating in the ERC.
- Member Organizations: A letter of commitment (one page maximum for each) from each firm/practitioner organization committed to joining the ERC as a member and providing (cash and/or in-kind) support.
Letters of Collaboration
The following Letters of Collaboration are required if applicable to the proposed ERC. These letters should state generic willingness to collaborate, but should not provide specific details on types or amounts of contributions and must follow the format for letters of collaboration given in the PAPPG:
- Officials of firms and agencies able to commit to membership.
- An administrator of each proposed pre-college or community college partners committing to their roles in the ERC as described in the Project Description.
- State or local government agencies and other organizations committed to partnership with the ERC.
- Domestic affiliated facult y if their projects are planned to be in place during years one through five. Note that no letters are required from the administrators of the universities providing affiliated faculty.
- Foreign collaborators , if any.
All letters should be addressed to:
ERC Program
Division of Engineering Education and Centers
U.S. National Science Foundation
All signed letters must be scanned and uploaded in the Other Supplementary Documents section of the proposal. Please instruct the letter writers not to mail, email, or fax copies to the NSF, as they will not be considered.
Draft Membership Agreement . Submit draft industry/practitioner membership agreement.
Data Management and Sharing Plan . Provide a Data Management and Sharing Plan according to guidance in the PAPPG. Go to ENG Data Management Plans | NSF - National Science Foundation ( https://www.nsf.gov/eng/general/dmp.jsp ) for Engineering-specific guidance.
Mentoring Plan . If applicable, provide a mentoring plan for postdoctoral scholars or graduate students who will be supported by ERC funds.
Single Copy Documents . Viewable only by NSF (also refer to the PAPPG Chapter II.C.1 on "Single-Copy Documents" for additional information):
Optional List of Suggested Reviewers or Reviewers Not to Include: Proposers may include in the single copy documents section a list of suggested reviewers who they believe are especially well qualified to review the proposal. Proposers also may designate persons they would prefer not to review the ERC proposal, indicating why. These suggestions are optional. PAPPG Exhibit II-2 contains information on conflicts of interest that may be useful in the preparation of this list. The cognizant Program Officer handling the proposal considers the suggestions and may contact the proposer for further information. However, the decision whether to use the suggestions remains with the Program Officer.
Required Cost Sharing Tables and Justification: Complete and submit the following tables: " Committed Cash and In-Kind Academic Support, Years 1-5 " and, if applicable, a table showing the " Nature of In-Kind Support " identifying any in-kind commitments and the sources of the commitments. A template of those tables can be found at (bullet #6): http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 . The tables should be uploaded into the single copy documents section of the full proposal. Appended to the cost sharing tables will be a justification/explanation of the source, nature, amount, and availability of any proposed cost sharing. The Proposers are directed not to include these tables and the cost sharing justification in any other part of the proposal, as cost sharing commitments are not provided to the reviewers. Refer to the section on Budgetary Information and Cost Sharing in this solicitation for information on cost sharing requirements and policies.
Proposal Update: If the proposed ERC is evaluated by a Site Visit Team (SVT), a 10-page reply that integrates changes in the proposed ERC based on comments from the SVT members and the Site Visit Report will be requested to facilitate the final stages of the review process.
INVITED FULL PROPOSAL REQUIREMENTS
(Note: This is NOT a total list of the ERC proposal requirements. Refer to the ERC Solicitation and the PAPPG for complete requirements).
|
|
Academic cost sharing (Lead and domestic core partner universities) | Yes, Single Copy Documents |
Identification of funded faculty/staff members from the lead and university-level partner institutions | Project Description |
Chart summarizing the leadership team | Project Description |
Organizational Chart | Project Description |
ERC 3-Plane Strategic Planning Chart | Project Description |
Research Thrusts Participant Tables | Project Description |
Functional Years 1-5 Budget Table | Project Description |
Years 1-5 Committed Industrial and Other Non-NSF, Non-Academic Support table | Project Description |
Years 1-5 Planned Distribution of NSF Funds | Project Description |
Draft membership agreement | Supplementary Documents |
Draft IP policy | Required following award |
Lead Institution: Two letters of commitment, one from the Dean of Engineering and one from a higher-level administrator, describing committed institutional resources | Yes - (but no cost sharing identified in letters) Supplementary Documents |
Core Partner Institutions: Letters of commitment from a senior administrator at the rank of Dean or equivalent from the partner institution, describing committed institutional resources | Yes - (but no cost sharing identified in letters)-Supplementary Documents |
Federal Laboratories: Letters of commitment from administrators of federal laboratories contributing support for staff in the ERC, attesting to laboratory support for that staff time | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of commitment to membership from firms / agencies / hospitals committed to joining the ERC as members and providing cash and in-kind support to the ERC | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of collaboration from firms / agencies / hospitals committed to joining the ERC as members | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of collaboration from pre-college partner administrators (school district or individual schools), community college administrators, or other education and outreach partners | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of collaboration from state or local government agency or state governor providing non-member financial support to the ERC | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of collaboration from foreign collaborators | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Table of "Committed Cash and In-Kind Academic Support, Years 1-5" and a table "Nature of In-Kind Support." Also, append to the tables a justification/explanation of any cost shared items | Single-Copy Documents |
| Yes, Supplementary Documents |
Post Proposal Submission to NSF: Other Required Documents
Cost Sharing:
Cost Sharing is required.
Invited full proposals will include a budget for each of the five years. Research.gov or Grants.gov will automatically provide a cumulative budget. Provide separate budgets for subawards to the domestic core partner institutions and any affiliated institutions whose faculty and students would be supported by the ERC's budget. Allowable budgets for the first five years are as follows: The budget for year one may be no more than $3,500,000, no more than $4,500,000 for year two, no more than $6,000,000 for year three, no more than $6,000,000 for year four, and for year five.
Cost Sharing: Mandatory Cost Sharing is required but inclusion of voluntary committed cost sharing is prohibited.
Mandatory Cost Sharing Requirements and Policies: Cost sharing is required of the lead university and core partner university(ies) to support and sustain the ERC. Cost sharing is not a review criterion for the ERCs; it is an eligibility criterion. Because cost sharing is not a review criterion, details on cost sharing will not be shared with the reviewers.
Upon issuance of the award, the lead university is responsible to secure, retain, manage, and certify to NSF the ERC cost sharing (cash and in-kind), at the level stated in the cooperative agreement. The total level of cost sharing proposed must be calculated using the "Cost Sharing Formula" below.
Cost sharing must not exceed the mandatory level stated in the ERC cost sharing formula. This would be considered "voluntary committed cost sharing" which is specifically prohibited according to NSF's cost sharing policies. ERC proposals that include cost sharing amounts in excess of the specified formula will be returned without review or declined.
Instructions for Disclosure and Non-Disclosure of Cost Sharing within the Proposal:
Cost Sharing and Letters of Commitment: Since cost sharing is not to be seen or considered by reviewers, any letters of commitment should not mention any cost sharing (cash or in-kind), since the reviewers will see these letters. See Section V.A for details concerning the letters of commitment.
Cost Sharing in the Budget Submission: The proposed cost sharing (including the estimated value of any in-kind cost sharing), according to the formula below, must be shown on Line M of the NSF proposal budget form. (Line M is masked from reviewers.)
Cumulative cost sharing should be entered for all 5 years on Line M of the first-year budget. Do not include the cost sharing figures on Line M of the budget for years 2-5. Do not include the justification / explanation for any cost-shared items in the budget justification section of the proposal. Only the non-cost shared items should be explained in the budget justification section, identifying the source, nature, amount and availability of non-cost shared items.
Cost Sharing Tables and Justification: The cost sharing commitment of the ERC must be documented in the proposal and the details presented in the tables of committed support. The lead institution is instructed to provide a table of "Committed Cash and In-Kind Academic Support, Years 1-5" (including any partner university providing cash for years 1-5). Proposers must also complete the table "Nature of In-Kind Support" identifying in-kind commitments and the sources of the commitments. A template of those tables can be found at (bullet #6) http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 . The tables should be uploaded into the "Single Copy Documents" section of the proposal. Append to the cost sharing tables a justification / explanation of the source, nature, amount and availability of any proposed cost sharing. Do not include these tables and the cost sharing justification in any other part of the proposal, as cost sharing commitments are not to be provided to reviewers.
Cost Sharing Formula:
ERC cost sharing requirements are determined based on classification at the time of the LOI submission deadline as defined in the "Carnegie Foundation's Classification of Institutions of Higher Education." Limited financial resources at smaller colleges and universities that lack high research activity may present significant challenges to cost sharing. Therefore:
- RU/VH: Research Universities - required cost sharing level is 20% of the allocation of the NSF budget to the lead or core partner university;
- RU/H: Research Universities - required cost sharing level is 15% of the allocation of the NSF budget to the lead or core partner university;
- DRU: Doctoral/Research Universities - cost sharing level is 10% of the allocation of the NSF budget to that core partner university.
- Master's L: Master's Colleges and Universities - cost sharing level is 10% of the allocation of the NSF budget to that core partner university/college;
- Bac/Diverse: Baccalaureate Colleges--Diverse Fields - cost sharing level is 5% of the allocation of the NSF budget to that core partner college.
If the university is classified in more than one Carnegie category, it must cost share at the highest cost sharing category as described above. The Carnegie classification shall remain throughout the duration of the competition and any subsequent award. The total ERC cost share shall be 20% or less, depending upon the Carnegie classifications for each of the partners.
ERC Support Cost-Sharing Sources:
The proposed cost sharing must be shown on Line M on the proposal budget. For purposes of budget preparation, the cumulative cost sharing amount must be entered on Line M of the first year’s budget. Should an award be made, the organization’s cost sharing commitment, as specified on the first year’s approved budget, must be met prior to award expiration.
Such cost sharing will be an eligibility, rather than a review criterion. Proposers are advised not to exceed the mandatory cost sharing level or amount specified in the solicitation.
When mandatory cost sharing is included on Line M, and accepted by the Foundation, the commitment of funds becomes legally binding and is subject to audit. When applicable, the estimated value of any in-kind contributions also should be included on Line M. An explanation of the source, nature, amount and availability of any proposed cost sharing must be provided in the budget justification. Contributions may be made from any non-Federal source, including non-Federal grants or contracts, and may be cash or in-kind. 2 CFR § 200.306 describes criteria and procedures for the allowability of cash and in-kind contributions in satisfying cost sharing and matching requirements. It should be noted that contributions derived from other Federal funds or counted as cost sharing toward projects of another Federal agency must not be counted towards meeting the specific cost sharing requirements of the NSF award.
Failure to provide the level of cost sharing required by the NSF solicitation and reflected in the NSF award budget may result in termination of the NSF award, disallowance of award costs and/or refund of award funds to NSF by the awardee.
The overall ERC-level budget should be prepared to assure sufficient funding from all sources to achieve the goals of the ERC. Hence, this budget would include faculty and staff to support the research, education, diversity and culture of inclusion, industrial collaboration/innovation, and management of the ERC. Budgets should include resources for reporting, site visit costs, and travel for cross-ERC collaboration and NSF meetings. The budget submitted to NSF will include an allocation plan for the NSF funding only.
May 09, 2025
D. Research.gov/Grants.gov Requirements
For Proposals Submitted Via Research.gov:
To prepare and submit a proposal via Research.gov, see detailed technical instructions available at: https://www.research.gov/research-portal/appmanager/base/desktop?_nfpb=true&_pageLabel=research_node_display&_nodePath=/researchGov/Service/Desktop/ProposalPreparationandSubmission.html . For Research.gov user support, call the Research.gov Help Desk at 1-800-381-1532 or e-mail [email protected] . The Research.gov Help Desk answers general technical questions related to the use of the Research.gov system. Specific questions related to this program solicitation should be referred to the NSF program staff contact(s) listed in Section VIII of this funding opportunity.
For Proposals Submitted Via Grants.gov:
Before using Grants.gov for the first time, each organization must register to create an institutional profile. Once registered, the applicant's organization can then apply for any federal grant on the Grants.gov website. Comprehensive information about using Grants.gov is available on the Grants.gov Applicant Resources webpage: https://www.grants.gov/applicants . In addition, the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide (see link in Section V.A) provides instructions regarding the technical preparation of proposals via Grants.gov. For Grants.gov user support, contact the Grants.gov Contact Center at 1-800-518-4726 or by email: [email protected] . The Grants.gov Contact Center answers general technical questions related to the use of Grants.gov. Specific questions related to this program solicitation should be referred to the NSF program staff contact(s) listed in Section VIII of this solicitation.
Submitting the Proposal: Once all documents have been completed, the Authorized Organizational Representative (AOR) must submit the application to Grants.gov and verify the desired funding opportunity and agency to which the application is submitted. The AOR must then sign and submit the application to Grants.gov. The completed application will be transferred to Research.gov for further processing.
The NSF Grants.gov Proposal Processing in Research.gov informational page provides submission guidance to applicants and links to helpful resources including the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide , Grants.gov Proposal Processing in Research.gov how-to guide , and Grants.gov Submitted Proposals Frequently Asked Questions . Grants.gov proposals must pass all NSF pre-check and post-check validations in order to be accepted by Research.gov at NSF.
When submitting via Grants.gov, NSF strongly recommends applicants initiate proposal submission at least five business days in advance of a deadline to allow adequate time to address NSF compliance errors and resubmissions by 5:00 p.m. submitting organization's local time on the deadline. Please note that some errors cannot be corrected in Grants.gov. Once a proposal passes pre-checks but fails any post-check, an applicant can only correct and submit the in-progress proposal in Research.gov.
Proposers that submitted via Research.gov may use Research.gov to verify the status of their submission to NSF. For proposers that submitted via Grants.gov, until an application has been received and validated by NSF, the Authorized Organizational Representative may check the status of an application on Grants.gov. After proposers have received an e-mail notification from NSF, Research.gov should be used to check the status of an application.
VI. NSF Proposal Processing And Review Procedures
Proposals received by NSF are assigned to the appropriate NSF program for acknowledgement and, if they meet NSF requirements, for review. All proposals are carefully reviewed by a scientist, engineer, or educator serving as an NSF Program Officer, and usually by three to ten other persons outside NSF either as ad hoc reviewers, panelists, or both, who are experts in the particular fields represented by the proposal. These reviewers are selected by Program Officers charged with oversight of the review process. Proposers are invited to suggest names of persons they believe are especially well qualified to review the proposal and/or persons they would prefer not review the proposal. These suggestions may serve as one source in the reviewer selection process at the Program Officer's discretion. Submission of such names, however, is optional. Care is taken to ensure that reviewers have no conflicts of interest with the proposal. In addition, Program Officers may obtain comments from site visits before recommending final action on proposals. Senior NSF staff further review recommendations for awards. A flowchart that depicts the entire NSF proposal and award process (and associated timeline) is included in PAPPG Exhibit III-1.
A comprehensive description of the Foundation's merit review process is available on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/bfa/dias/policy/merit_review/ .
Proposers should also be aware of core strategies that are essential to the fulfillment of NSF's mission, as articulated in Leading the World in Discovery and Innovation, STEM Talent Development and the Delivery of Benefits from Research - NSF Strategic Plan for Fiscal Years (FY) 2022 - 2026 . These strategies are integrated in the program planning and implementation process, of which proposal review is one part. NSF's mission is particularly well-implemented through the integration of research and education and broadening participation in NSF programs, projects, and activities.
One of the strategic objectives in support of NSF's mission is to foster integration of research and education through the programs, projects, and activities it supports at academic and research institutions. These institutions must recruit, train, and prepare a diverse STEM workforce to advance the frontiers of science and participate in the U.S. technology-based economy. NSF's contribution to the national innovation ecosystem is to provide cutting-edge research under the guidance of the Nation's most creative scientists and engineers. NSF also supports development of a strong science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) workforce by investing in building the knowledge that informs improvements in STEM teaching and learning.
NSF's mission calls for the broadening of opportunities and expanding participation of groups, institutions, and geographic regions that are underrepresented in STEM disciplines, which is essential to the health and vitality of science and engineering. NSF is committed to this principle of diversity and deems it central to the programs, projects, and activities it considers and supports.
A. Merit Review Principles and Criteria
The National Science Foundation strives to invest in a robust and diverse portfolio of projects that creates new knowledge and enables breakthroughs in understanding across all areas of science and engineering research and education. To identify which projects to support, NSF relies on a merit review process that incorporates consideration of both the technical aspects of a proposed project and its potential to contribute more broadly to advancing NSF's mission "to promote the progress of science; to advance the national health, prosperity, and welfare; to secure the national defense; and for other purposes." NSF makes every effort to conduct a fair, competitive, transparent merit review process for the selection of projects.
1. Merit Review Principles
These principles are to be given due diligence by PIs and organizations when preparing proposals and managing projects, by reviewers when reading and evaluating proposals, and by NSF program staff when determining whether or not to recommend proposals for funding and while overseeing awards. Given that NSF is the primary federal agency charged with nurturing and supporting excellence in basic research and education, the following three principles apply:
- All NSF projects should be of the highest quality and have the potential to advance, if not transform, the frontiers of knowledge.
- NSF projects, in the aggregate, should contribute more broadly to achieving societal goals. These "Broader Impacts" may be accomplished through the research itself, through activities that are directly related to specific research projects, or through activities that are supported by, but are complementary to, the project. The project activities may be based on previously established and/or innovative methods and approaches, but in either case must be well justified.
- Meaningful assessment and evaluation of NSF funded projects should be based on appropriate metrics, keeping in mind the likely correlation between the effect of broader impacts and the resources provided to implement projects. If the size of the activity is limited, evaluation of that activity in isolation is not likely to be meaningful. Thus, assessing the effectiveness of these activities may best be done at a higher, more aggregated, level than the individual project.
With respect to the third principle, even if assessment of Broader Impacts outcomes for particular projects is done at an aggregated level, PIs are expected to be accountable for carrying out the activities described in the funded project. Thus, individual projects should include clearly stated goals, specific descriptions of the activities that the PI intends to do, and a plan in place to document the outputs of those activities.
These three merit review principles provide the basis for the merit review criteria, as well as a context within which the users of the criteria can better understand their intent.
2. Merit Review Criteria
All NSF proposals are evaluated through use of the two National Science Board approved merit review criteria. In some instances, however, NSF will employ additional criteria as required to highlight the specific objectives of certain programs and activities.
The two merit review criteria are listed below. Both criteria are to be given full consideration during the review and decision-making processes; each criterion is necessary but neither, by itself, is sufficient. Therefore, proposers must fully address both criteria. (PAPPG Chapter II.C.2.d(i). contains additional information for use by proposers in development of the Project Description section of the proposal). Reviewers are strongly encouraged to review the criteria, including PAPPG Chapter II.C.2.d(i), prior to the review of a proposal.
When evaluating NSF proposals, reviewers will be asked to consider what the proposers want to do, why they want to do it, how they plan to do it, how they will know if they succeed, and what benefits could accrue if the project is successful. These issues apply both to the technical aspects of the proposal and the way in which the project may make broader contributions. To that end, reviewers will be asked to evaluate all proposals against two criteria:
- Intellectual Merit: The Intellectual Merit criterion encompasses the potential to advance knowledge; and
- Broader Impacts: The Broader Impacts criterion encompasses the potential to benefit society and contribute to the achievement of specific, desired societal outcomes.
The following elements should be considered in the review for both criteria:
- Advance knowledge and understanding within its own field or across different fields (Intellectual Merit); and
- Benefit society or advance desired societal outcomes (Broader Impacts)?
- To what extent do the proposed activities suggest and explore creative, original, or potentially transformative concepts?
- Is the plan for carrying out the proposed activities well-reasoned, well-organized, and based on a sound rationale? Does the plan incorporate a mechanism to assess success?
- How well qualified is the individual, team, or organization to conduct the proposed activities?
- Are there adequate resources available to the PI (either at the home organization or through collaborations) to carry out the proposed activities?
Broader impacts may be accomplished through the research itself, through the activities that are directly related to specific research projects, or through activities that are supported by, but are complementary to, the project. NSF values the advancement of scientific knowledge and activities that contribute to achievement of societally relevant outcomes. Such outcomes include, but are not limited to: full participation of women, persons with disabilities, and other underrepresented groups in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM); improved STEM education and educator development at any level; increased public scientific literacy and public engagement with science and technology; improved well-being of individuals in society; development of a diverse, globally competitive STEM workforce; increased partnerships between academia, industry, and others; improved national security; increased economic competitiveness of the United States; and enhanced infrastructure for research and education.
Proposers are reminded that reviewers will also be asked to review the Data Management Plan and the Postdoctoral Researcher Mentoring Plan, as appropriate.
Additional Solicitation Specific Review Criteria
PRELIMINARY Proposal Additional Review Criteria:
Reviewers should consider these high-level questions:
How well does the preliminary proposal narrative address the following in the project description?
- What is the compelling new idea and what is the potential high societal impact?
- What is the engineered system? Is it high-risk but high payoff?
- Is the 3-plane chart well-conceived and justified?
- How does the proposed Center's research benchmark against the state-of-the-art?
- What is the proposed management structure for the ERC? How will the proposed organization and management structure integrate and implement the four foundational components (CR, EWD, DCI, and IE) and foster team-formation?
- Does the proposed ERC create an inclusive environment where all the ERC participants learn to work on a team towards a common goal?
FULL Proposal Additional Review Criteria:
- What is the engineered system?
- Why is the proposed vision compelling?
- Why is the proposed research competitive when benchmarked against the state-of-the-art?
- How well does the proposed ERC justify the need for a center or institute-like approach?
High Societal Impact
- What is the potential for high societal impact?
- How realistic is the proposed plan for high societal impact?
- If the proposed strategy is high-risk does the potential payoff from anticipated impacts justify the investment?
Convergence Research
- Does the proposed research require a convergent approach and is its implementation well documented?
- How well justified is the argument that convergence is necessary for the desired impact?
- How well has the convergent approach been fully integrated into the proposal?
- What is the likelihood the research will lead to significant fundamental advances, new discoveries, and technological developments?
- How well does the proposed research use the testbeds to integrate and to advance proofs-of-concept to achieve the proposed vision?
- Are there well-defined implementation milestones for convergence research?
Stakeholder Engagement
- Are effective mechanisms to gather, engage, and implement feedback from appropriate stakeholders in place (i.e., collaborators, supporters, advisory boards, external committees)?
Team Formation
- How does the team formation and the implementation of team science support the proposed convergent research?
- How well has the ERC demonstrated strategies to overcome barriers for effective, dynamic teaming?
Strategic Plan
- How well does the Center present an integrated strategic plan for the ERC to address the key elements of each foundational component and their integration?
- How well does the proposal present an appropriate and compelling management structure and plan to carry out Center activities?
Management and Organization
- How appropriate are the qualifications of proposed leadership and management team?
- How well does the proposal present appropriate and compelling management structure and plan to carry out Center activities?
- Are effective mechanisms to gather and implement feedback from appropriate stakeholders in place, including advisory boards and external committees?
Engineering Workforce Development
- To what extent is the proposed program coherent and aligned with the overall goals and vision of the ERC?
- Do the proposed Engineering Workforce Development plans include appropriate strategies for recruiting participants and engaging with partners?
- Are the proposed Engineering Workforce Development plans evidence-based and likely to achieve the desired experiences, outcomes, and impact described?
Diversity and Culture of Inclusion
- How well does the discussion include a clear strategy to support Diversity and Culture of Inclusion?
- To what extent does the program propose evidence-based approaches for Diversity and Culture of Inclusion that are integrated with all dimensions of ERC operation?
- How well does the management plan include clear accountability for Diversity and Culture of Inclusion aspects of the ERC across all partners?
Innovation Ecosystem
- How well does the proposal describe a plan to build a network of trusted partners for innovation capacity?
- How appropriate is the proposed structure and processes for value creation to move from ideation to implementation?
Evaluation Plan
- How well has the Center developed a logic evaluation framework to guide the implementation of the strategic plan and evaluate Center performance?
- How well does the evaluation plan include formative aspects that allow the Center to make evidence-based decisions about changes in its activities and summative aspects to provide evidence of impact across all elements of the Center?
Financial Support and Resources
- Are the estimated budget allocations reasonable to achieve the proposed ERC vision?
- Does the Center have adequate capital (i.e., facilities, equipment, cyberinfrastructure) and procedural (i.e., safety, environmental) resources?
- Does the Center have a convincing plan for data sharing and management?
B. Review and Selection Process
Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation will be reviewed by
Ad hoc Review and/or Panel Review, Site Visit Review, or Reverse Site Review.
For Additional Review Criteria (see above listing)
Reviewers will be asked to evaluate proposals using two National Science Board approved merit review criteria and, if applicable, additional program specific criteria. A summary rating and accompanying narrative will generally be completed and submitted by each reviewer and/or panel. The Program Officer assigned to manage the proposal's review will consider the advice of reviewers and will formulate a recommendation.
After scientific, technical and programmatic review and consideration of appropriate factors, the NSF Program Officer recommends to the cognizant Division Director whether the proposal should be declined or recommended for award. NSF strives to be able to tell proposers whether their proposals have been declined or recommended for funding within six months. Large or particularly complex proposals or proposals from new recipients may require additional review and processing time. The time interval begins on the deadline or target date, or receipt date, whichever is later. The interval ends when the Division Director acts upon the Program Officer's recommendation.
After programmatic approval has been obtained, the proposals recommended for funding will be forwarded to the Division of Grants and Agreements or the Division of Acquisition and Cooperative Support for review of business, financial, and policy implications. After an administrative review has occurred, Grants and Agreements Officers perform the processing and issuance of a grant or other agreement. Proposers are cautioned that only a Grants and Agreements Officer may make commitments, obligations or awards on behalf of NSF or authorize the expenditure of funds. No commitment on the part of NSF should be inferred from technical or budgetary discussions with a NSF Program Officer. A Principal Investigator or organization that makes financial or personnel commitments in the absence of a grant or cooperative agreement signed by the NSF Grants and Agreements Officer does so at their own risk.
Once an award or declination decision has been made, Principal Investigators are provided feedback about their proposals. In all cases, reviews are treated as confidential documents. Verbatim copies of reviews, excluding the names of the reviewers or any reviewer-identifying information, are sent to the Principal Investigator/Project Director by the Program Officer. In addition, the proposer will receive an explanation of the decision to award or decline funding.
VII. Award Administration Information
A. notification of the award.
Notification of the award is made to the submitting organization by an NSF Grants and Agreements Officer. Organizations whose proposals are declined will be advised as promptly as possible by the cognizant NSF Program administering the program. Verbatim copies of reviews, not including the identity of the reviewer, will be provided automatically to the Principal Investigator. (See Section VI.B. for additional information on the review process.)
B. Award Conditions
An NSF award consists of: (1) the award notice, which includes any special provisions applicable to the award and any numbered amendments thereto; (2) the budget, which indicates the amounts, by categories of expense, on which NSF has based its support (or otherwise communicates any specific approvals or disapprovals of proposed expenditures); (3) the proposal referenced in the award notice; (4) the applicable award conditions, such as Grant General Conditions (GC-1)*; or Research Terms and Conditions* and (5) any announcement or other NSF issuance that may be incorporated by reference in the award notice. Cooperative agreements also are administered in accordance with NSF Cooperative Agreement Financial and Administrative Terms and Conditions (CA-FATC) and the applicable Programmatic Terms and Conditions. NSF awards are electronically signed by an NSF Grants and Agreements Officer and transmitted electronically to the organization via e-mail.
*These documents may be accessed electronically on NSF's Website at https://www.nsf.gov/awards/managing/award_conditions.jsp?org=NSF . Paper copies may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from [email protected] .
More comprehensive information on NSF Award Conditions and other important information on the administration of NSF awards is contained in the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) Chapter VII, available electronically on the NSF Website at https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg .
Administrative and National Policy Requirements
Build America, Buy America
As expressed in Executive Order 14005, Ensuring the Future is Made in All of America by All of America’s Workers (86 FR 7475), it is the policy of the executive branch to use terms and conditions of Federal financial assistance awards to maximize, consistent with law, the use of goods, products, and materials produced in, and services offered in, the United States.
Consistent with the requirements of the Build America, Buy America Act (Pub. L. 117-58, Division G, Title IX, Subtitle A, November 15, 2021), no funding made available through this funding opportunity may be obligated for an award unless all iron, steel, manufactured products, and construction materials used in the project are produced in the United States. For additional information, visit NSF’s Build America, Buy America webpage.
Special Award Conditions:
TBD - Programmatic Terms and Conditions: TBD - Financial and Administrative Terms and Conditions:
C. Reporting Requirements
For all multi-year grants (including both standard and continuing grants), the Principal Investigator must submit an annual project report to the cognizant Program Officer no later than 90 days prior to the end of the current budget period. (Some programs or awards require submission of more frequent project reports). No later than 120 days following expiration of a grant, the PI also is required to submit a final annual project report, and a project outcomes report for the general public.
Failure to provide the required annual or final annual project reports, or the project outcomes report, will delay NSF review and processing of any future funding increments as well as any pending proposals for all identified PIs and co-PIs on a given award. PIs should examine the formats of the required reports in advance to assure availability of required data.
PIs are required to use NSF's electronic project-reporting system, available through Research.gov, for preparation and submission of annual and final annual project reports. Such reports provide information on accomplishments, project participants (individual and organizational), publications, and other specific products and impacts of the project. Submission of the report via Research.gov constitutes certification by the PI that the contents of the report are accurate and complete. The project outcomes report also must be prepared and submitted using Research.gov. This report serves as a brief summary, prepared specifically for the public, of the nature and outcomes of the project. This report will be posted on the NSF website exactly as it is submitted by the PI.
More comprehensive information on NSF Reporting Requirements and other important information on the administration of NSF awards is contained in the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) Chapter VII, available electronically on the NSF Website at https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg .
NSF requires ERCs to submit annual reports that are more extensive in scope than those required of single investigator awards. NSF provides guidelines for these reports. NSF also requires ERCs to collect and submit to NSF data on indicators of progress, outcome, impact, and financial management. NSF provides data definition guidelines and templates for the recording and submission of these data through a secure web site.
VIII. Agency Contacts
Please note that the program contact information is current at the time of publishing. See program website for any updates to the points of contact.
General inquiries regarding this program should be made to:
For questions related to the use of NSF systems contact:
- NSF Help Desk: 1-800-381-1532
- Research.gov Help Desk e-mail: [email protected]
For questions relating to Grants.gov contact:
Grants.gov Contact Center: If the Authorized Organizational Representatives (AOR) has not received a confirmation message from Grants.gov within 48 hours of submission of application, please contact via telephone: 1-800-518-4726; e-mail: [email protected] .
IX. Other Information
The NSF website provides the most comprehensive source of information on NSF Directorates (including contact information), programs and funding opportunities. Use of this website by potential proposers is strongly encouraged. In addition, "NSF Update" is an information-delivery system designed to keep potential proposers and other interested parties apprised of new NSF funding opportunities and publications, important changes in proposal and award policies and procedures, and upcoming NSF Grants Conferences . Subscribers are informed through e-mail or the user's Web browser each time new publications are issued that match their identified interests. "NSF Update" also is available on NSF's website .
Grants.gov provides an additional electronic capability to search for Federal government-wide grant opportunities. NSF funding opportunities may be accessed via this mechanism. Further information on Grants.gov may be obtained at https://www.grants.gov .
About The National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent Federal agency created by the National Science Foundation Act of 1950, as amended (42 USC 1861-75). The Act states the purpose of the NSF is "to promote the progress of science; [and] to advance the national health, prosperity, and welfare by supporting research and education in all fields of science and engineering."
NSF funds research and education in most fields of science and engineering. It does this through grants and cooperative agreements to more than 2,000 colleges, universities, K-12 school systems, businesses, informal science organizations and other research organizations throughout the US. The Foundation accounts for about one-fourth of Federal support to academic institutions for basic research.
NSF receives approximately 55,000 proposals each year for research, education and training projects, of which approximately 11,000 are funded. In addition, the Foundation receives several thousand applications for graduate and postdoctoral fellowships. The agency operates no laboratories itself but does support National Research Centers, user facilities, certain oceanographic vessels and Arctic and Antarctic research stations. The Foundation also supports cooperative research between universities and industry, US participation in international scientific and engineering efforts, and educational activities at every academic level.
Facilitation Awards for Scientists and Engineers with Disabilities (FASED) provide funding for special assistance or equipment to enable persons with disabilities to work on NSF-supported projects. See the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide Chapter II.F.7 for instructions regarding preparation of these types of proposals.
The National Science Foundation has Telephonic Device for the Deaf (TDD) and Federal Information Relay Service (FIRS) capabilities that enable individuals with hearing impairments to communicate with the Foundation about NSF programs, employment or general information. TDD may be accessed at (703) 292-5090 and (800) 281-8749, FIRS at (800) 877-8339.
The National Science Foundation Information Center may be reached at (703) 292-5111.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Proposal Example/Sample. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level ...
er, the proposal deadline is December 1. During the proposal stage, students should discuss their research interests with CM faculty members, identify a research topic, conduct preliminary literatu. e review and develop a project proposal. The proposal should discuss problem statement, objectives, research methodology, research activities.
1. Research Proposal Format Example. Following is a general outline of the material that should be included in your project proposal. I. Title Page II. Introduction and Literature Review (Chapters 2 and 3) A. Identification of specific problem area (e.g., what is it, why it is important). B. Prevalence, scope of problem.
Research Proposal Template. The fastest (and smartest) way to craft a convincing proposal and get your dissertation or research project approved. Available in Google Doc, Word & PDF format. 4.9 star rating, 5000+ downloads. Download Now (Instant access)
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
As a general rule. Writing an Effective Research Proposal 28. of thumb, the sample size multiplied by the estimated population proportion should be at least 5. If it is smaller than advice from a statistician should be sought for calculating the necessary sample size. For example, 15 * 0.01 = 0.15.
Depending on the length of your research proposal, you may wish to include a contents page for the proposal itself (not for your main research project: suggested contents for this are included in your Proposed Chapter Outline, section 9), as follows (add page numbers/subsections when you know them, depending on your research).As you introduce sub-sections into your different sections, number ...
Research Proposals in a Nutshell: The basic purposes of all research proposals are to convince the reader that: the research project has clear objectives; the research project is worth doing (it is significant / important in some sense and will make an original contribution to knowledge / understanding in the field)
Style: If space allows, provide a clear project title. Structure your text - if allowed use section headings. Present the information in short paragraphs rather than a solid block of text. Write short sentences. If allowed, provide images/charts/diagrams to help break up the text.
For the Higher Degrees Committee, two copies of the proposal and for the Faculty Academic Ethics Committee three copies of the complete proposal must be handed in to the Faculty Research Administrator, Ms. Helen Selolo, room 7227, Johan Orr Building, Doornfontein Campus, Telephone 406 2660.
Sample Research Proposals. You will find here two examples of proposals for postgraduate research from the Department of Social Policy and Criminology. They both give good indication of the sorts of things that need to be included. The first, on fathering after divorce or separation, represents first thoughts on the proposed topic, but sets out ...
SCOPE. Following tasks will be undertaken as a part of the proposed research-. Task 1. Task 2. Task 3, etc. METHODOLOGY AND APPROACH. This section needs to answer self-imposed questions and should reflect that the student has good understanding of the problem and of the barriers in the path.
nd its implications for the research methods]Method:1. Conduct a l. te. ature review on leadership and communication in SMTs.2. Observe the group four hours per week for six weeks, focusing mostly on conversations at team meetings, especially those conversations in which the group addresses changes to their work proc. ss.
The research proposal is a summary of the plan you are contemplating for carr ying out in the form. of a dissertation - by making you put it down into a standard format and r equiring you to ...
research proposal is a valuable exercise even if you do not pursue a scientific career. You will have to sell and describe your ideas in any job, for example when writing quotations. 1.1 PURPOSE OF THIS GUIDE The purpose of this guide is to offer you an overview of the proposal writing process, the structure of
Research proposal - an example The following is a suggested format for a research proposal. Cover Page. The cover page should show: the title; the student's name and student number; the name of the University; the name of the degree sought; the name of the principal supervisor; and the date of submission. Abstract
Guide and the Supervision Guide. This Research Proposal Guide aims to help you develop a sound propo sal, one. that will help you to write your thesis in a focus ed and disciplined way. Research ...
Stay focused on your topic and make sure to fully answer the questions that are asked. Neglecting to answer or not focusing on the questions at hand will hurt your proposal. Guideline 2: Follow directions. Word and character limits, as well as format requirements, are given for a reason.
A title which clearly and succinctly explains what the research is about . e.g. "Incident hip fracture and socio-economic status in a regional population of Australian women aged 65 years and over." 2. PURPOSE OF STUDY* Describe the purpose, specific aims, or objectives. State the hypothesis to be tested or the research questions that
• An organized, well-written, concise, complete proposal = an easier to conduct experiment • A good proposal is like a good sales pitch. In the world of graduate studies and scientific research a proposal is the means by which funding is secured. • Good writing when paired with a thorough understanding of the subject matter is a valuable ...
Some writers find it helpful to review a research proposal sample PDF since this may also elevate your results. Once you have a research proposal sample, you can start working with a research proposal template APA-style to begin your work. There are several tools available, like Proposable, to help you track and manage your research proposals.
reer and academic advancement. What the reviewers are looking for is why you. re eager to. is not counted in the proposal page limit f. UR-UT programs, but typicallyshould. one to two pages (double-spaced). This concludes th. proposal template. Keep all o. all of these parts as ONE file.
Research Proposal Checklist. The simplest way to ensure that your research proposal ticks the necessary academic boxes and gets your study approved. Rating: 4.9 out of 5 Downloads: 5000 + Download Now (Instant access)
o Briefly describe the major issues and sub-problems to. be addressed by the research. o Identify the key independent and dependent variables. of the study. o State the hypothesis of the study, if ...
Full Proposal Preparation Instructions: Proposers may opt to submit proposals in response to this Program Solicitation via Research.gov or Grants.gov. Full Proposals submitted via Research.gov: Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation should be prepared and submitted in accordance with the general guidelines contained in the ...