
Consequences for Students Who Don’t Do Homework
Many parents wonder what are some consequences for students who don’t do homework.
It can be a challenge to get your students to do their homework especially if they don’t like the topic. When the situation occurs that they don’t want to start or complete their homework, it is time to implement consequences.
Before doing so, you need to first identify why they don’t want to complete it in the first place.
Find the Problem
Before handing down any consequences, you should first find out why they do not want to do their homework. There can be different reasons why and finding out the right one is important for fixing the situation.

1. Distraction
The first reason why they are not doing their homework would be because they are distracted.
Distraction is the worst thing you can experience when you are trying to get important things done. Whether it is a student in school or a worker at a job, it will take your attention away from what is important and make your mind wander around.
It is even worse if the person is dealing with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a condition that both children and adults have that limits their focus when attempting to finish a task.
If you are noticing that your student is not able to focus while doing their homework, the best way to solve this problem would be to limit their distraction. This would be by either placing them in a room with the least distractions or by taking away anything they use that distraction like electronics.
2. They are Struggling
Another reason why they might not want to do or start their homework would be because they are struggling and might not know the material they are doing the homework on. This is a very common problem for students who don’t do their homework because not knowing how to do it will discourage them and they will be stuck.
This will lead them to not want to do it and will use any excuse not to finish.
What you need to do in this situation is bring in a tutor to help your child understand the material and be encouraged to finish it.
We at Beingagoodparent realize the struggle that many students face when it comes to understanding a topic in school so we partnered with Redemption Tutoring to help parents find affordable qualified tutors to help their children. By mentioning Beingagoodparen t, they will give you a 20% discount on all tutoring when you sign up.
Click here to sign up for tutoring.

Limit Their Freedom
The first consequence you can implement for students who don’t do their homework would be to limit their freedom.
What I mean by that is limit what they want to do when trying to have fun. Whether it’s an 8-year-old from watching cartoons or a highschooler from going out with his friends, you need to find out what they love to do the most and limit their time of that.
When someone is restricted from doing what they love, they will do anything to try and regain their freedom of doing it and in this case, they will have to finish their homework before regaining the freedom to do what they love.
This works well for any age level and they will regret not finishing earlier because their time of fun will be cut out until they finish.
Take Away Electronics
A great consequence you can implement when your children don’t want to do their homework is to take away their electronics. Children nowadays are addicted to their electronics because it is their form of entertainment.
It is what they love to spend time on once they come back from school and it is most likely the reason they are distracted enough not to do their homework. If you take away their form of entertainment, they will have nothing else to do but to finish the assignments they have due.
Take a Different Approach in Fixing the Problem
Many parents want to punish their children for not doing their homework but a better strategy to have them finish their homework rather than punishing them would be to set rewards if they do finish.
This puts a positive approach for them to finish the homework rather than making it a negative situation if they don’t finish.
The reason why setting rewards is a better solution than threatening consequences would be because they will approach the homework assignment with a positive mindset rather than a negative one.
If they go in knowing that there is a prize at the end, they will be excited to finish and get it done. If they go in knowing that if they don’t finish, they will have a consequence, they will go in with fear and that will put a negative connotation on homework assignments.
Setting rewards also motivates them to finish.
Think of it like how people get paid at work. They know that if they go to work and do their job, they will get a paycheck so even though many people don’t like their job, they still go in every day and finish because they know that they will be getting a paycheck. They are motivated to work hard by knowing that they will receive a check after.
This is the same concept you should apply for any student that does not want to do their homework. They should have a motivating factor to work towards so it drives them to do it.
Many parents think that they should not be rewarded for doing homework but that is farther from the truth. If adults have to be motivated to work for a paycheck, the child should also have a motivating factor to do their homework.

Let’s start making homework a positive thing instead of pressuring them to finish so they don’t have a consequence.
If they are motivated and are going in with a good mindset to finish, they will most likely aim to finish and do it quickly to receive the prize. You can decide what that prize is or even set up a rewards program where if they get a certain amount of homework done in a week, they will get a bigger prize.
This of course does not mean that you take away the consequences if they don’t finish. This trick of setting up rewards won’t work for all students and they still might slack off and not finish so when explaining to them the reward system, let them know that they are not saved from the consequences and will receive them if they are not trying to finish.
Final Thoughts
There are consequences for students who don’t do homework when they are supposed to and it can be easy to choose one these days. Anything that the student loves to do in their free time should be limited or taken away and that will cause them to finish the homework they have due.
The first thing you have to do is find the reason why they are not finishing their homework and once you find that out, it is time to help them get started. Your child acting out in school can also play a role with they don’t want to finish their homework.
When dealing with this, a way you can take a different approach would be to motivate them by having rewards set up once they are able to complete their homework. This will cause a bigger effect than threatening consequences if they don’t finish.
Related Posts:
- Family Rules and Consequences Chart
- Teaching Honesty to Elementary Students
- Creative Punishments for High School Students
How Much Should I Pay my Parents for Rent
How much rent should you charge your 25-year-old son.
Home / Expert Articles / Child Behavior Problems / School & Homework
“My Child Refuses to Do Homework” — How to Stop the Nightly Struggle Over Schoolwork
By janet lehman, msw.

For many parents, getting their kids to do their homework is a nightly struggle. Some kids refuse to do their homework. Others claim that they don’t have homework, but then the report card comes out, and you realize that their work was not being done.
So why is homework time so difficult? In my opinion, one of the major reasons is that it’s hard for kids to focus at home. Look at it this way: when your child is in school, they’re in a classroom where there aren’t a lot of distractions. The learning is structured and organized, and all the students are focusing on the same thing.
But when your child comes home, their brain clicks over to “free time” mode. In their mind, home is a place to relax, have a snack, listen to music, and play video games. Kids simply don’t view the home as the place to do schoolwork.
If the homework struggles you experience are part of a larger pattern of acting out behavior, then the child is resisting to get power over you. They intend to do what they want to do when they want to do it, and homework just becomes another battlefield. And, as on any other battlefield, parents can use tactics that succeed or tactics that fail.
Regardless of why your child won’t do their homework, know that fighting over it is a losing proposition for both of you. You will end up frustrated, angry, and exhausted, and your child will have found yet another way to push your buttons. And, even worse, they will wind up hating school and hating learning.
A major part of getting your child to do their homework lies in establishing a system so that your child comes to see that homework is just a regular part of home life. Once they accept that, you’ve already won half the battle. Accordingly, my first few tips are around setting up this system. If you get the system right, things tend to fall into place.
Put this system in place with your child at a time when things are calm and going well rather than during the heat of an argument. Tell your child that you’re going to try something different starting next week with homework that will make it go better for everyone. Then explain the system.
You’ll find that this system will make your life easier as a parent, will make you more effective as a parent, and will help your child to get the work done. And when your child gets their work done, they’re more likely to succeed, and nothing drives motivation more than success.
Structure the Evening for Homework
When your kids come home, there should be a structure and a schedule set up each night. I recommend that you write this up and post it on the refrigerator or in some central location in the house. Kids need to know that there is a time to eat, a time to do homework, and also that there is free time. And remember, free time starts after homework is done.
Homework time should be a quiet time in your whole house. Siblings shouldn’t be in the next room watching TV or playing video games. The whole idea is to eliminate distractions. The message to your child is, “You’re not going to do anything anyway, so you might as well do your homework.”
Even if your child doesn’t have homework some nights, homework time should still mean no phone and no electronics. Instead, your child can read a book or a magazine in their room or work on longer-term assignments. Consistently adhering to the homework time structure is important to instill the homework habit.
Start the Evening Homework Habit When Your Kids are Young
If your children are younger and they don’t get homework yet, set aside quiet time each evening where your child can read or do some type of learning. Doing so will help children understand that evening quiet and study time is a part of everyday home life, just like chores. This habit will pay off when the real homework begins.
Use a Public Place for Homework
For a lot of kids, sending them to their rooms to do their homework is a mistake. Many children need your presence to stay focused and disciplined. And they need to be away from the stuff in their rooms that can distract them.
You know your child best. If you think they’re not being productive in their room, then insist they work at the kitchen table or in some other room where you can monitor them and where there will be fewer distractions.

If they do homework in their room, the door to the room should be open, and you should check in from time to time. No text messaging, no fooling around. Take the phone and laptop away and eliminate electronics from the room during study time. In short, you want to get rid of all the temptations and distractions.
Give Breaks During Homework Time
Many kids get tired halfway through homework time, and that’s when they start acting up. If your child is doing an hour of homework, have them take a 5-minute break every half-hour so that they can get up, have a snack, and stretch their legs. But don’t allow electronics during the break—electronics are just too distracting.
Monitor the break and ensure that your child gets back to work promptly.
Be sure to encourage your child when they’re discouraged. It’s okay to say things like:
“I know it’s a drag, but think of this—when you get your work done, the rest of the night is yours.”
“Look, if you do your work all week, you’ll have the whole weekend to do what you want.”
Show your child empathy—how many of us truly enjoyed homework every night? It’s work, pure and simple. But your child will be encouraged when they begin to have success with their work.
Help Your Child Get Started With Their Homework
Some kids have a hard time getting assignments started. They may be overwhelmed or unsure where to begin. Or the work may seem too difficult.
There’s a concept I explain in The Total Transformation® child behavior program called hurdle help . If you have a child who has a hard time getting started, spend the first five minutes with them to get them over the first couple of hurdles. Perhaps help them with the first math problem or make sure they understand the assignment.
For many kids who are slow starters, hurdle help is very effective. This doesn’t mean you are doing their homework for them—this is simply extra help designed to get them going on their own.
Help Your Child Manage Long-Term Assignments
If your child has a big, long-term project, then you want to work with them to estimate how much time it’s going to take. Then your child has to work within that time frame. So if your child has a science project, help them manage and structure their time. For instance, if the project is due in 30 days, ask them:
“How much time are you going to spend on it each night?”
They might say, “15 minutes a night,” and you hold them to that.
Don’t assume that your child knows how to manage their time effectively. As adults, we sometimes take for granted the habits we have spent a lifetime developing and forget that our kids are not there yet.
Make Sunday Night a School Night
The way that I structure the weekend is that Sunday night is a school night, not Friday. So if your child has homework for the weekend, and as long as they’re done all their work for the past week, they get Friday and Saturday night off and can do their homework on Sunday night.
If there’s a project or something big to do over the weekend, then work with your child to budget their time. They may have to put some time in on Saturday or Sunday during the day. But other than that, your child should have the weekend off too, just like adults do.
The Weekend Doesn’t Begin Until Overdue Work Is Done
If your child has overdue homework, their weekend shouldn’t begin until those assignments are done. In other words, Friday night is a homework night if their week’s work is not complete.
Believe me, this is a highly effective consequence for kids because it creates a great incentive to get their work done. Indeed, each minute they’re doing homework is a minute they could be hanging out with friends or playing video games.
If you can hold to this rule once and deal with the complaining, then next week the homework will be done.

By the way, if they say they can’t do their homework because they didn’t bring their school books home, they should be grounded for the weekend. You can say:
“I don’t want to hear that you can’t do it because you don’t have your books. You’d better call around and find a friend who you can borrow them from. Otherwise, you’ll be staying in this weekend.”
Make Homework a Higher Priority Than Activities
Kids are involved in a lot of after school activities these days. I understand that. But my priority has always been “homework comes first.”
In my opinion, if the homework isn’t done on Monday, then your child shouldn’t go to football on Tuesday. It’s fine if he misses a practice or two. You can say:
“Here’s the deal. We’re not going to football today. You need to get your work done first.”
If your child says, “Well, if I miss a practice, I’m going to get thrown off the team,” You can say:
“Well, then make sure your work is complete. Otherwise, you’re not going to practice. That’s all there is to it.”
I personally don’t put football, soccer, or any other extracurricular activities above homework and home responsibilities. I don’t believe parents should be going from soccer to karate to basketball with their kids while homework and school responsibilities are being neglected.
Use Rewards for Schoolwork, Not Bribes
Most kids get personal satisfaction out of getting good grades and completing their work, and that’s what we’re aiming for. Nevertheless, it’s important to reinforce positive behavior, and that may mean offering an incentive for getting good grades. For instance, my son knew that he would get a certain reward for his performance if he got all B’s or above. The reward was an incentive to do well.
One of the shortcuts we take as parents is to bribe our kids rather than rewarding them for performance. It can be a subtle difference. A reward is something that is given after an achievement. A bribe is something you give your child after negotiating with them over something that is already a responsibility.
If you bribe your child to do their homework or to do anything else that is an expected responsibility, then your child will come to expect something extra just for behaving appropriately. Bribes undermine your parental authority as kids learn that they can get things from you by threatening bad behavior. Bribes put your child in charge of you.
The appropriate parental response to not meeting a responsibility is a consequence, not a bribe. A bribe says, “If you do your homework, I will extend your curfew by an hour.” In contrast, a consequence says, “If you don’t do your homework, you’re grounded until it’s finished.” Never bribe your kids to do what they’re expected to do.
Use Effective Consequences
When giving consequences, be sure they’re effective consequences. What makes an effective consequence? An effective consequence motivates your child to good behavior. They put you back in control and teach your child how to problem-solve, giving your child the skills needed to be successful.
An effective consequence looks like this:
“If you fall below a B average, then you can no longer study in your room and must study at the kitchen table until you get your average back to a B.”
For the child who prefers to study in their room, this is an effective consequence.
Another effective consequence would be the following:
“If you choose not to study during the scheduled time, you will lose your electronics for the night. Tomorrow, you’ll get another chance to use them.”
And the next day, your child gets to try again to earn the privilege of electronics. Short-term consequences like this are very effective. Just don’t take away this privilege for more than a day as your child will have no incentive to do better the next time.
For more on consequences, read the article on how to give effective consequences to your child .
Be Prepared to Let Your Child Fail
Failure should be an option, and sometimes you just have to let your child fail . Parents often do their kids a disservice when they shield them from the consequences of their actions. If your child chooses not to study enough and they get a failing grade, that’s the natural consequence for their behavior. And they should experience the discomfort that results from their behavior.
Let me be clear. If you interfere and try to get your child’s teacher to change their grade, your child will learn the wrong lesson. Your child will learn that if they screw up enough, Mom and Dad will take care of them. And they don’t learn their math or science or whatever it is they failed.
To be sure, failing is a hard lesson, but it’s the right lesson when your child fails. And it’s not the end of the world. In fact, for many kids, it’s what turns them around.
Don’t Fight with Your Child Over Homework
Don’t get sucked into arguments with your child about homework. Make it very clear that if they don’t do their homework, then the next part of their night does not begin. Keep discussions simple. Say to your child:
“Right now is homework time. The sooner you get it done, the sooner you can have free time.”
Say this in a supportive way with a smile on your face. Again, it’s important not to get sucked into fights with your child. Remember, you don’t have to attend every argument you’re invited to. If your child refuses to do his or her work, then calmly give the consequence that you established for not doing homework.
Also, trying to convince your child that grades are important is a losing battle. You can’t make your child take school as seriously as you do. The truth is, they don’t typically think that way. To get your child to do homework, focus on their behavior, not their motivation. Rather than giving a lecture, just maintain the system that enables them to get their work done. Often, the motivation comes after the child has had a taste of success, and this system sets them up for that success.
Stay Calm When Helping Your Child With Their Homework
It’s important to be calm when helping your child with their homework. Don’t argue about the right answer for the math problem or the right way to do the geography quiz. If you get frustrated and start yelling and screaming at your child, this sets a negative tone and won’t help them get the work done. It’s better to walk away than it is to engage in an argument, even when you’re just trying to be helpful.
For couples, it may be that one of you is more patient and acceptable to your child. Let that person take on the homework monitoring responsibilities. And don’t take it personally if it isn’t you.
Remember, if you can’t stay calm when helping your child, or if you find that your help is making the situation worse, then it’s better not to help at all. Find someone else or talk to the teacher about how your child can get the help they need. And try not to blame your child for the frustration that you feel.
It’s Your Child’s Homework, Not Yours
Remember that your child is doing the homework as a school assignment. The teacher will ultimately be the judge of how good or bad, correct or incorrect the work is. You’re not responsible for the work itself; your job is to guide your child. You can always make suggestions, but ultimately it’s your child’s job to do their assignments. And it’s the teacher’s job to grade them.
Know the Teachers and the Assignments
Build good relationships with your child’s teachers. Meet with the teachers at the beginning of the school year and stay in touch as the year progresses. Your relationships with your child’s teachers will pay off if your child begins to have problems.
And if your child does have problems, then communicate with their teachers weekly. If they’re not handing in their work on time, ask the teachers to send you any assignments that they didn’t get done each week. Many schools have assignments available online, which is a big help for parents. Just don’t rely on your child to give you accurate information. Find out for yourself.
The bottom line is that you want to hold your child accountable for doing their work, and you can only do that if you know what the work is. If you keep yourself informed, then you won’t be surprised when report cards come out.
Work with your child on a system to keep track of assignments. I recommend an old-fashioned paper calendar simply because we already have too many distracting electronics in our lives—experiment and use what works best for your child.
Finally, try to see your child’s teachers as your allies. In my experience, most teachers are dedicated and caring, but I realize that this isn’t always the case. So, for your child’s sake, do your best to find a way to work with their teachers.
If You Think Your Child Might Have a Learning Disability
Kids are expected to do some difficult work, and your child may struggle. If your child is having an especially hard time, talk with their teacher. Ask if it’s typical for your child to be struggling in this area.
In some cases, the teacher may recommend testing to see if your child has a learning disability. While this can be hard to hear as a parent, it’s important to find out so that you can make the necessary adjustments.
If it turns out that your child does have a learning disability, then you want to get an Individualized Educational Plan (IEP) set up with the school.
Most kids don’t enjoy homework, and for some, it will always be a struggle. Our children all have different strengths and abilities, and while some may never be excellent students, they might be great workers, talented artists, or thoughtful builders.
I have to admit that dealing with my son’s homework was one of my least favorite experiences as a parent. It was overwhelming at times. Often, I just wasn’t equipped to offer the help he needed.
Our son struggled with a learning disability, which made the work feel unending at times. My husband James was much better at helping him, so he took on this responsibility. But even with this division of labor, we had to make adjustments to our schedules, our lives, and our expectations to make sure our son did his homework as expected.
Life would be easier if all children were self-motivated students who came home, sat down, and dug into their homework without being asked. This is hardly the case, though. Therefore, you need to set up a system that is right for your child, and it’s going to be easier for some kids than for others.
We’re trying to raise our kids to be responsible and accountable for their homework. And we’re trying to avoid fighting with them over it every night. When I had parents in my office, I would take these concepts and show them how they could make it work for their families in their own homes. The families I worked with were able to turn the nightly homework struggle around successfully time and time again.
Related content: The Homework Battle: How to Get Children to Do Homework
Empowering Parents Podcast: Apple, Spotify
About Janet Lehman, MSW
Janet Lehman, MSW, has worked with troubled children and teens for over 30 years. A veteran social worker, she specializes in child behavior issues — ranging from anger management and oppositional defiance to more serious criminal behavior in teens. She is co-creator of The Total Transformation® Program , The Complete Guide To Consequences™ , Getting Through To Your Child™ , and Two Parents One Plan™ .
You must log in to leave a comment. Don't have an account? Create one for free!
Hello, my grandson recently moved with me from another state. He is currently in 8th grade (but should be in 9th). He basically failed the last 2 years and was promoted. I would say he is at a 6th grade level. It's a daily fight with him to do his homework. He won't even try. I know a lot of this is because no one has ever made him do his homework before. I thought he would just have to get in a routine of doing it. He's been in school for a month now and its a fight every single day after school. I have lost all the patience I had. I am tired of being a broken record and being the "bad guy". I don't want to give up on him and send him back to his mom, where I know he will never graduate. I have made so many sacrifices to get him here, but I am literally at my wits end with this. I knew it wasn't going to be easy but I didn't think it was going to be this hard.
My rule is homework after school. If he comes home and does his homework after school, it was easier for him to complete. That lasted a week and a half. Now, he just sits there and does nothing. Does anyone have any suggestions? I couldn't live with myself if I sent him back and he became nothing but a drop out. I know I am not one to have patience, and I am trying but at the same time, I am almost over it. I don't like going to bed crying and knowing that he is crying too. I am open to all suggestions. Please and thank you.

I'm so sorry you are facing these struggles with your grandson. We here from many caregivers in similar situations, so you're not alone in your frustration. We have several articles that offer helpful tips for managing these homework struggles, which can be found here: https://www.empoweringparents.com/article-categories/child-behavior-problems/school-homework/
We appreciate you reaching out and wish you all the best moving forward. Be sure to check back and let us know how things are going.
Jessicar Thank you for this article and strategies. I echo many of the frustrations expressed by other parents here, including my opinion (as an educator) that homework should not exist. I agree that teachers and parents are in a struggle about which adult is responsible for supporting the child in getting More homework done. The best thing for my son was a free "homework club" in fourth and fifth grade where a teacher monitored completion of homework. He has nothing like this in middle school so far. Where I really disagree with the article is about extracurricular activities. Kids need physical activity through sports! They need enrichment beyond academics through the arts, theater, music. Many families send their children to religious, language, and/or cultural programs after school. If I sat in school all day, I'd want to move my body and interact with others too. The solution is not removing extracurricular activities that are healthy or motivating or valued. The solution is for schools to limit homework. Given that there is still homework as a reality--I'd like advice on when to have child do homework AFTER sports or extracurricular activity. When is the best time for homework if the goal is to go to bed on time (in my house in bed around 9 pm)? Between extracurricular and dinner--when the kid is tired? After dinner? My child is in 7th grade and I still can't figure it out. What do others do/think?
I found school to be extremely boring, as a teen. Looking back I realize that I hadn't found the work challenging enough. Personally, I struggled with this all through high school. I was completely disinterested in school, as a result.
I noticed that there wasn't a section addressing situations where children, who are motivated by challenges, do poorly as a result of boredom.
I enjoy reading many of the articles; even those which don't necessarily apply to my current situations with my child. One never knows what obstacles or challenges one may come across. Thank you
Here's what I know. Correcting our children when their behavior is displeasing is what most parents focus on. Without a lot of explanation I'm going to try to get you to change your focus. All children have 4 emotional needs:
1. A sense of belonging
2. A sense of personal power
3. To be heard and understood
4. Limits and boundaries
Rather than focus on your child's behavior, focus on meeting these needs. Meet the needs, change the behavior. There a 25 ways to meet these needs. One of the most effective is to spend regular one-on-one time with your child doing what your child wants to do. How do you spell love? T-I-M-E. It seems counter-intuitive, but just try it for a week. Do this for 1/2 hour every day for a week. See what happens.
Frustrated Confused Parent, I went through similar challenges with my son when he was in high school. As a grade school student his grades were always B and higher. The changes began when his mother and I separated; my son was 12yo. Prior to our separation I was the one who maintained, and enforced the habit of completing his assignments before extracurricular activities could be enjoyed. His mother never felt she had the patience or intelligence to assist him with his homework assignments and upon our separation she completely ignored his school work. Although he continued to follow the structure I had established through grade school, he soon began to realize that no one was showing interest any longer and, thus, began shirking school related responsibilities. My son and I were, and still are, close. I am certain that the separation likely had some affect on him, but it was more than that. He was reaching his teens and becoming more self-aware. Friends began to play a more integral and influential part in his life. Unfortunately my son's grades began slipping as he reached his early teens. For me, this was extremely frustrating since I was aware of how intelligent he was and of what he was capable. After many aggravating, lengthy, heated, and unyielding conversations with his mother about maintaining the structure established through grade school, it became clear she was incapable or simply unwilling. Essentially, he was on his own. Of course I would do whatever I could to help. For starters, I facilitated a transfer to a Charter School, realizing that he needed more individualized attention than that which a public school could provide. It seemed as though he was getting 'lost in the shuffle'.
Unfortunately the damage had already been done. After two years under his mother's lack of tutelage my son had developed some poor habits.
He struggled with maintaining good grades throughout his high school career. By 'maintaining good grades' I mean that he would take a grading of 45 in math and bring it to a 70 within three weeks of the end of a marking period. He ALWAYS passed, though. He would somehow get his grades to or even above passing by the end of the period. As I began to see this, I began to have more faith knowing that when the going got tough he would step up and take charge. It also indicated that he did well with what might perceive as an impossible goal. So, I started to have faith that he'd find his way.
He has since graduated, he has a good-paying job, and he is beginning school to become an electrician within the next month or so. In two weeks he moves into his own apartment, also. He's never done drugs, never drank alcohol, and never started smoking cigarettes. All of which I have done as a teen and well into my adult years. I am in recovery. My son is aware of my own struggles. Most importantly, I believe, is that he has a complete understanding that we all struggle in our own ways. Working through the difficulties, challenges, and obstacles are what makes us stronger and it's our compassion for others, and ourselves, which help us grow into decent adults.
I came to realize that the 'grades' he received in school had nothing to do with the amazing adult he's become; it was literally everything else.
NanaRound2 My 6 year old grandson has just taken 2 hours to write a list and write 3 sentences. He thinks if the words were shorter it wouldn't take so long. Already went through this with his dad. I celebrated more than he did when he graduated. Can't drag More another kid through school. Losing my mind and like the previous comment have tried EVERYTHING.
Yeah -been there, done that. Doesn't work. At least not for my child. I've read every *actual* parenting book out there ( You know, the books publishes by Harvard & Stanford professors who've been studying parenting and child psychology for the past 30 years?) ... and you're all missing something - because I've tried it all.
My kid DGAF. This was almost painful to read. "oh, yup - tried that one. That one too. Oh, hey - I've tried that as well."
This is so frustrating; tell me something I haven't already tried 50 times.
Psych Fan I'm with you my sophomore son DGAF . I tried so much stuff even set time stuff and he just doesn't go get his work out. He's 5'9 so I am 5'1 and I can't move him to do stuff . All he does is debate with me that More Grades really don't matter that he's like I'm just going to get D's because I'm not going to care to do better because I do not like school. He doesn't understand why I don't approve of D grades because I know he has better potential but he's like D grades I will pass and get my diploma .
The first thing on the list is to try and stay calm. While doing homework with my children I'm usually very calm. When I do get frustrated I'll leave the room for a moment, wash my face, and take a few deep breaths until I calm down. Or I'll make hot chocolate to help calm my nerves. It's not a perfect system, but what is?
Number two is to set clear expectations around homework time and responsibilities. We have a standard homework time at our house, with a timer and everything. If our kids meet the homework time goal they'll be rewarded later in the evening with family time. Each of our kids know their roles and responsibilities in the house whether the work gets done before dinner or not.
Number three is a relationship with the teachers, each of whom e-mail us, some two or three times a day. Contact with them has never been better. They're teachers are all pretty awesome too.
Number Four, play the parental role most useful to your child...I have three kids. One needs no help at all, one needs minor help and advisement, while the third requires constant supervision or their e-mail might 'accidentally' open up. This we've provided through double teaming. One parent works with them until the other gets home, then they switch while the other goes to make dinner.
Five, keep activities similar with all your kids. We all live on the same schedule, if one of them finishes homework early they get the reward of extra quiet reading time-my kids are ALL book worms.
Six, Set up a structured time and place for homework. Done. Homework table with a supplies basket right in the middle of the room. Big enough for all of them to work at and then some, it's an octagonal table which my husband built. I also always have their 'homework snacks' waiting for them when they get home, and I usually try to make it healthy-even if they don't realize it.
Seven, start early. My kids have been doing 'homework' with me since they were babies, and (as I pointed out to them yesterday) they loved it. We'd learn about cooking, dinosaurs, amphibians, insects, math, English, chemistry, even the periodic table came up. We'd do work pages every day and they'd love it.
Eight, hurdle help, works in area's like math, but not so much with history or English when the problems aren't as straight forward. But we do use this method where it applies.
Nine, choose the best person for the job. I'm best at English and my husband at math. When I get stuck on math I know who to go to, and I'll even study in my spare time to get better at it so I can be more useful in case he has to work late. That being said, we both devote a lot of our time to helping our kids with their homework.
Ten, show empathy and support. Done, not only can I relate to my kids, but I've pointed out that not getting their work done will make them feel bad bad enough, and that that's why we should work on getting it done together, so they have something to be proud of.
Use positive reinforcement and incentives. :) There was this one time I sat my son down at a table with a work book about 400 pages long. He was young, not even in school yet. Next to the book I placed a giant bag of M&Ms. I told him for every page he got done, he could have one m&m. About ten minutes later he finished the workbook and grinned up at me. When I found out he'd finished the book, I quickly checked it to see if it was done well, and then pushed the bag of M&M's towards him and told him he could just have it...Now they get rewarded in video games and computer time...
It seems that according to this article I'm doing everything right...So why is my child still struggling with homework/classwork? They've literally just refused to do it. Have seriously just sat in their chair without saying a word and stared at the table, or desk, or screen- as the majority of work is now done on computers...I'll sit with them, ask them if they need help, try to help them with problems. They will tell me the right answer to the questions being asked and then refuse to write it down. I feel like I've done everything I can as a parent to help them, but despite all my efforts, it isn't working. So...when all of these things fail, when a parent has done everything right, and there is nothing more they can do short of taking the pen or pencil into their own hands and doing it themselves, (but that would be cheating their child out of an education) what then should the parents do?
When our kids don't get their homework done before dinner, they're sent down the hall where it's quiet so they can finish it at the desk there, while the other kids have family time. They are told to come and get us if they really need help after that. But at this point it's like ostracizing our child for not doing homework.
I agree with most of what's on this page, and our family lifestyle reflects that, but I will disagree with one thing it said. It is our job to help our kids and be supportive of them yes, to nurture them and help them get the skills they need to take care of themselves and their home when they're older...but it is not our job to do the teachers work for them, they get paid for that. Some days it seems like that's what's expected of parents. Some even send home classwork if the kids don't finish it in class. Which means the child now has even more work to do on top of their homework. Though I understand that the teachers want the child to finish the lesson, and were the homework not a factor I probably wouldn't mind it as much. I don't even mind them sending home study guides to help kids before tests (Which is what homework was originally) but to send home overwhelming piles of work each night for parents to help kids with, (Each child with different homework so that parents need to bounce from history, to math to English) it's unreasonable. When teachers send home homework, they're dictating what the parents can do with the little time they have with their child. Which is wrong. We once had to cancel a trip to a science museum because our child had too much homework to finish and there was no way to make it in time and get their homework done. They could have had an amazing educational experience which would overall help them get excited about learning with new and fun tactile experiences, but their schedule (and therefore our schedule) was being dictated by the teacher while they weren't even in class. Of course I try not to talk bad about homework in front of my children, because that would make it even more difficult to get them to do it. But children NEED family time, they NEED to be kids. To be allowed to get away from their work and be themselves, to go outside and play with their friends, or even go out to dinner once in a while with their parents. Homework has made it difficult to grow a relationship with our children beyond the confines of what the teachers are dictating. It's violating in some ways and frustrating in others. It's grown into this monstrous thing which it was never meant to become, and the funny part about it is that most studies done on it show that schools who don't have homework have higher test scores and graduation rates. Not to mention better mental health rates. Studies also show, that after a child is taught something, they'll only really learn it after a good nights sleep, and that no amount of homework will change that. Sleep is what our bodies need to absorb important information we learn throughout the day, so staying up late with homework might even be harmful to a child's education...
Sorry I guess that turned into a bit of a rant...In the end I was hoping to find something useful in this article, something I hadn't tried that might work, but I've done it all, and will probably continue to do all of it in hopes that consistency might be the key...It's just that even after years of already doing All of this consistently, it's still not working. It's as if my child has made a conscious decision Not to work. He's not unintelligent, he understands it, he's even been tested and found to have an above average ability to learn. He just not doing it..So what now? What more can I do to actually inspire him to do the work?
AshumSmashum Out of all of this, most of which I've read and tried a billion times, your comment hit deeper. My son scores in the 99% on tests but cannot sit down and do the simplest homework. He does have autism and adhd so when he freezes up on homework, despite More knowing it, I'm lost at how to help him get it done. He knows the work so why does he need to show it with 20 math problems after school that take forever to complete one? (whatever honors algebra stuff he's in, I was lucky to learn division lol) He has a high IQ and excels in all subjects and yet is being tutored, so far, in English just to get the work done. I'm so done with the emotional toll it takes on me and him at home. Nobody wants to go to work for 8 hours and come home and do the same for another 5 so why do we think our kids want to come home and do more classwork? I'm so appreciative of your comment!
JC Hi Barb, thank you for bringing this up! My son sounds a lot like you...and he really wants to get good grades and go to an Ivy League school. What could someone do to help an 8th grader in the moment of struggle, while making sure they don't get more More anxious from falling behind for the rest of the year?
Tb Hi Barb, I'm the parent of an 8th grader and I want to thank you for the comment you left here. You helped me look at the deeper issues and I really appreciate that. I'm going to approach the conversation with my son differently, thanks to you. Thank More you!
My 11 year old daughter, Alice, has always helped her 7 year old sister, Chole, with homework. But just recently Alice has been giving Chole the wrong answers. We have been trying to get her to give Chole the correct answers
but she always yells at us. She has a baby sister 2 months named Ray and ever since Ray was born she has been giving Chole wrong answers. I once overheard her and Kevin, my husband, talking about how she felt left out. She came and talked to me and said exactly what she had told Kevin. She also told me she has been getting bad grades and doesn't get her homework. Me and Alice talked and she said "All the cool New York girls get straight A's and ever since I started getting D's and F's they said I wasn't cool anymore." We started having her grandparents come over and she would yell, hit, scream, and talk back to them. She is a great student but she spends all of her time on her phone. Breakfast, lunch, dinner, and even at school she is on her phone. All I'm asking is that 1. How do I make her stop screaming, yelling, hitting, and back talking? 2. How do I make her feel cool and get A's again?and 3. How do I get her off her phone?
sounds like you have a number of concerns around your daughter’s behavior, and
it certainly can feel overwhelming. We would suggest https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/its-never-too-late-7-ways-to-start-parenting-more-effectively/ and focusing on just one or two of the most serious, to get
started. Behaviors like verbal or physical abuse would be of top priority,
while behaviors like https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/how-to-walk-away-from-a-fight-with-your-child-why-its-harder-than-you-think/ we would recommend ignoring, and not giving it any power or control.
Empowering Parents author Sara Bean offers some great insight into the reason
for poor child behavior in her article, https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/the-surprising-reason-for-bad-child-behavior-i-cant-solve-problems/.It sounds like your daughter is struggling to
find more effective ways to solve the problems she is facing, and the result is
the acting out behavior. Keep in mind, you can’t make your daughter do anything, but what you can do is help her to
learn better tools to solve whatever problems may come her way. Best of luck to
you and your family as you continue to work on this.
Emma Reed Alice also swears at school and she swears to teachers. Please we have tried everything, even her sister at age 18. What have we done wrong?
Being away from loved ones when they are struggling can be
distressing. It may help to know that it’s not unusual to see changes in
behavior as kids move from the tweens into adolescence, as Janet Lehman
explains in the article https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/adolescent-behavior-changes-is-your-child-embarrassed-by-you/. Normally responsible
kids can start to push back against meeting expectations and disrespect towards
parents and other authority figures can become quite common. The behavior you
describe isn’t OK; it is normal though. I can hear how much you want to help
your daughter and granddaughter
work through these challenges. If your daughter is open to it, you could share
some Empowering Parents articles with her, such as the one above and this one, https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/my-childs-behavior-is-so-bad-where-do-i-begin-how-to-coach-your-child-forward/.
We appreciate you writing in. Best of luck to you and your family moving
forward. Take care.
mphyvr Thanks for all these "strategies", they might work for some parents, but quite simplistic and just plain old common sense for more defiant kids... Thanks anyways and hope this article helps many.
Psych Fan I'm a mom of a sophomore he's also a swearing boy and will have quite a tantrum even with consequences of take away all he does is sleep. He doesn't like school says school is a waste of time and that grades won't matter in his adulthood . He says More it over n over about how schooling won't help him in the future as I go it will help you do good on a ACT and SAT he is like getting good scores on those are only good if your going to college. He also is like jobs won't look at my grades . I tell him homework teaches him responsibility once a job sees your amount of effort in school your going to have a heck of time getting hired. I even ask him how is he going to succeed to work real well at a job when he doesn't work hard at school he goes I don't need to work hard at school but I will need to work hard at a job.
dcastillo68 If it was only this simple, but, in reality it is not. Middle school syndrome is the worst. Kids don't want to be labeled as nerds so they do everything to try to fail. I went through that with my first born, and now again with my youngest. It is More very frustrating when I was the total opposite when I was growing up. I cared about my grades an I took it for granted thinking they will feel the same way. Now seeing how they are happy with just getting by is really frustrating to me because I am such an over achiever. They didn't even get an ounce of this. Very very frustrating. And I wish I have never invited video games to this household. That is all they want to do. I keep using this an incentive to bring them back on track, but as soon as I give them their games back, they are back to their old habits. Sorry, but I can't wait until they are finished with school and hopefully moving out of state to hopefully a college career. I may change my mind later, but at the moment, this is just how I feel. It is very hard too when you don't get any help. I find today's teacher to be lazy and pushing on more responsibility to the parents. Who has time to do a full day's of work, only to do additional work at home? okay, enough venting.
@frustrated single dad Diane Lewis Hi there - I have a son adopted out of foster care. He is 6 1/2 and has been in 5 homes. He is totally the same! They learn this behavior and are incredibly manipulative. They are so insanely smart. I worry about exactly the same thing. They turn on and off the behavior depending on who they are with and what they want.
We did Parent Child Interactive Therapy (PCIT) at the Mailman Center (Jackson Hospital Miami). It made a huge difference in the short-term. They basically taught us to be full-time behavioral therapists with my son. The effects wore off after a few months as my son adapted and found ways to circumvent the consequences techniques taught to us. He is like the Borg! I am going back to get more ideas on how to adapt and change and stay one step ahead of my son. The gals there are really smart!
So, that being said - we have to be Jean Luc Picard and constantly change and adapt and outsmart them - just like changing the phasers on a laser gun! It is bloody hard work. And, harder the older they get -
eg. He drops like a dead weight - throws his book bag and will not get in the car to go to school - response - next morning I headed it off by calling out to the kids "LAST ONE IN THE CAR IS A ROTTEN EGG!" This has worked for 2 days now.
Wont do homework 2 nights ago - response - "ooh I like doing word puzzles - Im going to do them and win" - this worked one night but not the next - he just then just left me to do his work - so I have told his teacher that there will be no school party for Alex next week unless he gets his homework finished - we will see if this works.....
It is totally exhausting and you have to be on your A game all the time. Im telling you this but - I have to tell myself this too. We have to stay really fit (like cross fit) and work out like a marine. We have to be very disciplined with ourselves - a healthy body is a healthy mind - we cannot let up at all. We have to stay calm at all times (again self discipline).
Im always looking for concrete reactions to situations with my son. Like I said - the entire day goes on like this with everything except what he wants to do. Wont get dressed in the morning - put out his clothes in dining room where there are no distractions or toys - tell him that if he gets dressed and ready for school quickly - he can spend the left over time on the trampoline. That worked this morning.
STAY STRONG MY BROTHER IN ARMS!!! If you can get into a PCIT program - do it.
Love to you - R
My child comes home and says he doesn't have homework, does something easy to make it look like he's doing his homework, or says he did it during free time in class. How do you combat this without going to the school everyday? Neither my husband nor I can do More this because of work, and the we asked the teacher's if it was possible to send us the assignments via email or let us come pick them up once a week with no cooperation. He is a very smart kid and gets "A's' on the work he does, but he is failing all of his core classes because he won't do homework.
@atmywitsend , my child is the same way. I'm at my wits end. I feel like I'm a failure as a parent because I thought I taught my smart kid to succeed - and instead she's lying to me.
Psych Fan NinaMays I'm with the same feelings as my son can be above a C student but he choose to go oh I rather just get F's on this work than to actually get at least a B or A on these many assignments.. I ask him why he chooses F's More in many assignments when he could get a grade to bring his grades up and me telling me he's not being his full potential as by making him not do his work how can I truly believe he's going to be successful and he's like I have big brains . Then I'm like why not show me by doing your school work he goes I don't need do that and I show you of my big brains by telling you school isn't important. Telling me I am brainwashed. He is a sophomore in high school.
FRUSTRATED PARENT NinaMays This is my reality too - "relationship" with teachers is difficult when they won't co-operate with homework expectations, or follow up email - the schools complain that kids are on the internet - yet its them providing wifi passwords - so kids are playing in class - lying about More homework - and since I'm not in the class, I have no idea until report cards surface.
Responses to questions posted on EmpoweringParents.com are not intended to replace qualified medical or mental health assessments. We cannot diagnose disorders or offer recommendations on which treatment plan is best for your family. Please seek the support of local resources as needed. If you need immediate assistance, or if you and your family are in crisis, please contact a qualified mental health provider in your area, or contact your statewide crisis hotline.
We value your opinions and encourage you to add your comments to this discussion. We ask that you refrain from discussing topics of a political or religious nature. Unfortunately, it's not possible for us to respond to every question posted on our website.
- 1. The Homework Battle: How to Get Children to Do Homework
- 2. What to Do When Your Child or Teen is Suspended or Expelled From School
- 3. Acting Out in School: When Your Child is the Class Troublemaker
- 4. Young Kids in School: Help for the Top 4 Behavior Problems
- 5. When Your Child Has Problems at School: 6 Tips for Parents
- 140,000+ Subscribers Subscribe
- 50,000+ Fans Follow
- 10,000+ Followers Follow
- 6,000+ Followers Follow
Disrespect... defiance... backtalk... lack of motivation...
Frustrated and exhausted by your child's behavior?
Get your FREE Personal Parenting Plan today.
Does your child exhibit angry outbursts , such as tantrums, lashing out, punching walls, and throwing things?
Would you like to learn about how to use consequences more effectively?
Backtalk... complaints... arguments... attitude... just plain ignoring you
Do you struggle with disrespect or verbal abuse from your child?
Has your child been diagnosed with oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)?
Or does your child exhibit a consistent and severe pattern of anger, irritability, arguing, defiance, and vindictiveness toward you or other authority figures?
Intimidation... aggression... physical abuse and violence ...
Are you concerned that your child may physically hurt you or others?
You must select at least one category to create your Personal Parenting Plan:
We're just about finished! Create a secure account with Empowering Parents to access your Personal Parenting Plan.

ADHD And Refusal To Complete Assignments

- September 29, 2020
Instead Of Punishing, We Should Be Asking “Why”
A few days ago, I saw a post on a different group than the one I moderate for ADHD parent support. The post was from a parent asking for advice about how to punish a child for refusal to complete assignments in virtual school. The mom said she didn’t want to take recess away, as their pediatrician said that exercise is important for children with ADHD. (I can agree with that!) What followed were a lot of comments about other punishments that she could enact, like having the child walk or run the school yard instead of recess, or have them do extra work, or lose privileges for electronics.
It was at this point that I had to jump in.
Look at lists of symptoms for ADHD , and you will find all of the executive functions listed as possibly affected. At it’s core, ADHD is weakness in executive functioning. The child’s refusal to complete assignments is coming from a lagging skill in one or more areas. It is not just a behavioral problem.
No type or amount of punishment is going to change underlying executive functioning. It’s like punishing a child for not being able to ride a bike when they haven’t learned yet. So instead of asking how to punish, what we should be asking is “why did my child not do their work?” There is most definitely a reason. Making them run the school field won’t address that reason. Taking away a toy or privilege won’t address that reason. A punishment might gain short term compliance, but it is not going to solve this problem in the future. Most important in the asking of this question: it reframes the issue from one of blame to one of compassion.
Common Reasons For “Refusal” To Complete Assignments
The most common reasons that I am finding for kids and teens not completing their schoolwork are listed below. A new set of issues has cropped up with virtual and hybrid learning, but these refusals existed even before, when all school was conducted in-person. Don’t be fooled into thinking the “new way of learning” is causing these refusals!
- Don’t know what the assignment is and/or when it’s due
- Don’t know how to prioritize the order to begin assignments
- Forgot about an assignment because it wasn’t listed with the others
- Don’t understand how to do it (subject material, or confusing directions)
- It’s going to take too long, it’s uninteresting or perceived as irrelevant, and child or teen would rather engage in leisure activity than schoolwork
How To Find The “Why”
In order to provide the right amount of support your child needs so that they can succeed, you may need to engage in a little detective work. We want to ask specific questions to get to the answer. Instead of “why didn’t you do it?” (blaming), you can ask “what was difficult about it?” or “how can I help you understand this?” (showing compassion).
I’ll give you a real example. I have a client who has fallen behind in a few of his classes. He is staying current with the classes that are more concrete and that he is better at – math, science, and Spanish. He is weeks behind in English.
I sat down with him and assessed his learning style, executive functioning skills, and future goals. We looked at strengths, weaknesses, and what barriers he was encountering. I found that he has difficulty writing, researching, and organizing his thoughts. He struggles with decision making as well. He would land on a research topic, then change his mind repeatedly. He perceives the stakes as high in any decision involving school, as he truly does care and is quite a perfectionist. The assignments were multi-step, high school English that, in his mind, looked like they were going to take forever. He couldn’t even get started, so he didn’t.
Taking the time to address the underlying issues allowed me, and his parents, to come up with a plan to get back on track. He needed to see how to to break big assignments down into more manageable pieces, to schedule time for reading and research, and to figure out the best way to organize. It took some time, but he was eventually able to get caught up in all classes.
What would have happened if his mom had taken away his video games as punishment for the refusal to complete assignments? The assignments most likely wouldn’t have been done independently, as he truly did not know how to get started with organization, prioritizing, and time demands.
I have another, younger, client who is in elementary school full time in-person class instruction. He is not able to do his homework without me or one of his parents sitting next to him. He rushes ahead to complete his work as quickly as possible, and thus he struggles with making his writing legible, and reading for comprehension. Without the accountability of someone right next to him, he gets off task, he daydreams and fidgets, his writing is illegible, and he ends up having to re-do the work, which leads to frustration and further avoidance. When I sat next to him and reminded him of the three keys for neater writing, and tapped the table to help him re-focus, and asked him to take a breath, slow down, and think before writing any answer, I was teaching him how to become more disciplined and what strategies he needed in order to make homework time smoother. He is a smart boy, so pointing out that while this process seemed like it was taking longer, he was actually going to save time in the end by not having to re-write and re-read things he missed.
What would happen if mom had taken away his playtime on the trampoline in the backyard, or his nightly bike ride with the family around the neighborhood? Would that have helped him slow down, write neatly, use active reading techniques, and stay focused? Not even close!
I don’t have a checklist of questions to ask, as I let the conversation unfold naturally, but here are a few questions that come to mind:
- Do you know what you have to do? If the answer is yes, I ask them to explain it to me, so I can be sure that they understand. If the answer is no, I help them figure it out, then repeat it back.
- Do you know how to do it? If the answer is yes, I ask them to go ahead and start. If the answer is no, I ask how they can find out. Do they need to read the directions, look online, contact the teacher, call a friend, attend tutoring? I encourage kids and teens to solve their own problems. If it is a long project, they may know how to do it in general, but not how to break it down into smaller bits.
- Do you have everything you need? I am referring to materials as well as having any research or other work done that will be needed.
- Is there something about this (homework, assignment, etc) that is too hard or confusing for you? This is a similar question to do you know how, but it’s different in that they may know how, but it’s just too hard or will take too long. Sometimes I ask them to scale it from 1 – 5, 1 being “super easy” to 5 being “really hard”.
- What do you think about this (homework, assignment, topic, class subject, etc)? Sometimes we don’t want to do things simply because we don’t care, or don’t see the point, already understand it and resist repetition, or find the subject boring. This question gets to their thoughts and feelings about the actual task.
Less Obvious Reasons For Refusal To Complete Assignments
As an occupational therapist, I treat my clients holistically. This means that I look at the whole person. My clients are not a diagnosis or a deficit – they are complex human beings who have past influences and future goals. This is why I reject the “ABC” model of behavior therapy (antecedent- behavior – consequence) as the antecedent could have occurred hours (or even days) before the behavior. If we only look at what happened immediately prior to a behavior (the refusal to complete assignments, in this case) we are often missing the bigger picture!
A recent example is another high school student. She is in honors classes and has been staying current with all class and homework – until a creative writing paper was assigned that was to be graded by a peer. She did most of the work, but when she found out that it was going to be peer-graded, she completely shut down. She admitted to me that she did not want anything to do with it, because she was afraid of what this peer might think of her, reading her personal stories. In this case, there was not an executive functioning deficit, but there still was a clear reason behind the refusal.
What If There Is No Reason?
You can go through the entire process, and you still may not get a real answer. Alternatively, the answer may be “I don’t want to” or “I hate school” or something similar, which you may perceive as defiant. At this point of continued refusal to complete assignments, you have a few choices. You can use immediate rewards, you can develop a contingency plan, or you can enact a behavioral contract.
- Immediate rewards are most effective with young children. Remember potty training when your kiddo got an M & M or skittle for sitting on the potty, one for using it, etc? This is the same. Immediate, tangible rewards are offered in exchange for a word written, a page completed – whatever you choose. They will eventually need to be faded so your child does not learn to only work for rewards. (I usually caution against food rewards for this reason. A sticker chart or marble jar is preferred, with a bigger reward earned).
- Contingency plan, or “first/then”. With a contingency plan, your child is basically in lockdown until they complete what you want or need them to. Their freedom to engage in desirable activities depends upon finishing homework, studying, a project, etc. First you finish the work, then you get to (play, go out with friends, watch TV, etc). There is a clear goal/task that needs to be completed before the child can do what they want. It may change from day to day. The contingency has higher stakes and is more demanding than an immediate reward. It helps children overcome short term motivation problems by increasing the value of what they need to do (the homework or chore) beyond a sticker or toy as a currency.
- Behavioral contract. This is a step above the contingency. It spells out specifically desired behaviors AND consequences if they do not occur. Whereas in a contingency, the child would not get to play, in a behavioral contract, the “then” part will occur if an only if the child completes the criteria set for earning the enjoyable activity. Ideally, you get your child or teen to “buy-in” by signing and thus, agreeing to, the contract.
Obviously, we parents would love for our children to have the self-motivation to want to succeed. That is not always the case. I am speaking from personal experience when I say that no amount of logic, or punishment, will make this child or teen motivated. You, as the parent, can use a contingency or behavioral plan to get back on track. Once you begin to see results, you can back off and allow more autonomy. Build this into the written plan, so your child or teen knows exactly what outcomes will get him or her more freedom.
Finding they “why” and addressing any other underlying issues, will ultimately solve the problem of refusal to complete assignments. By doing this as soon as possible, you are setting your child or teen up for future success – and with that, everyone wins!
For much more on executive functioning skill building, motivation, and parenting help, check out my self-paced online courses for parents of elementary aged kids with ADHD and parents of teens with ADHD . For more 1:1 help, fill out my ADHD Questionnaire to see if we are a good fit to work together.
Recent Posts

Five Steps Parents Of Children With ADHD Can Take To Improve Their Parenting

Must-Haves for Students with ADHD

Back to School Tips for Middle and High School Aged Students
- Coaching (1)
- Community (2)
- Executive Function (11)
- Occupational Therapy (4)
- Privacy Policy
ADHD Services
- Kids Aged 4 - 11
- Teens Aged 12 - 19
- Young Adults
- Parent Coaching
- Information
- Practical Solutions for Parenting ADHD: Workbook to Help Kids of All Ages
- Practical Solutions for ADHD Workbook for Teens
- Online Self-Paced Executive Functioning Course for Parents
- On-Demand Webinar Courses for Parents
Connect with Us

Copyright 2024 © Kids Empowered 4 Life. All rights Reserved.
All information on the Website is presented as informational only and is not a replacement for therapy assessment, diagnosis, intervention, or medical advice. The information provided on the Website is provided “as is” without any representations or warranties, express or implied. Kids Empowered 4 Life assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions that may appear in the Website.
ONLINE PARENTING COACH
Help for parents with strong-willed, out-of-control teens and preteens.
Defiant Children Who Refuse To Do Homework: 30 Tips For Parents

- Your child doesn’t understand the work and needs some extra help. It’s possible that your youngster doesn’t want to do his homework because he really needs help. Also, it can be challenging for moms and dads to accept that their youngster might need help with homework, because there is often a stigma attached to kids who need tutoring.
- Your child is addicted to TV and video games. Moms and dads often find it very difficult to limit these activities. But, understand that playing video games and watching TV doesn’t relax a youngster’s brain. In fact, it actually over-stimulates the brain and makes it harder for him to learn and retain information. Too much of watching TV and playing video games contributes to your youngster struggling with school and homework in more ways than one.
- Your child is exhausted from a long day at school. In the last 10 to 20 years, the needs of kids have not changed, however the pace of life has. Most moms and dads are busy and have very little down time, which inevitably means that the youngster ends up with less down time too. He is going to be less likely to be motivated to work when there is chaos all around him.
- Your child is not sleeping enough. Sleep is one of the most under-appreciated needs in our society today. When a child doesn’t get enough sleep, it can cause him to be sick more often, lose focus, and have more emotional issues. Kids often need a great deal more sleep than they usually get.
- Your child is over-booked with other activities. Moms and dads want their youngster to develop skills other than academics. Because of this, they often sign-up their youngster for extracurricular activities (e.g., sports or arts).
- Your child is overwhelmed by your expectations. Moms and dads want their youngster to be well-rounded and to get ahead in life. Along with this comes getting good grades. All these expectations can put a lot of pressure on your youngster and may cause him to become burned-out and want to find an escape.
- instructions are unclear
- neither you nor your youngster can understand the purpose of assignments
- the assignments are often too hard or too easy
- the homework is assigned in uneven amounts
- you can't provide needed supplies or materials
- you can't seem to help your youngster get organized to finish the assignments
- your youngster has missed school and needs to make up assignments
- your youngster refuses to do her assignments, even though you've tried hard to get her to do them
- Do you understand what you're supposed to do?
- What do you need to do to finish the assignment?
- Do you need help in understanding how to do your work?
- Have you ever done any problems like the ones you're supposed to do right now?
- Do you have everything you need to do the assignment?
- Does your answer make sense to you?
- Are you still having problems? Maybe it would help to take a break or have a snack.
- Do you need to review your notes (or reread a chapter in your textbook) before you do the assignment?
- How far have you gotten on the assignment? Let's try to figure out where you're having a problem.

Parent's Use of Positive Reinforcement for Struggling Teenagers
Parenting a struggling and/or rebellious teenager can be a challenging and exhausting experience. It's easy to feel overwhelmed and frus...

- Would you suggest any further contact? Here's an email from a mother whose 17-year-old son is "on the run." He has a drug habit, and is basically floating from one l...


Battles Over Homework: Advice For Parents
Guidelines for helping children develop self-discipline with their homework..
Posted September 5, 2012 | Reviewed by Lybi Ma
- What Is Anxiety?
- Take our Generalized Anxiety Disorder Test
- Find a therapist to overcome anxiety
I would like to offer some advice about one of the most frequent problems presented to me in over 30 years of clinical practice: battles over homework. I have half-jokingly told many parents that if the schools of New York State no longer required homework, our children’s education would suffer (slightly). But, as a child psychologist, I would be out of business.
Many parents accept this conflict with their children as an unavoidable consequence of responsible parenting . These battles, however, rarely result in improved learning or performance in school. More often than not, battles over homework lead to vicious cycles of nagging by parents and avoidance or refusal by children, with no improvement in a child’s school performance. And certainly no progress toward what should be our ultimate goals : helping children enjoy learning and develop age-appropriate discipline and independence with respect to their schoolwork.
Before I present a plan for reducing battles over homework, it is important to begin with this essential reminder:
The solution to the problem of homework always begins with an accurate diagnosis and a recognition of the demands placed on your child. Parents should never assume that a child who resists doing homework is “lazy.”
Every child whose parents or teachers report ongoing resistance to completing schoolwork or homework; every child whose performance in school is below expectations based on his parents’ or teachers’ intuitive assessment of his intellectual potential; and every child who, over an extended period of time, complains that he “hates school” or “hates reading,” should be evaluated for the presence of an attention or learning disorder.
These children are not lazy. Your child may be anxious, frustrated, discouraged, distracted, or angry—but this is not laziness. I frequently explain to parents that, as a psychologist, the word lazy is not in my dictionary. Lazy, at best, is a description, not an explanation.
For children with learning difficulties, doing their homework is like running with a sprained ankle: It is possible, although painful, and he will look for ways to avoid or postpone this painful and discouraging task.
A Homework Plan
Homework, like any constructive activity, involves moments of frustration, discouragement, and anxiety . If you begin with some appreciation of your child’s frustration and discouragement, you will be better able to put in place a structure that helps him learn to work through his frustration—to develop increments of frustration tolerance and self-discipline.
I offer families who struggle with this problem a Homework Plan:
- Set aside a specified, and limited, time for homework. Establish, early in the evening, a homework hour.
- For most children, immediately after school is not the best time for homework. This is a time for sports, for music and drama, and free play.
- During the homework hour, all electronics are turned off—for the entire family.
- Work is done in a communal place, at the kitchen or dining room table. Contrary to older conventional wisdom , most elementary school children are able to work more much effectively in a common area, with an adult and even other children present, than in the “quiet” of their rooms.
- Parents may do their own ”homework” during this time, but they are present and continually available to help, to offer encouragement, and to answer children’s questions. Your goal is to create, to the extent possible, a library atmosphere in your home, again, for a specified and limited period of time. Ideally, therefore, parents should not make or receive telephone calls during this hour. And when homework is done, there is time for play.
- Begin with a reasonable, a doable, amount of time set aside for homework. If your child is unable to work for 20 minutes, begin with 10 minutes. Then try 15 minutes in the next week. Acknowledge every increment of effort, however small.
- Be positive and give frequent encouragement. Make note of every improvement, not every mistake.
- Be generous with your praise. Praise their effort, not their innate ability. But do not be afraid of praise.
- Anticipate setbacks. After a difficult day, reset for the following day.
- Give them time. A child’s difficulty completing homework begins as a problem of frustration and discouragement, but it is then complicated by defiant attitudes and feelings of unfairness. A homework plan will begin to reduce these defiant attitudes, but this will not happen overnight.
Most families have found these suggestions helpful, especially for elementary school children. Establishing a homework hour allows parents to move away from a language of threats (“If you don’t__ you won’t be able to__”) to a language of opportunities (“When” or “As soon as” you have finished__ we’ll have a chance to__”).
Of course, for many hurried families, there are complications and potential glitches in implementing any homework plan. It is often difficult, with children’s many activities, to find a consistent time for homework. Some flexibility, some amendments to the plan, may be required. But we should not use the complications of scheduling or other competing demands as an excuse, a reason not to establish the structure of a reasonable homework routine.

Copyright Ken Barish, Ph.D.
See Pride and Joy: A Guide to Understanding Your Child’s Emotions and Solving Family Problems .

Kenneth Barish, Ph.D. , is a clinical associate professor of Psychology at Weill Medical College, Cornell University.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

It’s increasingly common for someone to be diagnosed with a condition such as ADHD or autism as an adult. A diagnosis often brings relief, but it can also come with as many questions as answers.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Blog Post > “My Child Refuses to Do Homework” Here’s How to Stop the Struggle
- “My Child Refuses to Do Homework” Here’s How to Stop the Struggle

Over the past few weeks I have had many frustrated parents in my office discussing issues that they were having with their child refusing to do homework. Most of the parents I talked to described homework taking hours and ending with everyone frustrated and upset. This is a nightly occurrence and both the child and parent struggle with a solution. The following article from www.empoweringparents.com by Janet Lehman, MSW has some helpful hints that might just end this nightly struggle. — Megan Yaraschuk, M.Ed., PCC
“My Child Refuses to Do Homework” Here’s How to Stop the Struggle by Janet Lehman, MSW
Do you get sucked into a fight over homework with your child every night? So many parents tell me that this is one of their top struggles with their kids. If you’re dealing with this now, you probably dread saying the words, “Okay, time to do your homework,” because you know what’s coming next — screaming, stomping, book-throwing and slammed doors. Or it might simply be hours of dealing with your complaining, whining or non-compliant child or teen who just hates to do the work. Even though you reason, lecture, nag and yell, nothing seems to change — and each night turns into a battle with no victors.
Trust me, I get it. I have to admit that dealing with my son’s homework was one of my least favorite experiences as a parent. It felt overwhelming to me; often, I just wasn’t equipped to offer the help he needed. Our son struggled with a learning disability, which made the work and the amount of time required feel unending at times — both to him and to us. My husband James was much better at helping him, so he took on this responsibility — but even with this division of labor, we had to make adjustments to our schedules, our lives and our expectations to make sure our son turned it in on time.
They Don’t Call It “Homework” for Nothing
Here’s something I learned along the way: homework is work, and there’s no getting around that fact. It’s a chore for both the child and parent. It’s important to understand that schoolwork is often the most difficult part of your child’s busy schedule. Helping your kids manage it despite all the other activities they would rather be doing can be challenging at best. Remember that it’s your child’s job to go to school and learn (including getting homework completed) and your job to provide for your kids, run the house and offer love and guidance to your children.
I know from experience how easy it is to get caught up in power struggles over homework. These struggles begin for several reasons, but the most common one is because your child would rather be relaxing, playing, texting with friends, or doing almost anything else. Know that if you deal with their frustration by losing it and getting mad out of your own frustration, it will be a losing battle. Some kids are even able to manipulate parents this way, because they know the battle over homework may result in your giving up on expectations to get it done.
Here’s the truth: letting your child off the hook for their work will ultimately create problems in their lives. Instead, focus on the fact that as a parent, you need to teach your child how to follow through on expectations and be accountable. All the more reason to take control and make homework just another part of your child’s daily responsibilities.
Here’s my advice for reducing homework hassles in your home:
- Try to stay calm : Try to avoid losing your cool and yelling and screaming, arguing about the right answer for the math problem or the right way to do the geography quiz, ignoring the homework altogether or being inconsistent with what you expect, being overly critical, or giving up and just doing the work for your child. The first step is to try to stay as calm as you can. If you get frustrated and start yelling and screaming at your child, this sets a negative tone and is likely not going to help them get the work done.
- Set clear expectation around homework time and responsibilities. Let your children know that you expect them to get the work done on time and to the best of their abilities; the most important thing is that they try their best. Set aside the same time each afternoon or evening for them to do their work. Understand that kids are all different in how they feel about and approach homework. Some may find English easy, but get really frustrated with math. Another may be a science whiz, but have no patience when it comes to writing. It’s important to know your child: their strengths and struggles, and how they learn. Some kids need small breaks throughout a session, while others may need the task to be broken down into smaller pieces and then varied. While there are some children and teens who are self-directed and able to complete homework without assistance, most require some type of guidance and/or monitoring, depending on their age. This makes it especially challenging for parents, because it means you need to perform different functions with each child you have, depending on their needs.
- Have a relationship with your child’s teacher. Try your best to build a good relationship with your child’s teacher. Start off at the beginning of the school year and stay in touch as the year progresses. Your relationship with your child’s teachers will pay off during the good times as well as the challenging times.
- Play the parental role most useful to your child. Some kids need a coach; others need a “monitor,” while others need more hands-on guidance to complete tasks. Try to match your help with what is most needed. Remember also that your child is doing the homework as a school assignment. The teacher will ultimately be the judge of how good or bad, correct or incorrect the work is. You’re not responsible for the work itself, your responsibility is to guide your child. You can always make suggestions, but ultimately it’s your child’s responsibility to do his or her assignments, and the teacher’s job to grade them.
- Keep activities similar with all your kids. If you have several kids, have them all do similar activities during homework time. Even if one child has less homework or finishes more quickly, they need to be respectful of their siblings by doing quiet, non-disruptive activities.
- Set up a structured time and place for homework. Choose a time and place and stick to a routine as much as possible. Consider adding in break times for kids with shorter attention spans. They might work on their spelling words for 15 minutes, and then take a 5 minute break, for example. Offer snacks to keep kids “fueled” for the work. Keep the house generally quiet for everyone during homework time—turn off the TV (or at least keep the volume down). Make sure your kids have a “space” for doing their work. For some kids this will mean a large work space like a kitchen table to spread out their papers and books, and for others it may mean a small quiet area in their room.
- Start early: Start early with your young children setting up “homework” time, even if it’s just some quiet reading time each night. This helps get them used to the expectation of doing some “homework” each night and will pay off as the actual work gets harder and more time-consuming.
- Offer “Hurdle Help”: Some kids need what we call “hurdle help.” Let’s say your child has big test to study for, but can’t seem to get started. You can help out by running through the first few problems, for example, until he gets the hang of it. Or you might brainstorm with your teen to help her choose a topic for the big paper she has to write. You’re not doing the work for them, rather, you’re helping them get going so the task doesn’t seem so daunting.
- Choose the best person for the job: If you are part of a couple, consider that one of you might be better at “teaching” and then let that person take on the homework monitoring responsibilities. It will likely help the routine become more consistent and effective for your child. If you are a single parent, you might have a friend or family member (an older cousin who’s good at math, or a neighbor who’s a writer, for example) who would consider helping your child from time to time.
- Offer empathy and support. If your child is really struggling, give them some support and guidance and show some empathy. Kids are expected to do some difficult work, and your child may sincerely be struggling with it. If you have a child who is really having a hard time, it’s important to have communication with the teacher to see if this is typical for all kids, or if it’s unique to your child. If your child also has these problems in class, know that there are different approaches to helping them learn that can be useful. The teacher may recommend some testing to see if there are learning problems. While this can be hard to hear as a parent – as if something is wrong with your child – it’s important to find out how your child learns best and what your teacher and you can do to support their learning style.
- Use positive reinforcement and incentives: It’s always important to reinforce positive behavior, and that may mean offering some kind of incentive for completing homework or getting good grades. Most kids get personal satisfaction out of getting good grades and completing their work, and that’s what we’re aiming for. But, it’s also helpful to offer some incentives to encourage them. Rather than money, I would recommend offering rewarding activities for your child’s academic successes. This could include going shopping for some “goodie” the child has really wanted, renting their favorite movie and having “movie night” at home, or other ways of spending special time with a parent. These things can become more meaningful than money for most kids and they get to experience their parent in a loving, supportive and reinforcing role.
Most kids will never really “enjoy” homework, and for some it will always be a struggle. Our children all have different strengths and abilities, and while some may never be excellent students, they might be great workers, talented artists, or thoughtful builders. While it would be easier if all children were self-motivated students who came home, sat down and dug into their homework, this just isn’t going to be the case with most kids. As James often said to parents, “We need to learn to parent the child we have – not the child we’d like them to be.” Our role is to guide our children, support them through the challenging tasks, and teach them about personal responsibility.
Recent Posts
- Help with Parenting after Divorce
- Sitting Still
- Guilt: The Good and the Toxic
- “I’m bored!” Kids in the Summer Part I: Screen time
- August 2018
- September 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- B. Zoppetti
- Co-Parenting
- M. Yaraschuk
- sensory processing issues
- T. Tadlock-Smith
- Uncategorized
- W. Shackleford
- Ways We Can Help
- Ways You Can Help Others
- Ways You Can Help Yourself

For families of Children's Minnesota
Refuses to do homework, related behaviors, what to do:.
Self-Talk. Say to yourself, "I wish my child wanted to do his homework. But I can be calm when he fights doing it. It's his job to do it and mine to encourage his learning how."
Empathy. Tell yourself, "I need to know what my child is thinking and feeling to help him be motivated to do his homework. When I put myself in his shoes, I'll be able to help him better. Sometimes I don't want to do work around the house or on my job, and I always have to figure out why before I can be motivated to do it."
Teach. Tell yourself, "I can help my child learn the SOCS method of problem-solving to help him understand the (S)situation, the (O)options he has for solving the problem, the (C)consequences of choosing each of those options and the (S)best solution. This is a good problem-solving strategy for children to use when they can understand the meaning of these words-situation, options, consequences and solution-- that will be useful throughout their lives.
Make a Daily Routine. Routines are valuable tools that help us all stay organized, so we can get done all the things we need to do. Routines also help to motivate us to get our work done in a focused way. A homework routine, for example, could be: Right after dinner is now a quiet time. All homework will be done during that time. If a child believably claims not to have homework, he can read during quiet time because it is a time when all family members are reading or working on a project.
Make Rules. A simple rule could be: TV and all electronic devices will be off during homework. To enforce the rule, make sure all portable devices are off and are put in a place away from the homework site. A chore rule could be: All chores will be done and inspected before devices can be used or the child can have playtime.
Use SOCS to Support Your Child's Problem-Solving. When your child won't do his homework, talk with him about what he's feeling. Is he upset about something going on in the class? Does he not understand the assignment? Is he worried that his teacher and you expect him to never make a mistake? When you know what the situation is-what your child is thinking and feeling-you can help him understand the options he has for solving the problem, the consequences of choosing each of those options and the best solution. This SOCS method: Situation, Options, Consequences and Solution is a caring, supportive way to build a problem-solving partnership with your child that helps him learn how to be resilient and that he can cope with a problem by thinking it through logically to come up with a solution that works for him.
Check Homework Assignments. As a "family manager", your task is to know what your child's job is, and in this case it's homework. When you know the assignments, you will know whether they have been completed. In addition, you can judge the quality of the homework that has been done. If your child says he has no homework, it's possible to check the school website. Most schools now post homework for each class in each grade. You are not responsible for doing the homework or even knowing what the homework is. But it is important for your child to know that you care and want to know-just as you would share a work project of your own.
Involve Your Child in the Plan. If your child is doing poorly because of incomplete homework assignments, poorly done work, failure to turn in the assignments on time, or any of the other issues that you know are resulting in grades that are below your child's ability, ask him what he plans to do about the problems. If he says, "I'll try harder," don't accept that as an answer. Instead ask, "What's your plan?" and help him pull together a detailed plan to correct the problem: Do all homework immediately after school. Parent checks it. Put it in notebook which goes in the backpack. Turn it in immediately in class. I'll correct my mistakes as soon as I get them." Now, that's a plan. Again, make this your child's plan, not yours. He is responsible for the plan and the work. Here is an example. Ask your child for his ideas!
Check Chore Completion. Most assigned chores have visible proof of completion. Empty wastebaskets are evidence that the trash chore has been done. A made bed shows that making a bed each morning was done. Fun activities are allowed when all chores are done satisfactorily.
Make a Chore Calendar. In order to ensure that children know their chore assignments, a calendar with chores listed could be posted. Monday: Empty Dishwasher, Tuesday: Empty wastebaskets, Wednesday: Vacuum the family room floor, etc. Each child will then check off the chore on that date when completed.
Use Grandma's Rule. You may have noted that in each case we've cited, the child can have his privileges only after work is done, which is the essence of Grandma's Rule. The when-then contract simply states, "when you have done what you are required to do, then you may do what you want to do." You manage your child's access to all of his privileges, such as electronic devices or play activities.
What not to do:
Don't Nag, Beg, Threaten. These won't teach your child how to get work done when it needs to be done.
Don't Punish for Incomplete Homework or Chores. Grounding and other punishments when things aren't done won't teach your child how to get things done. Punishment encourages lying to avoid the punisher-not what you want to teach.
Don't Take on His Responsibility. If you take the responsibility of getting your child's work done, he will never learn to do it himself. Sitting with him to help him finish his homework won't teach him how to take that responsibility. Doing incomplete chores because it's easier than getting him to do them won't help him learn to be responsible.
Choose Which Section(s) to Print
The authors and Raised with Love and Limits Foundation disclaim responsibility for any harmful consequences, loss, injury or damage associated with the use and application of information or advice contained in these prescriptions and on this website. These protocols are clinical guidelines that must be used in conjunction with critical thinking and critical judgment.

Should You Ground Your Child for Bad Grades?
This post may contain affiliate links. If you buy through the link, I may earn a commission. Learn More.
Bad grades. What can you do when your child shows up with them?
Do you punish bad grades or do you find an alternative?
There are plenty of ways to tackle bad grades. Grounding might sometimes be a good solution, but it’s not the only option.
If grounding works for your kid, then it could be a good choice if they have bad grades. Grounding should only happen if your child is getting these bad grades because they are engaging in activities they shouldn’t be doing that are getting in the way of homework or studying.
Find a Tutor for Your Child
Whether it’s math, science, reading, or any other subject, help your child excel in school by finding a qualified tutor.
What is Grounding?

Grounding is the act of restricting a child’s activities due to misbehavior. It’s a common punishment that many parents use. Grounding is effective because it gives children time to think about what they have done. They also feel the sting of FOMO when their friends are taking part in activities that they cannot.
A child who has bad grades may fear retribution. Grounding is arguably the most common punishment for bad grades.
This can be either good or bad. It all comes down to the reason the child is getting poor grades.
Why Your Child’s Grades are Faltering?

There are several different reasons your child may have bad grades. You need to find the reason for your child’s grades before you react with punishment.
1. They’re Not Doing the Work
Your child might not be doing/turning in homework. Many schools have online platforms that allow parents to check their children’s homework and test scores.
You can look through this platform to see if your child is not doing their homework. This is a punishable offense. Even if the homework grades are poor, not doing it or turning it in should be unacceptable.
2. They’re Not Studying for Tests
Your child may not be studying for tests. Is your getting great grades on homework but tanking the tests?
It’s possible that they are not studying. Children sometimes have test anxiety . Studying will help them feel more prepared and do a better job studying.
On the other hand, they may not be studying because they are spending their time with friends or playing video games. If the latter is true, grounding might be an option.
3. They Don’t Understand the Material
Your child might not understand the material. The material may be more advanced than your child is able to manage at this moment.
If that is the case, talk with your child’s teacher. Ask about possibilities for tutoring or finding supplemental lessons.
A child should not be punished because they are having difficulty with the subject matter.
4. They’re Too Busy
Your child may be too busy to concentrate. Is your child in a large number of after-school activities? Does your teen work long hours?
If so, this drain on their time might be causing problems with their schoolwork. Consider having your child cut back on hours or activities until their grades go up again.
5. They Have a Learning Disability
Your child might have a learning disorder . It is never a bad idea to investigate possible learning disorders.
Have your child seen by a professional to rule out any issues that you might not have uncovered.
6. They Have Poor Eye Site
The issue may even be something as simple as poor eyesight. A child whose grades suddenly drop may need glasses. You won’t know until you check it out.
7. They Have Emotional Distress
Your child may be suffering from emotional issues. Emotional struggles can make schoolwork seem unimportant.
If you suspect your child might be feeling anxious or depressed, have them talk with a professional.
8. They Are Understimulated
Your child could be understimulated. There is an old wives’ tale that Albert Einstein failed math as a child.
It’s not true.
However, there are times when a gifted child is so bored in their class that they have difficulty concentrating.
Make sure your child is being challenged enough instead of punishing them.
Why Are Good Grades So Important?

Grades are not everything, but they are important. In a very practical way, good grades in high school help to determine which college or university your child will attend.
Good grades help with scholarships for those who cannot afford the constantly increasing cost of higher education.
Good grades in middle school help children prepare for their high school courses. Children in middle school are still learning how they learn.
Getting good grades at that age gives them the tools they need to continue succeeding as they age.
Good grades in elementary school have less impact on a child’s future. Instead, these grades help the school to learn where the child might be struggling so they can receive more help.
Some elementary schools no longer give letter grades because of this.
At the school district my children attend, students are only given checkmarks, pluses, and minuses until they reach seventh grade.
Alternative Punishments for Bad Grades
My husband and I don’t punish our children for bad grades. Our kids are bright and generally bring in As with little effort.
When they have lower grades, we ask a few questions.
Did you turn in your homework? Did you do your best? If both answers are yes, we don’t have a problem.
Some of that is a judgment call. We can look at our children’s student profiles to verify that homework has been turned in, but we can’t look up the amount of effort each child expends.
We have to decide for ourselves if we think they are being honest when they say they put forth their best work. In almost all instances, we err on the side of believing our children.
Conversely, we have found, on occasion, that homework hasn’t been turned in. If this happens, a punishment takes place.
The child is not allowed to attend any activities until all homework is completed and handed in.
That is a form of grounding that has a time limit determined by how quickly the child is willing to work. This punishment is not for bad grades but for not doing assigned work.
Children with bad grades, who have no intellectual or emotional reason for having them, may need to be punished in order to encourage improvement.
Punishment should be light and should fit the situation.
For instance, you might tell your child they can’t have screen time or spend time with friends unless they have studied for 30 minutes to an hour.
How to Motivate Kids to Improve Their Grades

Kids need to understand why grades are important. Explain to them the impact their grades will have on their future.
Ask them about their future goals, and then explain how they reach them. Good grades are paramount for going to college . Students who want to go to trade school can get scholarships with good grades.
Those who are interested in the military will find that they can join as an officer if they are accepted into college and enter the ROTC program. Once again, this requires good grades.
What if your student isn’t interested in higher education or the military? Let them know that employers will look at your high school GPA if you are seeking a job directly out of school. In all instances, good grades are important.
PRO TIP Keep in mind, the term “good grades” means just that: Good. It doesn’t mean perfect. Don’t tell your kids they have to have perfect grades because that puts too much pressure on young minds. As I tell my children, I expect improvement, not perfection.
Key Takeaways
There may be times when you need to ground your child for bad grades. For the most part, bad grades shouldn’t be punished.
They should be investigated and managed. Do you agree or disagree? Talk to us in the comments!
Have You Read These Yet?
- Should You Let Your Boyfriend or Girlfriend Discipline Your Child?
- How to Deal with a Controlling Child
- House Rules For 18-Year-Olds
- How to Deal with an Ungrateful Child
- How to Deal with a Lazy Child
About the Author
ParentsPlusKids.com is the go-to resource for new moms and dads who are trying to survive motherhood and fatherhood.
What if they just randomly get bad grades instead of straight as then can you ground the,

The child does not want to study or to do their homework: what should parents do?

The school year is now starting again and with that, the Internet is blowing up with parents’ search engine inputs: “my child doesn’t want to study”, “how to make my child do their homework?”, “what to do if the child is bored with their studies?”. Every parent is willing to see a studious child in their son or daughter, the one who is running to school with joy and carefully doing their homework. However, what needs to be done if the child is now lacking the willingness to study? Is it worth forcing them or are there any alternative options? You will find the answers to these questions in this article.
Stop having an overly caring approach for your child and give their developing personality an opportunity for freedom. At the same time, do not worry about your child, always know where they are, which path they take to get somewhere and what is happening around them with the “Findmykids” app that can be downloaded from AppStore and GooglePlay .
Finding out the underlying reason
The correct approach of the parents.
- The tips of a psychologist
8 effective ways to motivate for good study
Does the homework need to be done together with parents.
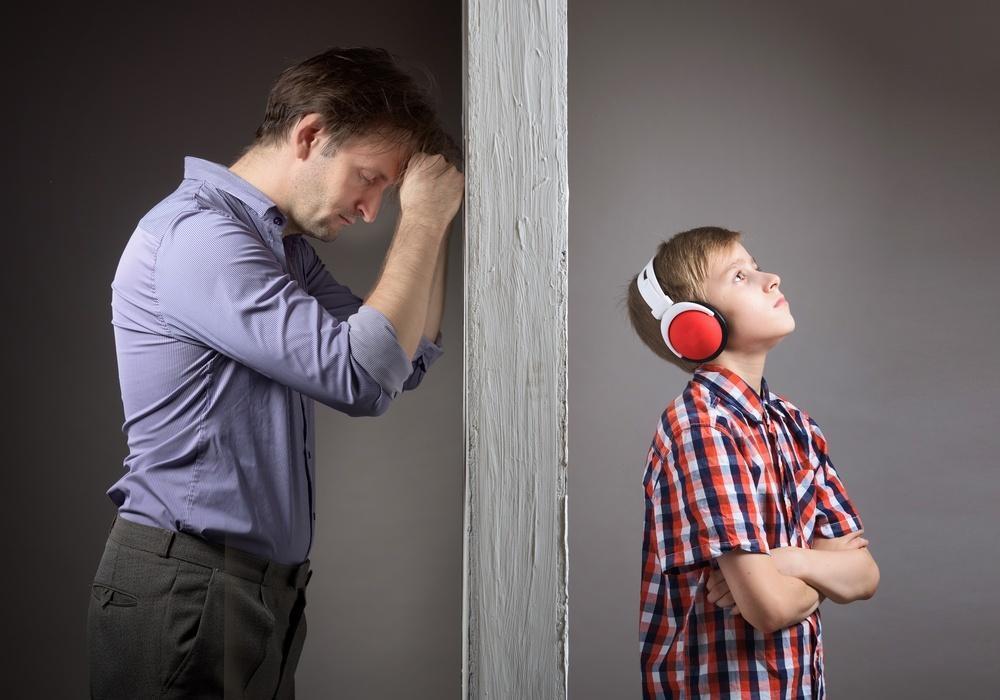

Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com
In order to find out why did the urge to acquire new knowledge at school disappears suddenly, the reason for such behavior needs to be found out. This may mean the following:
1. Lack of motivation
The child does not understand the importance and the need of the learning process. In the classroom, they are bored, they do not listen to the teacher, and they prefer to go about their business or chat with classmates.
Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com[/caption] Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com[/caption] Why don’t kids want to do homework? The answer is very simple. They are not interested in it.Unfortunately, the school allows only for little practical experience for life and success, together with having plenty of gadgets and “distractions”. Therefore, children at school often do not understand why . Why do they need it? How is it useful in life? It is important to talk with children and to provide answers to these questions. To show and explain things to them through the example of famous “young” people. To try to apply the knowledge gained at school, in life, together. Praise the child’s actions. For example, you can gather your child’s friends and arrange the quest “Why do we need mathematics?” The team that finds more practical examples, gets a pizza.
2. Issues in the relationship between the teacher and the student
⠀ Even one careless word from a teacher can offend a child and affect their attitude towards learning, not to mention obvious conflicts. This is especially true for anxious and vulnerable children.
3. Conflicts with classmates, teasing, bullying

⠀ It is important for parents to pay attention to all sudden changes in the behavior of their son or daughter and to be able to help their child in time if they become the victim of bullying .
4. The unfavorable situation within the family
When parents constantly quarrel, it is difficult for the child to concentrate on educational activities. Well, how can you solve a problem in physics when dad shouts that he will leave the family, and mom replies by saying that she wasted her life on a worthless person?
5. Excessive parental control

There are parents (these are mainly mothers) who are interested in controlling everything that happens within the family, including the school life of the child. This omnipresent control stretches out even to backpacks and birthday presents for classmates. What motivation can we be demanding from a child, if in those situations, mom always knows better, and mom decides on everything?
6. Low self-esteem and a lack of self-confidence
It is difficult for such children to prove themselves at school. Raising a hand to answer a teacher’s question, calling a classmate and asking them about homework proves itself to be very problematic for them. If at the same time parents also have excessive expectations for the child and criticize them for the smallest mistakes, the son or daughter starts being anti-social and acts according to the principle of “choosing something with the smallest negative impact”. The child starts skipping lessons, stops doing homework and starts getting bad grades. Why bother if their efforts will still not be appreciated?
7. Excessive workload of the child after school

Swimming classes on Monday and Thursday, dance on Wednesday and Tuesday, art school on other days. Sounds familiar? Many parents strive to oversaturate the schedule of their child. As a result, the psyche turns on defense mechanisms, protecting their brain from the excessive effort. The child begins to be lazy and to postpone their homework until late at night.
8. Physiological reasons
Hyperactivity , weak self-control, somatic diseases – here is an incomplete list of what can also affect a child’s lack of desire to sit at a desk and to do their homework.
A combination of reasons
The next example is exactly about that.
As it can be seen, a child may have several reasons not to be willing to study. Most often, it is not one single reason, but rather a whole set, with which parents need to get familiar.

Dear mums and dads! If you would be actually forcing the child to study, it would be unlikely that something good will turn out from this. Anything that is done when being forced or under pain of punishment will not be beneficial. So let’s not force children to learn, but rather encourage them to do so. The competent stance of the parent will help them with this.
Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com[/caption] Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com[/caption] It is surely possible to force the child to study. However, this will need to be done throughout the entire 9 to 11 years.When we force children, we assume our responsibility for them. On the other hand, we also really want the children to be independent and to do their homework. Therefore, should this be possible, we need to establish the rules for learning right from primary school. There is no need to do homework with a first grader – the parent’s function is to help them not to get distracted from this activity. If the student is older, the issue needs to be solved through motivation and encouragement.
Realistic perception of the situation
What do most parents do if their child doesn’t want to learn? That’s right, they turn to drastic measures, such as physical punishment. It is very likely that your parents did this, and that you also often do this.
Let’s leave the screaming, the abuse and the punishment out of the picture. They won’t do help in any way. “Horror stories” about becoming a janitor without the willingness to do study, will not be of any help either.
Parents need to understand that a child’s reluctance to learn always stems from a specific reason.
Learn how to react correctly to the child misbehaving in the article about the 10 ways to punish your child without screaming, hitting and humiliation .

In order for the child to start dealing with their problems in autonomy, it is important for them to hear the following from their parents:
- “I believe in you”;
- “Everything will work out”;
- “We will sort out this problem together”;
- “There are no unresolvable problems”.
Parents can do the following:
- explain what has not been understood on their own;
- hire a tutor;
- talk to the teacher;
- alter the position of the parent;
- go to the neurologist together;
- find a solution to problems at school collectively with your son or daughter.
Find out whether your child is being bullied at school and whether they are being treated well by their teachers, in order to solve the problem in a timely manner. Listen to the sounds around them and monitor their location in real-life conditions with the “Findmykids” app.
Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com[/caption] Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com[/caption] Sign an agreement with the child, an actual written one. Clearly outline what they are entitled to for “voluntary” completion of the lessons and what is the “punishment” for not completing a task. Incentive schemes work well with older children, for example, if the child was doing their homework all week, on the weekend the whole family goes where the child chooses to go. Stickers with “well done” on them, work great with younger students.
How to help your child?

The tips of a psychologist
From generation to generation, we have passed on an unwillingness to learn. Children start being scared of learning right from kindergarten: “When you go to school, the teacher will not take your tantrums into consideration, they will immediately give you a bad grade”, “if you behave badly, you will be taken to the headmaster’s office”. The child is prepared for the fact that it will be difficult, uninteresting, and painful to study, in advance.
- Try to talk positively about the school and the teachers. The school is the foundation and base of the child’s entire future life.
When a child’s feelings are denied, they quickly lose interest in any activity, including studying. The child says, “This is a very difficult task. I will never complete it, and receives in response: “You are just very lazy, everything seems difficult for you”.
- Let the children share their fears and concerns with you, even if they seem like they are blown out of proportion to you.
- In a family, a child can find everything they need. Listen more and judge less, and then the children themselves will want to share their problems with you.
The desire to raise a genius out of a child with excellent grades in all subjects leads to nervous breakdowns and low self-esteem, because a son or daughter cannot always reach the standard set by their parents. The same applies to unfulfilled parental expectations, when, for instance, a mother dreamed of becoming a ballet dancer so much, that she decided that her daughter must make her dream come true.
The issue of all parents is to be comparing them with other children. “You see, Pete always gets straight As, and you only get Cs and Ds”, “you see, Lara has been doing the homework on her own for a while now, and you are still asking for my help”. The child starts silently hating Pete and other kids, thinking of themselves as the biggest loser.
- If you are comparing the child with someone, compare them only with themselves: “You see, last year it was hard for you to learn the rules of multiplication, and this year it is super easy for you!”
- Praise your children more often for their achievements, even for small ones.
- Explain why it is so important to go to school and what it will give your child in the future.
- Do not scold them for poor grades, the child is already upset with this. Try to figure out the reason for them in the first place.
- Don’t “reimburse” good grades with gadgets, fashionable items or other purchases.
- Talk to the child more often about their dreams and plans for the future.
- It is important to teach the child the time management skills for their time after school, so that there is enough time for both rest and homework.
- The stance that “grades are not important, however, the acquired knowledge is”, is a useful one for both parents and children.
- Do homework with your child only if they ask for help.

Now let’s address the question that worries many parents. Should I help my child with homework? If you do not help, they will make a bunch of mistakes, or forget to learn the poem or will not even turn in the DIY airplane model for their arts & crafts project.
According to the “biggest-ever” study on parents and children carried out in 2018 by the Varkey Foundation on a sample of 27 000 people from 29 countries, suggests that overall, only 25% of parents spend on average 7 or more hours a week helping their children with homework. Moreover, nearly 30% of all parents feel that they need to help their children more and to be more responsive to their needs.
Here is what today’s mums and dads recall about their childhood:
1. “I always had problems with math at school. Well, I did not understand all these sin and cos, integrals and functions! In the 6th grade, my father took over my education. And since he was not a very good teacher, he explained all the topics to me in a raised voice, got angry when I did not understand something. As a result, we quarreled, he called me stupid and said that nothing good would turn out from me. Maybe some mathematical knowledge remained in my head, but my relationship with my father got fully ruined”.
2. “My mother took the matter of my homework into her own hands from my first grade. We sat down with her and did it for hours until she was happy with the result. Sometimes my mother was annoyed that I was doing it very slowly, and she did some of the tasks instead of me. When she was not at home, I never did the homework myself. What for? She wouldn’t be happy about something in it anyway, and I’ll have to redo it”.
As we can see, the parental attempts to control the process of performing the tasks may not always be beneficial for the child.
What is recommended by professionals:
- in the first grade, parents need to do their homework with their child, but only in order to organize the whole process. Teach your son or daughter some easy tricks, for example, starting off with doing written tasks followed by oral tasks, that a complex math problem is to be firstly done on a draft and that a test or an exam requires some preparation in advance;
- allocate a special time for homework with your child, for example, from 5 pm to 7 pm. Help them organize their workplace and space, ensure they have good lighting;
- do not refuse to help if the child asks you for it. However, don’t try to do it instead of them, but rather do it together with them;
- homework is the workload of a child, and only they should be responsible for it, not mom or dad, as they have completed all of their homework a long time ago.
Dear parents, remember: your goal is not to force the son or the daughter to study, but to create such an atmosphere within the family where the child would have an opportunity to share any of their problems, where they are recognized and appreciated not through their grades and where they will be able to acquire the knowledge for their future adult life.

Imagine that you have gotten yourself into a difficult situation or unfamiliar or dangerous circumstances….

Welcome to the exciting whirlwind of Back-to-School Night! If you’re a parent, you likely have…

With Columbus Day 2022 fast approaching, we thought now is a great time to take…
Subscribe now!
Glad you've joined us🎉🎉.

COMMENTS
Many parents want to punish their children for not doing their homework but a better strategy to have them finish their homework rather than punishing them would be to set rewards if they do finish. This puts a positive approach for them to finish the homework rather than making it a negative situation if they don’t finish.
If your child refuses to do his or her work, then calmly give the consequence that you established for not doing homework. Also, trying to convince your child that grades are important is a losing battle.
It’s like punishing a child for not being able to ride a bike when they haven’t learned yet. So instead of asking how to punish, what we should be asking is “why did my child not do their work?”
Yet, your child refuses to do her homework, which causes her to fail. Neither you nor your child know why she is sabotaging herself. Most moms and dads struggle with getting their youngster to complete homework after school.
More often than not, battles over homework lead to vicious cycles of nagging by parents and avoidance or refusal by children, with no improvement in a child’s school performance.
Ages 3 to 5. As your child grows and begins to understand the connection between actions and consequences, make sure you start communicating the rules of your family's home. Explain to kids what you expect of them before you punish them for a behavior.
The first step is to try to stay as calm as you can. If you get frustrated and start yelling and screaming at your child, this sets a negative tone and is likely not going to help them get the work done. Set clear expectation around homework time and responsibilities.
If your child is doing poorly because of incomplete homework assignments, poorly done work, failure to turn in the assignments on time, or any of the other issues that you know are resulting in grades that are below your child's ability, ask him what he plans to do about the problems.
1. They’re Not Doing the Work. Your child might not be doing/turning in homework. Many schools have online platforms that allow parents to check their children’s homework and test scores. You can look through this platform to see if your child is not doing their homework. This is a punishable offense.
Clearly outline what they are entitled to for “voluntary” completion of the lessons and what is the “punishment” for not completing a task. Incentive schemes work well with older children, for example, if the child was doing their homework all week, on the weekend the whole family goes where the child chooses to go.