

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

Table of Contents
The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1
What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
What is the introduction for a research paper?
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
Why is the introduction important in a research paper?
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
Check out how Peace Alemede uses Paperpal to write her research paper

Peace Alemede, Student, University of Ilorin
Paperpal has been an excellent and beneficial tool for editing my research work. With the help of Paperpal, I am now able to write and produce results at a much faster rate. For instance, I recently used Paperpal to edit a research article that is currently being considered for publication. The tool allowed me to align the language of my paragraph ideas to a more academic setting, thereby saving me both time and resources. As a result, my work was deemed accurate for use. I highly recommend this tool to anyone in need of efficient and effective research paper editing. Peace Alemede, Student, University of Ilorin, Nigeria
Start Writing for Free
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address.
Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
1. Introduce the research topic:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
2. Determine a research niche:
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
3. Place your research within the research niche:
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the introduction in research papers.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
How long should the research paper introduction be?
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2
For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
What should be included in the research paper introduction?
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3
Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction.
- Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic.
- Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects.
- Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought.
- Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance.
- Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study
- Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Should I include citations in the introduction for a research paper?
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through.
Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review.
A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
Should I provide a literature review in the research paper introduction?
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following:
- Introduces the topic
- Establishes the study’s significance
- Provides an overview of the relevant literature
- Provides context for the study using literature
- Identifies knowledge gaps
However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction:
- Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research
- Avoid direct quoting
- Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Key points to remember
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
- Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
- Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
- Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
- Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, how to write a case study in research..., online ai writing tools: cost-efficient help for dissertation..., how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
AI Research Assist Your go-to AI-powered research assistant
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
Plan Writing & Consulting We create a business plan for you
Business Plan Review Get constructive feedback on your plan
Financial Forecasting We create financial projections for you
SBA Lending Assistance We help secure SBA loans for your business
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
How to Write a Compelling Business Plan Introduction (W/ Example)

Business Plan Template
- July 8, 2024

Be it a blog post, your business plan, or even a grocery list—catchy introductions can turn casual skimmers into avid readers.
Now imagine turning these casual readers into people who hang on to every word, eager to dive deeper into what your business has to offer. That’s the magic of a stellar business plan introduction!
But the main question is: How do you write such an irresistible introduction?
Well, we’ll help you with that in this blog post. We’ve also added a template and an example to enhance your overall understanding.
So let’s get started.
What is a business plan introduction?
An introduction sets the stage for your business plan by offering context and a high-level overview of what the subsequent sections will cover.
It’s different from your executive summary and is placed right after it. Rather than summarizing the entire plan, this section of your business plan focuses on providing essential background information.
Introductions are crisp and can be anywhere between 2 paragraphs to 1 page long.
Why do you need a business plan introduction?
You must be wondering: Why do I need an introduction when there’s an executive summary summarizing my entire plan?
Well, primarily to set the readers’ expectations straight. With its contextual overview, an introduction helps the readers understand what details they will uncover in the plan.
Besides, business plans are quite extensive. If a reader just wants a basic business overview and understanding of your objectives, they shouldn’t have to read your entire plan. An introduction should offer that by providing a quick insight into your business.
Additionally, introductions give your business plan a professional and organized head start. It sets the tone of your plan and generates excitement amongst readers to read further.
Whether you need a business plan to establish credibility for your business or generate funds—an introduction plays a huge role in setting up your business plan for success.
Let’s now understand the process of writing an introduction for your business plan.
How to write a compelling introduction for business plans?
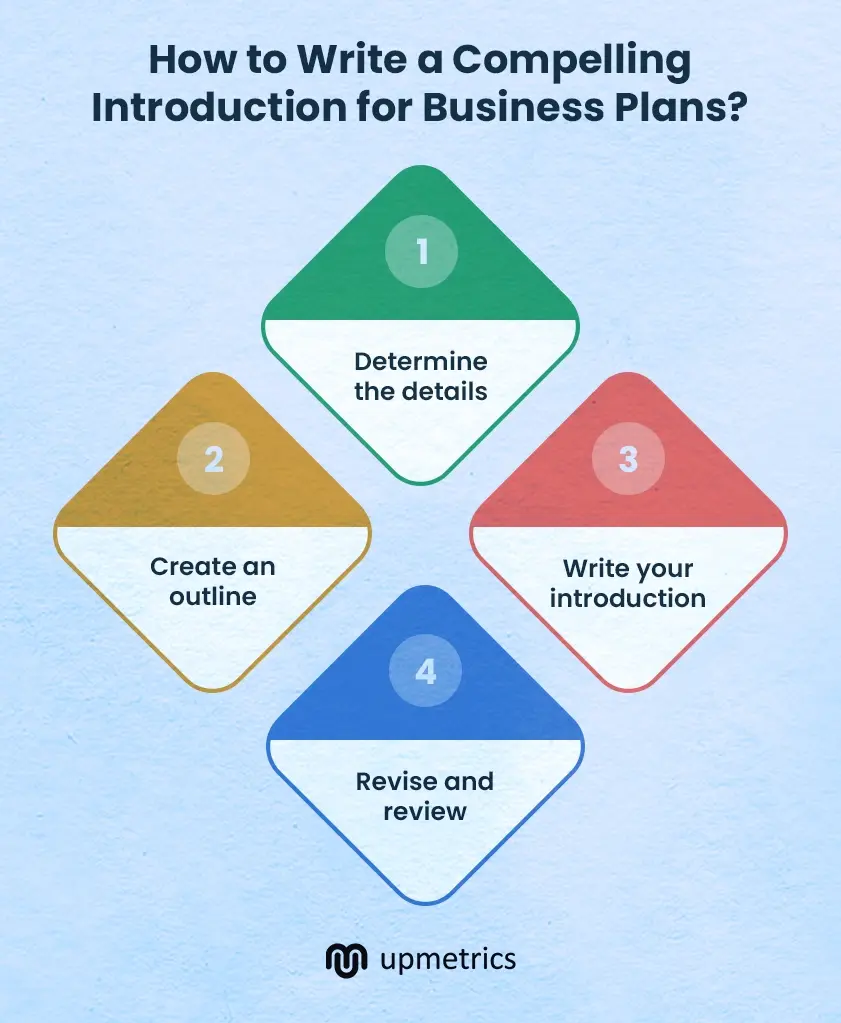
Wondering what you should include in your introduction and how to place it together? Check this step-by-step process and learn:
1. Determine the details
Writing an introduction gets much easier when you have a thorough understanding of what to include in it.
While there’s no fixed rule, here are a few points you can quickly touch in your introduction:
- Business background
- Business objectives
- Management overview
- Mission statement
- Core values
However, depending on the specialty or core focus of your plan, you can also include a general overview of a financial plan, marketing plan, target market, competitive analysis, and customer segments in your introduction.
Determine which of these will add value and context to your business plan before creating an outline of your introduction.
2. Create an outline
Before you start writing, take some time to create an outline. It will help you fill in the details more quickly and efficiently.
A general outline or structure of an introduction can be as follows:
- Opening statement
- Business overview
- Purpose of a business plan
- Preview of each section (optional)
- Closing statement
You don’t need to cover these sections in detail (specific sections of a business plan will do that). Just a line or two offering a macro overview of these aspects is enough.
3. Write your introduction
It’s now time to write an introduction by filling in the outline.
However, before that, finish writing your business plan . This will help translate the essence of your business plan more efficiently.
Now, place all the information you want to add to your introduction and weave them together in a cohesive narrative. Keep the tone persuasive and the content short.
4. Revise and review
Ask people from your team or someone professional to read your introduction.
Could they gather the context of your plan? Can they merely understand what the business does and aims to achieve from an introduction? Are they compelled to read your entire plan after reading an introduction?
If the answer to any of these questions is no, your introduction needs a revision and rework. Get it right before adding it to your business plan.
That’s how you write an introduction. Not a ninja task after all!
Business plan introduction template
Introductions don’t follow a strict structure. It simply answers a few core fundamental questions and sets the tone for your business plan.
Refer to this business plan introduction template and answer its questions to structure your section.
- Why are you starting this business?
- What are the problems you’re trying to solve?
- Who will buy from you?
- What makes your business different from competitors?
- How will you become profitable?
- When will you become profitable?
- What can the reader expect from your business plan?
It’s just a template. You can refine and remove these questions to suit your needs.
Business plan introduction example
Refer to this introduction example for a new-age gourmet restaurant, TasteBites, in the city.
TasteBites aims to create a unique dining experience combining gourmet flavors with a cozy, family-friendly atmosphere. Positioned in the heart of downtown, our location is ideal, surrounded by offices and residential areas, ensuring a steady stream of customers seeking high-quality dining options.
Managed by culinary experts and seasoned restaurateurs, TasteBites will feature a diverse menu highlighting local ingredients, catering to various tastes while maintaining high-profit margins. Our strategic location and commitment to quality will establish TasteBites as a beloved dining destination in the community.
The bottom line
Introductions are supposed to be exciting and persuasive. It should offer a true overview of your business opportunity and must reflect your preparedness to start this new venture.
Don’t focus too hard on proving your business’s capabilities in this section. You have an entire plan to do so. The idea here is to excite your readers and nudge them to read your business plan further.
Now, before you work on the introduction, ensure that you have your entire plan ready. If not, use Upmetrics’s AI business plan generator to whip up a fresh business plan in less than 10 minutes.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can i modify the introduction after writing the rest of the business plan.
Yes, you can. In fact , it’s r ecommended to review and edit your introduction in the end. By doing so, you can ensure that the introduction covers all the high-value points and that it offers an appropriate contextual overview of your plan.
What tone should I use in the business plan introduction?
You should use a professional confident tone while writing your business plan introduction. The introduction should portray your business in the best light and should confide in the reader’s interest. It should be sincere and subtle; persuading the readers to read your plan till the end.
How can I make my business plan introduction engaging?
To make your introduction engaging, start with a compelling question or statement to highlight the unique aspect of your business. Include details about profitability, new technology, or a strategic location to generate excitement in your readers. And most importantly, adapt a storytelling narrative to keep your readers hooked.
How long should the business plan introduction be?
A business plan introduction is ideally 2-3 paragraphs long. However, if there’s a lot to cover you can extend your introduction to 1 page. Anything longer than that needs to be redone.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Get started with Upmetrics Al
- 400+ sample business plans
- Al-powered financial planning
- Collaborative workspace
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning

Introductions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of introductions, offer strategies for creating effective introductions, and provide some examples of less effective introductions to avoid.
The role of introductions
Introductions and conclusions can be the most difficult parts of papers to write. Usually when you sit down to respond to an assignment, you have at least some sense of what you want to say in the body of your paper. You might have chosen a few examples you want to use or have an idea that will help you answer the main question of your assignment; these sections, therefore, may not be as hard to write. And it’s fine to write them first! But in your final draft, these middle parts of the paper can’t just come out of thin air; they need to be introduced and concluded in a way that makes sense to your reader.
Your introduction and conclusion act as bridges that transport your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis. If your readers pick up your paper about education in the autobiography of Frederick Douglass, for example, they need a transition to help them leave behind the world of Chapel Hill, television, e-mail, and The Daily Tar Heel and to help them temporarily enter the world of nineteenth-century American slavery. By providing an introduction that helps your readers make a transition between their own world and the issues you will be writing about, you give your readers the tools they need to get into your topic and care about what you are saying. Similarly, once you’ve hooked your readers with the introduction and offered evidence to prove your thesis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. (See our handout on conclusions .)
Note that what constitutes a good introduction may vary widely based on the kind of paper you are writing and the academic discipline in which you are writing it. If you are uncertain what kind of introduction is expected, ask your instructor.
Why bother writing a good introduction?
You never get a second chance to make a first impression. The opening paragraph of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions of your argument, your writing style, and the overall quality of your work. A vague, disorganized, error-filled, off-the-wall, or boring introduction will probably create a negative impression. On the other hand, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will start your readers off thinking highly of you, your analytical skills, your writing, and your paper.
Your introduction is an important road map for the rest of your paper. Your introduction conveys a lot of information to your readers. You can let them know what your topic is, why it is important, and how you plan to proceed with your discussion. In many academic disciplines, your introduction should contain a thesis that will assert your main argument. Your introduction should also give the reader a sense of the kinds of information you will use to make that argument and the general organization of the paragraphs and pages that will follow. After reading your introduction, your readers should not have any major surprises in store when they read the main body of your paper.
Ideally, your introduction will make your readers want to read your paper. The introduction should capture your readers’ interest, making them want to read the rest of your paper. Opening with a compelling story, an interesting question, or a vivid example can get your readers to see why your topic matters and serve as an invitation for them to join you for an engaging intellectual conversation (remember, though, that these strategies may not be suitable for all papers and disciplines).
Strategies for writing an effective introduction
Start by thinking about the question (or questions) you are trying to answer. Your entire essay will be a response to this question, and your introduction is the first step toward that end. Your direct answer to the assigned question will be your thesis, and your thesis will likely be included in your introduction, so it is a good idea to use the question as a jumping off point. Imagine that you are assigned the following question:
Drawing on the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , discuss the relationship between education and slavery in 19th-century America. Consider the following: How did white control of education reinforce slavery? How did Douglass and other enslaved African Americans view education while they endured slavery? And what role did education play in the acquisition of freedom? Most importantly, consider the degree to which education was or was not a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
You will probably refer back to your assignment extensively as you prepare your complete essay, and the prompt itself can also give you some clues about how to approach the introduction. Notice that it starts with a broad statement and then narrows to focus on specific questions from the book. One strategy might be to use a similar model in your own introduction—start off with a big picture sentence or two and then focus in on the details of your argument about Douglass. Of course, a different approach could also be very successful, but looking at the way the professor set up the question can sometimes give you some ideas for how you might answer it. (See our handout on understanding assignments for additional information on the hidden clues in assignments.)
Decide how general or broad your opening should be. Keep in mind that even a “big picture” opening needs to be clearly related to your topic; an opening sentence that said “Human beings, more than any other creatures on earth, are capable of learning” would be too broad for our sample assignment about slavery and education. If you have ever used Google Maps or similar programs, that experience can provide a helpful way of thinking about how broad your opening should be. Imagine that you’re researching Chapel Hill. If what you want to find out is whether Chapel Hill is at roughly the same latitude as Rome, it might make sense to hit that little “minus” sign on the online map until it has zoomed all the way out and you can see the whole globe. If you’re trying to figure out how to get from Chapel Hill to Wrightsville Beach, it might make more sense to zoom in to the level where you can see most of North Carolina (but not the rest of the world, or even the rest of the United States). And if you are looking for the intersection of Ridge Road and Manning Drive so that you can find the Writing Center’s main office, you may need to zoom all the way in. The question you are asking determines how “broad” your view should be. In the sample assignment above, the questions are probably at the “state” or “city” level of generality. When writing, you need to place your ideas in context—but that context doesn’t generally have to be as big as the whole galaxy!
Try writing your introduction last. You may think that you have to write your introduction first, but that isn’t necessarily true, and it isn’t always the most effective way to craft a good introduction. You may find that you don’t know precisely what you are going to argue at the beginning of the writing process. It is perfectly fine to start out thinking that you want to argue a particular point but wind up arguing something slightly or even dramatically different by the time you’ve written most of the paper. The writing process can be an important way to organize your ideas, think through complicated issues, refine your thoughts, and develop a sophisticated argument. However, an introduction written at the beginning of that discovery process will not necessarily reflect what you wind up with at the end. You will need to revise your paper to make sure that the introduction, all of the evidence, and the conclusion reflect the argument you intend. Sometimes it’s easiest to just write up all of your evidence first and then write the introduction last—that way you can be sure that the introduction will match the body of the paper.
Don’t be afraid to write a tentative introduction first and then change it later. Some people find that they need to write some kind of introduction in order to get the writing process started. That’s fine, but if you are one of those people, be sure to return to your initial introduction later and rewrite if necessary.
Open with something that will draw readers in. Consider these options (remembering that they may not be suitable for all kinds of papers):
- an intriguing example —for example, Douglass writes about a mistress who initially teaches him but then ceases her instruction as she learns more about slavery.
- a provocative quotation that is closely related to your argument —for example, Douglass writes that “education and slavery were incompatible with each other.” (Quotes from famous people, inspirational quotes, etc. may not work well for an academic paper; in this example, the quote is from the author himself.)
- a puzzling scenario —for example, Frederick Douglass says of slaves that “[N]othing has been left undone to cripple their intellects, darken their minds, debase their moral nature, obliterate all traces of their relationship to mankind; and yet how wonderfully they have sustained the mighty load of a most frightful bondage, under which they have been groaning for centuries!” Douglass clearly asserts that slave owners went to great lengths to destroy the mental capacities of slaves, yet his own life story proves that these efforts could be unsuccessful.
- a vivid and perhaps unexpected anecdote —for example, “Learning about slavery in the American history course at Frederick Douglass High School, students studied the work slaves did, the impact of slavery on their families, and the rules that governed their lives. We didn’t discuss education, however, until one student, Mary, raised her hand and asked, ‘But when did they go to school?’ That modern high school students could not conceive of an American childhood devoid of formal education speaks volumes about the centrality of education to American youth today and also suggests the significance of the deprivation of education in past generations.”
- a thought-provoking question —for example, given all of the freedoms that were denied enslaved individuals in the American South, why does Frederick Douglass focus his attentions so squarely on education and literacy?
Pay special attention to your first sentence. Start off on the right foot with your readers by making sure that the first sentence actually says something useful and that it does so in an interesting and polished way.
How to evaluate your introduction draft
Ask a friend to read your introduction and then tell you what they expect the paper will discuss, what kinds of evidence the paper will use, and what the tone of the paper will be. If your friend is able to predict the rest of your paper accurately, you probably have a good introduction.
Five kinds of less effective introductions
1. The placeholder introduction. When you don’t have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don’t really say much. They exist just to take up the “introduction space” in your paper. If you had something more effective to say, you would probably say it, but in the meantime this paragraph is just a place holder.
Example: Slavery was one of the greatest tragedies in American history. There were many different aspects of slavery. Each created different kinds of problems for enslaved people.
2. The restated question introduction. Restating the question can sometimes be an effective strategy, but it can be easy to stop at JUST restating the question instead of offering a more specific, interesting introduction to your paper. The professor or teaching assistant wrote your question and will be reading many essays in response to it—they do not need to read a whole paragraph that simply restates the question.
Example: The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass discusses the relationship between education and slavery in 19th century America, showing how white control of education reinforced slavery and how Douglass and other enslaved African Americans viewed education while they endured. Moreover, the book discusses the role that education played in the acquisition of freedom. Education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
3. The Webster’s Dictionary introduction. This introduction begins by giving the dictionary definition of one or more of the words in the assigned question. Anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and copy down what Webster says. If you want to open with a discussion of an important term, it may be far more interesting for you (and your reader) if you develop your own definition of the term in the specific context of your class and assignment. You may also be able to use a definition from one of the sources you’ve been reading for class. Also recognize that the dictionary is also not a particularly authoritative work—it doesn’t take into account the context of your course and doesn’t offer particularly detailed information. If you feel that you must seek out an authority, try to find one that is very relevant and specific. Perhaps a quotation from a source reading might prove better? Dictionary introductions are also ineffective simply because they are so overused. Instructors may see a great many papers that begin in this way, greatly decreasing the dramatic impact that any one of those papers will have.
Example: Webster’s dictionary defines slavery as “the state of being a slave,” as “the practice of owning slaves,” and as “a condition of hard work and subjection.”
4. The “dawn of man” introduction. This kind of introduction generally makes broad, sweeping statements about the relevance of this topic since the beginning of time, throughout the world, etc. It is usually very general (similar to the placeholder introduction) and fails to connect to the thesis. It may employ cliches—the phrases “the dawn of man” and “throughout human history” are examples, and it’s hard to imagine a time when starting with one of these would work. Instructors often find them extremely annoying.
Example: Since the dawn of man, slavery has been a problem in human history.
5. The book report introduction. This introduction is what you had to do for your elementary school book reports. It gives the name and author of the book you are writing about, tells what the book is about, and offers other basic facts about the book. You might resort to this sort of introduction when you are trying to fill space because it’s a familiar, comfortable format. It is ineffective because it offers details that your reader probably already knows and that are irrelevant to the thesis.
Example: Frederick Douglass wrote his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave , in the 1840s. It was published in 1986 by Penguin Books. In it, he tells the story of his life.
And now for the conclusion…
Writing an effective introduction can be tough. Try playing around with several different options and choose the one that ends up sounding best to you!
Just as your introduction helps readers make the transition to your topic, your conclusion needs to help them return to their daily lives–but with a lasting sense of how what they have just read is useful or meaningful. Check out our handout on conclusions for tips on ending your paper as effectively as you began it!
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . New York: Dover.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
How to write an effective introduction for your research paper
Last updated
20 January 2024
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
However, the introduction is a vital element of your research paper . It helps the reader decide whether your paper is worth their time. As such, it's worth taking your time to get it right.
In this article, we'll tell you everything you need to know about writing an effective introduction for your research paper.
- The importance of an introduction in research papers
The primary purpose of an introduction is to provide an overview of your paper. This lets readers gauge whether they want to continue reading or not. The introduction should provide a meaningful roadmap of your research to help them make this decision. It should let readers know whether the information they're interested in is likely to be found in the pages that follow.
Aside from providing readers with information about the content of your paper, the introduction also sets the tone. It shows readers the style of language they can expect, which can further help them to decide how far to read.
When you take into account both of these roles that an introduction plays, it becomes clear that crafting an engaging introduction is the best way to get your paper read more widely. First impressions count, and the introduction provides that impression to readers.
- The optimum length for a research paper introduction
While there's no magic formula to determine exactly how long a research paper introduction should be, there are a few guidelines. Some variables that impact the ideal introduction length include:
Field of study
Complexity of the topic
Specific requirements of the course or publication
A commonly recommended length of a research paper introduction is around 10% of the total paper’s length. So, a ten-page paper has a one-page introduction. If the topic is complex, it may require more background to craft a compelling intro. Humanities papers tend to have longer introductions than those of the hard sciences.
The best way to craft an introduction of the right length is to focus on clarity and conciseness. Tell the reader only what is necessary to set up your research. An introduction edited down with this goal in mind should end up at an acceptable length.
- Evaluating successful research paper introductions
A good way to gauge how to create a great introduction is by looking at examples from across your field. The most influential and well-regarded papers should provide some insights into what makes a good introduction.
Dissecting examples: what works and why
We can make some general assumptions by looking at common elements of a good introduction, regardless of the field of research.
A common structure is to start with a broad context, and then narrow that down to specific research questions or hypotheses. This creates a funnel that establishes the scope and relevance.
The most effective introductions are careful about the assumptions they make regarding reader knowledge. By clearly defining key terms and concepts instead of assuming the reader is familiar with them, these introductions set a more solid foundation for understanding.
To pull in the reader and make that all-important good first impression, excellent research paper introductions will often incorporate a compelling narrative or some striking fact that grabs the reader's attention.
Finally, good introductions provide clear citations from past research to back up the claims they're making. In the case of argumentative papers or essays (those that take a stance on a topic or issue), a strong thesis statement compels the reader to continue reading.
Common pitfalls to avoid in research paper introductions
You can also learn what not to do by looking at other research papers. Many authors have made mistakes you can learn from.
We've talked about the need to be clear and concise. Many introductions fail at this; they're verbose, vague, or otherwise fail to convey the research problem or hypothesis efficiently. This often comes in the form of an overemphasis on background information, which obscures the main research focus.
Ensure your introduction provides the proper emphasis and excitement around your research and its significance. Otherwise, fewer people will want to read more about it.
- Crafting a compelling introduction for a research paper
Let’s take a look at the steps required to craft an introduction that pulls readers in and compels them to learn more about your research.
Step 1: Capturing interest and setting the scene
To capture the reader's interest immediately, begin your introduction with a compelling question, a surprising fact, a provocative quote, or some other mechanism that will hook readers and pull them further into the paper.
As they continue reading, the introduction should contextualize your research within the current field, showing readers its relevance and importance. Clarify any essential terms that will help them better understand what you're saying. This keeps the fundamentals of your research accessible to all readers from all backgrounds.
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information
Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes:
It helps to clarify the topic for the reader
It establishes the depth of your research
The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
For argumentative papers, you'll want to develop engaging background narratives. These should provide context for the argument you'll be presenting.
For empirical papers, highlighting past research is the key. Often, there will be some questions that weren't answered in those past papers. If your paper is focused on those areas, those papers make ideal candidates for you to discuss and critique in your introduction.
Step 3: Pinpointing the research challenge
To capture the attention of the reader, you need to explain what research challenges you'll be discussing.
For argumentative papers, this involves articulating why the argument you'll be making is important. What is its relevance to current discussions or problems? What is the potential impact of people accepting or rejecting your argument?
For empirical papers, explain how your research is addressing a gap in existing knowledge. What new insights or contributions will your research bring to your field?
Step 4: Clarifying your research aims and objectives
We mentioned earlier that the introduction to a research paper can serve as a roadmap for what's within. We've also frequently discussed the need for clarity. This step addresses both of these.
When writing an argumentative paper, craft a thesis statement with impact. Clearly articulate what your position is and the main points you intend to present. This will map out for the reader exactly what they'll get from reading the rest.
For empirical papers, focus on formulating precise research questions and hypotheses. Directly link them to the gaps or issues you've identified in existing research to show the reader the precise direction your research paper will take.
Step 5: Sketching the blueprint of your study
Continue building a roadmap for your readers by designing a structured outline for the paper. Guide the reader through your research journey, explaining what the different sections will contain and their relationship to one another.
This outline should flow seamlessly as you move from section to section. Creating this outline early can also help guide the creation of the paper itself, resulting in a final product that's better organized. In doing so, you'll craft a paper where each section flows intuitively from the next.
Step 6: Integrating your research question
To avoid letting your research question get lost in background information or clarifications, craft your introduction in such a way that the research question resonates throughout. The research question should clearly address a gap in existing knowledge or offer a new perspective on an existing problem.
Tell users your research question explicitly but also remember to frequently come back to it. When providing context or clarification, point out how it relates to the research question. This keeps your focus where it needs to be and prevents the topic of the paper from becoming under-emphasized.

Step 7: Establishing the scope and limitations
So far, we've talked mostly about what's in the paper and how to convey that information to readers. The opposite is also important. Information that's outside the scope of your paper should be made clear to the reader in the introduction so their expectations for what is to follow are set appropriately.
Similarly, be honest and upfront about the limitations of the study. Any constraints in methodology, data, or how far your findings can be generalized should be fully communicated in the introduction.
Step 8: Concluding the introduction with a promise
The final few lines of the introduction are your last chance to convince people to continue reading the rest of the paper. Here is where you should make it very clear what benefit they'll get from doing so. What topics will be covered? What questions will be answered? Make it clear what they will get for continuing.
By providing a quick recap of the key points contained in the introduction in its final lines and properly setting the stage for what follows in the rest of the paper, you refocus the reader's attention on the topic of your research and guide them to read more.
- Research paper introduction best practices
Following the steps above will give you a compelling introduction that hits on all the key points an introduction should have. Some more tips and tricks can make an introduction even more polished.
As you follow the steps above, keep the following tips in mind.
Set the right tone and style
Like every piece of writing, a research paper should be written for the audience. That is to say, it should match the tone and style that your academic discipline and target audience expect. This is typically a formal and academic tone, though the degree of formality varies by field.
Kno w the audience
The perfect introduction balances clarity with conciseness. The amount of clarification required for a given topic depends greatly on the target audience. Knowing who will be reading your paper will guide you in determining how much background information is required.
Adopt the CARS (create a research space) model
The CARS model is a helpful tool for structuring introductions. This structure has three parts. The beginning of the introduction establishes the general research area. Next, relevant literature is reviewed and critiqued. The final section outlines the purpose of your study as it relates to the previous parts.
Master the art of funneling
The CARS method is one example of a well-funneled introduction. These start broadly and then slowly narrow down to your specific research problem. It provides a nice narrative flow that provides the right information at the right time. If you stray from the CARS model, try to retain this same type of funneling.
Incorporate narrative element
People read research papers largely to be informed. But to inform the reader, you have to hold their attention. A narrative style, particularly in the introduction, is a great way to do that. This can be a compelling story, an intriguing question, or a description of a real-world problem.
Write the introduction last
By writing the introduction after the rest of the paper, you'll have a better idea of what your research entails and how the paper is structured. This prevents the common problem of writing something in the introduction and then forgetting to include it in the paper. It also means anything particularly exciting in the paper isn’t neglected in the intro.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 9 November 2024
Last updated: 24 October 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 14 July 2023
Last updated: 30 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, a whole new way to understand your customer is here, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents
A research paper is a detailed academic document that presents the results of a study or investigation. It involves critical analysis, evidence-based arguments, and a thorough exploration of a specific topic. Writing a research paper requires following a structured format to ensure clarity, coherence, and academic rigor. This article explains the structure of a research paper, provides examples, and offers a practical writing guide.

Research Paper
A research paper is a formal document that reports on original research or synthesizes existing knowledge on a specific topic. It aims to explore a research question, present findings, and contribute to the broader field of study.
For example, a research paper in environmental science may investigate the effects of urbanization on local biodiversity, presenting data and interpretations supported by credible sources.
Importance of Research Papers
- Knowledge Contribution: Adds to the academic or professional understanding of a subject.
- Skill Development: Enhances critical thinking, analytical, and writing skills.
- Evidence-Based Arguments: Encourages the use of reliable sources to support claims.
- Professional Recognition: Serves as a medium for sharing findings with peers and stakeholders.
Structure of a Research Paper
1. title page.
The title page includes the paper’s title, author’s name(s), affiliation(s), and submission date.
- Title: “The Impact of Remote Work on Employee Productivity During the COVID-19 Pandemic”
- Author: Jane Doe
- Affiliation: XYZ University
2. Abstract
A concise summary of the research, typically 150–300 words, covering the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions.
- Example: “This study examines the effects of remote work on employee productivity. Data collected from surveys and interviews revealed that productivity increased for 65% of respondents, primarily due to flexible schedules and reduced commuting times.”
3. Introduction
The introduction sets the context for the research, explains its significance, and presents the research question or hypothesis.
- Background information.
- Problem statement.
- Objectives and research questions.
- Example: “With the rapid shift to remote work during the pandemic, understanding its impact on productivity has become crucial. This study aims to explore the benefits and challenges of remote work in various industries.”
4. Literature Review
The literature review summarizes and critiques existing research, identifying gaps that the current study addresses.
- Overview of relevant studies.
- Theoretical frameworks.
- Research gaps.
- Example: “Previous studies highlight improved flexibility in remote work but lack comprehensive insights into its impact on team collaboration and long-term productivity.”
5. Methodology
This section explains how the research was conducted, ensuring transparency and replicability.
- Research design (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods).
- Data collection methods (surveys, interviews, experiments).
- Data analysis techniques.
- Ethical considerations.
- Example: “A mixed-methods approach was adopted, using online surveys to collect quantitative data from 200 employees and semi-structured interviews with 20 managers to gather qualitative insights.”
The results section presents the findings of the research in an objective manner, often using tables, graphs, or charts.
- Example: “Survey results indicated that 70% of employees reported higher job satisfaction, while 40% experienced challenges with communication.”
7. Discussion
This section interprets the results, relates them to the research questions, and compares them with findings from previous studies.
- Analysis and interpretation.
- Implications of the findings.
- Limitations of the study.
- Example: “The findings suggest that while remote work enhances individual productivity, it poses challenges for team-based tasks, highlighting the need for improved communication tools.”
8. Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the key findings, emphasizes their significance, and suggests future research directions.
- Example: “This study demonstrates that remote work can enhance productivity, but organizations must address communication barriers to maximize its benefits. Future research should focus on sector-specific impacts of remote work.”
9. References
A list of all the sources cited in the paper, formatted according to the required style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
10. Appendices
Supplementary materials, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or additional analyses, are included here.
Examples of Research Papers
1. education.
Title: “The Effectiveness of Interactive Learning Tools in Enhancing Student Engagement”
- Abstract: Summarizes findings that interactive tools like Kahoot and Quizlet improved engagement by 45% in middle school classrooms.
- Methods: Quantitative surveys with 300 students and qualitative interviews with 15 teachers.
2. Healthcare
Title: “Telemedicine in Rural Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges”
- Abstract: Highlights how telemedicine improved access to healthcare for 80% of surveyed rural residents, despite connectivity issues.
- Methods: Mixed methods involving patient surveys and interviews with healthcare providers.
3. Business
Title: “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Customer Experience”
- Abstract: Discusses how AI tools like chatbots reduced response times by 30%, improving customer satisfaction in the e-commerce sector.
- Methods: Case studies of three leading e-commerce companies and customer feedback analysis.
Writing Guide for a Research Paper
Step 1: choose a topic.
Select a topic that aligns with your interests, is relevant to your field, and has sufficient scope for research.
Step 2: Conduct Preliminary Research
Review existing literature to understand the context and identify research gaps.
Step 3: Develop a Thesis Statement
Formulate a clear and concise statement summarizing the main argument or purpose of your research.
Step 4: Create an Outline
Organize your ideas and structure your paper into sections, ensuring a logical flow.
Step 5: Write the First Draft
Focus on content rather than perfection. Start with the sections you find easiest to write.
Step 6: Edit and Revise
Review for clarity, coherence, grammar, and adherence to formatting guidelines. Seek feedback from peers or mentors.
Step 7: Format and Finalize
Ensure your paper complies with the required citation style and formatting rules.
Tips for Writing an Effective Research Paper
- Be Clear and Concise: Avoid jargon and lengthy explanations; focus on delivering clear arguments.
- Use Credible Sources: Rely on peer-reviewed articles, books, and authoritative data.
- Follow a Logical Structure: Maintain a coherent flow from introduction to conclusion.
- Use Visual Aids: Include tables, charts, and graphs to summarize data effectively.
- Cite Sources Properly: Avoid plagiarism by adhering to proper citation standards.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Lack of Focus: A vague or overly broad topic can weaken the paper’s impact.
- Poor Organization: A disorganized structure makes the paper hard to follow.
- Inadequate Analysis: Merely presenting data without interpreting its significance undermines the paper’s value.
- Ignoring Guidelines: Failing to meet formatting or citation requirements can detract from professionalism.
A research paper is a critical academic tool that requires careful planning, organization, and execution. By following a clear structure that includes essential components like the introduction, methodology, results, and discussion, researchers can effectively communicate their findings. Understanding the elements and employing best practices ensures a well-crafted and impactful research paper that contributes meaningfully to the field.
- Babbie, E. (2020). The Practice of Social Research . Cengage Learning.
- Bryman, A. (2016). Social Research Methods . Oxford University Press.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., & Williams, J. M. (2016). The Craft of Research . University of Chicago Press.
- APA (2020). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types

APA Table of Contents – Format and Example

Survey Instruments – List and Their Uses

Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to...

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Resources
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly the methodological approach used to examine the research problem, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and outlining the remaining structure and organization of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools; Swales, John, and Hazem Najjar. "The Writing of Research Article Introductions." Written Communication 4 (April 1987): 175-191.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding?
According to Reyes, there are three overarching goals of a good introduction: 1) ensure that you summarize prior studies about the topic in a manner that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem; 2) explain how your study specifically addresses gaps in the literature, insufficient consideration of the topic, or other deficiency in the literature; and, 3) note the broader theoretical, empirical, and/or policy contributions and implications of your research.
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraphs of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will lead your readers to think highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach. All introductions should conclude with a brief paragraph that describes the organization of the rest of the paper.
Hirano, Eliana. “Research Article Introductions in English for Specific Purposes: A Comparison between Brazilian, Portuguese, and English.” English for Specific Purposes 28 (October 2009): 240-250; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide. Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education; Swales, John, and Hazem Najjar. "The Writing of Research Article Introductions." Written Communication 4 (April 1987): 175-191.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why should I read it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow your analysis to more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your research problem and the rationale for studying it [often written as a series of key questions to be addressed or framed as a hypothesis or set of assumptions to be tested] and, whenever possible, a description of the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
Below is a general outline for thinking about the introduction: 1. Establish an area to research by:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
2. Identify a research niche by:
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
3. Place your research within the research niche by:
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: It is often useful to review the introduction late in the writing process. This is appropriate because outcomes are unknown until you've completed the study. After you complete writing the body of the paper, go back and review introductory descriptions of the structure of the paper, the method of data gathering, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion. Reviewing and, if necessary, rewriting the introduction ensures that it correctly matches the overall structure of your final paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your research . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the topic.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction. For example, a delimitating statement could read, "Although many factors can be understood to impact the likelihood young people will vote, this study will focus on socioeconomic factors related to the need to work full-time while in school." The point is not to document every possible delimiting factor, but to highlight why previously researched issues related to the topic were not addressed.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation,
- The time period your study covers, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. Not only do you clearly establish what you intend to accomplish in your research, but you should also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria understood as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
ANOTHER NOTE: Do not view delimitating statements as admitting to an inherent failing or shortcoming in your research. They are an accepted element of academic writing intended to keep the reader focused on the research problem by explicitly defining the conceptual boundaries and scope of your study. It addresses any critical questions in the reader's mind of, "Why the hell didn't the author examine this?"
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review--that comes next. It consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature [with citations] that establishes a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down menu under this tab for " Background Information " regarding types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
A research problem in the social sciences can come across as dry and uninteresting to anyone unfamiliar with the topic . Therefore, one of the goals of your introduction is to make readers want to read your paper. Here are several strategies you can use to grab the reader's attention:
- Open with a compelling story . Almost all research problems in the social sciences, no matter how obscure or esoteric , are really about the lives of people. Telling a story that humanizes an issue can help illuminate the significance of the problem and help the reader empathize with those affected by the condition being studied.
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected, anecdote . During your review of the literature, make note of any quotes or anecdotes that grab your attention because they can used in your introduction to highlight the research problem in a captivating way.
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question . Your research problem should be framed by a set of questions to be addressed or hypotheses to be tested. However, a provocative question can be presented in the beginning of your introduction that challenges an existing assumption or compels the reader to consider an alternative viewpoint that helps establish the significance of your study.
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity . This involves highlighting an interesting quandary concerning the research problem or describing contradictory findings from prior studies about a topic. Posing what is essentially an unresolved intellectual riddle about the problem can engage the reader's interest in the study.
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important . Draw upon the findings of others to demonstrate the significance of the problem and to describe how your study builds upon or offers alternatives ways of investigating this prior research.
NOTE: It is important that you choose only one of the suggested strategies for engaging your readers. This avoids giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance and does not distract from the substance of your study.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies. Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction. Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Swales, John and Christine B. Feak. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Skills and Tasks . 2nd edition. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2004 ; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific terminology that readers may be unfamiliar with. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source because it doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term or concept may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, use a subject specific dictionary or encyclopedia [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology]. A good database for obtaining definitive definitions of concepts or terms is Credo Reference .
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper. Florida International University; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "Where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance. For example, a study that investigates coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exports in Africa. If a research problem requires a substantial exploration of the historical context, do this in the literature review section. In your introduction, make note of this as part of the "roadmap" [see below] that you use to describe the organization of your paper.
Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a brief description of the rest of the paper [the "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect. A roadmap is important because it helps the reader place the research problem within the context of their own perspectives about the topic. In addition, concluding your introduction with an explicit roadmap tells the reader that you have a clear understanding of the structural purpose of your paper. In this way, the roadmap acts as a type of promise to yourself and to your readers that you will follow a consistent and coherent approach to addressing the topic of inquiry. Refer to it often to help keep your writing focused and organized.
Cassuto, Leonard. “On the Dissertation: How to Write the Introduction.” The Chronicle of Higher Education , May 28, 2018; Radich, Michael. A Student's Guide to Writing in East Asian Studies . (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Writing n. d.), pp. 35-37.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: The C.A.R.S. Model >>
- Last Updated: Nov 22, 2024 3:49 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The five steps in this article will help you put together an effective introduction for either type of research paper. Scribbr's grammar checker can help ensure your research paper is free of grammar and punctuation errors! Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes
In this article, we explain what a business plan introduction is and provide a template and example of an effective introduction to help you write your own. Related: What Is a Business Plan? What is a business plan introduction?
The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation. The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the ...
What is a business plan introduction? An introduction sets the stage for your business plan by offering context and a high-level overview of what the subsequent sections will cover. It's different from your executive summary and is placed right after it.
This handout will explain the functions of introductions, offer strategies for creating effective introductions, and provide some examples of less effective introductions to avoid. Introductions and conclusions can be the most difficult parts of papers to write.
Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us: Poor planning is the number one reason I see a business fail. Being prepared is why people succeed. This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
In this article, we'll tell you everything you need to know about writing an effective introduction for your research paper. The primary purpose of an introduction is to provide an overview of your paper. This lets readers gauge whether they want to continue reading or not.
A research paper is a detailed academic document that presents the results of a study or investigation. It involves critical analysis, evidence-based arguments, and a thorough exploration of a specific topic. Writing a research paper requires following a structured format to ensure clarity, coherence, and academic rigor.
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly ...
The 4-step approach to writing the Introduction section As a rule of thumb, this section accounts for about 10% of the total word count of the body of a typical research paper, or about 400 words spread over three paragraphs in a 4000-word paper. 1 With that, let us now understand how to write the Introduction section step-by-step: 1.