- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews

How to Write an Article Review (With Examples)
Last Updated: July 27, 2024 Fact Checked
Preparing to Write Your Review
Writing the article review, sample article reviews, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,132,174 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Article Review 101
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information.

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?

Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016
Nov 27, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Google is Shoving Its Apps Onto New Windows Laptops
Three 55-inch tvs under $400 during best buy’s tech fest sale, a bloodier, more mediocre the crow, conventional wisdom: dnc delegates dish on news media preferences, favorite tv shows and who should play kamala harris in a biopic, silverbear, an investor named in bolt’s financial docs for a $450m raise, says it was “never in this deal”, as some investors consider legal action against bolt (forbes), apple to update eu browser options, make more apps deletable, microsoft confirms the windows control panel, which debuted in 1985 with windows 1.0, is “in the process of being deprecated in favor of the settings app” (sayan sen/neowin), ilhan omar joined a pro-palestine protest at the dnc, trump promotes family’s new crypto platform, ‘the defiant ones’, jenna ortega’s nakedest looks on her ‘beetlejuice 2’ press tour, how to write an article review (with sample reviews) .

An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review:
1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification.
3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review’s introduction, briefly outline the primary themes and arguments presented by the author(s). Keep it concise but sufficiently informative so that readers can quickly grasp the essence of the article.
4. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses: In subsequent paragraphs, assess the strengths and limitations of the article based on factors such as methodology, quality of evidence presented, coherence of arguments, and alignment with existing literature in the field. Be fair and objective while providing your critique.
5. Discuss any implications: Deliberate on how this particular piece contributes to or challenges existing knowledge in its discipline. You may also discuss potential improvements for future research or explore real-world applications stemming from this study.
6. Provide recommendations: Finally, offer suggestions for both the author(s) and readers regarding how they can further build on this work or apply its findings in practice.
7. Proofread and revise: Once your initial draft is complete, go through it carefully for clarity, accuracy, and coherence. Revise as necessary, ensuring your review is both informative and engaging for readers.
Sample Review:
A Critical Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health”
Introduction:
“The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is a timely article which investigates the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being. The authors present compelling evidence to support their argument that excessive use of social media can result in decreased self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a negative impact on interpersonal relationships.
Strengths and weaknesses:
One of the strengths of this article lies in its well-structured methodology utilizing a variety of sources, including quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. This approach provides a comprehensive view of the topic, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the effects of social media on mental health. However, it would have been beneficial if the authors included a larger sample size to increase the reliability of their conclusions. Additionally, exploring how different platforms may influence mental health differently could have added depth to the analysis.
Implications:
The findings in this article contribute significantly to ongoing debates surrounding the psychological implications of social media use. It highlights the potential dangers that excessive engagement with online platforms may pose to one’s mental well-being and encourages further research into interventions that could mitigate these risks. The study also offers an opportunity for educators and policy-makers to take note and develop strategies to foster healthier online behavior.
Recommendations:
Future researchers should consider investigating how specific social media platforms impact mental health outcomes, as this could lead to more targeted interventions. For practitioners, implementing educational programs aimed at promoting healthy online habits may be beneficial in mitigating the potential negative consequences associated with excessive social media use.
Conclusion:
Overall, “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is an important and informative piece that raises awareness about a pressing issue in today’s digital age. Given its minor limitations, it provides valuable
3 Ways to Make a Mini Greenhouse ...
3 ways to teach yourself to play ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

4 Ways to Set Up a Guitar

7 Ways to Do a Sugar Facial

How to Cut a Pumpkin: 10 Steps

How to Stain Veneer

How to Grow Orchids: 13 Steps

How to Be Popular
How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)

The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader’s guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide step-by-step guidance on how to craft your own, along with examples.
Why you need an introduction for a literature review
In academic writing , the introduction for a literature review is an indispensable component. Effective academic writing requires proper paragraph structuring to guide your reader through your argumentation. This includes providing an introduction to your literature review.
It is imperative to remember that you should never start sharing your findings abruptly. Even if there isn’t a dedicated introduction section .
When you need an introduction for a literature review
There are three main scenarios in which you need an introduction for a literature review:
What to include in a literature review introduction
It is crucial to customize the content and depth of your literature review introduction according to the specific format of your academic work.
Academic literature review paper
The introduction of an academic literature review paper, which does not rely on empirical data, often necessitates a more extensive introduction than the brief literature review introductions typically found in empirical papers. It should encompass:
Regular literature review section in an academic article or essay
In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction. It should encompass:
Introduction to a literature review chapter in thesis or dissertation
Some students choose to incorporate a brief introductory section at the beginning of each chapter, including the literature review chapter. Alternatively, others opt to seamlessly integrate the introduction into the initial sentences of the literature review itself. Both approaches are acceptable, provided that you incorporate the following elements:
Examples of literature review introductions
Example 1: an effective introduction for an academic literature review paper.
To begin, let’s delve into the introduction of an academic literature review paper. We will examine the paper “How does culture influence innovation? A systematic literature review”, which was published in 2018 in the journal Management Decision.
Example 2: An effective introduction to a literature review section in an academic paper
The second example represents a typical academic paper, encompassing not only a literature review section but also empirical data, a case study, and other elements. We will closely examine the introduction to the literature review section in the paper “The environmentalism of the subalterns: a case study of environmental activism in Eastern Kurdistan/Rojhelat”, which was published in 2021 in the journal Local Environment.
Thus, the author successfully introduces the literature review, from which point onward it dives into the main concept (‘subalternity’) of the research, and reviews the literature on socio-economic justice and environmental degradation.
Examples 3-5: Effective introductions to literature review chapters
Numerous universities offer online repositories where you can access theses and dissertations from previous years, serving as valuable sources of reference. Many of these repositories, however, may require you to log in through your university account. Nevertheless, a few open-access repositories are accessible to anyone, such as the one by the University of Manchester . It’s important to note though that copyright restrictions apply to these resources, just as they would with published papers.
Master’s thesis literature review introduction
Phd thesis literature review chapter introduction.
The second example is Deep Learning on Semi-Structured Data and its Applications to Video-Game AI, Woof, W. (Author). 31 Dec 2020, a PhD thesis completed at the University of Manchester . In Chapter 2, the author offers a comprehensive introduction to the topic in four paragraphs, with the final paragraph serving as an overview of the chapter’s structure:
PhD thesis literature review introduction
The last example is the doctoral thesis Metacognitive strategies and beliefs: Child correlates and early experiences Chan, K. Y. M. (Author). 31 Dec 2020 . The author clearly conducted a systematic literature review, commencing the review section with a discussion of the methodology and approach employed in locating and analyzing the selected records.
Steps to write your own literature review introduction
Master academia, get new content delivered directly to your inbox, the best answers to "what are your plans for the future", 10 tips for engaging your audience in academic writing, related articles, co-authorship guidelines to successfully co-author a scientific paper, minor revisions: sample peer review comments and examples, how to write effective cover letters for a paper submission, 10 things to do when you feel like your dissertation is killing you.
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Editor's Choice
- CME Reviews
- Best of 2021 collection
- Abbreviated Breast MRI Virtual Collection
- Contrast-enhanced Mammography Collection
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Accepted Papers Resource Guide
- About Journal of Breast Imaging
- About the Society of Breast Imaging
- Guidelines for Reviewers
- Resources for Reviewers and Authors
- Editorial Board
- Advertising Disclaimer
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

- < Previous
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Scientific Review Article
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Manisha Bahl, A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Scientific Review Article, Journal of Breast Imaging , Volume 5, Issue 4, July/August 2023, Pages 480–485, https://doi.org/10.1093/jbi/wbad028
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Scientific review articles are comprehensive, focused reviews of the scientific literature written by subject matter experts. The task of writing a scientific review article can seem overwhelming; however, it can be managed by using an organized approach and devoting sufficient time to the process. The process involves selecting a topic about which the authors are knowledgeable and enthusiastic, conducting a literature search and critical analysis of the literature, and writing the article, which is composed of an abstract, introduction, body, and conclusion, with accompanying tables and figures. This article, which focuses on the narrative or traditional literature review, is intended to serve as a guide with practical steps for new writers. Tips for success are also discussed, including selecting a focused topic, maintaining objectivity and balance while writing, avoiding tedious data presentation in a laundry list format, moving from descriptions of the literature to critical analysis, avoiding simplistic conclusions, and budgeting time for the overall process.
- narrative discourse

Society of Breast Imaging members
Personal account.
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Short-term Access
To purchase short-term access, please sign in to your personal account above.
Don't already have a personal account? Register
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| May 2023 | 171 |
| June 2023 | 115 |
| July 2023 | 113 |
| August 2023 | 5,013 |
| September 2023 | 1,500 |
| October 2023 | 1,810 |
| November 2023 | 3,849 |
| December 2023 | 308 |
| January 2024 | 401 |
| February 2024 | 312 |
| March 2024 | 415 |
| April 2024 | 361 |
| May 2024 | 306 |
| June 2024 | 283 |
| July 2024 | 309 |
| August 2024 | 192 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Librarian
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 2631-6129
- Print ISSN 2631-6110
- Copyright © 2024 Society of Breast Imaging
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Credit: Getty
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
WENTING ZHAO: Be focused and avoid jargon
Assistant professor of chemical and biomedical engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
When I was a research student, review writing improved my understanding of the history of my field. I also learnt about unmet challenges in the field that triggered ideas.
For example, while writing my first review 1 as a PhD student, I was frustrated by how poorly we understood how cells actively sense, interact with and adapt to nanoparticles used in drug delivery. This experience motivated me to study how the surface properties of nanoparticles can be modified to enhance biological sensing. When I transitioned to my postdoctoral research, this question led me to discover the role of cell-membrane curvature, which led to publications and my current research focus. I wouldn’t have started in this area without writing that review.

Collection: Careers toolkit
A common problem for students writing their first reviews is being overly ambitious. When I wrote mine, I imagined producing a comprehensive summary of every single type of nanomaterial used in biological applications. It ended up becoming a colossal piece of work, with too many papers discussed and without a clear way to categorize them. We published the work in the end, but decided to limit the discussion strictly to nanoparticles for biological sensing, rather than covering how different nanomaterials are used in biology.
My advice to students is to accept that a review is unlike a textbook: it should offer a more focused discussion, and it’s OK to skip some topics so that you do not distract your readers. Students should also consider editorial deadlines, especially for invited reviews: make sure that the review’s scope is not so extensive that it delays the writing.
A good review should also avoid jargon and explain the basic concepts for someone who is new to the field. Although I trained as an engineer, I’m interested in biology, and my research is about developing nanomaterials to manipulate proteins at the cell membrane and how this can affect ageing and cancer. As an ‘outsider’, the reviews that I find most useful for these biological topics are those that speak to me in accessible scientific language.

Bozhi Tian likes to get a variety of perspectives into a review. Credit: Aleksander Prominski
BOZHI TIAN: Have a process and develop your style
Associate professor of chemistry, University of Chicago, Illinois.
In my lab, we start by asking: what is the purpose of this review? My reasons for writing one can include the chance to contribute insights to the scientific community and identify opportunities for my research. I also see review writing as a way to train early-career researchers in soft skills such as project management and leadership. This is especially true for lead authors, because they will learn to work with their co-authors to integrate the various sections into a piece with smooth transitions and no overlaps.
After we have identified the need and purpose of a review article, I will form a team from the researchers in my lab. I try to include students with different areas of expertise, because it is useful to get a variety of perspectives. For example, in the review ‘An atlas of nano-enabled neural interfaces’ 2 , we had authors with backgrounds in biophysics, neuroengineering, neurobiology and materials sciences focusing on different sections of the review.
After this, I will discuss an outline with my team. We go through multiple iterations to make sure that we have scanned the literature sufficiently and do not repeat discussions that have appeared in other reviews. It is also important that the outline is not decided by me alone: students often have fresh ideas that they can bring to the table. Once this is done, we proceed with the writing.
I often remind my students to imagine themselves as ‘artists of science’ and encourage them to develop how they write and present information. Adding more words isn’t always the best way: for example, I enjoy using tables to summarize research progress and suggest future research trajectories. I’ve also considered including short videos in our review papers to highlight key aspects of the work. I think this can increase readership and accessibility because these videos can be easily shared on social-media platforms.
ANKITA ANIRBAN: Timeliness and figures make a huge difference
Editor, Nature Reviews Physics .
One of my roles as a journal editor is to evaluate proposals for reviews. The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic.
It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the most interesting reviews instead provide a discussion about disagreements in the field.

Careers Collection: Publishing
Scientists often centre the story of their primary research papers around their figures — but when it comes to reviews, figures often take a secondary role. In my opinion, review figures are more important than most people think. One of my favourite review-style articles 3 presents a plot bringing together data from multiple research papers (many of which directly contradict each other). This is then used to identify broad trends and suggest underlying mechanisms that could explain all of the different conclusions.
An important role of a review article is to introduce researchers to a field. For this, schematic figures can be useful to illustrate the science being discussed, in much the same way as the first slide of a talk should. That is why, at Nature Reviews, we have in-house illustrators to assist authors. However, simplicity is key, and even without support from professional illustrators, researchers can still make use of many free drawing tools to enhance the value of their review figures.

Yoojin Choi recommends that researchers be open to critiques when writing reviews. Credit: Yoojin Choi
YOOJIN CHOI: Stay updated and be open to suggestions
Research assistant professor, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon.
I started writing the review ‘Biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells and bacteriophages’ 4 as a PhD student in 2018. It took me one year to write the first draft because I was working on the review alongside my PhD research and mostly on my own, with support from my adviser. It took a further year to complete the processes of peer review, revision and publication. During this time, many new papers and even competing reviews were published. To provide the most up-to-date and original review, I had to stay abreast of the literature. In my case, I made use of Google Scholar, which I set to send me daily updates of relevant literature based on key words.
Through my review-writing process, I also learnt to be more open to critiques to enhance the value and increase the readership of my work. Initially, my review was focused only on using microbial cells such as bacteria to produce nanomaterials, which was the subject of my PhD research. Bacteria such as these are known as biofactories: that is, organisms that produce biological material which can be modified to produce useful materials, such as magnetic nanoparticles for drug-delivery purposes.
Synchronized editing: the future of collaborative writing
However, when the first peer-review report came back, all three reviewers suggested expanding the review to cover another type of biofactory: bacteriophages. These are essentially viruses that infect bacteria, and they can also produce nanomaterials.
The feedback eventually led me to include a discussion of the differences between the various biofactories (bacteriophages, bacteria, fungi and microalgae) and their advantages and disadvantages. This turned out to be a great addition because it made the review more comprehensive.
Writing the review also led me to an idea about using nanomaterial-modified microorganisms to produce chemicals, which I’m still researching now.
PAULA MARTIN-GONZALEZ: Make good use of technology
PhD student, University of Cambridge, UK.
Just before the coronavirus lockdown, my PhD adviser and I decided to write a literature review discussing the integration of medical imaging with genomics to improve ovarian cancer management.
As I was researching the review, I noticed a trend in which some papers were consistently being cited by many other papers in the field. It was clear to me that those papers must be important, but as a new member of the field of integrated cancer biology, it was difficult to immediately find and read all of these ‘seminal papers’.
That was when I decided to code a small application to make my literature research more efficient. Using my code, users can enter a query, such as ‘ovarian cancer, computer tomography, radiomics’, and the application searches for all relevant literature archived in databases such as PubMed that feature these key words.
The code then identifies the relevant papers and creates a citation graph of all the references cited in the results of the search. The software highlights papers that have many citation relationships with other papers in the search, and could therefore be called seminal papers.
My code has substantially improved how I organize papers and has informed me of key publications and discoveries in my research field: something that would have taken more time and experience in the field otherwise. After I shared my code on GitHub, I received feedback that it can be daunting for researchers who are not used to coding. Consequently, I am hoping to build a more user-friendly interface in a form of a web page, akin to PubMed or Google Scholar, where users can simply input their queries to generate citation graphs.
Tools and techniques
Most reference managers on the market offer similar capabilities when it comes to providing a Microsoft Word plug-in and producing different citation styles. But depending on your working preferences, some might be more suitable than others.
Reference managers
Attribute | EndNote | Mendeley | Zotero | Paperpile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cost | A one-time cost of around US$340 but comes with discounts for academics; around $150 for students | Free version available | Free version available | Low and comes with academic discounts |
Level of user support | Extensive user tutorials available; dedicated help desk | Extensive user tutorials available; global network of 5,000 volunteers to advise users | Forum discussions to troubleshoot | Forum discussions to troubleshoot |
Desktop version available for offline use? | Available | Available | Available | Unavailable |
Document storage on cloud | Up to 2 GB (free version) | Up to 2 GB (free version) | Up to 300 MB (free version) | Storage linked to Google Drive |
Compatible with Google Docs? | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Supports collaborative working? | No group working | References can be shared or edited by a maximum of three other users (or more in the paid-for version) | No limit on the number of users | No limit on the number of users |
Here is a comparison of the more popular collaborative writing tools, but there are other options, including Fidus Writer, Manuscript.io, Authorea and Stencila.
Collaborative writing tools
Attribute | Manubot | Overleaf | Google Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
Cost | Free, open source | $15–30 per month, comes with academic discounts | Free, comes with a Google account |
Writing language | Type and write in Markdown* | Type and format in LaTex* | Standard word processor |
Can be used with a mobile device? | No | No | Yes |
References | Bibliographies are built using DOIs, circumventing reference managers | Citation styles can be imported from reference managers | Possible but requires additional referencing tools in a plug-in, such as Paperpile |
*Markdown and LaTex are code-based formatting languages favoured by physicists, mathematicians and computer scientists who code on a regular basis, and less popular in other disciplines such as biology and chemistry.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

How to harness AI’s potential in research — responsibly and ethically
Career Feature 23 AUG 24

Partners in drug discovery: how to collaborate with non-governmental organizations

Time to refocus for South Korean science
Nature Index 21 AUG 24

South Korean science on the global stage

How South Korea can build better gender diversity into research

The citation black market: schemes selling fake references alarm scientists
News 20 AUG 24
Senior Researcher-Experimental Leukemia Modeling, Mullighan Lab
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Assistant or Associate Professor (Research-Educator)
The Center for Molecular Medicine and Genetics in the Wayne State University School of Medicine (http://genetics.wayne.edu/) is expanding its high-...
Detroit, Michigan
Wayne State University
Postdoctoral Fellow – Cancer Immunotherapy
Tampa, Florida
H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute
Postdoctoral Associate - Specialist
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Postdoctoral Associate- CAR T Cells, Synthetic Biology
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
How to Write an Article Review: Practical Tips and Examples
Table of contents
- 1 What Is an Article Review?
- 2 Different Types of Article Review
- 3.1 Critical review
- 3.2 Literature review
- 3.3 Mapping review/systematic map
- 3.4 Meta-analysis
- 3.5 Overview
- 3.6 Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
- 3.7 Rapid review
- 3.8 Scoping review
- 3.9 Systematic review
- 3.10 Umbrella review
- 4 Formatting
- 5 How To Write An Article Review
- 6 Article Review Outline
- 7 10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
- 8 An Article Review Example
What Is an Article Review?
Before you get started, learn what an article review is. It can be defined as a work that combines elements of summary and critical analysis. If you are writing an article review, you should take a close look at another author’s work. Many experts regularly practice evaluating the work of others. The purpose of this is to improve writing skills.
This kind of work belongs to professional pieces of writing because the process of crafting this paper requires reviewing, summarizing, and understanding the topic. Only experts are able to compose really good reviews containing a logical evaluation of a paper as well as a critique.
Your task is not to provide new information. You should process what you have in a certain publication.
Different Types of Article Review
In academic writing, the landscape of article reviews is diverse and nuanced, encompassing a variety of formats that cater to different research purposes and methodologies. Among these, three main types of article reviews stand out due to their distinct approaches and applications:
- Narrative. The basic focus here is the author’s personal experience. Judgments are presented through the prism of experiences and subsequent realizations. Besides, the use of emotional recollections is acceptable.
- Evidence. There is a significant difference from the narrative review. An in-depth study of the subject is assumed, and conclusions are built on arguments. The author may consider theories or concrete facts to support that.
- Systematic. The structure of the piece explains the approach to writing. The answer to what’s a systematic review lies on the surface. The writer should pay special attention to the chronology and logic of the narrative.
Understanding 10 Common Types
Don`t rush looking at meta-analysis vs. systematic review. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with other formats and topics of texts. This will allow you to understand the types of essays better and select them based on your request. For this purpose, we`ll discuss the typology of reviews below.
Critical review
The critical review definition says that the author must be objective and have arguments for each thought. Sometimes, amateur authors believe that they should “criticize” something. However, it is important to understand the difference since objectivity and the absence of emotional judgments are prioritized. The structure of this type of review article is as follows:
- Introduction;
- Conclusion.
“Stuffing” of the text is based on such elements as methodology, argumentation, evidence, and theory base. The subject of study is stated at the beginning of the material. Then follows the transition to the main part (facts). The final word summarizes all the information voiced earlier.
It is a mistake to believe that critical reviews are devoid of evaluation. The author’s art lies in maneuvering between facts. Smooth transition from one argument to another and lays out the conclusions in the reader. That is why such texts are used in science. The critical reviews meaning is especially tangible in medical topics.
Literature review
Literature is the basis for this type of work ─ books, essays, and articles become a source of information. Thus, the author should rethink the voiced information. After that, it is possible to proceed to conclusions. The methodology aims to find interconnections, repetitions, and even “gaps” in the literature. One important item is the referencing of sources. Footnotes are possible in the work itself or the list of resources used.
These types of research reviews often explore myths since there are often inconsistencies in mythology. Sometimes, there is contrary information. In this case, the author has to gather all existing theories. The essence does not always lie in the confirmation of facts. There are other different types of reviews for this purpose. In literary reviews, the object of study may be characters or traditions. This is where the author’s space for discovery opens up. Inconsistencies in the data can tell important details about particular periods or cultures. At the same time, patterns reveal well-established facts. Make sure to outline your work before you write. This will help you with essay writing .
Mapping review/systematic map
A mapping review, also known as a systematic map, is a unique approach to surveying and organizing existing literature, providing a panoramic view of the research landscape. This paper systematically categorizes and maps out the available literature on a particular topic, emphasizing breadth over depth. Its primary goal is to present a comprehensive visual representation of the research distribution, offering insights into the overall scope of a subject.
One of the strengths of systematic reviews is that they deeply focus on a research question with detailed analysis and synthesis, while mapping review prioritizes breadth. It identifies and categorizes a broad range of studies without necessarily providing in-depth critique or content synthesis. This approach allows for a broader understanding of the field, making it especially useful in the early stages of research. Mapping reviews excel in identifying gaps in the existing body of literature.
By systematically mapping the distribution of research, researchers can pinpoint areas where studies are scarce or nonexistent, helping to guide future research directions. This makes mapping reviews a valuable tool for researchers seeking to contribute meaningfully to a field by addressing unexplored or underexplored areas.
Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a powerful statistical technique. It systematically combines the results of multiple studies to derive comprehensive and nuanced insights. This method goes beyond the limitations of individual studies, offering a more robust understanding of a particular phenomenon by synthesizing data from diverse sources.
Meta-analysis employs a rigorous methodology. It involves the systematic collection and statistical integration of data from multiple studies. This methodological rigor ensures a standardized and unbiased approach to data synthesis. It is applied across various disciplines, from medicine and psychology to social sciences, providing a quantitative assessment of the overall effect of an intervention or the strength of an association.
In evidence-based fields, where informed decision-making relies on a thorough understanding of existing research, meta-analysis plays a pivotal role. It offers a quantitative overview of the collective evidence, helping researchers, policymakers, and practitioners make more informed decisions. By synthesizing results from diverse studies, meta-analysis contributes to the establishment of robust evidence-based practices, enhancing the reliability and credibility of findings in various fields. To present your research findings in the most readable way possible, learn how to write a summary of article .
If the key purpose of systematic review is to maximize the disclosure of facts, the opposite is true here. Imagine a video shot by a quadcopter from an altitude. The viewer sees a vast area of terrain without focusing on individual details. Overviews follow the same principle. The author gives a general picture of the events or objects described.
These types of reviews often seem simple. However, the role of the researcher becomes a very demanding one. The point is not just to list facts. Here, the search for information comes to the fore. After all, it is such reports that, in the future, will provide the basis for researching issues more narrowly. In essence, you yourself create a new source of information ─ students who worry that somebody may critique the author’s article love this type of material. However, there are no questions for the author; they just set the stage for discussions in different fields.
An example of this type of report would be a collection of research results from scientists. For example, statistics on the treatment of patients with certain diseases. In such a case, reference is made to scientific articles and doctrines. Based on this information, readers can speak about the effectiveness of certain treatment methods.
Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
One of the next types of review articles represents a meticulous effort to synthesize and analyze qualitative studies within a specific research domain.
The focus is synthesizing qualitative studies, employing a systematic and rigorous approach to extract meaningful insights. Its significance lies in its ability to provide a nuanced understanding of complex phenomena, offering a qualitative lens to complement quantitative analyses. Researchers can uncover patterns, themes, and contextual nuances that may elude traditional quantitative approaches by systematically reviewing and synthesizing qualitative data.
Often, you may meet discussion: is a systematic review quantitative or qualitative? The application of qualitative systematic reviews extends across diverse research domains, from healthcare and social sciences to education and psychology. For example, this approach can offer a comprehensive understanding of patient experiences and preferences in healthcare. In social sciences, it can illuminate cultural or societal dynamics. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for researchers exploring, interpreting, and integrating qualitative findings to enrich their understanding of complex phenomena within their respective fields.
Rapid review
If you don’t know how to write an article review , try starting with this format. It is the complete opposite of everything we talked about above. The key advantage and feature is speed. Quick overviews are used when time is limited. The focus can go to individual details (key). Often, the focus is still on the principal points.
Often, these types of review papers are critically needed in politics. This method helps to communicate important information to the reader quickly. An example can be a comparison of the election programs of two politicians. The author can show the key differences. Or it can make an overview based on the theses of the opponents’ proposals on different topics.
Seeming simplicity becomes power. Such texts allow the reader to make a quick decision. The author’s task is to understand potential interests and needs. Then, highlight and present the most important data as concisely as possible. In addition to politics, such reports are often used in communications, advertising, and marketing. Experienced writers mention the one-minute principle. This means you can count on 60 seconds of the reader’s attention. If you managed to hook them ─ bravo, you have done the job!
Scoping review
If you read the official scoping review definition, you may find similarities with the systematic type of review. However, recall is a sequential and logical study in the second case. It’s like you stack things on a shelf by color, size, and texture.
This type of review can be more difficult to understand. The basic concept is to explore what is called the field of subjects. This means, on the one hand, exploring a particular topic through the existing data about it. The author tries to find gaps or patterns by drawing on sources of information.
Another good comparison between systematic and this type of review is imagining as if drawing a picture. In the first case, you will think through every nuance and detail, why it is there, and how it “moves the story.” In the second case, it is as if you are painting a picture with “broad strokes.” In doing so, you can explain your motives for choosing the primary color. For example: “I chose the emerald color because all the cultural publications say it’s a trend”. The same goes for texts.
Systematic review
Sometimes, you may encounter a battle: narrative review vs. systematic review. The point is not to compare but to understand the different types of papers. Once you understand their purpose, you can present your data better and choose a more readable format. The systematic approach can be called the most scientific. Such a review relies on the following steps:
- Literature search;
- Evaluating the information;
- Data processing;
- Careful analysis of the material.
It is the fourth point that is key. The writer should carefully process the information before using it. However, 80% of your work’s result depends on this stage’s seriousness.
A rigorous approach to data selection produces an array of factual data. That is why this method is so often used in science, education, and social fields. Where accuracy is important. At the same time, the popularity of this approach is growing in other directions.
Systematic reviews allow for using different data and methodologies,, but with one important caveat ─ if the author manages to keep the narrative structured and explain the reason for certain methods. It is not about rigor. The task of this type of review is to preserve the facts, which dictates consistency and rationality.
Umbrella review
An umbrella review is a distinctive approach that involves the review of existing reviews, providing a comprehensive synthesis of evidence on a specific topic. The methodology of an umbrella review entails systematically examining and summarizing findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
This method ensures a rigorous and consolidated analysis of the existing evidence. The application of an umbrella review is broad, spanning various fields such as medicine, public health, and social sciences. It is particularly useful when a substantial body of systematic reviews exists, allowing researchers to draw overarching conclusions from the collective findings.
It allows the summarization of existing reviews and provides a new perspective on individual subtopics of the main object of study. In the context of the umbrella method, the comparison “bird’s eye view” is often cited. A bird in flight can see the whole panorama and shift its gaze to specific objects simultaneously. What becomes relevant at a particular moment? The author will face the same task.
On the one hand, you must delve into the offshoots of the researched topic. On the other hand, focus on the topic or object of study as a whole. Such a concept allows you to open up new perspectives and thoughts.

Different types of formatting styles are used for article review writing. It mainly depends on the guidelines that are provided by the instructor, sometimes, professors even provide an article review template that needs to be followed.
Here are some common types of formatting styles that you should be aware of when you start writing an article review:
- APA (American Psychological Association) – An APA format article review is commonly used for social sciences. It has guidelines for formatting the title, abstract, body paragraphs, and references. For example, the title of an article in APA format is in sentence case, whereas the publication title is in title case.
- MLA (Modern Language Association): This is a formatting style often used in humanities, such as language studies and literature. There are specific guidelines for the formatting of the title page, header, footer, and citation style.
- Chicago Manual of Style: This is one of the most commonly used formatting styles. It is often used for subjects in humanities and social sciences, but also commonly found in a newspaper title. This includes guidelines for formatting the title page, end notes, footnotes, publication title, article citation, and bibliography.
- Harvard Style: Harvard style is commonly used for social sciences and provides specific guidelines for formatting different sections of the pages, including publication title, summary page, website publisher, and more.
To ensure that your article review paper is properly formatted and meets the requirements, it is crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for the formatting style you are using. This helps you write a good article review.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
How To Write An Article Review
There are several steps that must be followed when you are starting to review articles. You need to follow these to make sure that your thoughts are organized properly. In this way, you can present your ideas in a more concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to start an article review and how to cater to each writing stage.
- Read the Article Closely: Even before you start to write an article review, it’s important to make sure that you have read the specific article thoroughly. Write down the central points and all the supporting ideas. It’s important also to note any questions or comments that you have about the content.
- Identify the Thesis: Make sure that you understand the author’s main points, and identify the main thesis of the article. This will help you focus on your review and ensure that you are addressing all of the key points.
- Formulate an Introduction: The piece should start with an introduction that has all the necessary background information, possibly in the first paragraph or in the first few paragraphs. This can include a brief summary of the important points or an explanation of the importance.
- Summarize the Article : Summarize the main points when you review the article, and make sure that you include all supporting elements of the author’s thesis.
- Start with Personal Critique : Now is the time to include a personal opinion on the research article or the journal article review. Start with evaluating all the strengths and weaknesses of the reviewed article. Discuss all of the flaws that you found in the author’s evidence and reasoning. Also, point out whether the conclusion provided by the author was well presented or not.
- Add Personal Perspective: Offer your perspective on the original article, do you agree or disagree with the ideas that the article supports or not. Your critical review, in your own words, is an essential part of a good review. Make sure you address all unanswered questions in your review.
- Conclude the Article Review : In this section of the writing process, you need to be very careful and wrap up the whole discussion in a coherent manner. This is should summarize all the main points and offer an overall assessment.
Make sure to stay impartial and provide proof to back up your assessment. By adhering to these guidelines, you can create a reflective and well-structured article review.
Article Review Outline
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review.
Introduction
- Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article’s main topic
Summary section
- Summarize the key points in the article as well as any arguments Identify the findings and conclusion
Critical Review
- Assess and evaluate the positive aspects and the drawbacks
- Discuss if the authors arguments were verified by the evidence of the article
- Identify if the text provides substantial information for any future paper or further research
- Assess any gaps in the arguments
- Restate the thesis statement
- Provide a summary for all sections
- Write any recommendations and thoughts that you have on the article
- Never forget to add and cite any references that you used in your article
10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
Have you ever written such an assignment? If not, study the helpful tips for composing a paper. If you follow the recommendations provided here, the process of writing a summary of the article won’t be so time-consuming, and you will be able to write an article in the most effective manner.
The guidelines below will help to make the process of preparing a paper much more productive. Let’s get started!
- Check what kind of information your work should contain. After answering the key question “What is an article review?” you should learn how to structure it the right way. To succeed, you need to know what your work should be based on. An analysis with insightful observations is a must for your piece of writing.
- Identify the central idea: In your first reading, focus on the overall impression. Gather ideas about what the writer wants to tell, and consider whether he or she managed to achieve it.
- Look up unfamiliar terms. Don’t know what certain words and expressions mean? Highlight them, and don’t forget to check what they mean with a reliable source of information.
- Highlight the most important ideas. If you are reading it a second time, use a highlighter to highlight the points that are most important to understanding the passage.
- Write an outline. A well-written outline will make your life a lot easier. All your thoughts will be grouped. Detailed planning helps not to miss anything important. Think about the questions you should answer when writing.
- Brainstorm headline ideas. When choosing a project, remember: it should reflect the main idea. Make it bold and concise.
- Check an article review format example. You should check that you know how to cite an article properly. Note that citation rules are different in APA and MLA formats. Ask your teacher which one to prioritize.
- Write a good introduction. Use only one short paragraph to state the central idea of the work. Emphasize the author’s key concepts and arguments. Add the thesis at the end of the Introduction.
- Write in a formal style. Use the third person, remembering that this assignment should be written in a formal academic writing style.
- Wrap up, offer your critique, and close. Give your opinion on whether the author achieved his goals. Mention the shortcomings of the job, if any, and highlight its strengths.
If you have checked the tips and you still doubt whether you have all the necessary skills and time to prepare this kind of educational work, follow one more tip that guarantees 100% success- ask for professional assistance by asking the custom writing service PapersOwl to craft your paper instead of you. Just submit an order online and get the paper completed by experts.

An Article Review Example
If you have a task to prepare an analysis of a certain piece of literature, have a look at the article review sample. There is an article review example for you to have a clear picture of what it must look like.
Journal Article on Ayn Rand’s Works Review Example
“The purpose of the article is to consider the features of the poetics of Ayn Rand’s novels “Atlas Shrugged,” “We the living,” and “The Fountainhead.” In the analysis of the novels, the structural-semantic and the method of comparative analysis were used.
With the help of these methods, genre features of the novels were revealed, and a single conflict and a cyclic hero were identified.
In-depth reading allows us to more fully reveal the worldview of the author reflected in the novels. It becomes easier to understand the essence of the author’s ideas about the connection between being and consciousness, embodied in cyclic ideas and images of plot twists and heroes. The author did a good job highlighting the strong points of the works and mentioning the reasons for the obvious success of Ayn Rand.“
You can also search for other relevant article review examples before you start.
In conclusion, article reviews play an important role in evaluating and analyzing different scholarly articles. Writing a review requires critical thinking skills and a deep understanding of the article’s content, style, and structure. It is crucial to identify the type of article review and follow the specific guidelines for formatting style provided by the instructor or professor.
The process of writing an article review requires several steps, such as reading the article attentively, identifying the thesis, and formulating an introduction. By following the tips and examples provided in this article, students can write a worthy review that demonstrates their ability to evaluate and critique another writer’s work.
Learning how to write an article review is a critical skill for students and professionals alike. Before diving into the nitty-gritty of reviewing an article, it’s important to understand what an article review is and the elements it should include. An article review is an assessment of a piece of writing that summarizes and evaluates a work. To complete a quality article review, the author should consider the text’s purpose and content, its organization, the author’s style, and how the article fits into a larger conversation. But if you don’t have the time to do all of this work, you can always purchase a literature review from Papers Owl .
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

How to Review a Journal Article

For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review , you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article. This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research. That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper level. As a college student, this might sound intimidating. However, as you engage with the research process, you are becoming immersed in a particular topic, and your insights about the way that topic is presented are valuable and can contribute to the overall conversation surrounding your topic.
IMPORTANT NOTE!!
Some disciplines, like Criminal Justice, may only want you to summarize the article without including your opinion or evaluation. If your assignment is to summarize the article only, please see our literature review handout.
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating , and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings, major conclusions, tone, and publication information. Depending on your writing context, some of these items may not be applicable.
Questions to Consider
To evaluate a source, consider some of the following questions. They are broken down into different categories, but answering these questions will help you consider what areas to examine. With each category, we recommend identifying the strengths and weaknesses in each since that is a critical part of evaluation.
Evaluating Purpose and Argument
- How well is the purpose made clear in the introduction through background/context and thesis?
- How well does the abstract represent and summarize the article’s major points and argument?
- How well does the objective of the experiment or of the observation fill a need for the field?
- How well is the argument/purpose articulated and discussed throughout the body of the text?
- How well does the discussion maintain cohesion?
Evaluating the Presentation/Organization of Information
- How appropriate and clear is the title of the article?
- Where could the author have benefited from expanding, condensing, or omitting ideas?
- How clear are the author’s statements? Challenge ambiguous statements.
- What underlying assumptions does the author have, and how does this affect the credibility or clarity of their article?
- How objective is the author in his or her discussion of the topic?
- How well does the organization fit the article’s purpose and articulate key goals?
Evaluating Methods
- How appropriate are the study design and methods for the purposes of the study?
- How detailed are the methods being described? Is the author leaving out important steps or considerations?
- Have the procedures been presented in enough detail to enable the reader to duplicate them?
Evaluating Data
- Scan and spot-check calculations. Are the statistical methods appropriate?
- Do you find any content repeated or duplicated?
- How many errors of fact and interpretation does the author include? (You can check on this by looking up the references the author cites).
- What pertinent literature has the author cited, and have they used this literature appropriately?
Following, we have an example of a summary and an evaluation of a research article. Note that in most literature review contexts, the summary and evaluation would be much shorter. This extended example shows the different ways a student can critique and write about an article.
Chik, A. (2012). Digital gameplay for autonomous foreign language learning: Gamers’ and language teachers’ perspectives. In H. Reinders (ed.), Digital games in language learning and teaching (pp. 95-114). Eastbourne, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Be sure to include the full citation either in a reference page or near your evaluation if writing an annotated bibliography .
In Chik’s article “Digital Gameplay for Autonomous Foreign Language Learning: Gamers’ and Teachers’ Perspectives”, she explores the ways in which “digital gamers manage gaming and gaming-related activities to assume autonomy in their foreign language learning,” (96) which is presented in contrast to how teachers view the “pedagogical potential” of gaming. The research was described as an “umbrella project” consisting of two parts. The first part examined 34 language teachers’ perspectives who had limited experience with gaming (only five stated they played games regularly) (99). Their data was recorded through a survey, class discussion, and a seven-day gaming trial done by six teachers who recorded their reflections through personal blog posts. The second part explored undergraduate gaming habits of ten Hong Kong students who were regular gamers. Their habits were recorded through language learning histories, videotaped gaming sessions, blog entries of gaming practices, group discussion sessions, stimulated recall sessions on gaming videos, interviews with other gamers, and posts from online discussion forums. The research shows that while students recognize the educational potential of games and have seen benefits of it in their lives, the instructors overall do not see the positive impacts of gaming on foreign language learning.
The summary includes the article’s purpose, methods, results, discussion, and citations when necessary.
This article did a good job representing the undergraduate gamers’ voices through extended quotes and stories. Particularly for the data collection of the undergraduate gamers, there were many opportunities for an in-depth examination of their gaming practices and histories. However, the representation of the teachers in this study was very uneven when compared to the students. Not only were teachers labeled as numbers while the students picked out their own pseudonyms, but also when viewing the data collection, the undergraduate students were more closely examined in comparison to the teachers in the study. While the students have fifteen extended quotes describing their experiences in their research section, the teachers only have two of these instances in their section, which shows just how imbalanced the study is when presenting instructor voices.
Some research methods, like the recorded gaming sessions, were only used with students whereas teachers were only asked to blog about their gaming experiences. This creates a richer narrative for the students while also failing to give instructors the chance to have more nuanced perspectives. This lack of nuance also stems from the emphasis of the non-gamer teachers over the gamer teachers. The non-gamer teachers’ perspectives provide a stark contrast to the undergraduate gamer experiences and fits neatly with the narrative of teachers not valuing gaming as an educational tool. However, the study mentioned five teachers that were regular gamers whose perspectives are left to a short section at the end of the presentation of the teachers’ results. This was an opportunity to give the teacher group a more complex story, and the opportunity was entirely missed.
Additionally, the context of this study was not entirely clear. The instructors were recruited through a master’s level course, but the content of the course and the institution’s background is not discussed. Understanding this context helps us understand the course’s purpose(s) and how those purposes may have influenced the ways in which these teachers interpreted and saw games. It was also unclear how Chik was connected to this masters’ class and to the students. Why these particular teachers and students were recruited was not explicitly defined and also has the potential to skew results in a particular direction.
Overall, I was inclined to agree with the idea that students can benefit from language acquisition through gaming while instructors may not see the instructional value, but I believe the way the research was conducted and portrayed in this article made it very difficult to support Chik’s specific findings.
Some professors like you to begin an evaluation with something positive but isn’t always necessary.
The evaluation is clearly organized and uses transitional phrases when moving to a new topic.
This evaluation includes a summative statement that gives the overall impression of the article at the end, but this can also be placed at the beginning of the evaluation.
This evaluation mainly discusses the representation of data and methods. However, other areas, like organization, are open to critique.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to write a review article?
In the medical sciences, the importance of review articles is rising. When clinicians want to update their knowledge and generate guidelines about a topic, they frequently use reviews as a starting point. The value of a review is associated with what has been done, what has been found and how these findings are presented. Before asking ‘how,’ the question of ‘why’ is more important when starting to write a review. The main and fundamental purpose of writing a review is to create a readable synthesis of the best resources available in the literature for an important research question or a current area of research. Although the idea of writing a review is attractive, it is important to spend time identifying the important questions. Good review methods are critical because they provide an unbiased point of view for the reader regarding the current literature. There is a consensus that a review should be written in a systematic fashion, a notion that is usually followed. In a systematic review with a focused question, the research methods must be clearly described. A ‘methodological filter’ is the best method for identifying the best working style for a research question, and this method reduces the workload when surveying the literature. An essential part of the review process is differentiating good research from bad and leaning on the results of the better studies. The ideal way to synthesize studies is to perform a meta-analysis. In conclusion, when writing a review, it is best to clearly focus on fixed ideas, to use a procedural and critical approach to the literature and to express your findings in an attractive way.
The importance of review articles in health sciences is increasing day by day. Clinicians frequently benefit from review articles to update their knowledge in their field of specialization, and use these articles as a starting point for formulating guidelines. [ 1 , 2 ] The institutions which provide financial support for further investigations resort to these reviews to reveal the need for these researches. [ 3 ] As is the case with all other researches, the value of a review article is related to what is achieved, what is found, and the way of communicating this information. A few studies have evaluated the quality of review articles. Murlow evaluated 50 review articles published in 1985, and 1986, and revealed that none of them had complied with clear-cut scientific criteria. [ 4 ] In 1996 an international group that analyzed articles, demonstrated the aspects of review articles, and meta-analyses that had not complied with scientific criteria, and elaborated QUOROM (QUality Of Reporting Of Meta-analyses) statement which focused on meta-analyses of randomized controlled studies. [ 5 ] Later on this guideline was updated, and named as PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses). [ 6 ]
Review articles are divided into 2 categories as narrative, and systematic reviews. Narrative reviews are written in an easily readable format, and allow consideration of the subject matter within a large spectrum. However in a systematic review, a very detailed, and comprehensive literature surveying is performed on the selected topic. [ 7 , 8 ] Since it is a result of a more detailed literature surveying with relatively lesser involvement of author’s bias, systematic reviews are considered as gold standard articles. Systematic reviews can be diivded into qualitative, and quantitative reviews. In both of them detailed literature surveying is performed. However in quantitative reviews, study data are collected, and statistically evaluated (ie. meta-analysis). [ 8 ]
Before inquring for the method of preparation of a review article, it is more logical to investigate the motivation behind writing the review article in question. The fundamental rationale of writing a review article is to make a readable synthesis of the best literature sources on an important research inquiry or a topic. This simple definition of a review article contains the following key elements:
- The question(s) to be dealt with
- Methods used to find out, and select the best quality researches so as to respond to these questions.
- To synthetize available, but quite different researches
For the specification of important questions to be answered, number of literature references to be consulted should be more or less determined. Discussions should be conducted with colleagues in the same area of interest, and time should be reserved for the solution of the problem(s). Though starting to write the review article promptly seems to be very alluring, the time you spend for the determination of important issues won’t be a waste of time. [ 9 ]
The PRISMA statement [ 6 ] elaborated to write a well-designed review articles contains a 27-item checklist ( Table 1 ). It will be reasonable to fulfill the requirements of these items during preparation of a review article or a meta-analysis. Thus preparation of a comprehensible article with a high-quality scientific content can be feasible.
PRISMA statement: A 27-item checklist
| Title | ||
| Title | 1 Identify the article as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both | |
| Summary | ||
| Structured summary | 2 Write a structured summary including, as applicable, background; objectives; data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, treatments, study appraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions and implications of key findings; and systematic review registration number | |
| Introduction | ||
| Rationale | 3 Explain the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known | |
| Objectives | 4 Provide an explicit statement of questions being addressed with reference to participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design (PICOS) | |
| Methods | ||
| Protocol and registration | 5 Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (such as a web address), and, if available, provide registration information including the registration number | |
| Eligibility criteria | 6 Specify study characteristics (such as PICOS, length of follow-up) and report characteristics (such as years considered, language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale | |
| Sources of Information | 7 Describe all information sources in the survey (such as databases with dates of coverage, contact with study authors to identify additional studies) and date last searched | |
| Survey | 8 Present the full electronic search strategy for at least one major database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated | |
| Study selection | 9 State the process for selecting studies (that is, for screening, for determining eligibility, for inclusion in the systematic review, and, if applicable, for inclusion in the meta-analysis) | |
| Data collection process | 10 Describe the method of data extraction from reports (such as piloted forms, independently by two reviewers) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators | |
| Data items | 11 List and define all variables for which data were sought (such as PICOS, funding sources) and any assumptions and simplifications made | |
| Risk of bias in individual studies | 12 Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias in individual studies (including specification of whether this was done at the study or outcome level, or both), and how this information is to be used in any data synthesis | |
| Summary measures | 13 State the principal summary measures (such as risk ratio, difference in means) | |
| Synthesis of outcomes | 14 For each meta-analysis, explain methods of data use, and combination methods of study outcomes, and if done consistency measurements should be indicated (ie P test) | |
| Risk of bias across studies | 15 Specify any assessment of risk of bias that may affect the cumulative evidence (such as publication bias, selective reporting within studies). | |
| Additional analyses | 16 Describe methods of additional analyses (such as sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done, indicating which were pre-specified. | |
| Results | ||
| Study selection | 17 Give numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram. | |
| Study characteristics | 18 For each study, present characteristics for which data were extracted (such as study size, PICOS, follow-up period) and provide the citation. | |
| Risk of bias within studies | 19 Present data on risk of bias of each study and, if available, any outcome-level assessment (see item 12) | |
| Results of individual studies | 20 For all outcomes considered (benefits and harms), present, for each study, simple summary data for each intervention group and effect estimates and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest plot (a type of graph used in meta-analyses which demonstrates relat, ve success rates of treatment outcomes of multiple scientific studies analyzing the same topic) | |
| Syntheses of resxults | 21 Present the results of each meta-analyses including confidence intervals and measures of consistency | |
| Risk of bias across studies | 22 Present results of any assessment of risk of bias across studies (see item 15). | |
| Additional analyses | 23 Give results of additional analyses, if done such as sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression (see item 16) | |
| Discussion | ||
| Summary of evidence | 24 Summarize the main findings, including the strength of evidence for each main outcome; consider their relevance to key groups (such as healthcare providers, users, and policy makers) | |
| Limitations | 25 Discuss limitations at study and outcome level (such as risk of bias), and at review level such as incomplete retrieval of identified research, reporting bias | |
| Conclusions | 26 Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence, and implications for future research | |
| Funding | ||
| Funding | 27 Indicate sources of funding or other support (such as supply of data) for the systematic review, and the role of funders for the systematic review |
Contents and format
Important differences exist between systematic, and non-systematic reviews which especially arise from methodologies used in the description of the literature sources. A non-systematic review means use of articles collected for years with the recommendations of your colleagues, while systematic review is based on struggles to search for, and find the best possible researches which will respond to the questions predetermined at the start of the review.
Though a consensus has been reached about the systematic design of the review articles, studies revealed that most of them had not been written in a systematic format. McAlister et al. analyzed review articles in 6 medical journals, and disclosed that in less than one fourth of the review articles, methods of description, evaluation or synthesis of evidence had been provided, one third of them had focused on a clinical topic, and only half of them had provided quantitative data about the extend of the potential benefits. [ 10 ]
Use of proper methodologies in review articles is important in that readers assume an objective attitude towards updated information. We can confront two problems while we are using data from researches in order to answer certain questions. Firstly, we can be prejudiced during selection of research articles or these articles might be biased. To minimize this risk, methodologies used in our reviews should allow us to define, and use researches with minimal degree of bias. The second problem is that, most of the researches have been performed with small sample sizes. In statistical methods in meta-analyses, available researches are combined to increase the statistical power of the study. The problematic aspect of a non-systematic review is that our tendency to give biased responses to the questions, in other words we apt to select the studies with known or favourite results, rather than the best quality investigations among them.
As is the case with many research articles, general format of a systematic review on a single subject includes sections of Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion ( Table 2 ).
Structure of a systematic review
| Introduction | Presents the problem and certain issues dealt in the review article |
| Methods | Describes research, and evaluation process Specifies the number of studies evaluated orselected |
| Results | Describes the quality, and outcomes of the selected studies |
| Discussion | Summarizes results, limitations, and outcomes of the procedure and research |
Preparation of the review article
Steps, and targets of constructing a good review article are listed in Table 3 . To write a good review article the items in Table 3 should be implemented step by step. [ 11 – 13 ]
Steps of a systematic review
| Formulation of researchable questions | Select answerable questions |
| Disclosure of studies | Databases, and key words |
| Evaluation of its quality | Quality criteria during selection of studies |
| Synthesis | Methods interpretation, and synthesis of outcomes |
The research question
It might be helpful to divide the research question into components. The most prevalently used format for questions related to the treatment is PICO (P - Patient, Problem or Population; I-Intervention; C-appropriate Comparisons, and O-Outcome measures) procedure. For example In female patients (P) with stress urinary incontinence, comparisons (C) between transobturator, and retropubic midurethral tension-free band surgery (I) as for patients’ satisfaction (O).
Finding Studies
In a systematic review on a focused question, methods of investigation used should be clearly specified.
Ideally, research methods, investigated databases, and key words should be described in the final report. Different databases are used dependent on the topic analyzed. In most of the clinical topics, Medline should be surveyed. However searching through Embase and CINAHL can be also appropriate.
While determining appropriate terms for surveying, PICO elements of the issue to be sought may guide the process. Since in general we are interested in more than one outcome, P, and I can be key elements. In this case we should think about synonyms of P, and I elements, and combine them with a conjunction AND.
One method which might alleviate the workload of surveying process is “methodological filter” which aims to find the best investigation method for each research question. A good example of this method can be found in PubMed interface of Medline. The Clinical Queries tool offers empirically developed filters for five different inquiries as guidelines for etiology, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis or clinical prediction.
Evaluation of the Quality of the Study
As an indispensable component of the review process is to discriminate good, and bad quality researches from each other, and the outcomes should be based on better qualified researches, as far as possible. To achieve this goal you should know the best possible evidence for each type of question The first component of the quality is its general planning/design of the study. General planning/design of a cohort study, a case series or normal study demonstrates variations.
A hierarchy of evidence for different research questions is presented in Table 4 . However this hierarchy is only a first step. After you find good quality research articles, you won’t need to read all the rest of other articles which saves you tons of time. [ 14 ]
Determination of levels of evidence based on the type of the research question
| I | Systematic review of Level II studies | Systematic review of Level II studies | Systematic review of Level II studies | Systematic review of Level II studies |
| II | Randomized controlled study | Crross-sectional study in consecutive patients | Initial cohort study | Prospective cohort study |
| III | One of the following: Non-randomized experimental study (ie. controlled pre-, and post-test intervention study) Comparative studies with concurrent control groups (observational study) (ie. cohort study, case-control study) | One of the following: Cross-sectional study in non-consecutive case series; diagnostic case-control study | One of the following: Untreated control group patients in a randomized controlled study, integrated cohort study | One of the following: Retrospective cohort study, case-control study (Note: these are most prevalently used types of etiological studies; for other alternatives, and interventional studies see Level III |
| IV | Case series | Case series | Case series or cohort studies with patients at different stages of their disease states |
Formulating a Synthesis
Rarely all researches arrive at the same conclusion. In this case a solution should be found. However it is risky to make a decision based on the votes of absolute majority. Indeed, a well-performed large scale study, and a weakly designed one are weighed on the same scale. Therefore, ideally a meta-analysis should be performed to solve apparent differences. Ideally, first of all, one should be focused on the largest, and higher quality study, then other studies should be compared with this basic study.
Conclusions
In conclusion, during writing process of a review article, the procedures to be achieved can be indicated as follows: 1) Get rid of fixed ideas, and obsessions from your head, and view the subject from a large perspective. 2) Research articles in the literature should be approached with a methodological, and critical attitude and 3) finally data should be explained in an attractive way.
How to Write an Article Review: Examples and Tips
.webp)
In today's information-rich world, mastering the skill of discerning valuable insights from the overwhelming noise is a game-changer. Whether you're a student striving for success or a professional aiming to stay sharp, knowing how to critique an article is your key.
Our article review writing service explains the intricacies of writing an article review, categorizes different types and shares insights into impactful formatting. It's not just theory – we'll guide you step by step, from pre-writing to a tangible review article example, and refine your abilities with essential proofreading tips.
What Is an Article Review?
An article review is more than a mere summary; it is a thoughtful analysis and critique that goes beyond the surface of the title. It's an intellectual exercise that challenges you to engage deeply with the author's ideas, question their methodology, and evaluate the significance of their findings.
Consider it as a journey through the landscape of someone else's thoughts. It's not just about where the writer takes you; it's about the path they choose, the landmarks they highlight, and the potential detours they overlook. An effective examination is a conversation with the author, a dialogue where you appreciate their insights, challenge assumptions, and perhaps even find alternative routes through the intellectual terrain they've explored.
As you start to understand how to review the article, encourage thought by asking questions.
- What assumptions underlie the author's arguments?
- Are there alternative perspectives that could enrich the discussion?
- How does the author's methodology shape their conclusions, and are there potential biases to consider?
- How does the title contribute to the clarity and coherence of the author's arguments?
- In what ways does the title influence the reader's perception of the author's
At EssayHub, our book review writing service experts believe an article review is an opportunity not just to absorb information but to actively engage with it, to question, to ponder, and to contribute your own insights to the scholarly conversation.
Types of Review
When tackling article reviews, there isn't a one-size-fits-all approach; it's a task that allows for versatile strategies. Think of understanding the different types of reviews as having a multifaceted toolkit ready for use. In this part, we'll guide you through the varied types of a review article, each showing a unique viewpoint and serving a specific purpose. Whether you're analyzing a scholarly piece on your own or asking someone to 'write an article review for me,' you'll get valuable insights.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves critically evaluating and analyzing scholarly pieces published in an academic journal. It requires a thorough understanding of the author's research, methodology, results, and conclusions. The reviewer assesses the journal's contributions to the field, its theoretical framework, and the validity of the research methods employed. The goal is to provide a comprehensive summary and critique that highlights both the strengths and limitations of the piece.
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on the evaluation of a scientific or academic research paper. This type of examination involves examining the research question, experimental design, data collection methods, statistical analysis, and the interpretation of findings. For example, it can be research on teen vaping statistics , which includes all of above. The reviewer assesses the reliability and validity of the research, considers the implications of the study, and offers insights into its potential impact on the broader academic community.
Science Article Review
A science article review encompasses a critical analysis of a piece in the field of science, covering disciplines such as physics, chemistry, biology, or any other scientific domain. This review type involves assessing the clarity of scientific concepts presented, the validity of experimental procedures, and the significance of the study's findings. According to our literature review writing service , reviewers may also consider the article's potential contributions to advancing scientific knowledge and its relevance to current scientific debates or issues.

Article Review Format
Ensuring the proper formatting of an article examination is crucial, and it should consistently align with the citation style specified by your instructor. If you're uncertain, don't hesitate to ask us - write my article review for me, along with additional guidelines to effectively structure your piece.
Meanwhile, here are some questions to consider:
- What citation style (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.) should you employ?
- What is the recommended length for your article review?
- Should your assignment encompass a summary, critique, or include personal opinions?
- Is it necessary to highlight a theme or central idea from the articles?
- Does your instructor expect background information to be incorporated?
APA Format Article Review
An APA review sticks to the rules of the American Psychological Association. When unsure how to write an article review in APA format, remember that it carefully cites the article, using a title page, intro, summary, critique, conclusion, and references. Citations follow the author-date format, focusing on being clear and objective. The review digs into the article's methods, results, and overall impact.
When you write an article review in APA, your in-text citation might read: (Anderson & Ramirez, 2019)
The corresponding entry in the reference list would be: Anderson, L., & Ramirez, C. (2019). Unveiling the Dynamics of Urban Green Spaces. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 25(3), 112-128.
MLA Format Article Review
For an MLA writing review, it follows the Modern Language Association's style. It's important to know how sources are cited in the text and in the Works Cited page. The structure usually has an intro, summary, critique, and conclusion. MLA citations often have the author's last name and page number in brackets in the text. This review might highlight the document's literary or humanities aspects, such as style, language, and cultural context.
In an MLA format publication, the citation within the text could look like: (Anderson and Ramirez 112)
The Works Cited entry for this publication: Anderson, Laura, and Carlos Ramirez. 'Exploring the Impact of Urban Green Spaces on Well-being.' Journal of Environmental Psychology, vol. 25, no. 3, 2019, pp. 112-128.
Review Article Outline
As you read your writing piece, organize your thoughts into sections in an outline. Note down key facts, contributions, and any contradictions. Identify strengths and weaknesses, and start mapping your outline.
If your professor doesn't want a summary or personal critique, skip those parts. Like other assignments, your examination needs an introduction, body, and conclusion. Consider dividing your outline accordingly, with subheadings in the body. If you need help starting, find a sample outline.
Your article assessment should have the following:
- Pre-Title Page: Essential details like publication type, publication title, author names with affiliations, and corresponding author info.
- Running Head (APA format): A concise title for consistent formatting.
- Summary Page (optional but useful): Summarize the document in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology.
- Title Page: Full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction: Engage your reader with an overview.
- Body: Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References: Properly cite all sources.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page: If allowed, suggest further readings.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed): Include visuals when requested for clarity.
Writing an Article Review in 7 Steps
Use our essay writer service or move on to understanding how to write a review paper covering everything from creating the title to summarizing key points. This step-by-step guide breaks it down into seven simple steps, making the entire process more manageable.
.webp)
Step 1: Create the Title
The very first question you might have is how to start an article review. It's crucial to develop a title that not only captures the essence of the publication but also reflects your perspective. For instance, consider the title: ' Decoding Data: A Critical Exploration of Privacy Concerns in Online Health Platforms. ' This title not only introduces the main theme but also hints at the critical evaluation that will unfold in the writing. It sets the tone for your analysis and sparks interest from the outset.
Step 2: Reference the Article
In the second step, it's essential to ensure accurate citation by providing specific details. Take a look at this example:
- Author: Rodriguez, M., & Chen, L.
- Title: 'Privacy Matters: Analyzing the Impact of Health Apps on User Data'
- Publication Date: 2023
- Source: Journal of Digital Ethics, 8(2), 87-105.
By including these details, you not only acknowledge the authors and the publication but also provide your readers with the necessary information to locate and verify the article. This step lays the foundation for a credible and well-referenced examination.
Step 3: Article Identification
Identify key elements of the publication, such as the writer's main argument, methodology, and key findings. Pinpoint any theoretical frameworks or models used in the title.
For example: The writing by Garcia and Kim examines the correlation between social media usage and mental health outcomes among adolescents. The authors employ a longitudinal study approach, utilizing surveys and interviews to gather data.
Step 4: Make an Introduction
In your introduction, provide a brief overview of the title's subject and purpose. Capture the reader's attention and clearly state your thesis or main point related to the title. For instance, you might start your article review template like this.
In the digital age, the impact of social media on mental health has become a topic of increasing concern. Garcia and Kim's recent study delves into this issue, aiming to uncover the nuanced relationship between social media engagement and the psychological well-being of adolescents. This writing piece critically analyzes the methodology, findings, and implications of their research.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Summarize the main points of your assessment, highlighting key arguments, evidence, and results. Offer a concise overview without adding personal opinions.
Example: Garcia and Kim's study reveals a significant positive association between increased social media use and heightened levels of anxiety and depression among the adolescent population. The longitudinal study tracked participants over a two-year period, employing both quantitative and qualitative measures to assess mental health outcomes.
Step 6: Provide Critique
Critically assess the strengths and weaknesses of the writing. Well, how to critique an article , you might wonder. Discuss aspects such as methodology, data interpretation, and potential biases.
Example: While the study offers valuable insights, the reliance on self-reported data may introduce response bias. Additionally, the research predominantly focuses on mainstream social media platforms, potentially overlooking the impact of emerging platforms. Despite these limitations, the study's comprehensive approach contributes to the ongoing discourse surrounding the intersection of social media and mental health.
Step 7: Conclude
In the conclusion, summarize your overall assessment of the article and restate your main points. Offer insights into the broader implications of the research and suggest areas for future exploration.
For example: To conclude, Garcia and Kim's study sheds light on the complex relationship between social media use and adolescent mental health. Despite certain methodological limitations, the research underscores the need for continued investigation in this field. As we navigate the digital landscape, understanding these dynamics becomes crucial for devising effective interventions and support systems for the well-being of our youth.
Example of an Article Review
Why are we taking the time to discuss article review examples in this article? It might not be immediately apparent, but exploring a well-crafted article review sample is a vital step in the writing process for the following reasons:
- Introduction to Key Works: Helps you to familiarize yourself with the important works of experts in your field.
- Identification of Key Figures: You can recognize key figures contributing to a specific scientific field.
- Understanding Field Advancements: Helps you define significant discoveries and advances made in your area of study.
- Identification of Knowledge Gaps: You can uncover major gaps in existing knowledge, contributing to the formulation of fresh solutions.
- Reference and Argumentation Resources: You discover solid references and arguments that can enhance your own writing.
- Idea Generation: Helps you generate ideas for potential future research directions.
- Becoming an Expert: Assists in gaining a deeper understanding of the subject area, moving towards expertise.
- Writing Guidance: You acquire a clear idea of how to craft a well-structured review.

Can Anyone Write an Article Review for Me?
Is writing a review article worth it, how to write an apa format article review, how do you write an article review from the beginning, what is the proper article review format.
Ryan Acton is an essay-writing expert with a Ph.D. in Sociology, specializing in sociological research and historical analysis. By partnering with EssayHub, he provides comprehensive support to students, helping them craft well-informed essays across a variety of topics.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.

Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Writing Guide
- Article Writing
How To Write an Article Review
- Definition of article review
- Why do students write article reviews
- Types of article review
- Structure and outline
- Step-by-step guide
Article review format
- How to write a good article review
- Article review examples
Definition of article review assignments
Why do students write article reviews.
- Article writing is a deeply analytical process that helps students to correct vague terms when and if they are present. Likewise, when composing an article review or an original assignment, such work provides more clarity regarding using appropriate words. If an article has colloquial language or logical gaps, it is one of those aspects to mention in an article review. It also allows writers to determine whether certain terms must be replaced and edited.
- Article review essay writing helps to clarify scientific questions.
- Writing an article review allows students to see and understand how others approach specific issues and what perspectives should be studied regarding the problems at hand. Once a person reads the review, it makes it easier to get rid of bias.
- Article review assignments also provide students with editing and grammar work to help with more accurate papers.
- Most importantly, an article review is a way to encourage better work and provide critical analysis with due criticism and evaluation of the original article.
Types of article review tasks
- Original Research Article Review. The original research article review is close to what is often seen as the literature review. An author must explore the author’s hypothesis and some background studies with due analysis to outline scientific methods. It’s one of the most challenging tasks to write as one must interpret the findings and talk about future implications. This type of work can also get lengthy and be up to 6,000 words in subjects like History or Sociology.
- Critical Analysis. As the name implies, it critically evaluates the author’s work and can be up to 3,000 words.
- Literature Review. It stands for the review of secondary literature sources. As a rule, such reviews do not present much new data and only evaluate the importance of sources and information that supports the author’s arguments.
- Systematic Review. This case stands for research questions and articles that require a deeper synthesis of available facts or certain evidence. The purpose here is to define and evaluate the quality of the data obtained by the author.
- Meta-Analysis Reviews. Once again, it is a systematic review focusing on a specific topic, the literature issues. You must provide a special quantitative estimate for exposure and intervention.
- Clinical Trial Reviews. It means that one must provide a study related to an investigation offered by the author. It can relate to a drug or talk about a sample group of people, thus bringing it into the field of a defined population or a group of participants.
- Perspective or Opinion Article Review. This is where one poses an opinion, meaning things can get biased toward a certain opinion. In writing a good review, a student can look for perspectives and evaluate the importance of the original article. Likewise, posing an opinion is one of the obligatory aspects.
Article review structure and outline
Article review structure.
- Title page.
- An article introduction presenting the main subject and/or a problem.
- Brief article summary.
- Critical article evaluation and/or a summary.
- Conclusion with the moral lesson and discussion on the findings’ pros/cons.
- Bibliography with relevant citations.
Article review outline
- You provide an evaluation and summary of the author’s article.
- Your audience can receive sufficient knowledge regarding the subject.
- You have made points about the strongest arguments of the author.
- You have criticized the author’s work and explained how it contributes to the scientific field.
- You conclude your article review with your original thoughts and opinions without turning to additional research unless the grading rubric required it.
Step-by-step writing guide
Step 1: learn about the article’s agenda., step 2: summarize the main article ideas, step 3: organization aspect of the review, step 4: article preview and take notes, step 5: paraphrasing and analysis, step 6: final evaluation.

- An introduction. The topic of your study must be mentioned here in the first sentence. Indicate what your article contains and talk about the author’s background. Provide an order of the subjects you plan to discuss to explain what your readers expect. The introduction should provide the author’s claims and the main arguments that result in your thesis statement. When writing an introduction, you must determine the main argument.
- Body paragraphs. This is where you provide an evaluation with a summary and write about the author’s work.
- Conclusion. Speak of your reasons for providing a review and talk about whether you could support your thesis and what you have learned.
- Works Cited page. Refer to your grading rubric to identify what citation style must be used.
How to write a good article review?
- Do not write the statements in the first person. It is recommended to use the third person instead by turning to a formal academic tone.
- Your introduction with the information about the original article should take from 10 to 25% of your assignment’s volume.
- An introduction must end with a strong thesis and make an assumption or research the author’s main claim. A typical thesis to start an article review for an assignment may look this way:
- Write down all the important points and share your findings. It will help to show that you have done your homework correctly.
- Discuss how the article supports the claims and whether it provides good evidence.
- Always provide background information about the author.
- Use direct quotes to support your claims by turning to the original article.
- Read your summary twice to evaluate whether it follows the main thesis.
- Talk about the contributions of the author to the academic community.
- Provide reasons for whether you support the author’s view or not. Why or why not?
- Summarize all the important points in a conclusion part.
Why choose article review examples?
- Wright State University’s Journal Article Review Example .
- University of Illinois Springfield’s Article How-to Review Guide .
- UC Merced Library’s Article Review Sample
- Identify recent and important changes in your field of study.
- Determine who works in a specific field of science and why.
- Narrow things down and identify essential information to help you start with research.
- Use obtained information in school debates, and references work.
- Generate new ideas and conduct lab experiments.
- Write an article review through the lens of personal experience and expertise.

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
- How to Order
Article Review
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Struggling to write a review that people actually want to read? Feeling lost in the details and wondering how to make your analysis stand out?
You're not alone!
Many writers find it tough to navigate the world of article reviews, not sure where to start or how to make their reviews really grab attention.
No worries!
In this blog, we're going to guide you through the process of writing an article review that stands out. We'll also share tips, and examples to make this process easier for you.
Let’s get started.
- 1. What is an Article Review?
- 2. Types of Article Reviews
- 3. Article Review Format
- 4. How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
- 5. Article Review Outline
- 6. Article Review Examples
- 7. Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical evaluation and analysis of a piece of writing, typically an academic or journalistic article.
It goes beyond summarizing the content; it involves an in-depth examination of the author's ideas, arguments, and methodologies.
The goal is to provide a well-rounded understanding of the article's strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in the realm of academic or professional discourse. Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring your approach.
Here are some common types of article reviews:
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves a thorough evaluation of scholarly articles published in academic journals.
It requires summarizing the article's key points, methodology, and findings, emphasizing its contributions to the academic field.
Take a look at the following example to help you understand better.
Example of Journal Article Review
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on scrutinizing articles with a primary emphasis on research.
This type of review involves evaluating the research design, methodology, results, and their broader implications.
Discussions on the interpretation of results, limitations, and the article's overall contributions are key.
Here is a sample for you to get an idea.
Example of Research Article Review
Science Article Review
A science article review specifically addresses articles within scientific disciplines. It includes summarizing scientific concepts, hypotheses, and experimental methods.
The type of review assesses the reliability of the experimental design, and evaluates the author's interpretation of findings.
Take a look at the following example.
Example of Science Article Review
Critical Review
A critical review involves a balanced critique of a given article. It encompasses providing a comprehensive summary, highlighting key points, and engaging in a critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses.
To get a clearer idea of a critical review, take a look at this example.
Critical Review Example
Article Review Format
When crafting an article review in either APA or MLA format, it's crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for citing sources.
Below are the bibliographical entries for different types of sources in both APA and MLA styles:
| : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link} : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp. : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. Xx-xx. |
| : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed. : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print. : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed. |
How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
Writing an effective article review involves a systematic approach. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure a comprehensive and well-structured analysis.
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before diving into the review, carefully read and understand the assignment guidelines.
Pay attention to specific requirements, such as word count, formatting style (APA, MLA), and the aspects your instructor wants you to focus on.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly
Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author.
Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
Step 3: Create a Summary
Summarize the main points of the article. Highlight the author's key arguments and findings.
While writing the summary ensure that you capture the essential elements of the article to provide context for your analysis.
Step 4: Identify the Author's Thesis
In this step, pinpoint the author's main thesis or central argument. Understand the purpose of the article and how the author supports their position.
This will serve as a foundation for your critique.
Step 5: Evaluate the Author's Evidence and Methodology
Examine the evidence provided by the author to support their thesis. Assess the reliability and validity of the methodology used.
Consider the sources, data collection methods, and any potential biases.
Step 6: Analyze the Author's Writing Style
Evaluate the author's writing style and how effectively they communicate their ideas.
Consider the clarity of the language, the organization of the content, and the overall persuasiveness of the article.
Step 7: Consider the Article's Contribution
Reflect on the article's contribution to its field of study. Analyze how it fits into the existing literature, its significance, and any potential implications for future research or applications.
Step 8: Write the Introduction
Craft an introduction that includes the article's title, author, publication date, and a brief overview.
State the purpose of your review and your thesis—the main point you'll be analyzing in your review.
Step 9: Develop the Body of the Review
Organize your review by addressing specific aspects such as the author's thesis, methodology, writing style, and the article's contribution.
Use clear paragraphs to structure your analysis logically.
Step 10: Conclude with a Summary and Evaluation
Summarize your main points and restate your overall assessment of the article.
Offer insights into its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with any recommendations for improvement or suggestions for further research.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Article Review Outline
Creating a well-organized outline is an essential part of writing a coherent and insightful article review.
This outline given below will guide you through the key sections of your review, ensuring that your analysis is comprehensive and logically structured.
|
Refer to the following template to understand outlining the article review in detail.
Article Review Format Template
Article Review Examples
Examining article review examples can provide valuable insights into the structure, tone, and depth of analysis expected.
Below are sample article reviews, each illustrating a different approach and focus.
Example of Article Review
Sample of article review assignment pdf
Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
Crafting an effective article review involves a combination of critical analysis, clarity, and structure.
Here are some valuable tips to guide you through the process:
- Start with a Clear Introduction
Kick off your article review by introducing the article's main points and mentioning the publication date, which you can find on the re-title page. Outline the topics you'll cover in your review.
- Concise Summary with Unanswered Questions
Provide a short summary of the article, emphasizing its main ideas. Highlight any lingering questions, known as "unanswered questions," that the article may have triggered. Use a basic article review template to help structure your thoughts.
- Illustrate with Examples
Use examples from the article to illustrate your points. If there are tables or figures in the article, discuss them to make your review more concrete and easily understandable.
- Organize Clearly with a Summary Section
Keep your review straightforward and well-organized. Begin with the start of the article, express your thoughts on what you liked or didn't like, and conclude with a summary section. This follows a basic plan for clarity.
- Constructive Criticism
When providing criticism, be constructive. If there are elements you don't understand, frame them as "unanswered questions." This approach shows engagement and curiosity.
- Smoothly Connect Your Ideas
Ensure your thoughts flow naturally throughout your review. Use simple words and sentences. If you have questions about the article, let them guide your review organically.
- Revise and Check for Clarity
Before finishing, go through your review. Correct any mistakes and ensure it sounds clear. Check if you followed your plan, used simple words, and incorporated the keywords effectively. This makes your review better and more accessible for others.
In conclusion , writing an effective article review involves a thoughtful balance of summarizing key points, and addressing unanswered questions.
By following a simple and structured approach, you can create a review that not only analyzes the content but also adds value to the reader's understanding.
Remember to organize your thoughts logically, use clear language, and provide examples from the article to support your points.
Ready to elevate your article reviewing skills? Explore the valuable resources and expert assistance at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our team of experienced writers is here to help you with article reviews and other school tasks.
So why wait? Place your " write my essays online " request today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
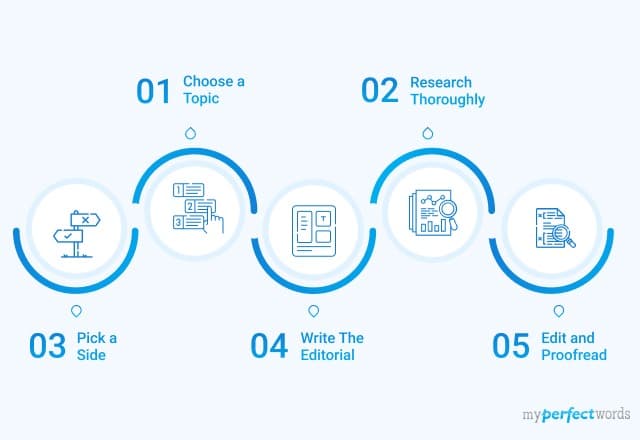

Sample Papers
This page contains sample papers formatted in seventh edition APA Style. The sample papers show the format that authors should use to submit a manuscript for publication in a professional journal and that students should use to submit a paper to an instructor for a course assignment. You can download the Word files to use as templates and edit them as needed for the purposes of your own papers.
Most guidelines in the Publication Manual apply to both professional manuscripts and student papers. However, there are specific guidelines for professional papers versus student papers, including professional and student title page formats. All authors should check with the person or entity to whom they are submitting their paper (e.g., publisher or instructor) for guidelines that are different from or in addition to those specified by APA Style.
Sample papers from the Publication Manual
The following two sample papers were published in annotated form in the Publication Manual and are reproduced here as PDFs for your ease of use. The annotations draw attention to content and formatting and provide the relevant sections of the Publication Manual (7th ed.) to consult for more information.
- Student sample paper with annotations (PDF, 5MB)
- Professional sample paper with annotations (PDF, 2.7MB)
We also offer these sample papers in Microsoft Word (.docx) format with the annotations as comments to the text.
- Student sample paper with annotations as comments (DOCX, 42KB)
- Professional sample paper with annotations as comments (DOCX, 103KB)
Finally, we offer these sample papers in Microsoft Word (.docx) format without the annotations.
- Student sample paper without annotations (DOCX, 36KB)
- Professional sample paper without annotations (DOCX, 96KB)
Sample professional paper templates by paper type
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different professional paper types. Professional papers can contain many different elements depending on the nature of the work. Authors seeking publication should refer to the journal’s instructions for authors or manuscript submission guidelines for specific requirements and/or sections to include.
- Literature review professional paper template (DOCX, 47KB)
- Mixed methods professional paper template (DOCX, 68KB)
- Qualitative professional paper template (DOCX, 72KB)
- Quantitative professional paper template (DOCX, 77KB)
- Review professional paper template (DOCX, 112KB)
Sample papers are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 2 and the Concise Guide Chapter 1
Related handouts
- Heading Levels Template: Student Paper (PDF, 257KB)
- Heading Levels Template: Professional Paper (PDF, 213KB)
Other instructional aids
- Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS)
- APA Style Tutorials and Webinars
- Handouts and Guides
- Paper Format
View all instructional aids
Sample student paper templates by paper type
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
APA does not set formal requirements for the nature or contents of an APA Style student paper. Students should follow the guidelines and requirements of their instructor, department, and/or institution when writing papers. For instance, an abstract and keywords are not required for APA Style student papers, although an instructor may request them in student papers that are longer or more complex. Specific questions about a paper being written for a course assignment should be directed to the instructor or institution assigning the paper.
- Discussion post student paper template (DOCX, 31KB)
- Literature review student paper template (DOCX, 37KB)
- Quantitative study student paper template (DOCX, 53KB)
Sample papers in real life
Although published articles differ in format from manuscripts submitted for publication or student papers (e.g., different line spacing, font, margins, and column format), articles published in APA journals provide excellent demonstrations of APA Style in action.
APA journals began publishing papers in seventh edition APA Style in 2020. Professional authors should check the author submission guidelines for the journal to which they want to submit their paper for any journal-specific style requirements.
Credits for sample professional paper templates
Quantitative professional paper template: Adapted from “Fake News, Fast and Slow: Deliberation Reduces Belief in False (but Not True) News Headlines,” by B. Bago, D. G. Rand, and G. Pennycook, 2020, Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 149 (8), pp. 1608–1613 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000729 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Qualitative professional paper template: Adapted from “‘My Smartphone Is an Extension of Myself’: A Holistic Qualitative Exploration of the Impact of Using a Smartphone,” by L. J. Harkin and D. Kuss, 2020, Psychology of Popular Media , 10 (1), pp. 28–38 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000278 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Mixed methods professional paper template: Adapted from “‘I Am a Change Agent’: A Mixed Methods Analysis of Students’ Social Justice Value Orientation in an Undergraduate Community Psychology Course,” by D. X. Henderson, A. T. Majors, and M. Wright, 2019, Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology , 7 (1), 68–80. ( https://doi.org/10.1037/stl0000171 ). Copyright 2019 by the American Psychological Association.
Literature review professional paper template: Adapted from “Rethinking Emotions in the Context of Infants’ Prosocial Behavior: The Role of Interest and Positive Emotions,” by S. I. Hammond and J. K. Drummond, 2019, Developmental Psychology , 55 (9), pp. 1882–1888 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000685 ). Copyright 2019 by the American Psychological Association.
Review professional paper template: Adapted from “Joining the Conversation: Teaching Students to Think and Communicate Like Scholars,” by E. L. Parks, 2022, Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology , 8 (1), pp. 70–78 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/stl0000193 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Credits for sample student paper templates
These papers came from real students who gave their permission to have them edited and posted by APA.
Journal Article Review in APA Style
Journal article reviews refer to the appraisal of potencies and limitations of an article’s opinion and subject matter. The article reviews offer the readers with an explanation, investigation and clarification to evaluate the importance of the article. A journal article review usually follows the APA style, which is in itself an exceptional mode of writing. Writing a journal article review in APA style requires a thorough reading of an article and then present our personal opinions on its subject matter.
In order to write a journal article review in APA style, one must necessarily conform to the detailed guidelines of APA style of writing. As such, a few tips for writing a journal article review in APA style have been provided in details below.
Tips for Writing Journal Article Review in APA Style
Getting started.
Read the complete article. Most journal articles use highly complicated and difficult language and wording. Thus, it is suggested to read the article thoroughly several times to understand it perfectly. Select a statement that effectively conveys the main idea of your review. Present the ideas in a rational order, keeping in mind that all opinions must sustain the main idea.
Start with a header with citation
Journal article reviews start with a header, including citation of the sources being reviewed. This citation is mentioned at the top of the review, following the APA style (refer to the APA style manual for more information). We will need the author’s name for the article, title of the article, journal of the published article, volume and issue number, publication date, and page numbers for the article.
Write a summary
The introductory paragraph of the review should provide a brief summary of the article, strictly limiting it to one to three paragraphs depending on the article length. The summary should discuss only the most imperative details about the article, like the author’s intention in writing the article, how the study was conducted, how the article relates to other work on the same subject, the results and other relevant information from the article.
Body of the review
The succeeding paragraphs of the review should present your ideas and opinions on the article. Discuss the significance and suggestion of the results of the study. The body of the article review should be limited to one to two paragraphs, including your understanding of the article, quotations from the article demonstrating your main ideas, discussing the article’s limitations and how to overcome them.
Concluding the review
The concluding paragraphs of the review should provide your personal appraisal of the journal article. Discuss whether the article is well-written or not, whether any information is missing, or if further research is necessary on the subject. Also, write a paragraph on how the author could develop the study results, what the information means on a large scale, how further investigation can develop the subject matter, and how the knowledge of this field can be extended further.
Citation and Revision
In-text citation of direct quotes or paraphrases from the article can be done using the author’s name, year of publication and page numbers (refer to the APA-style manual for citation guidelines). After finishing the writing of journal article review in APA style, it would be advised to re-visit the review after a few days and then re-read it altogether. By doing this, you will be able to view the review with a new perspective and may detect mistakes that were previously left undetected.
The above mentioned tips will help and guide you for writing a journal article review in APA style. However, while writing a journal article review, remember that you are undertaking more than just a narrative review. Thus, the article review should not merely focus on discussing what the article is about, but should reveal your personal ideas and opinions on the article.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Article review writing format, steps, examples and illustration PDF Compiled by Mohammed Yismaw

2021, Article review writing format, steps, examples and illustration PDF Compiled by Mohammed Yismaw
The purpose of this document is to help students and researchers understand how a review of an academic journal is conducted and reported in different fields of study. Review articles in academic journals that analyze or discuss researches previously published by others, rather than reporting new research results or findings. Summaries and critiques are two ways to write a review of a scientific journal article. Both types of writing ask you first to read and understand an article from the primary literature about your topic. The summary involves briefly but accurately stating the key points of the article for a reader who has not read the original article. The critique begins by summarizing the article and then analyzes and evaluates the author’s research. Summaries and critiques help you learn to synthesize information from different sources and are usually limited to two pages maximum.
Related Papers
Harald von Kortzfleisch , Christoph Kahle
Neue Technologien und Innovationen stellen heutzutage wichtige Schlüsselelemente der Wachstums und Erfolgssicherung von Unternehmen dar. Durch einen in Geschwindigkeit und Intensität immer schneller zunehmenden Wettbewerb nehmen Innovationen eine immer zentralere Rolle im Praxisalltag von Unternehmen ein. Dieser technische Fortschritt treibt auch in der Wissenschaft das Thema des Innovationsmanagements in den letzten Jahrzehnten immer stärker voran und wird dort ausgiebig diskutiert. Die Bedeutung von Innovationen wächst dabei ebenfalls aus der Sicht der Kunden, welche heutzutage viel differenzierter als früher Produkte und Dienste nachfragen und somit Unternehmen vor neue Herausforderungen stellen. Ãberdies stellen Innovationen heute ein entscheidendes Bindeglied zwischen Marktorientierung und erhofften Unternehmenserfolg dar. Seit einigen Jahren lässt sich eine Ãffnung der Unternehmensgrenzen für externe Quellen wie Kunden, Zulieferer, Universitäten oder teilweise auch M...
SSRN Electronic Journal
Helmut Krcmar
Dominic Lindner
Alexandra Waluszewski
Research Policy
Nuria Gonzalez Alvarez
Creativity and Innovation Management
Matti Pihlajamaa
Firms tap into user knowledge to learn about the users’ needs. While users have been recognized as a valuable source of knowledge for innovation, few studies have investigated how their knowledge is integrated into innovation processes in the context of complex products and systems (CoPS). The purpose of this study is to reveal the practices of CoPS manufacturers to facilitate user knowledge utilization for innovation. We investigate two case companies, a medical device manufacturer and an aircraft manufacturer, and report on seven managerial practices for utilizing user knowledge. We adopt the absorptive capacity model in structuring our findings and elaborate three of the model's sub-capabilities (recognition of the value of user knowledge, acquisition of user knowledge, and assimilation/transformation of user knowledge) by proposing that each is associated with a distinct managerial goal and related practices: (1) Sensitizing the organization to the innovation potential of user knowledge, (2) identifying and gaining access to suitable user knowledge, and (3) analyzing and interpreting user knowledge and integrating it into product development. Our study contributes to the innovation management literature by analyzing the capabilities required to utilize user knowledge throughout the CoPS innovation process.
Information & Management
Diffusion of digital technologies into the manufacturing industry has created new opportunities for innovation that firms must address to remain competitive. We investigate the role of customer and user knowledge in the digital innovation processes of three global B2B manufacturing companies. We find that the B2B manufacturing industry's characteristics influence how users and customers may be leveraged. Customers making the purchasing decisions are considered for knowledge about short-term changes in market needs, while users working directly with the products provide long-term guidance for digital innovation. We identify practices for acquiring, distributing, and using customer and user knowledge for digital innovation.
Journal of business market management
Patricia Sandmeier
Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation
Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation JEMI
Given the rising role of users in innovation processes and the increasing amount of research in this field the aim of this paper is to explore the limits of our understanding of the user innovation (UI) concept. In doing so, the study addresses four basic questions: (1) Why do users create and share innovation? (2) Who is the user-innovator? (3) What type of innovation do users create? (4) How do users innovate? The results of a systematic literature review identified the main research streams on user innovation, together with weaknesses of past research and perspectives for future studies.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Gernot Grabher
Journal of Computer‐ …
Petra Schubert , Kathrin Möslein
Mossimo Sesom
Shahab Zare
Arthur Shulman
International Journal of Technology Management
Richard Farr
European Journal of Dental Education
Y.P. CHANDRA
Chandra Yanto
Management Science
John Roberts
Maria Antikainen
Johanna Bragge
intechopen.com
Ivona Vrdoljak Raguz
Service Science
Tuure Tuunanen
Jouni K Juntunen
Benji Decker
Eva Heiskanen
Handbook of Marketing
Jerome Hauser
Service Industries Journal
Christian Kowalkowski
Journal of Engineering Design
Anna Rönnbäck , Ola Isaksson
Journal of Management
Bettina Bastian
International Journal of Innovation Management
Harald von Kortzfleisch
Guido H Baltes
Technology Analysis & Strategic Management
Raimo Lovio
Marco Bertoni , Christian Johansson
Dominik Walcher
Managing Service Quality
Tor W. Andreassen
Journal of Product Innovation Management
Gary Schirr
System Sciences, 2004. …
Dominik Walcher , Ralf Reichwald
Edina Vadovics
Jouni Similä
Luis Cancino Muñoz
Shell Artillery
Ralf Reichwald
Journal of the Academy of …
Ian Wilkinson , Subroto Roy
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
| 🗞️ Popular articles are: | 🎓 Scholarly articles are: |
|---|---|
| Written by a professional or non-professional author. | Written by someone with academic credentials. |
| Meant for the general audience. | Published for the peer academic community. |
| Featuring reader-friendly, simple language. | Containing professional jargon and vocabulary. |
| Illustrated by simple and engaging visuals. | Illustrated by tables and graphs. |
| Structured in a simple way. | Structured according to a scholarly publication’s standards. |
| Checked by the magazine’s editorial staff only. | Thoroughly reviewed by peer researchers. |
| Featuring no or scarce references. | Featuring a full list of references. |
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
| ✔️ | Both a reaction paper and an article review will start with a content summary. |
| ✔️ | For scholarly material, you will present a structured review after the summary. |
| ✔️ | For popular magazine content, you will write a response that sums up your emotions, thoughts, and reactions that the material aroused. |
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type, your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
| This type of research is the most common and highly valued in the scholarly community. It uses primary data collected by the author specifically for this article and offers original findings and insights into the discussed research area. | |
| This research type examines a particular event, phenomenon, or object closely by considering its environment, details, and context. It’s a close-up of the research object that can be achieved via different observation and data collection techniques. | |
| These articles address new research procedures or methods for testing hypotheses in a specific area of research. |
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement, or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
| cover the article’s purpose comprehensively? | |
| in data presentation? | |
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations, like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries.
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
| Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year). Publisher. | |
| Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year). . Name of Website. URL. |
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
| Author’s last name, First name. Publisher, Year. | |
| Author’s last name, First name. “Webpage Title.” , Date, URL. Accessed Day Month Year. |
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
| Frequently, assignment instructions will ask you to include a full citation of your chosen text at the top of the first page of your article review. | |
| In the introduction, you should summarize the background information and purpose of the research under review. In addition, consider explaining why you chose it for your assignment. | |
| Next, summarize the article. If you review the original research, consider including the following points: If you review a or a book, include the following in your summary: This section should be no more than a third of your total article review. | |
| Then, you should critically evaluate the article. Consider answering these questions: | |
| In the , share your reasoned opinion on the reviewed piece. Was it worth reading? Did you learn any lessons from it? Would you recommend it to someone else, and why? | |
| In the end, add a separate page with bibliographic citations of your reviewed article and any other sources used in your paper. |
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: So, let’s start digging deeper into this topic! ♻️ What Is Process Analysis? A process analysis describes and explains the succession of...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
Page Content
Overview of the review report format, the first read-through, first read considerations, spotting potential major flaws, concluding the first reading, rejection after the first reading, before starting the second read-through, doing the second read-through, the second read-through: section by section guidance, how to structure your report, on presentation and style, criticisms & confidential comments to editors, the recommendation, when recommending rejection, additional resources, step by step guide to reviewing a manuscript.
When you receive an invitation to peer review, you should be sent a copy of the paper's abstract to help you decide whether you wish to do the review. Try to respond to invitations promptly - it will prevent delays. It is also important at this stage to declare any potential Conflict of Interest.
The structure of the review report varies between journals. Some follow an informal structure, while others have a more formal approach.
" Number your comments!!! " (Jonathon Halbesleben, former Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Informal Structure
Many journals don't provide criteria for reviews beyond asking for your 'analysis of merits'. In this case, you may wish to familiarize yourself with examples of other reviews done for the journal, which the editor should be able to provide or, as you gain experience, rely on your own evolving style.
Formal Structure
Other journals require a more formal approach. Sometimes they will ask you to address specific questions in your review via a questionnaire. Or they might want you to rate the manuscript on various attributes using a scorecard. Often you can't see these until you log in to submit your review. So when you agree to the work, it's worth checking for any journal-specific guidelines and requirements. If there are formal guidelines, let them direct the structure of your review.
In Both Cases
Whether specifically required by the reporting format or not, you should expect to compile comments to authors and possibly confidential ones to editors only.

Following the invitation to review, when you'll have received the article abstract, you should already understand the aims, key data and conclusions of the manuscript. If you don't, make a note now that you need to feedback on how to improve those sections.
The first read-through is a skim-read. It will help you form an initial impression of the paper and get a sense of whether your eventual recommendation will be to accept or reject the paper.
Keep a pen and paper handy when skim-reading.
Try to bear in mind the following questions - they'll help you form your overall impression:
- What is the main question addressed by the research? Is it relevant and interesting?
- How original is the topic? What does it add to the subject area compared with other published material?
- Is the paper well written? Is the text clear and easy to read?
- Are the conclusions consistent with the evidence and arguments presented? Do they address the main question posed?
- If the author is disagreeing significantly with the current academic consensus, do they have a substantial case? If not, what would be required to make their case credible?
- If the paper includes tables or figures, what do they add to the paper? Do they aid understanding or are they superfluous?
While you should read the whole paper, making the right choice of what to read first can save time by flagging major problems early on.
Editors say, " Specific recommendations for remedying flaws are VERY welcome ."
Examples of possibly major flaws include:
- Drawing a conclusion that is contradicted by the author's own statistical or qualitative evidence
- The use of a discredited method
- Ignoring a process that is known to have a strong influence on the area under study
If experimental design features prominently in the paper, first check that the methodology is sound - if not, this is likely to be a major flaw.
You might examine:
- The sampling in analytical papers
- The sufficient use of control experiments
- The precision of process data
- The regularity of sampling in time-dependent studies
- The validity of questions, the use of a detailed methodology and the data analysis being done systematically (in qualitative research)
- That qualitative research extends beyond the author's opinions, with sufficient descriptive elements and appropriate quotes from interviews or focus groups
Major Flaws in Information
If methodology is less of an issue, it's often a good idea to look at the data tables, figures or images first. Especially in science research, it's all about the information gathered. If there are critical flaws in this, it's very likely the manuscript will need to be rejected. Such issues include:
- Insufficient data
- Unclear data tables
- Contradictory data that either are not self-consistent or disagree with the conclusions
- Confirmatory data that adds little, if anything, to current understanding - unless strong arguments for such repetition are made
If you find a major problem, note your reasoning and clear supporting evidence (including citations).
After the initial read and using your notes, including those of any major flaws you found, draft the first two paragraphs of your review - the first summarizing the research question addressed and the second the contribution of the work. If the journal has a prescribed reporting format, this draft will still help you compose your thoughts.
The First Paragraph
This should state the main question addressed by the research and summarize the goals, approaches, and conclusions of the paper. It should:
- Help the editor properly contextualize the research and add weight to your judgement
- Show the author what key messages are conveyed to the reader, so they can be sure they are achieving what they set out to do
- Focus on successful aspects of the paper so the author gets a sense of what they've done well
The Second Paragraph
This should provide a conceptual overview of the contribution of the research. So consider:
- Is the paper's premise interesting and important?
- Are the methods used appropriate?
- Do the data support the conclusions?
After drafting these two paragraphs, you should be in a position to decide whether this manuscript is seriously flawed and should be rejected (see the next section). Or whether it is publishable in principle and merits a detailed, careful read through.
Even if you are coming to the opinion that an article has serious flaws, make sure you read the whole paper. This is very important because you may find some really positive aspects that can be communicated to the author. This could help them with future submissions.
A full read-through will also make sure that any initial concerns are indeed correct and fair. After all, you need the context of the whole paper before deciding to reject. If you still intend to recommend rejection, see the section "When recommending rejection."
Once the paper has passed your first read and you've decided the article is publishable in principle, one purpose of the second, detailed read-through is to help prepare the manuscript for publication. You may still decide to recommend rejection following a second reading.
" Offer clear suggestions for how the authors can address the concerns raised. In other words, if you're going to raise a problem, provide a solution ." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Preparation
To save time and simplify the review:
- Don't rely solely upon inserting comments on the manuscript document - make separate notes
- Try to group similar concerns or praise together
- If using a review program to note directly onto the manuscript, still try grouping the concerns and praise in separate notes - it helps later
- Note line numbers of text upon which your notes are based - this helps you find items again and also aids those reading your review
Now that you have completed your preparations, you're ready to spend an hour or so reading carefully through the manuscript.
As you're reading through the manuscript for a second time, you'll need to keep in mind the argument's construction, the clarity of the language and content.
With regard to the argument’s construction, you should identify:
- Any places where the meaning is unclear or ambiguous
- Any factual errors
- Any invalid arguments
You may also wish to consider:
- Does the title properly reflect the subject of the paper?
- Does the abstract provide an accessible summary of the paper?
- Do the keywords accurately reflect the content?
- Is the paper an appropriate length?
- Are the key messages short, accurate and clear?
Not every submission is well written. Part of your role is to make sure that the text’s meaning is clear.
Editors say, " If a manuscript has many English language and editing issues, please do not try and fix it. If it is too bad, note that in your review and it should be up to the authors to have the manuscript edited ."
If the article is difficult to understand, you should have rejected it already. However, if the language is poor but you understand the core message, see if you can suggest improvements to fix the problem:
- Are there certain aspects that could be communicated better, such as parts of the discussion?
- Should the authors consider resubmitting to the same journal after language improvements?
- Would you consider looking at the paper again once these issues are dealt with?
On Grammar and Punctuation
Your primary role is judging the research content. Don't spend time polishing grammar or spelling. Editors will make sure that the text is at a high standard before publication. However, if you spot grammatical errors that affect clarity of meaning, then it's important to highlight these. Expect to suggest such amendments - it's rare for a manuscript to pass review with no corrections.
A 2010 study of nursing journals found that 79% of recommendations by reviewers were influenced by grammar and writing style (Shattel, et al., 2010).
1. The Introduction
A well-written introduction:
- Sets out the argument
- Summarizes recent research related to the topic
- Highlights gaps in current understanding or conflicts in current knowledge
- Establishes the originality of the research aims by demonstrating the need for investigations in the topic area
- Gives a clear idea of the target readership, why the research was carried out and the novelty and topicality of the manuscript
Originality and Topicality
Originality and topicality can only be established in the light of recent authoritative research. For example, it's impossible to argue that there is a conflict in current understanding by referencing articles that are 10 years old.
Authors may make the case that a topic hasn't been investigated in several years and that new research is required. This point is only valid if researchers can point to recent developments in data gathering techniques or to research in indirectly related fields that suggest the topic needs revisiting. Clearly, authors can only do this by referencing recent literature. Obviously, where older research is seminal or where aspects of the methodology rely upon it, then it is perfectly appropriate for authors to cite some older papers.
Editors say, "Is the report providing new information; is it novel or just confirmatory of well-known outcomes ?"
It's common for the introduction to end by stating the research aims. By this point you should already have a good impression of them - if the explicit aims come as a surprise, then the introduction needs improvement.
2. Materials and Methods
Academic research should be replicable, repeatable and robust - and follow best practice.
Replicable Research
This makes sufficient use of:
- Control experiments
- Repeated analyses
- Repeated experiments
These are used to make sure observed trends are not due to chance and that the same experiment could be repeated by other researchers - and result in the same outcome. Statistical analyses will not be sound if methods are not replicable. Where research is not replicable, the paper should be recommended for rejection.
Repeatable Methods
These give enough detail so that other researchers are able to carry out the same research. For example, equipment used or sampling methods should all be described in detail so that others could follow the same steps. Where methods are not detailed enough, it's usual to ask for the methods section to be revised.
Robust Research
This has enough data points to make sure the data are reliable. If there are insufficient data, it might be appropriate to recommend revision. You should also consider whether there is any in-built bias not nullified by the control experiments.
Best Practice
During these checks you should keep in mind best practice:
- Standard guidelines were followed (e.g. the CONSORT Statement for reporting randomized trials)
- The health and safety of all participants in the study was not compromised
- Ethical standards were maintained
If the research fails to reach relevant best practice standards, it's usual to recommend rejection. What's more, you don't then need to read any further.
3. Results and Discussion
This section should tell a coherent story - What happened? What was discovered or confirmed?
Certain patterns of good reporting need to be followed by the author:
- They should start by describing in simple terms what the data show
- They should make reference to statistical analyses, such as significance or goodness of fit
- Once described, they should evaluate the trends observed and explain the significance of the results to wider understanding. This can only be done by referencing published research
- The outcome should be a critical analysis of the data collected
Discussion should always, at some point, gather all the information together into a single whole. Authors should describe and discuss the overall story formed. If there are gaps or inconsistencies in the story, they should address these and suggest ways future research might confirm the findings or take the research forward.
4. Conclusions
This section is usually no more than a few paragraphs and may be presented as part of the results and discussion, or in a separate section. The conclusions should reflect upon the aims - whether they were achieved or not - and, just like the aims, should not be surprising. If the conclusions are not evidence-based, it's appropriate to ask for them to be re-written.
5. Information Gathered: Images, Graphs and Data Tables
If you find yourself looking at a piece of information from which you cannot discern a story, then you should ask for improvements in presentation. This could be an issue with titles, labels, statistical notation or image quality.
Where information is clear, you should check that:
- The results seem plausible, in case there is an error in data gathering
- The trends you can see support the paper's discussion and conclusions
- There are sufficient data. For example, in studies carried out over time are there sufficient data points to support the trends described by the author?
You should also check whether images have been edited or manipulated to emphasize the story they tell. This may be appropriate but only if authors report on how the image has been edited (e.g. by highlighting certain parts of an image). Where you feel that an image has been edited or manipulated without explanation, you should highlight this in a confidential comment to the editor in your report.
6. List of References
You will need to check referencing for accuracy, adequacy and balance.
Where a cited article is central to the author's argument, you should check the accuracy and format of the reference - and bear in mind different subject areas may use citations differently. Otherwise, it's the editor’s role to exhaustively check the reference section for accuracy and format.
You should consider if the referencing is adequate:
- Are important parts of the argument poorly supported?
- Are there published studies that show similar or dissimilar trends that should be discussed?
- If a manuscript only uses half the citations typical in its field, this may be an indicator that referencing should be improved - but don't be guided solely by quantity
- References should be relevant, recent and readily retrievable
Check for a well-balanced list of references that is:
- Helpful to the reader
- Fair to competing authors
- Not over-reliant on self-citation
- Gives due recognition to the initial discoveries and related work that led to the work under assessment
You should be able to evaluate whether the article meets the criteria for balanced referencing without looking up every reference.
7. Plagiarism
By now you will have a deep understanding of the paper's content - and you may have some concerns about plagiarism.
Identified Concern
If you find - or already knew of - a very similar paper, this may be because the author overlooked it in their own literature search. Or it may be because it is very recent or published in a journal slightly outside their usual field.
You may feel you can advise the author how to emphasize the novel aspects of their own study, so as to better differentiate it from similar research. If so, you may ask the author to discuss their aims and results, or modify their conclusions, in light of the similar article. Of course, the research similarities may be so great that they render the work unoriginal and you have no choice but to recommend rejection.
"It's very helpful when a reviewer can point out recent similar publications on the same topic by other groups, or that the authors have already published some data elsewhere ." (Editor feedback)
Suspected Concern
If you suspect plagiarism, including self-plagiarism, but cannot recall or locate exactly what is being plagiarized, notify the editor of your suspicion and ask for guidance.
Most editors have access to software that can check for plagiarism.
Editors are not out to police every paper, but when plagiarism is discovered during peer review it can be properly addressed ahead of publication. If plagiarism is discovered only after publication, the consequences are worse for both authors and readers, because a retraction may be necessary.
For detailed guidelines see COPE's Ethical guidelines for reviewers and Wiley's Best Practice Guidelines on Publishing Ethics .
8. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
After the detailed read-through, you will be in a position to advise whether the title, abstract and key words are optimized for search purposes. In order to be effective, good SEO terms will reflect the aims of the research.
A clear title and abstract will improve the paper's search engine rankings and will influence whether the user finds and then decides to navigate to the main article. The title should contain the relevant SEO terms early on. This has a major effect on the impact of a paper, since it helps it appear in search results. A poor abstract can then lose the reader's interest and undo the benefit of an effective title - whilst the paper's abstract may appear in search results, the potential reader may go no further.
So ask yourself, while the abstract may have seemed adequate during earlier checks, does it:
- Do justice to the manuscript in this context?
- Highlight important findings sufficiently?
- Present the most interesting data?
Editors say, " Does the Abstract highlight the important findings of the study ?"
If there is a formal report format, remember to follow it. This will often comprise a range of questions followed by comment sections. Try to answer all the questions. They are there because the editor felt that they are important. If you're following an informal report format you could structure your report in three sections: summary, major issues, minor issues.
- Give positive feedback first. Authors are more likely to read your review if you do so. But don't overdo it if you will be recommending rejection
- Briefly summarize what the paper is about and what the findings are
- Try to put the findings of the paper into the context of the existing literature and current knowledge
- Indicate the significance of the work and if it is novel or mainly confirmatory
- Indicate the work's strengths, its quality and completeness
- State any major flaws or weaknesses and note any special considerations. For example, if previously held theories are being overlooked
Major Issues
- Are there any major flaws? State what they are and what the severity of their impact is on the paper
- Has similar work already been published without the authors acknowledging this?
- Are the authors presenting findings that challenge current thinking? Is the evidence they present strong enough to prove their case? Have they cited all the relevant work that would contradict their thinking and addressed it appropriately?
- If major revisions are required, try to indicate clearly what they are
- Are there any major presentational problems? Are figures & tables, language and manuscript structure all clear enough for you to accurately assess the work?
- Are there any ethical issues? If you are unsure it may be better to disclose these in the confidential comments section
Minor Issues
- Are there places where meaning is ambiguous? How can this be corrected?
- Are the correct references cited? If not, which should be cited instead/also? Are citations excessive, limited, or biased?
- Are there any factual, numerical or unit errors? If so, what are they?
- Are all tables and figures appropriate, sufficient, and correctly labelled? If not, say which are not
Your review should ultimately help the author improve their article. So be polite, honest and clear. You should also try to be objective and constructive, not subjective and destructive.
You should also:
- Write clearly and so you can be understood by people whose first language is not English
- Avoid complex or unusual words, especially ones that would even confuse native speakers
- Number your points and refer to page and line numbers in the manuscript when making specific comments
- If you have been asked to only comment on specific parts or aspects of the manuscript, you should indicate clearly which these are
- Treat the author's work the way you would like your own to be treated
Most journals give reviewers the option to provide some confidential comments to editors. Often this is where editors will want reviewers to state their recommendation - see the next section - but otherwise this area is best reserved for communicating malpractice such as suspected plagiarism, fraud, unattributed work, unethical procedures, duplicate publication, bias or other conflicts of interest.
However, this doesn't give reviewers permission to 'backstab' the author. Authors can't see this feedback and are unable to give their side of the story unless the editor asks them to. So in the spirit of fairness, write comments to editors as though authors might read them too.
Reviewers should check the preferences of individual journals as to where they want review decisions to be stated. In particular, bear in mind that some journals will not want the recommendation included in any comments to authors, as this can cause editors difficulty later - see Section 11 for more advice about working with editors.
You will normally be asked to indicate your recommendation (e.g. accept, reject, revise and resubmit, etc.) from a fixed-choice list and then to enter your comments into a separate text box.
Recommending Acceptance
If you're recommending acceptance, give details outlining why, and if there are any areas that could be improved. Don't just give a short, cursory remark such as 'great, accept'. See Improving the Manuscript
Recommending Revision
Where improvements are needed, a recommendation for major or minor revision is typical. You may also choose to state whether you opt in or out of the post-revision review too. If recommending revision, state specific changes you feel need to be made. The author can then reply to each point in turn.
Some journals offer the option to recommend rejection with the possibility of resubmission – this is most relevant where substantial, major revision is necessary.
What can reviewers do to help? " Be clear in their comments to the author (or editor) which points are absolutely critical if the paper is given an opportunity for revisio n." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Recommending Rejection
If recommending rejection or major revision, state this clearly in your review (and see the next section, 'When recommending rejection').
Where manuscripts have serious flaws you should not spend any time polishing the review you've drafted or give detailed advice on presentation.
Editors say, " If a reviewer suggests a rejection, but her/his comments are not detailed or helpful, it does not help the editor in making a decision ."
In your recommendations for the author, you should:
- Give constructive feedback describing ways that they could improve the research
- Keep the focus on the research and not the author. This is an extremely important part of your job as a reviewer
- Avoid making critical confidential comments to the editor while being polite and encouraging to the author - the latter may not understand why their manuscript has been rejected. Also, they won't get feedback on how to improve their research and it could trigger an appeal
Remember to give constructive criticism even if recommending rejection. This helps developing researchers improve their work and explains to the editor why you felt the manuscript should not be published.
" When the comments seem really positive, but the recommendation is rejection…it puts the editor in a tough position of having to reject a paper when the comments make it sound like a great paper ." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Visit our Wiley Author Learning and Training Channel for expert advice on peer review.
Watch the video, Ethical considerations of Peer Review
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Tele-medicine controlled hospital at home is associated with better outcomes than hospital stay
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Faculty of Data and Decision Sciences, Technion–Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Biostatistics and Biomathematics Unit, Gertner Institute of Epidemiology and Health Policy Research, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Roles Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft
Affiliation Sheba Beyond Virtual Hospital, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Roles Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Management Wing, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Sheba Beyond Virtual Hospital, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, Education Authority, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, Faculty of Healthcare and Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel
- Noa Zychlinski,
- Ronen Fluss,
- Yair Goldberg,
- Daniel Zubli,
- Galia Barkai,
- Eyal Zimlichman,

- Published: August 19, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0309077
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
Hospital-at-home (HAH) is increasingly becoming an alternative for in-hospital stay in selected clinical scenarios. Nevertheless, there is still a question whether HAH could be a viable option for acutely ill patients, otherwise hospitalized in departments of general-internal medicine.
This was a retrospective matched study, conducted at a telemedicine controlled HAH department, being part of a tertiary medical center. The objective was to compare clinical outcomes of acutely ill patients (both COVID-19 and non-COVID) admitted to either in-hospital or HAH. Non-COVID patients had one of three acute infectious diseases: urinary tract infections (UTI, either lower or upper), pneumonia, or cellulitis.
The analysis involved 159 HAH patients (64 COVID-19 and 95 non-COVID) who were compared to a matched sample of in-hospital patients (192 COVID-19 and 285 non-COVID). The median length-of-hospital stay (LOS) was 2 days shorter in the HAH for both COVID-19 patients (95% CI: 1–3; p = 0.008) and non-COVID patients (95% CI; 1–3; p < 0.001). The readmission rates within 30 days were not significantly different for both COVID-19 patients (Odds Ratio (OR) = 1; 95% CI: 0.49–2.04; p = 1) and non-COVID patients (OR = 0.7; 95% CI; 0.39–1.28; p = 0.25). The differences remained insignificant within one year. The risk of death within 30 days was significantly lower in the HAH group for COVID-19 patients (OR = 0.34; 95% CI: 0.11–0.86; p = 0.018) and non-COVID patients (OR = 0.38; 95% CI: 0.14–0.9; p = 0.019). For one year survival period, the differences were significant for COVID-19 patients (OR = 0.5; 95% CI: 0.31–0.9; p = 0.044) and insignificant for non-COVID patients (OR = 0.63; 95% CI: 0.4–1; p = 0.052).
Conclusions
Care for acutely ill patients in the setting of telemedicine-based hospital at home has the potential to reduce hospitalization length without increasing readmission risk and to reduce both 30 days and one-year mortality rates.
Citation: Zychlinski N, Fluss R, Goldberg Y, Zubli D, Barkai G, Zimlichman E, et al. (2024) Tele-medicine controlled hospital at home is associated with better outcomes than hospital stay. PLoS ONE 19(8): e0309077. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0309077
Editor: Filomena Pietrantonio, San Giuseppe Hospital, ITALY
Received: April 18, 2024; Accepted: August 5, 2024; Published: August 19, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Zychlinski et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All de-identified data will become available upon request from the Principal Investigator (Prof. Gad Segal, MD). This is a mandatory, legal term on behalf of our institutional ethics committee. Upon request, data will go through a double check of anonymization and then sent direct to whoever requested the data. Aside from the Principal Investigator, a non-author contact that can be addressed is our local IRB at the following email address: [email protected] . The aforementioned restrictions are warranted since the patients’ data could potentially include sensitive patients’ information.
Funding: The Research was supported in part by an Israel Science Foundation [Grant 277/21] and the Israel National Institute for Health Policy Research [Grant 2021/160/R]. Guarantor: No guarantees were given regarding this study.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
Hospital-at-home (hah) services worldwide.
Globally, healthcare systems in general and their hospitalization arms in particular, are experiencing hardships in terms of infrastructure, resources, and lower availability of skilled healthcare professionals. These hardships were worsened, as stated by the World Economic Forum, by the unprecedented disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic [ 1 ]. As a result, it was recently published, in a 2023 survey, that 46% of adults worldwide encounter limited access to treatment and prolonged waiting times to reach affordable health resources with lack of staff being the biggest challenge [ 2 ]. These challenges are being answered by social, financial, and healthcare organizations, with innovative approaches and solutions being advocated. One such approach was recently introduced by a global consulting firm, presenting the concept of hospitals without walls [ 3 ]. This wide-span concept of health without boundaries, includes the adoption of advanced high-technology in the service of telemedicine, serving as an enabler for making the HAH services the safest and most effective as can be attained. Recent years brought success in this realm, mainly with regard to COVID-19 patients [ 4 – 6 ].
Telemedicine-controlled hospital-at-home services
A predominantly important factor contributing to the prognosis of patients during hospitalization in an internal medicine department, is the experience of their attending, senior physicians. These practitioners are becoming less available and practically inexistent in some peripheral areas. One way of coping with this problem would depend on the ability of experienced, senior internal-medicine specialists to diagnose and treat their patients from a distance, upscaling their influence on population health. Recent advancements in telemedicine, another consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, have paved the way for sophisticated remote medical services, introducing home hospitalization as a viable alternative to traditional on-site care. Recently published studies’ results, relating to the advantages of tele-monitoring and miniaturized technologies, either in the HAH settings or post-hospital-discharges plans, enhance our ability of rely on tele-medicine services in terms of patients’ safety, risks of re-admission and other, in-hospital related side events [ 7 – 9 ].
During the year 2020, Sheba Beyond was established as an integral part of the Sheba Medical Center, encompassing all tele-health services in this tertiary hospital. By enabling remote physical examinations, monitoring, and online rehabilitation programs, Sheba Beyond aims to make high-quality medical expertise accessible to broader audiences. This aligns with the growing expectation that remote hospitalization will become a widely available service among major hospital networks, across many specialties. During the past several years, the unique HAH service at Sheba Beyond served not only as a clinical service but also as a validation laboratory for essential, telemedicine technologies and methodologies: TytoCare © technology, serving as a remote, digital stethoscope, was clinically investigated, with measurements of physicians’ compliance [ 10 ], validity and inter-observers’ consensus of clinical interpretations [ 11 ]. Biobeat © technology for wireless, remote monitoring of several physiologic vital signs and parameters was validated for its reliability of telemetric transmission and comparison to overhead monitors, and potential to accumulate patients’ data that could foresee future patients’ deterioration [ 12 ]. A six-lead, self-handled electrocardiography (ECG) device transmitting heart rhythm description and analysis was also validated and the level of consensus of agreement was tested versus a gold-standard, legacy 12-lead ECG machine [ 13 ]. Alongside these technologies, methodologies of telemedicine based HAH were also investigated, such as a clinical pivotal trial done with a specialist in internal medicine, based within an in-hospital, internal medicine department, managed patients that stayed in their elderly home [ 14 ]. The ability of safeguarding acutely ill patients in the HAH setting was also shown to be feasible in a significant portion of patients, diagnosed as suffering from an acute, infectious disease, who demonstrate laboratory evidence of myocardial damage and still, are enjoying the efficacy and safety of the HAH service [ 15 ]. The concept of assimilating a virtual medicine-based department into the structure of a conventional medical center was also recently described [ 16 ].
Aim of the current study
Prior research has focused on the efficacy of telemedicine-based medical services to various patients’ populations including remote rehabilitation across various indications including deterioration of patients suffering from chronic congestive heart failure [ 17 ], sarcopenia [ 18 ], post-stroke recovery [ 19 ], exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [ 20 ], and post-acute therapy [ 21 ]. However, limited attention has been directed towards investigating remote hospitalization of patients in the setting of acute illness, regularly directed to in-hospital stay in internal medicine wards. Some of the studies who addressed acute illness HAH services, included telemedicine visits in various proportions, however none of the programs were based on physician telemedicine visits [ 22 – 24 ].
This study focused on the distinctive remote telemedicine-based internal medicine model. Unlike traditional on-site admissions, patients underwent admission by a remote physician, receiving a personalized treatment plan that integrates home visits and adequate medical monitoring utilizing cutting-edge technologies. The full spectrum of nursing services was performed at patients’ homes, along with laboratory testing and chest x-rays as indicated by the attending physicians who delivered service via remote, telemedicine platforms. The present study investigated the efficacy and safety of this service in a retrospective comparison and analysis of both COVID-19 and non-COVID matched patient populations.
Study design and patients’ care
This study was performed by the Sheba Medical Center, 1,900 beds, tertiary hospital, largest of its kind in Israel. This was a retrospective matched study with 159 Sheba-Beyond hospitalizations (64 for COVID-19 and 95 for non-COVID) categorized as Group HAH. They were compared to a matched sample of controls, denoted as Group C, out of 6,817 patients who were hospitalized in the internal-medicine departments of Sheba Medical Center (2,242 for COVID-19 and 4,924 for one of three acute, infectious diseases: urinary tract infections (UTI, either lower or upper), pneumonia, or cellulitis) over the years 2021–2023 inclusive. The study included patients aged 18 and older. Respiratory and hemodynamically unstable patients as well as mild COVID-19 patients were excluded from the study. All patients’ data were extracted from their electronic medical records (EMR) which serve for clinical purposes. Fig 1 details the above patient consort flow and exclusion diagram.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0309077.g001
Ethic statement: Data was mined after approval by a local, institutional review board (approval # SMC-21-8828) and after patients’ written consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study. Clinical data was approached during the months between August 2023 and February 2024.
Eligible patients for home hospitalization were transitioned to receive care in the comfort of their homes. The HAH team attending these patients consists of internal medicine specialists, licensed case management nurses, home visiting nurses, X-ray technicians and call center nurses. The patient receives daily a minimum of one remote physician visit, 2 nurses visit (1 at home) and an individualized treatment plan that may include imaging, blood testing and IV, and oral treatment. Medical directives, encompassing vital signs monitoring regimen and treatments, are either carried out by the patients themselves or administered by the nursing staff during scheduled home visits. A video conversation with the attending physician was conducted at least once daily, typically in the morning, with the visiting nurse present at the patient’s home. Video calls were done using a designated platform for telemedicine purposes (DATOS). During these sessions, a remote physical examination was facilitated using the TytoCare ® system. This digital platform incorporates a digital stethoscope enabling heart, lung and abdominal (peristalsis) auscultation, a digital otoscope for visualizing the tympanic membrane, a digital thermometer, and a tongue depressor for visual examination of the pharynx. The device guides patients (or their assistants) through the examination process and records data and visuals, which are then transmitted through the internet for review by the physician. Video conferences were conducted whenever a specialist consultation was deemed necessary, with one of Sheba’s specialists, as regularly done in the in-hospital settings. Each daily visit was documented in the patient’s electronic medical record, including orders for blood tests, oxygen enrichment, prescribed medications, and recommendations for either hospital readmission in case of deterioration or discharge in case of improvement.
In the event of patient deterioration during home hospitalization, immediate coordination with the physician would facilitate the patient’s return to the hospital’s emergency department. Conversely, when the patient was ready for discharge, a discharge letter was sent, and the ongoing treatment plan was communicated to the staff via phone to ensure optimal continuity of care. The attending physician remained available for further consultation regarding the patient’s care for an additional week after discharge.
Data mining and analysis
All relevant patients’ characteristics were extracted from their EMR: age, severity of disease as categorized by clinicians for COVID-19 patients, gender; chronic / background diagnoses and chronic medications. We gathered individual diagnoses to the following silos: active malignancy, past malignancy, hematologic diseases, neurologic, metabolic, cardiovascular, respiratory, autoimmune, and gastrointestinal diseases. Similarly, chronic medications were also listed and grouped, as relating to either malignant, neurologic, metabolic, cardiovascular, respiratory, autoimmune, or gastrointestinal, as well as chronic medication for ophthalmic use.
The analysis compared outcomes of COVID-19 and non-COVID patients in groups HAH and C. Clinical outcome measures included mean length of stay (LOS) in days, readmission rates within 30 days or one year from discharge and mortality rates from admission within the same time frames. In the readmission analyses, patients who died before discharge were excluded and patients who died within the follow-up period were regarded as readmissions.
We used propensity scores (PSs) to match patients from the HAH with those from C group. Four risk factors (RF) deemed relevant, up front to the study outcomes, and were therefore included in the PS for patients’ matching: age, presence of active malignancy, dementia, and chronic kidney disease (CKD). For COVID-19 patients, grade of disease severity (as indicated during the period of hospitalization) was also incorporated. Additional risk factors were scrutinized individually in separate univariate logistic regressions for each one of the clinical outcomes serving as the dependent variable, while controlling for the four risk factors mentioned above. We retained those risk factors which had a p value less than 0.05 in at least one outcome. PSs were obtained, representing the estimated probability of being in the HAH group, using a logistic regression that included the RFs selected in the previous stage as predictors. Controls were matched to patients in the HAH group using the PS with a ratio of 1:3. In case of COVID-19 hospitalizations, we enforced exact matching of severity. We assessed the similarity of the resulting matched groups both graphically and by the calculating the standardized mean differences (SMD) of the RFs and PS. An absolute SMD less than 0.25 is usually regarded as a good balance [ 25 ].
A univariate analysis was used to compare the matched groups. The LOS was tested using the Wilcoxon test and the 95% CI was obtained by bootstrap resampling. The mortality rates were compared using the Fisher exact test. The readmission rates were compared using a weighted logistic regression. The weights were used to keep the balance of the matched samples after we excluded those who died before discharge. We also used Cox regression to compare time to death or readmission within one year.
Table 1 includes demographic and clinical features of all patients included in the two HAH groups and the two control groups. All the reported ratios compared the HAH group to the C group.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0309077.t001
Length of Stay (LOS)
The median LOS among COVID-19 patients was 5 and 7 in patients’ groups HAH and C, respectively, with a statistically significant 2-day difference, and the 95% CI was 1–3 (p value = 0.008). Among non-COVID patients, the median LOS was 2 and 4 days, in groups HAH and C, respectively, with a statistically significant 2-day difference, and the 95% CI was 1–3 (p value < 0.001).
Readmission within 30 days and one year duration
The Odds Ratio (OR) for readmission within 30 days among COVID-19 patients was 1, and the 95% CI was 0.49–2.04 (p value = 1). For non-COVID patients, the OR was 0.7 and the 95% CI was 0.39–1.28 (p value = 0.25). The OR for readmission within one year among COVID-19 patients was 1.05 and the 95% CI was 0.57–1.93 (p value = 0.8). For non-COVID patients, the OR was 0.67 and the 95% CI was 0.41–1.09 (p value = 0.11).
The Hazard Ratio (HR) for the time to readmission within one-year from discharge for COVID-19 patients was 1.06 and the 95% CI was 0.67–1.96 (p value = 0.8). For non-COVID patients, the HR was 0.81 and the 95% CI was 0.59–1.13 (p value = 0.21). Fig 2 shows the one-year Kaplan–Meier estimated survival curves for re-readmission among the COVID-19 and non-COVID patients: HAH versus their controls. For COVID-19 patients, the control and HAH groups are very close with no significant difference. For non-COVID, the probability of no readmission was lower, though not significantly, in the HAH group.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0309077.g002
Mortality within 30 days and one year duration
The OR for mortality within 30 days among COVID-19 patients was 0.34 and the 95% CI was 0.11–0.86 (p value = 0.018). Among non-COVID patients, the OR was 0.38 and the 95% CI was 0.14–0.90 (p value = 0.019). The OR for mortality within one year among COVID-19 patients was 0.51 and the 95% CI was 0.24–1.02 (p value = 0.046 using Fisher exact test). Among non-COVID patients, the OR was 0.64 and the exact 95% CI was 0.37–1.10 (p value = 0.103 using Fisher exact test).
The HR for COVID-19 patients was 0.55, the 95% CI was 0.31–0.98 (p value = 0.044). For non-COVID patients, the HR was 0.63 and the 95% CI was 0.40–1.00 (p value = 0.052). Fig 3 shows the one-year Kaplan–Meier estimated survival curves for COVID-19 and non-COVID patients: HAH versus their controls.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0309077.g003
Hospital-at-home as an alternative to in-hospital stay
The results of this study were reached after strict matching of the compared patients’ groups. The scrutinizing match process has significantly diminished our study population reaching the final analysis and still, statistically significant results were reached, enabling further conclusions to be drawn relating to the study clinical outcomes. In face of our results, the initial motivation to show that HAH would be non-inferior to in-hospital stay, should be substituted with the notion that HAH, when delivered in the above-described meticulous methodology and appropriate technologies, could be superior to in-hospital stay in terms of less readmissions and longer patients’ survival. It should be stated that during this study, we used technologies and staff that are being used in the routine HAH service in our medical center. All study results and the derived insights should be counted regarding the above. We foresee even better possible achievements as technology will continue to evolve and designated healthcare professionals gain even more experience in the realm of HAH.
The novelty of the described HAH setting
The main novelty in the above results is the fact that the HAH arm was based on telemedicine performed by the attending physician. Reliance on remote care technology enabled us to employ an experienced specialist in internal medicine, otherwise unavailable in case there was a need for large-scale home visits. We believe that the experience of the attending physicians was key to achieving superior clinical outcomes in the HAH arm over the C arm of this study. Also, the technologies employed were already used for several years (e.g. DATOS, a designated telemedicine-based platform) and already validated in clinical use cases. These technologies enable bridging the geographical gap between the physician and the patient. Moreover, the nursing staff, delivering both diagnostic and therapeutic measures to our patients is based on experienced nurses, almost all with several years of experience, holding advanced nursing degrees and qualifications.
Clinical outcomes
Relating to the shortened length of stay in the HAH group: this could potentially help HAH organizations in their struggle to prove affordability. Nevertheless, we do not see the shorter LOS as a predominant achievement in the HAH bundle. As in-hospital departments become more crowded, length of in-hospital stay will inevitably become shorter–not due to better treatment but due to earlier, at times, too early patients’ discharge. Therefore, we anticipate that HAH will prove to be as long as in-hospital stays and even longer. At home, the patients are not expected to make place to the next admissions and the length of hospitalization can and should stem only from the measures of good clinical practice.
Relating to the lower rates of re-admissions. These would have been easier to explain if indeed the HAH LOS were longer, providing the optimal treatment length needed. Since this was not the case, we assume that indeed, the experience of the attending physicians made the HAH hospitalizations more effective, putting the patients “on track” to better health, avoiding a larger number of re-admissions. It should be stated however that the retrospective nature of this study could be associated with a bias: it is possible that those patients that were suited to HAH continued to prefer their home environment and succeeded in maintaining themselves in the community while those who stayed in-hospital were more easily re-admitted. The fact that amongst COVID-19 patients there was no difference in readmissions could be related to the fact that for many patients, in-hospital stay due to COVID-19 was compulsory by healthcare regulations and the same for re-admission. Therefore, the motivation of patients contributed less to this end point. This study was not designed to assess financial endpoints, typically affected by re-admissions. Such analyses should be sought in future, prospective studies.
Regarding the end point of survival at 30 days, HAH was associated with less mortality, in a statistically significant manner, for both COVID-19 and non-COVID patients. We assume that this difference stem from the higher chances of in-hospital acquisition of secondary infections, practically nonexistent in the HAH setting. However, it should be stated that hospital-aquiered infections and other, hospital–acquired complications were not monitored in this study nor we recorded the causes of death. Relating to the one-year survival rates: these continued to be significantly higher for HAH patients in the COVID-19 patients’ group while losing statistical significance in the non-COVID-19 patients. This could be explained by the significant frailty characteristics of post-COVID-19 patients and the fact that on the one-year scale, in-hospital complications became less relevant for the non-COVID patients.
The place of our results in perspective of current literature
Freund et al. (2023) compared early discharge of COVID-19 patients with controls and found out that a transference of such patients to their homes with continuing oxygen support was associated with shortened in-hospital stay but also with increased rate of readmissions and no benefits relating to long-term outcomes [ 26 ]. Their findings emphasize the difference between continuing medical attention and support in the community and the full bundle of services in the form of HAH. In their comprehensive meta-analysis, Chauhan, and McAlister (2022) reviewed 24 randomized clinical trials, including 10,876 patients, comparing post-discharge transference of patients to continuing attendance of virtual wards (VW) versus usual post discharge community care [ 27 ]. Although these were heterogenous services, none at the full scale HAH service, they found out that VW were associated with reduction in readmissions and lower healthcare costs. Nevertheless, favorable survival was shown only for patients suffering from congestive heart failure. Tierney et al. (2021) compared an acute care, home service for elderlies with continuing care within an elderly hospitalization unit [ 28 ]. In their 1-year analysis of 505 patients, they found out that the home care was associated with higher readmission rates and higher mortality at 30 days, 3- and 6-months duration. They concluded that their results stemmed from the fact that their home-care patients’ population had a higher proportion of dependent, frail older patients. Their findings emphasize the need for thorough populations’ matching as done in our study. Leong et al. (2021) identified ten systematic reviews comparing conventional hospitalization with two models of HAH: early support discharge (ESD) and admission avoidance (AA) [ 29 ]. ESD services were found to have comparable mortality and readmissions’ rates as in-hospital stay but were associated with shorter hospitalizations. AA services showed a trend towards lower mortality, comparable or lower readmission rates. In summary, it can be concluded, from the existing literature, that medical services, at patients’ homes, are heterogenous and as they become more similar to the HAH service, they are anticipated to provide better clinical outcomes.
Sensitivity and generalizability of results
The results of our study provide promising evidence for the efficacy of tele-medicine controlled HAH care for acutely ill patients. The generalizability of these findings to other jurisdictions must account for several factors.
The first factor concerns healthcare infrastructure and technology. Regions or hospitals with well-developed telecommunication networks, electronic health record systems, and advanced remote monitoring technologies are more likely to achieve positive outcomes. Furthermore, effective tele-medicine implementation requires skilled healthcare professionals who are proficient in using digital tools and remote monitoring technologies. Variations in training, availability of skilled personnel, and access to advanced technology across different regions could impact the consistency and effectiveness of HAH programs.
The second factor is cultural and socioeconomic considerations. Patient demographics, cultural attitudes towards tele-medicine, and socioeconomic status influence the acceptance and effectiveness of HAH programs. In the current study, that was a single-center study, patients in both groups came from the same area, the Dan district in central Israel. Therefore, both groups were similar in their demographics, including financial capabilities and social status.
The third factor includes the hospital location, which can affect the feasibility and efficiency of HAH care. In regions where patients are located far from healthcare facilities, providing timely tele-medicine services may be challenging, especially if patients deteriorate and need urgent immediate care. Areas with a higher density of healthcare resources, however, may see better integration and outcomes.
Costs and resources analysis
As a retrospective analysis this study was not powered to produce a thorough cost analysis. Nevertheless, since all patients were treated by the same medical center, either in-hospital or by the HAH service, we can compare the resources needed for both treatment arms. While the net cost of one hospitalization day in-hospital is estimated at 2,830 NIS (~760 USD), the net cost of an HAH hospitalization day is only 1,660 NIS (~ 445USD) reflecting a 41.5% lowering of costs when moving from in-hospital to the HAH settings. Moreover, the HAH service personnel are engaged in other in-hospital activities and provide telemedicine services aside from the HAH service.
Future prospects of advanced technologies and artificial intelligence in the tele-health sector
The telemedicine controlled HAH service described in this manuscript included application of several advanced, designated tele-health technologies: we used a tele-health dedicated platform for monitoring and documentation of vital signs and for video calls with our patients (DATOS). We also used TytoCare system as a digital recording stethoscope and a 6-lead electrocardiography machine for patients’ self-usage. All of the above were previously validated by us in the HAH settings [ 10 – 14 ]. We did not use AI-based computing capabilities in this study. Several publications however reviewed the potential of assimilating AI into different telehealth domains: tele-diagnosis, tele-interactions, and tele-monitoring [ 30 , 31 ]. Widely described as the fourth industrial revolution, authors emphasize the potential obstacles facing whoever would assimilate AI into its telehealth services: including conflicts of patients’ privacy, transparency, and safety concerns [ 32 ]. In their recent update on ethics and governance of artificial intelligence for health, the WHO (world health organization) declared that the following principles should guide the use of AI in health: autonomy protection, promotion of human well-being, human safety and the public interest, ensuring transparency, explainability and intelligibility, foster responsibility and accountability, ensuring inclusiveness and equity and promoting AI that is responsive and sustainable [ 33 ].
This study offers compelling evidence supporting the effectiveness of home telemedicine-based hospitalization as a viable alternative to in-hospital internal medicine hospitalization. The results indicate a significantly shorter LOS without significant difference in readmission rates for both COVID-19 and non-COVID patients in home-hospitalization. Both COVID-19 and non-COVID patients receiving home hospitalization showed a significant reduction in the risk of death. The results of this study support further research in the field, preferably in the setting of prospective, controlled randomized studies.
Limitations
This study was conducted as a retrospective study at a single center. Consequently, even though we employed a thorough matching of patients’ groups, it is imperative that our results and conclusions undergo further investigation due to probable bias of patient selection. The necessity for future prospective, randomized controlled trials, where patients are randomly assigned to either home or in-hospital hospitalization, is underscored to provide more robust evidence. Several limitations were also described earlier in the “ sensitivity and generalizability of results” paragraph of the discussion.
- 1. Global Health and Healthcare Strategic Outlook: Shaping the Future of Health and Healthcare | World Economic Forum [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 12]. Available from: https://www.weforum.org/publications/global-health-and-healthcare-strategic-outlook-shaping-the-future-of-health-and-healthcare/
- 2. Leading problems in healthcare systems worldwide 2023 | Statista [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 12]. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/917153/leading-problems-healthcare-systems-worldwide/
- 3. Care delivered in hospitals today will be delivered in the community and at home tomorrow | Deloitte Global [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 12]. Available from: https://www.deloitte.com/global/en/Industries/life-sciences-health-care/perspectives/hospital-future-without-walls.html
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
- 6. Bokolo Anthony Jnr. Use of Telemedicine and Virtual Care for Remote Treatment in Response to COVID-19 Pandemic. J Med Syst. 2020 Jul 1;44(7).
- 33. Health Organization W. Ethics and governance of artificial intelligence for health Guidance on large multi-modal models. 2024 [cited 2024 Jun 8]; Available from: http://apps.who.int/bookorders .
Effect of Endurance Exercise on Markers of Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review
- Review Article
- Published: 20 August 2024
Cite this article

- Gregg S. Mallett ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0075-4999 1 &
- Kim McGrath 2
Explore all metrics
The aim of this review was to methodically consider oxidative stress biomarkers in endurance performance events. The health benefits of exercise come at the cost of reactive oxygen species production. Reactive oxygen species and the continued development of oxidative stress may bring about muscular damage and inflammation, ultimately impairing exercise performance.
A search for applicable articles was performed using PubMed/Medline, Scopus, and ScienceDirect with dates of January 1, 2010, to April 30, 2023. Inclusion criteria consisted of (1) original, peer-reviewed studies with human participants; (2) studies written in English; (3) studies available as full free text. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses checklist and flow-chart were followed.
Thirty studies were included in the final review. Four studies collected blood and urine samples, while 26 studies collected blood samples only for assessment. Thirteen studies on ultramarathons, seven on military training and survival, four on Ironman and endurance running, and one on running/cycling and swimming were discovered throughout the course of the research. Well-trained, elite, recreational, amateur, moderately active, ultra-marathon runners, triathletes, cadets/soldiers, physical education students, and untrained individuals comprised the study subjects.
According to the evidence, extended duration events do not always induce supraphysiological oxidative stress and muscle damage which are indicated by the presence of absence of reactive oxygen species and inflammatory biomarkers. Still, more importantly, oxidative damage markers of lipids, proteins, and different enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants develop depending on the individual’s level of training.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others

Redox Homeostasis and Inflammation Responses to Training in Adolescent Athletes: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis

Acute Effects of Training Loads on Muscle Damage Markers and Performance in Semi-elite and Elite Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Alterations in redox homeostasis in the elite endurance athlete, data availability.
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analyzed.
Anderson E, Durstine JL. Physical activity, exercise, and chronic diseases: a brief review. Sports Med Health Sci. 2019;1(1):3–10.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Andrade MS, Ferrer CRL, Vancini RL, Nikolaidis PT, Knechtle B, Rosemann T, Bachi ALL, Seffrin A, de Lira CAB. The effect of muscle strength on Marathon Race-Induced muscle soreness. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(21):11258.
Atakan MM, Li Y, Koşar ŞN, Turnagöl HH, Yan X. Evidence-based effects of high-intensity interval training on exercise capacity and health: a review with historical perspective. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(13):7201.
Baird MF, Graham SM, Baker JS, Bickerstaff GF. Creatine-kinase- and exercise-related muscle damage implications for muscle performance and recovery. J Nutr Metabolism. 2012;2012:960363.
Article Google Scholar
Bartlett JD, Hawley JA, Morton JP. Carbohydrate availability and exercise training adaptation: too much of a good thing? Eur J Sport Sci. 2015;15(1):3–12.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Besson T, Macchi R, Rossi J, Morio CYM, Kunimasa Y, Nicol C, Vercruyssen F, Millet GY. Sex differences in endurance running. Sports Med. 2022;52(6):1235–57.
Google Scholar
Birben E, Sahiner UM, Sackesen C, Erzurum S, Kalayci O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ J. 2012;5(1):9–19.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Bouviere J, Fortunato RS, Dupuy C, Werneck-de-Castro JP, Carvalho DP, Louzada RA. Exercise-stimulated ROS sensitive signaling pathways in skeletal muscle. Antioxid (Basel). 2021;10(4):537.
Brancaccio P, Maffulli N, Limongelli FM. Creatine kinase monitoring in sport medicine. Br Med Bull. 2007;81–82:209–30.
Brawner CA, Churilla JR, Keteyian SJ. Prevalence of physical activity is lower among individuals with chronic disease. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016;48(6):1062–7.
Chalchat E, Charlot K, Garcia-Vicencio S, Hertert P, Baugé S, Bourdon S, Bompard J, Farges C, Martin V, Bourrilhon C, Siracusa J. Circulating microRNAs after a 24-h ultramarathon run in relation to muscle damage markers in elite athletes. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(9):1782–95.
Chevion S, Moran DS, Heled Y, Shani Y, Regev G, Abbou B, Berenshtein E, Stadtman ER, Epstein Y. Plasma antioxidant status and cell injury after severe physical exercise. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(9):5119–23.
Collin F. Chemical basis of reactive oxygen species reactivity and involvement in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2407.
Cooper CE, Vollaard NB, Choueiri T, Wilson MT. Exercise, free radicals and oxidative stress. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30(2):280–5.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Cowley E, Olenick A, McNulty K. Invisible sportswomen: the sex data gap in sport and exercise science research. Women Sport Phys Activity J. 2021;29:1–6.
Danielsson T, Carlsson J, Schreyer H, Ahnesjö J, Ten Siethoff L, Ragnarsson T, Tugetam Å, Bergman P. Blood biomarkers in male and female participants after an ironman-distance triathlon. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(6):e0179324–0179324.
Deaner RO, Balish SM, Lombardo MP. Sex differences in sports interest and motivation: an evolutionary perspective. Evolution Behav Sci. 2016;10(2):73–97.
Demirci-Çekiç S, Ozkan G, Avan AN, Uzunboy S, Capanoglu E, Apak R. Biomarkers of oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022;209:114477.
Devries MC, Jakobi JM. Importance of considering sex and gender in exercise and nutrition research. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2021;46(6):iii–vii.
Di Meo S, Napolitano G, Venditti P. Mediators of physical activity protection against ROS-Linked skeletal muscle damage. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):3024.
Di Meo S, Venditti P, Napolitano G. Physiological and pathological role of ROS: benefits and limitations of antioxidant treatment 2.0. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(16):9437.
Dillard CJ, Litov RE, Savin WM, Dumelin EE, Tappel AL. Effects of exercise, vitamin E, and ozone on pulmonary function and lipid peroxidation. J Appl Physiol. 1978;45(6):927–32.
Eyileten C, Fitas A, Jakubik D, Czajka P, Mróz A, Czajkowska A, Witek K, Bakalarski W, De Rosa S, Postuła M, Małek ŁA. Alterations in circulating microRNAs and the relation of microRNAs to maximal oxygen consumption and intima-media thickness in ultra-marathon runners. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(14):7234.
Eyileten C, Wicik Z, Fitas A, Marszalek M, Simon JE, De Rosa S, Wiecha S, Palatini J, Postula M, Malek LA. Altered circulating microRNA profiles after endurance training: a cohort study of Ultramarathon runners. Front Physiol. 2021;12:792931.
Fahrenholtz IL, Sjödin A, Benardot D, Tornberg ÅB, Skouby S, Faber J, Sundgot-Borgen JK, Melin AK. Within-day energy deficiency and reproductive function in female endurance athletes. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28(3):1139–46.
Gagnon DD, Dorman S, Ritchie S, Mutt SJ, Stenbäck V, Walkowiak J, Herzig KH. Multi-day prolonged low- to moderate-intensity endurance Exercise mimics training improvements in metabolic and oxidative profiles without concurrent chromosomal changes in healthy adults. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1123.
Guerrero C, Collado-Boira E, Martinez-Navarro-I, Hernando B, Hernando C, Balino P, Muriach M. Impact of plasma oxidative stress markers on post-race recovery in Ultramarathon runners: a sex and age perspective overview. Antioxid (Basel). 2021;10(3):355.
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. Free radicals in biology and medicine. New York City: Oxford University Press; 2015.
Hamadeh MJ, Devries MC, Tarnopolsky MA. Estrogen supplementation reduces whole body leucine and carbohydrate oxidation and increases lipid oxidation in men during endurance exercise. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(6):3592–9.
Hamarsland H, Paulsen G, Solberg PA, Slaathaug OG, Raastad T. Depressed physical performance outlasts hormonal disturbances after military training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(10):2076–84.
He F, Li J, Liu Z, Chuang CC, Yang W, Zuo L. Redox mechanism of reactive oxygen species in exercise. Front Physiol. 2016;7:486.
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2nd Edition. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons; 2019.
Hoppel F, Calabria E, Pesta DH, Kantner-Rumplmair W, Gnaiger E, Burtscher M. Effects of ultramarathon running on mitochondrial function of platelets and oxidative stress parameters: a pilot study. Front Physiol. 2021;12:632664.
Il’yasova D, Scarbrough P, Spasojevic I. Urinary biomarkers of oxidative status. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;413(19–20):1446–53.
Islam MN, Rauf A, Fahad FI, Emran TB, Mitra S, Olatunde A, Shariati MA, Rebezov M, Rengasamy KRR, Mubarak MS.. Superoxide dismutase: an updated review on its health benefits and industrial applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(26):7282–300.
Janciauskiene S. The beneficial effects of antioxidants in health and diseases. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2020;7(3):182–202.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jówko E, Różański P, Tomczak A. Effects of a 36-h survival training with sleep deprivation on oxidative stress and muscle damage biomarkers in young healthy men. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(10):2066.
Kabasakalis A, Kyparos A, Tsalis G, Loupos D, Pavlidou A, Kouretas D. Blood oxidative stress markers after ultramarathon swimming. J Strength Conditioning Res. 2011;25(3):805–11.
Kaufmann CC, Wegberger C, Tscharre M, Haller PM, Piackova E, Vujasin I, Kassem M, Tentzeris I, Freynhofer MK, Jäger B, Wojta J, Huber K. Effect of marathon and ultra-marathon on inflammation and iron homeostasis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(3):542–52.
Kawamura T, Muraoka I. Exercise-Induced oxidative stress and the effects of antioxidant intake from a physiological viewpoint. Antioxid (Basel). 2018;7(9):119.
Kłapcińska B, Waśkiewicz Z, Chrapusta SJ, Sadowska-Krępa E, Czuba M, Langfort J. Metabolic responses to a 48-h ultra-marathon run in middle-aged male amateur runners. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(11):2781–93.
Knechtle B, Nikolaidis PT. Physiology and pathophysiology in ultra-marathon running. Front Physiol. 2018;9:634.
Knechtle B, Valeri F, Nikolaidis PT, Zingg MA, Rosemann T, Rüst CA. Do women reduce the gap to men in ultra-marathon running? Springerplus. 2016;5(1):672.
Knez WL, Coombes JS, Jenkins DG. Ultra-endurance exercise and oxidative damage: implications for cardiovascular health. Sports Med. 2006;36(5):429–41.
Ko SH, Jung Y. Energy metabolism changes and dysregulated lipid metabolism in postmenopausal women. Nutrients. 2021;13(12):4556.
Laufs U, Scharnagl H, Halle M, Windler E, Endres M, März W. Treatment options for Statin-Associated muscle symptoms. Deutsches Arzteblatt Int. 2015;112(44):748–55.
Le Goff C, Kaux JF, Dulgheru R, Seidel L, Pincemail J, Cavalier E, Melon P. The impact of an ultra-trail on the dynamic of cardiac, inflammatory, renal and oxidative stress biological markers correlated with electrocardiogram and echocardiogram. Acta Cardiol. 2021;76(7):739–47.
Lecina M, Castellar C, Pradas F, López-Laval I. 768-km multi-stage ultra-trail case study-muscle damage, biochemical alterations and strength loss on lower limbs. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(2):876.
Legaz-Arrese A, López-Laval I, George K, Puente-Lanzarote JJ, Mayolas-Pi C, Serrano-Ostáriz E, Revilla-Martí P, Moliner-Urdiales D, Reverter-Masià J. Impact of an endurance training program on exercise-induced cardiac biomarker release. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;308(8):H913–920.
Lian D, Chen MM, Wu H, Deng S, Hu X. The role of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle myogenesis and muscle disease. Antioxid (Basel). 2022;11(4):755.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700.
Liguori I, Russo G, Curcio F, Bulli G, Aran L, Della-Morte D, Gargiulo g, Testa G, Cacciatore F, Bonaduce D, Abete P. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:757–72.
Lu Y, Wiltshire HD, Baker JS, Wang Q. Effects of high intensity exercise on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in untrained humans: a systematic review. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(12):1272.
PubMed Google Scholar
Maher CG, Sherrington C, Herbert RD, Moseley AM, Elkins M. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys Ther. 2003;83(8):713–21.
Martinez MP, Kannan K. Simultaneous analysis of seven biomarkers of oxidative damage to lipids, proteins, and DNA in urine. Environ Sci Technol. 2018;52(11):6647–55.
Martinez-Navarro I, Montoya-Vieco A, Collado E, Hernando B, Hernando C. Ultra trail performance is differently predicted by endurance variables in men and women. Int J Sports Med. 2022;43(7):600–7.
McKenzie JE, Brennan SE, Ryan RE, Thomson HJ, Johnston RV. Summarizing study characteristics and preparing for synthesis. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2nd Edition. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons; 2019.
McKenzie JE, Brennan SE, Ryan RE, Thomson HJ, Johnston RV, Thomas J. Defining the criteria for including studies and how they will be grouped for the synthesis. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2nd Edition. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons; 2019.
McNulty KL, Elliott-Sale KJ, Dolan E, Swinton PA, Ansdell P, Goodall S, Thomas K, Hicks KM. The effects of menstrual cycle phase on exercise performance in eumenorrheic women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2020;50(10):1813–27.
Michielsen EC, Wodzig WK, Van Dieijen-Visser MP. Cardiac troponin T release after prolonged strenuous exercise. Sports Med. 2008;38(5):425–35.
Millet GY, Banfi JC, Kerherve H, Morin JB, Vincent L, Estrade C, Geyssant A, Feasson L. Physiological and biological factors associated with a 24 h treadmill ultra-marathon performance. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011;21(1):54–61.
Morris G, Gevezova M, Sarafian V, Maes M. Redox regulation of the immune response. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19(10):1079–101.
Moseley AM, Elkins MR, Van der Wees PJ, Pinheiro MB. Using research to guide practice: the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro). Braz J Phys Ther. 2020;24(5):384–91.
Mrakic-Sposta S, Gussoni M, Moretti S, Pratali L, Giardini G, Tacchini P, Dellanoce C, Tonacci A, Mastorci F, Borghini A, Montorsi M, Vezzoli A. Effects of mountain ultra-marathon running on ROS production and oxidative damage by micro-invasive analytic techniques. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(11):e0141780.
Mrakic-Sposta S, Gussoni M, Vezzoli A, Dellanoce C, Comassi M, Giardini G, Bruno RM, Montorsi M, Corciu A, Greco F, Pratali L. Acute effects of Triathlon race on oxidative stress biomarkers. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:3062807.
Munteanu IG, Apetrei C. Analytical methods used in determining antioxidant activity: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3380.
Murphy MP, Bayir H, Belousov V, Chang CJ, Davies KJA, Davies MJ, Dick TP, Finkel T, Forman HJ, Janssen-Heininger Y, Gems D, Kagan VE, Kalyanaraman B, Larsson NG, Milne GL, Nyström T, Poulsen HE, Radi R, Van Remmen H, Schumacker PT, Thornalley PJ, Toyokuni S, Winterbourn CC, Yin H, Halliwell B. Guidelines for measuring reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage in cells and in vivo. Nat Metabolism. 2022;4(6):651–62.
Myers J. Exercise. Cardiovasc Health Circulation. 2003;107(1):e2–5.
Nieman DC, Luo B, Dréau D, Henson DA, Shanely RA, Dew D, Meaney MP. Immune and inflammation responses to a 3-day period of intensified running versus cycling. Brain Behav Immun. 2014;39:180–5.
Partyka A, Waśkiewicz Z. The consequences of training and competition to the musculoskeletal system in ultramarathon runners: a narrative review. Front Physiol. 2021;12:738665.
Pate RR, Pratt M, Blair SN. Physical activity and public health: a recommendation from the centers for disease control and prevention and the American college of sports medicine. JAMA. 1995;273(5):402–7.
Peake JM, Markworth JF, Nosaka K, Raastad T, Wadley GD, Coffey VG. Modulating exercise-induced hormesis: does less equal more? J Appl Physiol. 2015;119(3):172–89.
Peserico CS, Machado FA. Association between endurance performance, oxidative stress, and antioxidant markers during a running training program in untrained men. Sport Sci Health. 2022;18(1):249–56.
Pettersson J, Hindorf U, Persson P, Bengtsson T, Malmqvist U, Werkström V, Ekelund M. Muscular exercise can cause highly pathological liver function tests in healthy men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;65(2):253–9.
Pinho RA,Silva LA, Pinho CA, Scheffer DL, Souza CT, Benetti M, Carvalho T, Dal-Pizzol F. Oxidative stress and inflammatory parameters after an Ironman race. Clin J Sport Med. 2010;20(4):306–11.
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Bitto A. Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:8416763.
Plavina L, Kolesova O, Eglite J, Cakstins A, Cakstina S, Kolesovs A. Antioxidative system capacity after a 10-day-long intensive training course and one-month-long recovery in military cadets. Phys Activity Rev. 2021;9:2021.
Powers SK, Jackson MJ. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(4):1243–76.
Powers SK, Deminice R, Ozdemir M, Yoshihara T, Bomkamp MP, Hyatt H. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: friend or foe? J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5):415–25.
Powers SK, Goldstein E, Schrager M, Ji LL. Exercise training and skeletal muscle antioxidant enzymes: an update. Antioxidants. 2023;12(1):39.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Radak Z, Zhao Z, Koltai E, Ohno H, Atalay M. Oxygen consumption and usage during physical exercise: the balance between oxidative stress and ROS-dependent adaptive signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18(10):1208–46.
Rahal A, Kumar A, Singh V, Yadav B, Tiwari R, Chakraborty S, Dhama K. Oxidative stress, prooxidants, and antioxidants: the interplay. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:761264.
Ramos-Campo D, Ávila-Gandía V, Alacid F, Soto-Méndez F, Alcaraz PE, López-Román FJ, Rubio-Arias JÁ. Muscle damage, physiological changes and energy balance in ultra-endurance mountain event athletes. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016;41(8):872–8.
Reid MB. Redox interventions to increase exercise performance. J Physiol. 2016;594(18):5125–33.
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49(11):1603–16.
Revan S, Erol A. Effects of endurance training on exhaustive exercise-induced oxidative stress markers. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011;5:437–41.
Riegel B, Moser DK, Buck HG, Dickson VV, Dunbar SB, Lee CS, Lennie TA, Lindenfeld J, Mitchell JE, Treat-Jacobson DJ, Webber DE; American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research. Self-care for the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease and stroke: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(9):e006997.
Rifkind JM, Mohanty JG, Nagababu E. The pathophysiology of extracellular hemoglobin associated with enhanced oxidative reactions. Front Physiol. 2014;5:500.
Roebuck GS, Urquhart DM, Knox L, Fitzgerald PB, Cicuttini FM, Lee S, Fitzgibbon BM. Psychological factors associated with Ultramarathon runners’ supranormal pain tolerance: a pilot study. J Pain. 2018;19(12):1406–15.
Rosales XQ, Chu ML, Shilling S, Wall C, Pastores GM, Mendell JR Fidelity of gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) in differentiating skeletal muscle from liver damage. J Child Neurol. 2008;23(7):748–51.
Rowlands DS, Pearce E, Aboud A, Gillen JB, Gibala MJ, Donato S, Waddington JM, Green JG, Tarnopolsky MA. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and muscle soreness in an 894-km relay trail run. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(5):1839–48.
Różański P, Jówko E, Tomczak A. Assessment of the levels of oxidative stress, muscle damage, and psychomotor abilities of special force soldiers during military survival training. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(13):4886.
Ruzicic R, Jakovljevic V. and Djordjevic D. Oxidative stress in training, overtraining and detraining: from experimental to applied Research. Serbian J Experimental Clin Res. 2016;17(4):343–8.
Sánchez-Rodríguez MA, Mendoza-Núñez VM. Oxidative stress indexes for diagnosis of health or disease in humans. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4128152.
Scheer V. Participation trends of ultra endurance events. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2019;27(1):3–7.
Scheer V, Rojas-Valverde D. Long-term health issues in ultraendurance runners: should we be concerned? BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021;7(3):e001131.
Scheer V, Tiller NB, Doutreleau S, Khodaee M, Knechtle B, Pasternak A, Rojas-Valverde D.. Potential long-term health problems associated with ultra-endurance running: a narrative review. Sports Med. 2022;52(4):725–40.
Scheffer DL, Latini A. Exercise-induced immune system response: anti-inflammatory status on peripheral and central organs. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(10):165823.
Schieber M, Chandel NS. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biology: CB. 2014;24(10):R453–462.
Sharifi-Rad M, Anil Kumar NV, Zucca P, Varoni EM, Dini L, Panzarini E, Rajkovic J, Tsouh Fokou PV, Azzini E, Peluso I, Prakash Mishra A, Nigam M, El Rayess Y, Beyrouthy ME, Polito L, Iriti M, Martins N, Martorell M, Docea AO, Setzer WN, Calina D, Cho WC, Sharifi-Rad J. Lifestyle, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: back and forth in the Pathophysiology of chronic diseases. Front Physiol. 2020;11:694.
Sies H, Cadenas E. Oxidative stress: damage to intact cells and organs. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985;311(1152):617–31.
Sies H, Jones DP. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(7):363–83.
Simioni C, Zauli G, Martelli AM, Vitale M, Sacchetti G, Gonelli A, Neri LM. Oxidative stress: role of physical exercise and antioxidant nutraceuticals in adulthood and aging. Oncotarget. 2018;9(24):17181–98.
Spanidis Y, Stagos D, Orfanou M, Goutzourelas N, Bar-Or D, Spandidos D, Kouretas D.. Variations in oxidative stress levels in 3 days follow-up in ultramarathon mountain race athletes. J Strength Cond Res.2017;31(3):582–94.
Stein JA, Farina EK, Karl JP, Thompson LA, Knapik JJ, Pasiakos SM, McClung JP, Lieberman HR. Biomarkers of oxidative stress, diet and exercise distinguish soldiers selected and non-selected for special forces training. Metabolomics. 2023;19(4):39.
Tanskanen MM, Uusitalo AL, Kinnunen H, Häkkinen K, Kyröläinen H, Atalay M. Association of military training with oxidative stress and overreaching. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(8):1552–60.
Taylor KS, Mahtani KR, Aronson JK. Summarising good practice guidelines for data extraction for systematic reviews and meta-analysis. BMJ Evidence-Based Med. 2021;26(3):88–90.
Thirupathi A, Pinho RA, Ugbolue UC, He Y, Meng Y, Gu Y. Effect of running exercise on oxidative stress biomarkers: a systematic review. Front Physiol. 2021;11:610112.
Thirupathi A, Wang M, Lin JK, Fekete G, István B, Baker JS, Gu Y. Effect of different Exercise modalities on oxidative stress: a systematic review. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:1947928.
Tian D, Meng J. Exercise for prevention and relief of cardiovascular disease: prognoses, mechanisms, and approaches. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:3756750.
Tiller NB, Elliott-Sale K, Knechtle B, Wilson PB, Roberts JD, Millet GY. Do sex differences in physiology confer a female advantage in ultra-endurance sport? Sports Med. 2021;51(5):895–915.
Tomczak A, Jówko E. Survival Training effects on oxidative stress and muscle damage biomarkers of Naval cadets. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2020;91(9):720–4.
Torres MJ, Kew KA, Ryan TE, Pennington ER, Lin CT, Buddo KA, Fix AM, Smith CA, Gilliam LA, Karvinen S, Lowe DA, Spangenburg EE, Zeczycki TN, Shaikh SR, Neufer PD.. 17β-Estradiol directly lowers mitochondrial membrane microviscosity and improves bioenergetic function in skeletal muscle. Cell Metabol. 2018;27(1):167–e179167.
Turrens JF. Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. J Physiol. 2003;552(Pt 2):335–44.
van Beek JHDA, de Moor MH, de Geus EJ, Lubke GH, Vink JM, Willemsen G, Boomsma DI.. The genetic architecture of liver enzyme levels: GGT, ALT and AST. Behav Genet. 2013;43(4):329–39.
Vázquez-Meza H, Vilchis-Landeros MM, Vázquez-Carrada M, Uribe-Ramírez D, Matuz-Mares D. Cellular compartmentalization, glutathione transport and its relevance in some pathologies. Antioxidants. 2023;12(4):834.
Vezzoli A, Dellanoce C, Mrakic-Sposta S, Montorsi M, Moretti S, Tonini A, Pratali L, Accinni R. Oxidative stress assessment in response to ultraendurance exercise: thiols redox status and ROS production according to duration of a competitive race. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:6439037.
Vollaard NB, Cooper CE, Shearman JP. Exercise-induced oxidative stress in overload training and tapering. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38(7):1335–41.
Wagner KH, Reichhold S, Hölzl C, Knasmüller S, Nics L, Meisel M, Neubauer O. Well-trained, healthy triathletes experience no adverse health risks regarding oxidative stress and DNA damage by participating in an ultra-endurance event. Toxicology. 2010;278(2):211–6.
Wagner KH, Reichhold S, Neubauer O. Impact of endurance and ultraendurance exercise on DNA damage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1229:115–23.
Wang F, Wang X, Liu Y, Zhang Z. Effects of exercise-induced ROS on the pathophysiological functions of skeletal muscle. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:3846122.
Warburton DE, Nicol CW, Bredin SS. Health benefits of physical activity: the evidence. CMAJ. 2006;174(6):801–9.
Waśkiewicz Z, Kłapcińska B, Sadowska-Krępa E, Czuba M, Kempa K, Kimsa E, Gerasimuk D. Acute metabolic responses to a 24-h ultra-marathon race in male amateur runners. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(5):1679–88.
Wesolowski LT, Semanchik PL, White-Springer SH. Beyond antioxidants: selenium and skeletal muscle mitochondria. Front Veterinary Sci. 2022;9:1011159.
Zhu JW, Reed JL, Van Spall HGC. The underrepresentation of female athletes in sports research: considerations for cardiovascular health. Eur Heart J. 2021;43(17):1609–11.
Zuo J, Zhang Z, Luo M, Zhou L, Nice EC, Zhang W, Wang C, Huang C. Redox signaling at the crossroads of human health and disease. MedComm (2020). 2022;3(2):e127.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors have no financial or equipment disclosures to be made related to the current systematic review.
No funding was received by either author.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Kinesiology, Health Promotion, and Recreation, University of North Texas Denton, TX, USA
Gregg S. Mallett
Modus Energy, San Diego, CA, USA
Kim McGrath
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GM and KMcG contributed to the study’s conception. GM completed the concept and design. GM and KMcG contributed to the search and extraction of studies. GM and KMcG completed the vetting and approval.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gregg S. Mallett .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Mallett, G.S., McGrath, K. Effect of Endurance Exercise on Markers of Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review. J. of SCI. IN SPORT AND EXERCISE (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42978-024-00305-9
Download citation
Received : 23 December 2023
Accepted : 20 July 2024
Published : 20 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42978-024-00305-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Endurance training
- Free radicals
- Military performance
- Oxidative stress
- Reactive oxygen species
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Methodology
- Open access
- Published: 22 August 2024
Patient and public involvement and engagement in the ASCEND PLUS trial: reflections from the design of a streamlined and decentralised clinical trial
- Muram El-Nayir 1 na1 ,
- Rohan Wijesurendra ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8261-8343 1 na1 ,
- David Preiss 1 ,
- Marion Mafham 1 ,
- Leandros Tsiotos 1 ,
- Sadman Islam 1 ,
- Anne Whitehouse 1 ,
- Sophia Wilkinson 1 ,
- Hannah Freeman 1 ,
- Ryonfa Lee 1 ,
- Wojciech Brudlo 1 ,
- Genna Bobby 1 ,
- Bryony Jenkins 1 ,
- Robert Humphrey 1 ,
- Amy Mallorie 1 ,
- Andrew Toal 2 ,
- Elnora C. Barker 2 ,
- Dianna Moylan 2 ,
- Graeme Thomson 2 ,
- Firoza Davies 2 ,
- Hameed Khan 2 ,
- Ian Allotey 2 ,
- Susan Dickie 2 na1 &
- John Roberts 2 na1
Trials volume 25 , Article number: 554 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Introduction
ASCEND PLUS is a randomised controlled trial assessing the effects of oral semaglutide on the primary prevention of cardiovascular events in around 20,000 individuals with type 2 diabetes in the UK. The trial’s innovative design includes a decentralised direct-to-participant invitation, recruitment, and follow-up model, relying on self-completion of online forms or telephone or video calls with research nurses, with no physical sites. Extensive patient and public involvement and engagement (PPIE) was essential to the design and conduct of ASCEND PLUS.
To report the process and conduct of PPIE activity in ASCEND PLUS, evaluate effects on trial design, reflect critically on successes and aspects that could have been improved, and identify themes and learning relevant to implementation of PPIE in future trials.
PPIE activity was coordinated centrally and included six PPIE focus groups and creation of an ASCEND PLUS public advisory group (PAG) during the design phase. Recruitment to these groups was carefully considered to ensure diversity and inclusion, largely consisting of adults living with type 2 diabetes from across the UK. Two members of the PAG also joined the trial Steering Committee. Steering Committee meetings, focus groups, and PAG meetings were conducted online, with two hybrid workshops to discuss PPIE activity and aspects of the trial.
PPIE activity was critical to shaping the design and conduct of ASCEND PLUS. Key examples included supporting choice for participants to either complete the screening/consent process independently online, or during a telephone or video call interview with a research nurse. A concise ‘initial information leaflet’ was developed to be sent with the initial invitations, with the ‘full’ information leaflet sent later to those interested in joining the trial. The PAG reviewed the content and format of participant- and public-facing materials, including written documents, online screening forms, animated videos, and the trial website, to aid clarity and accessibility, and provided input into the choice of instruments to assess quality of life.
Conclusions
PPIE is integral in ASCEND PLUS and will continue throughout the trial. This involvement has been critical to optimising the trial design, successfully obtaining regulatory and ethical approval, and conducting the trial.
Peer Review reports
ASCEND PLUS is an ongoing randomised placebo-controlled trial assessing the effects of oral semaglutide on cardiovascular and other outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes and no history of heart attack or stroke (NCT05441267). ASCEND PLUS will recruit approximately 20,000 participants in the UK. Potential participants are sent an invitation by post and the trial requires no in-person visits. Study medication is mailed directly to participants’ homes. This design represents a shift from the traditional concept of face-to-face interaction between research staff and participants at a clinical site and has become more common in recent years, perhaps accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic [ 1 ]. Decentralised direct-to-participant designs, including that of ASCEND PLUS, offer the possibility to expand participation in clinical trials and increase the generalisability of results [ 1 ].
The ASCEND PLUS trial design was developed with extensive patient and public involvement and engagement (PPIE), to ensure that the participant experience is as good as it can be, the safety and wellbeing of the participants is protected, recruitment to the trial is successful, and the engagement and adherence of participants is maintained. ASCEND PLUS commenced recruitment in March 2023, and the estimated primary completion date of the trial is 2028.
PPIE is increasingly recognised as a key element in the development of all research [ 2 ], including clinical trial proposals and protocols. PPIE can harness the valuable insights of those living with and affected by a disease or health condition, and ensure that the trial findings are relevant to the needs of patients, and their relatives and carers [ 3 ]. “Involvement” can be defined as activities and research carried out “with” or “by” members of the public or patients, rather than “to”, “about”, or “for” them. In this instance, this refers to the active involvement of patients and members of the public in the development of the trial design and the conduct of the trial [ 4 ]. In contrast, “engagement” focuses on how the trial findings can be shared with patients and the public in a two-way process that encourages communication and interactions with researchers [ 4 ]. Despite the recognition of the importance and potential value of PPIE in clinical trials, implementation remains variable at present with inconsistency between trials [ 5 ].
Here, we aim to report the process and details of PPIE activity during the planning and initiation of ASCEND PLUS, evaluate how this helped to shape the final trial design, reflect critically on successes and aspects that could have been improved, and draw out themes and learning relevant to the implementation of PPIE in future trials.
Methods and results
Theoretical considerations.
The revised Guidance for Reporting the Involvement of Patients and the Public (GRIPP-2) long-form checklist [ 6 ] was used to guide the drafting of this report (see Supplementary Table 1).
Resourcing of PPIE activities
PPIE in ASCEND PLUS was organised by dedicated PPIE officers working within the communications team alongside the core trial team comprised of investigators, trial managers, and administrative staff at the Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford (which sponsors the trial). An appropriate level of funding was available in the trial budget for PPIE activity, and all PPIE representatives were able to claim monetary compensation for their time, lived experience, and contribution, in line with guidance from the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) [ 7 ] and accepted best practice. Any out-of-pocket expenses (such as travel) incurred by PPIE representatives were reimbursed in full, and refreshments were provided at in-person meetings.
Format of PPIE activities
PPIE activity in ASCEND PLUS consisted of several linked components, beginning early in the design phase of the trial and is planned to continue through to trial completion and dissemination of the results.
Firstly, a series of six patient and public focus groups were convened to address specific issues. These focus group meetings largely involved people living with type 2 diabetes and included people from diverse backgrounds from across the UK.
Secondly, a trial-specific Public Advisory Group (PAG) was established. The PAG is responsible for providing feedback, advice, and opinions on many different aspects of ASCEND PLUS over the entire lifecycle of the trial.
Thirdly, in order to ensure patient involvement in the design and conduct of ASCEND PLUS at a strategic level, two members of the PAG who are individuals living with diabetes were also invited to join the Trial Steering Committee.
Steering Committee meetings, focus groups, and PAG meetings were largely conducted online using remote meeting software. Two in-person PPIE workshops were convened in Oxford. This combination of online and in-person meetings has been suggested to be favourable in a previous mixed methods study [ 8 ].
Recruitment and selection of focus groups and the PAG
The recruitment and selection of the focus groups and the PAG was carefully considered to ensure inclusivity and representation, for features including age, sex, and ethnicity. People living with type 2 diabetes were prioritised, given that ASCEND PLUS is a trial in this population.
The six focus groups were organised with support from the Nuffield Department of Population Health’s Public Advisory Group and four external organisations (Table 1 ). Each focus group was drawn from a specific geographic location (Leicester, Oxford, the north of England [two groups], Wales, and Scotland), to provide coverage of the areas of the UK in which ASCEND PLUS plans to recruit. The focus group based in Leicester was from the Centre for Ethnic Health Research and consisted of individuals of South Asian, Black Caribbean, and Black African ethnicity. The size of, and strategy used to achieve diverse representation within, each group was usually determined by the groups themselves.
Members of the PAG were invited from an existing departmental public advisory panel and the focus groups described above. The PAG was chosen to comprise a diverse group of patients and the public.
Involvement of PPIE panels and the PPIE advisory group in the research proposal
During the design phase of ASCEND PLUS, the six online PPIE focus groups (described above) were convened to address specific issues. Given the remote design of the trial with no in-person visits, the main topics discussed were the consent model and the recruitment/invitation methods. There was also discussion about other aspects of the trial design, including the active run-in, in which all participants receive the active drug prior to randomisation. These concepts were serially developed across the six focus groups, which took place between June and September 2021, with revisions made to the study design in response to the feedback received prior to the application for ethical approval.
Two people living with diabetes were next invited to join the Steering Committee. These individuals attended the first Steering Committee meeting in June 2021 and will continue to attend Steering Committee meetings until the completion of the trial. These patient and public contributors are members of the Steering Committee, contribute to discussions at meetings, and can vote on any decisions made by the Committee. They are also the joint senior authors of this publication (SD and JR).
The trial PAG was then assembled, including SD and JR amongst the members. The PAG contributed in detail to the design and review of all patient-facing study material, the online forms and videos used for the trial, and the trial website. This activity was organised through emails and online group meetings, as well as one face-to-face workshop in Oxford. The PAG will continue to contribute during the remainder of the trial, for example by reviewing planned patient newsletters and advising on local activities to aid recruitment. The PAG will also input on the interpretation of the trial results in due course, and specifically on their presentation and dissemination to patients and the public.
Impact of PPIE on ASCEND PLUS design and conduct
The six PPIE focus groups were critical to shaping the design and conduct of ASCEND PLUS. Full details of the composition and date of each of the six focus groups, the subjects discussed, and the feedback and impact are summarised in Table 1 .
Initially, it had been planned to invite all participants to complete self-directed online screening and consent, with an option of a telephone or video call if needed. A clear theme that emerged in the focus groups was support for choice in how participants interact with the trial: i.e. either online completion of study assessments on their own device (with the option to speak to a research nurse or study doctor at any time) or completion of study assessments during interviews with a research nurse. Therefore, recording of informed consent also needed to include both an online consent option (that can be completed by a participant independently) and the option to give consent during a telephone or video call with a research nurse. It was also felt to be important that participants can switch between these two methods of participation at any stage if they wish to. The exception to this concept was for non-English speakers, in whom a telephone or video call with a research nurse (aided by a translator) was recommended to ensure adequate understanding. In light of this feedback from the focus groups, the trial procedures were modified. The updated trial design now asks potential participants to indicate on the initial reply form which method (self-directed online versus telephone/video call with a research nurse) they prefer. Options have also been added to allow participants to change their trial interaction method during the course of the trial.
Another key impact on design and conduct of the trial resulted from feedback that the patient information leaflet was very long, due to the need to contain multiple items deemed mandatory by regulatory bodies. The focus group supported provision of an abbreviated “initial information leaflet” (rather than the “full” participant information leaflet) with the invitation letter, with the “full” patient information leaflet [ 9 ] subsequently supplied to those individuals who had declared interest in participating after reviewing the abbreviated leaflet.
The PPIE focus groups supported the proposed invitation method for ASCEND PLUS. In brief, this is conducted with the support of the NHS DigiTrials recruitment support service who undertake a search of electronic medical records to identify individuals who are potentially eligible (without individual patient consent at this stage). The name, address, and postcode of these individuals are then passed securely to a mailing house (who also handle patient letters for the NHS) who then send out study invitation letters. The details of potential participants are not disclosed to the ASCEND PLUS study team unless and until the participant returns the reply form, which includes the participant’s name and the details they add to it (such as telephone number, or email address). The reply form also contains a unique identifier which the ASCEND PLUS team send to NHS DigiTrials to obtain the participant’s name, address, sex, date of birth, NHS number, and GP surgery details from NHS records. The positive feedback from the PPI focus groups regarding the use of healthcare data in this way was cited in the application for regulatory approval. This recruitment method was supported by the Health Research Authority (HRA), who also followed advice from the Confidentiality Advisory Group (an independent body which provides expert advice on the use of confidential patient information). A separate data protection leaflet which is supplied to prospective participants covers all aspects of how data about ASCEND PLUS participants is processed [ 10 ].
The ASCEND PLUS PAG also undertook a detailed review of the three leaflets discussed above (initial information leaflet, full participant information leaflet, data protection leaflet), the trial invitation letter, and the study treatment information leaflets (one of which is included with each pack of study treatment mailed to a participant). Recommended text and content changes were made accordingly, ensuring that the text of each document remained consistent with trial processes. This extensive PPIE review and consultation process has resulted in documents which are easier to understand and more inclusive. This also included feedback about accommodating people with visual impairments. Examples of specific changes made to the text of study documents are shown in Fig. 1 .

Examples of specific changes made to the text of the ASCEND PLUS participant information leaflet after PPIE input
The PAG were then involved in co-developing an animated video to support the self-directed online consent process. The PAG initially contributed to the development of the script and then provided feedback on the images used in the storyboard, with many of the specific points raised implemented in the final version. For example, the images of potential participants in the video were updated to ensure greater diversity, and a border line was drawn on a map of the UK to highlight the geographical areas in which ASCEND PLUS plans to recruit.
The PAG was instrumental in the selection of quality of life questionnaires included in ASCEND PLUS. Whilst inclusion of the EQ5D questionnaire is commonplace due to its importance to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), several options existed for an additional questionnaire to capture diabetes-specific quality of life. The Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID), Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), Diabetes-Dependent Quality of Life questionnaire (ADDQoL), and the Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire (DTSQ) were all considered. PAG members ranked the questionnaires separately on whether they thought they collected a meaningful and relevant assessment for people with diabetes, and whether participants would be willing to complete them. The PAG members were also separately asked to consider the feasibility of participants completing the 36-Item Short Form Survey questionnaire (SF-36) compared to the 12-item version (SF-12). Following detailed feedback from the PAG, the SF-12 and the PAID questionnaire were included in the final ASCEND PLUS protocol.
The PAG also reviewed the text and format of the questions included in the draft screening form (to be completed either by participants on their own devices or by research nurses in conversation with participants) and provided detailed feedback. A number of changes were implemented based on this, including changes to the order in which questions are asked and revisions to the working of particular questions to make them easier to understand.
A summary of PPIE in ASCEND PLUS is included in a dedicated page on the trial website, which also includes a video of two public contributors discussing their experience [ 11 ]. This activity, and the impact that it has had on the final design of ASCEND PLUS, is also summarised in Fig. 2 .

Summary of Public Advisory Group activity and impact in ASCEND PLUS
Impact of PPIE on individuals involved, and wider impact
The impact of PPIE in ASCEND PLUS on the individuals involved and the wider impact was considered in detail at a workshop convened on 26 November 2022, which included ten members of the PAG as well as investigators, trial managers, research fellows, and PPIE officers from the Nuffield Department of Population Health.
The context and process of PPIE in ASCEND PLUS were considered in some detail. Themes that emerged in this discussion included the fact that PAG members reported an overall highly positive experience. They commented that on-boarding for new members worked well and that the process had been well organised, with all members having a clear idea of upcoming tasks with regular updates from the study team. Having a single point of contact (the PPIE team at the Nuffield Department of Population Health) to coordinate the PPIE for the study was felt to be a major advantage. The logistical aspects of PAG group meetings were discussed and the format of online meetings scheduled in the evenings or at weekends was felt to be beneficial in avoiding travel time and allowing individuals the flexibility of contributing from their own home. Many meetings took place during periods of COVID-19 lockdowns, and being able to hold online meetings enabled these to go ahead and brought people together at a time of isolation. The benefits of in-person events (such as the PPIE workshop) were also discussed, and it was felt that some aspects, such as the ability to arrive early for social discussion and remain behind after the main meeting to ask questions and have private conversations, could also be implemented using the existing features offered by major online meeting platforms.
The inclusive nature of the PPIE process in ASCEND PLUS was praised. Specifically, discussion focused on the decision to actively encourage the involvement of contributors without previous PPIE experience, as well as the expectation in PAG meetings that everyone is listened to equally and that there are “no silly questions”. Members of the PAG also reflected that external feedback on ASCEND PLUS documents (created with their input) has been very positive. For example, the Departmental Information Governance lead commented that the ASCEND PLUS data information leaflet was the best such example they had seen in their experience of advising on multiple trials over a number of years. Similarly, the process of conducting PPIE in ASCEND PLUS has been used as an exemplar in the MSc in Clinical Trials postgraduate course that is run by the Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford for students from across the world.
Some areas that could have been improved were also identified. Occasionally, too much information could be presented in PAG meetings, and key questions cropping up towards the end of a meeting might have meant that they received less attention than they should have. It was also highlighted that technology can be a barrier for some people, particularly those lacking the digital skills or hardware to be able to participate in online meetings. For example, printed materials may need to be offered as not all individuals will have access to a printer. In a few cases, deadlines for responding to tasks were shorter than ideal, and it was recommended that circulation of slides and materials should be undertaken well in advance of a meeting to allow members enough time to consider them carefully. Finally, it was suggested that it would have been helpful to have a “global overview” of the planned PAG activities so that members had an idea of what had been completed already and what would be coming up next.
In terms of the effect on themselves as individuals, PAG members reported that they had found participation in PPIE activities for ASCEND PLUS highly enjoyable and reported that there was more “behind-the-scenes” activity than they had initially expected. There was consensus that it was highly rewarding being part of helping to create a study that may have a huge impact on people’s lives, and in ensuring that the study is accessible to people from all walks of life including groups who are traditionally under-represented in research. From a personal perspective, some members reported that they had found participation intellectually stimulating and that it helped them to keep up to date with diabetes research, and be more confident when talking about research in general.
Finally, it is recognised that this manuscript only presents qualitative reflections on PPIE in ASCEND PLUS. ASCEND PLUS is still early in recruitment at the present time, and presentation of quantitative data on recruitment and retention would not be particularly meaningful in the absence of a relevant control. Of note, a sub-study is planned to specifically evaluate consent in ASCEND PLUS, given the decentralised trial design.
Study design of ASCEND PLUS and the relevance to the PPIE strategy
At the outset of ASCEND PLUS, a number of challenges and opportunities were identified that would be critical to the success of the trial, including:
Gaining approval from the relevant bodies for an innovative, streamlined trial design that has no in-person visits and requires a non-traditional participant consent process.
Recruitment of a large number of people (20,000), aged 55 and over, living with type 2 diabetes from across the UK, who have not yet experienced a heart attack or stroke. In addition, ethnic diversity among trial participants is highly desirable, to ensure a trial population broadly representative of that of the wider UK.
Implementation of a trial where all interactions with participants would be conducted directly using innovative patient-centred web-based technology, supplemented by telephone, video-call contact and mailed letters.
A decentralised enrolment and consent process that is sufficiently flexible and adaptable to suit all participants, irrespective of preference for self-directed online interaction versus a telephone/video call with a research nurse.
A lengthy participation timescale of 5 years.
The role of PPIE was particularly critical in ASCEND PLUS, helping to optimise the trial design in the context of each of these points. As discussed in the above sections, various aspects of the trial design were altered in line with the public contributors’ feedback, sometimes in quite a major way such as the decision to allow choice in the method of interaction with the study.
Contextual and process factors influencing PPIE in ASCEND PLUS
PPIE in ASCEND PLUS has included several distinct phases, including six focus groups, the construction of a trial-specific PAG, and inclusion of two members of the PAG on the trial Steering Committee.
PPIE activity in ASCEND PLUS has been greatly enhanced by the recruitment of enthusiastic and dedicated members to the focus groups and PAG, coordination and organisation by experienced and professional PPIE officers, the willingness and desire of the trial investigators to modify the trial design in response to PPIE feedback, and adequate resourcing for PPIE activity in the trial budget. The use of digital technology and online meetings aided the efficiency and inclusivity of the process.
Some areas of difficulty were identified. The tight trial timeline meant that occasionally PAG members were under pressure to meet challenging deadlines for review of various materials, and some online sessions perhaps contained too much information. Adequate resourcing of PPIE activity is key to spreading the load on each individual member.
Influence of PPIE on the final ASCEND PLUS study design
PPIE greatly enhanced the final ASCEND PLUS study design. The changes made in response to the PPIE scoping exercises made the trial more inclusive, most notably in influencing the decision to give all participants a free choice in the method by which they interact with the study. The PPIE activity also heavily influenced almost all of the written and online material for the trial, making this more accessible and understandable, and also available in different formats and to those with visual impairment. Specifically, the experience afforded by individuals living with diabetes was highly valuable when considering the nature of the trial and the target population. The impact of PPIE activity on the study was evaluated by direct comparison of the final trial design to the initial proposals (with some examples included here), and by qualitative discussion with relevant stakeholders in a dedicated workshop convened for this purpose.
Learnings and recommendations for future large-scale clinical trials
Comprehensive and early PPIE is critical to gain input on all aspects of the proposed trial design and to optimise the relevance and acceptability to people living with diabetes. This involvement should start well before regulatory submissions, in order to allow time for changes to be made in response to PPIE group feedback. Involvement of dedicated and professional PPIE officers should be strongly considered to streamline the process, and adequate resourcing of PPIE activity is essential. Careful consideration should be given to how recruitment to focus groups and advisory groups is undertaken, making sure that assembled panels are inclusive and representative, and are able to work in a cohesive group and provide constructive comments and feedback in a timely manner. Feedback on participant- and public-facing supporting material such as information leaflets, animations, and the trial website helps to make these accessible and should improve recruitment and adherence, as well as the experience of recruited individuals. Inclusion of public contributors on the trial Steering Committee is important to ensure PPIE input to decision-making during the course of the trial. A summary of these recommendations is outlined in Fig. 3 . Finally, ASCEND PLUS is a UK-based trial, and there may be limited applicability to different healthcare systems and cultural contexts, or in resource-limited settings.

Learnings and recommendations for PPIE in future large-scale clinical trials
ASCEND PLUS is a large-scale trial with an innovative, streamlined design with a non-traditional participant consent process and no in-person study visits. Extensive PPIE has proven integral to the design and initiation of ASCEND PLUS and will continue throughout the trial. This involvement has been critical to optimising the trial design, successfully obtaining ethical and regulatory approvals, and conducting the trial.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Cummings SR. Clinical trials without clinical sites. JAMA Intern Med. 2021;181. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.9223 .
Richards T. Patient and public involvement in research goes global. 2017. https://blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2017/11/30/tessa-richards-patient-and-public-involvement-in-research-goes-global/ .
Aiyegbusi OL, McMullan C, Hughes SE, Turner GM, Subramanian A, Hotham R, Davies EH, Frost C, Alder Y, Agyen L, et al. Considerations for patient and public involvement and engagement in health research. Nat Med. 2023;29:1922–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02445-x .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
NIHR. What is Patient and Public Involvement and Public Engagement? 2024. https://www.spcr.nihr.ac.uk/PPI/what-is-patient-and-public-involvement-and-engagement .
Selman LE, Clement C, Douglas M, Douglas K, Taylor J, Metcalfe C, Lane JA, Horwood J. Patient and public involvement in randomised clinical trials: a mixed-methods study of a clinical trials unit to identify good practice, barriers and facilitators. Trials. 2021;22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-021-05701-y .
Staniszewska S, Brett J, Simera I, Seers K, Mockford C, Goodlad S, Altman DG, Moher D, Barber R, Denegri S, et al. GRIPP2 reporting checklists: tools to improve reporting of patient and public involvement in research. BMJ. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j3453 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
NIHR. Payment for public involvement in health and care research: a guide for organisations on employment status and tax. 2023. https://www.nihr.ac.uk/documents/Payment-for-Public-Involvement-in-Health-and-Care-Research-A-guide-for-organisations-on-determining-the-most-appropriate-payment-approach/30838 .
Jones E, Frith L, Gabbay M, Tahir N, Hossain M, Goodall M, Bristow K, Hassan S. Remote working in public involvement: findings from a mixed methods study. Res Involv Engagem. 2022;8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-022-00396-0 .
ASCEND PLUS Patient Information Leaflet. https://www.ascend-plus-trial.org/files/ascend-plus-pil_full-a4_v-1-3_rgb-for-web.pdf .
ASCEND PLUS Data Information Leaflet. https://www.ascend-plus-trial.org/files/ascend-plus-data-information-a4_v1-4_rgb-for-web.pdf .
ASCEND PLUS website: patients and the public page. https://www.ascend-plus-trial.org/patients-and-the-public .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the input from Parminder Hothi and other present and past members of the ASCEND PLUS Public Advisory Group who chose to remain anonymous and who are therefore not named as co-authors of this publication.
ASCEND PLUS is coordinated and sponsored by the University of Oxford and run with support from the National Institute for Health and Care Research. Novo Nordisk produces oral semaglutide and is providing the treatment for the study free of charge. Novo Nordisk has given a grant to the University of Oxford to help with the cost of running of the study but is not directly involved with either coordinating the study or analysing the results.
Author information
Muram El-Nayir, Rohan Wijesurendra, Susan Dickie, and John Roberts contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Clinical Trial Service and Epidemiological Studies Unit, Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX3 7LF, UK
Muram El-Nayir, Rohan Wijesurendra, David Preiss, Marion Mafham, Leandros Tsiotos, Sadman Islam, Anne Whitehouse, Sophia Wilkinson, Hannah Freeman, Ryonfa Lee, Wojciech Brudlo, Genna Bobby, Bryony Jenkins, Robert Humphrey & Amy Mallorie
Public Advisory Group; ASCEND PLUS Clinical Trial, Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX3 7LF, UK
Andrew Toal, Elnora C. Barker, Dianna Moylan, Graeme Thomson, Firoza Davies, Hameed Khan, Ian Allotey, Susan Dickie & John Roberts
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ME and RW: Lead authors of the manuscript with regular involvement in PAG meetings. DP and MM: Chief investigators of the ASCEND PLUS trial and the initiators of PPIE involvement throughout. Major contributors in writing and reviewing the manuscript. LT, SI, AW, SW and HF: PPIE officers for the ASCEND PLUS trial with substantial involvement in the recruitment and organisation of PAG meetings and collation of input obtained. RL, WB, RH, AM, BJ and GB: ASCEND PLUS Clinical & Administrative team involved in organisation of PAG meetings. AT, ECB, DM, GT, FD, HK and IA: PAG members who were major contributors in writing and reviewing the manuscript. SD and JR: Senior members of the PAG, who oversaw the writing of this manuscript. Major contributors in writing and reviewing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rohan Wijesurendra .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The ASCEND PLUS clinical trial has been approved by the Research Ethics Committee.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1. table 1: gripp-2 checklist., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
El-Nayir, M., Wijesurendra, R., Preiss, D. et al. Patient and public involvement and engagement in the ASCEND PLUS trial: reflections from the design of a streamlined and decentralised clinical trial. Trials 25 , 554 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08393-2
Download citation
Received : 14 April 2024
Accepted : 08 August 2024
Published : 22 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08393-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Patient and public involvement and engagement
- Clinical trial
ISSN: 1745-6215
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Maintenance work is planned from 21:00 BST on Tuesday 20th August 2024 to 21:00 BST on Wednesday 21st August 2024, and on Thursday 29th August 2024 from 11:00 to 12:00 BST.
During this time the performance of our website may be affected - searches may run slowly, some pages may be temporarily unavailable, and you may be unable to log in or to access content. If this happens, please try refreshing your web browser or try waiting two to three minutes before trying again.
We apologise for any inconvenience this might cause and thank you for your patience.

Journal of Materials Chemistry A
Advancements in thermoelectric materials: optimization strategies for enhancing energy conversion.

* Corresponding authors
a School of Material and Science, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang 212000, China E-mail: [email protected] , [email protected] , [email protected]
Thermoelectric materials are a highly promising category of energy conversion materials. In this paper, we present a multitude of approaches to enhance the efficacy of these materials. The review begins with an introduction to the fundamental concept of the thermoelectric figure of merit ( ZT ), a key parameter for assessing the performance of thermoelectric materials, as well as theories of electrical and thermal transport, which lay the groundwork for understanding and improving the performance of thermoelectric materials. Subsequently, this paper delves into several typical optimization strategies, including the enhancement of material performance through low-dimensionalization and quantum confinement effects, with detailed discussions on two-dimensional, one-dimensional, and zero-dimensional materials. The role of point defect engineering in modulating material properties and the significance of nano-composite materials in enhancing thermoelectric performance are also explored. Band engineering, an effective optimization technique, offers multiple possibilities for enhancing thermoelectric performance through the adjustment of carrier effective mass, utilization of resonance states, band degeneracy, band convergence, and bandgap tuning. Additionally, the application of phonon engineering in reducing thermal conductivity and improving thermoelectric conversion efficiency is highlighted. Discussions on special structures such as textures, single crystals, core–shell structures, and porous structures, as well as symmetry control strategies, highlight the importance of microstructural control in optimizing thermal conductivity. Consequently, the review explores the significance of the synergistic effects of different strategies, noting that an integrated application of these strategies can maximize the performance of thermoelectric materials. The use of materials genomics and machine learning in screening highly potential thermoelectric materials is also highlighted. Finally, the paper addresses the challenges and developments related to the stability, scalability, sustainability, and integration of thermoelectric materials with other systems. Overall, this article summarizes a series of optimization strategies for thermoelectric materials, providing valuable references and inspiration for researchers in the field, with the aim of further advancing the science of thermoelectric materials.

- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry A Recent Review Articles
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
H. Han, L. Zhao, X. Wu, B. Zuo, S. Bian, T. Li, X. Liu, Y. Jiang, C. Chen, J. Bi, J. Xu and L. Yu, J. Mater. Chem. A , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D4TA03666B
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements

A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of Guanfacine Extended Release for aggression and self-injurious behavior associated with Prader-Willi Syndrome
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Theresa Jacob
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
Introduction: Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS), a rare genetic disorder, affects development and behavior, frequently resulting in self-injury, aggression, hyperphagia, oppositional behavior, impulsivity and over-activity causing significant morbidity. Currently, limited therapeutic options are available to manage these neuropsychiatric manifestations. The aim of this clinical trial was to assess the efficacy of guanfacine-extended release (GXR) in reducing aggression and self-injury in individuals with PWS. Trial Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted under IRB approval. Methods: Subjects with a diagnosis of PWS, 6-35 years of age, with moderate to severe aggressive and/or self-injurious behavior as determined by the Clinical Global Impression (CGI)-Severity scale, were included in an 8-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-flexible dose clinical trial of GXR, that was followed by an 8-week open-label extension phase. Validated behavioral instruments and physician assessments measured the efficacy of GXR treatment, its safety and tolerability. Results: GXR was effective in reducing aggression/agitation and hyperactivity/noncompliance as measured by the Aberrant Behavior Checklist (ABC) scales (p=0.03). Overall aberrant behavior scores significantly reduced in the GXR arm. Aggression as measured by the Modified Overt Aggression Scale (MOAS) also showed a significant reduction. Skin-picking lesions as measured by the Self Injury Trauma (SIT) scale decreased in response to GXR. No serious adverse events were experienced by any of the study participants. Fatigue /sedation was the only adverse event significantly associated with GXR. The GXR group demonstrated significant overall clinical improvement as measured by the CGI-Improvement (CGI-I) scale. (p<0.01). Conclusion: Findings of this pragmatic trial strongly support the use of GXR for treatment of aggression, skin picking, and hyperactivity in children, adolescents, and adults with PWS. Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier - NCT05657860
Competing Interest Statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: DS has served as a consultant to Soleno Therapeutics, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Tonix Pharmaceuticals, and Consynance Therapeutics. MS and TJ have no other competing interests to report.
Clinical Trial
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05657860
Funding Statement
Author declarations.
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below:
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Maimonides Medical Center (# 2020-11-03-MMC). Written, IRB-approved informed consent was obtained from each participant's parent or legal guardian, and assent was obtained from each participant, as applicable.
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files and will be available upon its publication.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
Subject Area
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology
- Addiction Medicine (341)
- Allergy and Immunology (665)
- Anesthesia (180)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2624)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (314)
- Dermatology (221)
- Emergency Medicine (397)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (929)
- Epidemiology (12169)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (756)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (4061)
- Geriatric Medicine (384)
- Health Economics (675)
- Health Informatics (2620)
- Health Policy (997)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (976)
- Hematology (359)
- HIV/AIDS (843)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13657)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (789)
- Medical Education (398)
- Medical Ethics (109)
- Nephrology (429)
- Neurology (3829)
- Nursing (209)
- Nutrition (569)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (734)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (690)
- Oncology (2005)
- Ophthalmology (581)
- Orthopedics (238)
- Otolaryngology (304)
- Pain Medicine (250)
- Palliative Medicine (73)
- Pathology (471)
- Pediatrics (1107)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (459)
- Primary Care Research (447)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3397)
- Public and Global Health (6497)
- Radiology and Imaging (1388)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (806)
- Respiratory Medicine (869)
- Rheumatology (400)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (406)
- Sports Medicine (338)
- Surgery (441)
- Toxicology (52)
- Transplantation (185)
- Urology (165)

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest. 4. Write the introduction.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification. 3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review's introduction, briefly ...
These sections serve to establish a scholarly basis for the research or discussion within the paper. In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction.
The process involves selecting a topic about which the authors are knowledgeable and enthusiastic, conducting a literature search and critical analysis of the literature, and writing the article, which is composed of an abstract, introduction, body, and conclusion, with accompanying tables and figures.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review. Introduction. Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article's main topic.
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating, and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings ...
Here, I provide tips on planning and writing a review article, with examples of well-crafted review articles published in The FEBS Journal. The advice given here is mostly relevant for the writing of a traditional literature-based review rather than other forms of review such as a systematic review or meta-analysis, which have their own ...
The purpose of this chapter is to provide an introduction to the review process and give step by step guidance in conducting reviews for scientific journals. Interested readers might wish to read Lovejoy et al.'s (2011) primer for manuscript review, which contains annotated examples of reviews and an editor's decision letter.
Title: Title: 1 Identify the article as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both: Summary: Structured summary: 2 Write a structured summary including, as applicable, background; objectives; data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, treatments, study appraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions and implications of key findings; and systematic review ...
Step 4: Make an Introduction. In your introduction, provide a brief overview of the title's subject and purpose. Capture the reader's attention and clearly state your thesis or main point related to the title. For instance, you might start your article review template like this.
Journal Article Review. Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom. Here's how your outline might look: 1. Summary of the research and your overall impression. In your own words, summarize what the manuscript ...
Step 3: Organization aspect of the review. It is essential to focus on the structure you want to follow. It is necessary to help you understand how to approach your future work and process the article's content. The best and safest method to do an article review would be to summarize the article.
Article Review Definition of Genre Summaries and critiques are two ways to write a review of a scientific journal article. Both types of writing ask you first to read and understand an article from the primary literature about your topic. The summary involves briefly but accurately stating the key points of the article for a reader who has
Introduction The length of an introduction is usually one paragraph for a journal article review and two or three paragraphs for a longer book review. Include a few opening sentences that announce the author(s) and the title, and briefly explain the topic of the text. Present the aim of the text and summarise the main finding or key argument.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly. Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author. Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
Journal article reviews start with a header, including citation of the sources being reviewed. This citation is mentioned at the top of the review, following the APA style (refer to the APA style manual for more information). We will need the author's name for the article, title of the article, journal of the published article, volume and ...
Summaries and critiques are two ways to write a review of a scientific journal article. Both types of writing ask you first to read and understand an article from the primary literature about your topic. ... Article review writing Introduction The purpose of this document is to help students and researchers understand how review of an academic ...
Article Review vs. Response Paper . Now, let's consider the difference between an article review and a response paper: If you're assigned to critique a scholarly article, you will need to compose an article review.; If your subject of analysis is a popular article, you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper.; The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of ...
Briefly summarize what the paper is about and what the findings are. Try to put the findings of the paper into the context of the existing literature and current knowledge. Indicate the significance of the work and if it is novel or mainly confirmatory. Indicate the work's strengths, its quality and completeness.
Background Hospital-at-home (HAH) is increasingly becoming an alternative for in-hospital stay in selected clinical scenarios. Nevertheless, there is still a question whether HAH could be a viable option for acutely ill patients, otherwise hospitalized in departments of general-internal medicine. Methods This was a retrospective matched study, conducted at a telemedicine controlled HAH ...
Purpose The aim of this review was to methodically consider oxidative stress biomarkers in endurance performance events. The health benefits of exercise come at the cost of reactive oxygen species production. Reactive oxygen species and the continued development of oxidative stress may bring about muscular damage and inflammation, ultimately impairing exercise performance. Methods A search for ...
Introduction The length of an introduction is usually one paragraph for a journal article review and two or three paragraphs for a longer book review. Include a few opening sentences that announce the author(s) and the title, and briefly explain the topic of the text. Present the aim of the text and summarise the main finding or key argument.
Introduction ASCEND PLUS is a randomised controlled trial assessing the effects of oral semaglutide on the primary prevention of cardiovascular events in around 20,000 individuals with type 2 diabetes in the UK. The trial's innovative design includes a decentralised direct-to-participant invitation, recruitment, and follow-up model, relying on self-completion of online forms or telephone or ...
Thermoelectric materials are a highly promising category of energy conversion materials. In this paper, we present a multitude of approaches to enhance the efficacy of these materials. The review begins with an introduction to the fundamental concept of the thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT), a key parameter for a Journal of Materials Chemistry A Recent Review Articles
This literature review explores the significance of transparency in mitigating information asymmetry and its role in establishing trust among stakeholders. In the realm of banking, the concept of information transparency holds paramount significance, as it pertains to the perceived caliber of information disseminated by banks to their esteemed ...
Introduction: Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS), a rare genetic disorder, affects development and behavior, frequently resulting in self-injury, aggression, hyperphagia, oppositional behavior, impulsivity and over-activity causing significant morbidity. Currently, limited therapeutic options are available to manage these neuropsychiatric manifestations. The aim of this clinical trial was to assess ...